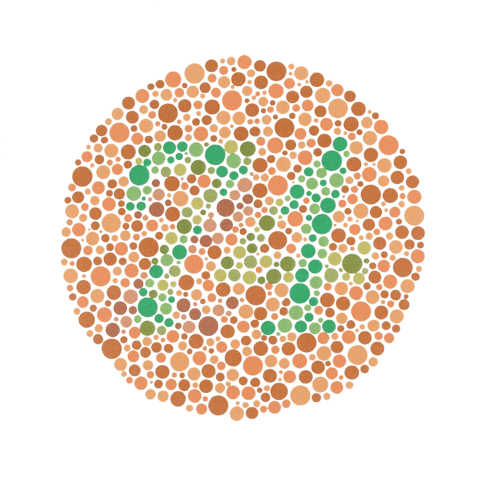5.12 门德利人继承遗产
章节大纲
-
Albinism
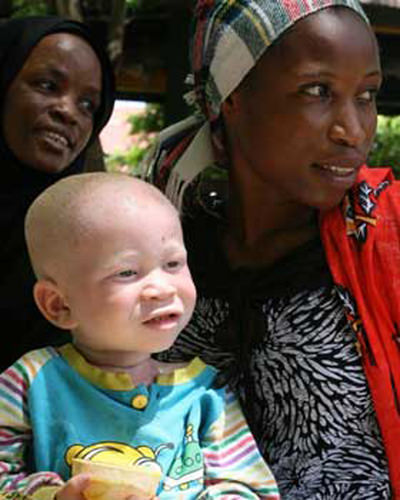
::白白化病This child has much lighter skin and hair than his parents. He has a condition called albinism, which results from a lack of the pigment melanin in the skin, hair, and . Although he looks different than his parents, albinism is actually a genetic trait . Genetic traits are characteristics that are encoded in . Most forms of albinism are recessive , which is why the child's parents were able to pass the trait to him without exhibiting the condition themselves. You will learn more about this type of inheritance in this concept. A lbinism is one of the few human traits that actually has a simple inheritance pattern, similar to the traits that Gregor studied in . The way these traits are inherited by offspring from their parents is called Mendelian inheritance.
::这个孩子的皮肤和头发比父母轻得多。 他有一个叫做白化病的症状, 其原因是皮肤、头发和.虽然他看起来不同于父母,但白化病实际上是一种遗传特征。 遗传特征是被编码的特征。 大多数白化病形式是休眠的, 这就是为什么孩子的父母能够在不展示病情的情况下将病情传给他。 你会更多地了解这个概念中的这种遗产类型。 白化病是一种人类特征,实际上具有简单的继承模式, 类似于格雷戈研究过的特征。 这些特征由父母的后代继承的方式被称为孟德利安继承。What Is Mendelian Inheritance?
::什么是门德利的继承?Mendelian inheritance refers to the inheritance of traits controlled by a single gene with two , one of which may be completely dominant to the other. The pattern of inheritance of Mendelian traits depends on whether the traits are controlled by genes on autosomes , or by genes on sex chromosomes .
::孟德尔人的继承是指由两种基因的单一基因所控制的特征的继承,其中一种可能完全主导另一种。 孟德尔人的继承模式取决于这些特征是受异体基因的控制,还是受性染色体基因的控制。-
Autosomal traits
are controlled by genes on one of the 22 pairs of human autosomes. Autosomes are all the
except the X or
Y chromosome
, and they do not differ between males and females, so autosomal traits are inherited in the same way, regardless of the sex of the parent or offspring.
::22对人类异体中的基因之一控制着自给性特征。 自给性特征除了X或Y染色体之外,全部都是异性特征,男性和女性之间没有区别,因此自给性特征以同样的方式传承,而无论父母或后代的性别如何。 -
Traits controlled by genes on the sex chromosomes are called
sex-linked traits
.
Because of the small size of the Y chromosome, most sex-linked traits are controlled by genes on the
X chromosome
. These traits are called
X-linked traits
. Single-gene X-linked traits have a different pattern of inheritance than single-gene autosomal traits, because males have just one X chromosome. In addition, males always inherit their X chromosome from their mother, and they pass on their X chromosome to all of their daughters, but none of their sons.
::在性染色体上的基因控制下,性染色体上的基因轨迹被称为与性有关的特性。由于Y染色体的大小,大多数与性有关的特性都由X染色体上的基因控制。这些特性被称为X相联特性。单基因X相联特性的继承模式不同于单基因的自动染色体特征,因为男性只有一个X染色体。此外,男性总是从母亲那里继承X染色体,他们把X染色体传给所有女儿,但没有一个儿子。
Studying Inheritance Patterns
::研究继承模式There are two very useful tools for studying how traits are passed from one generation to the next. One tool is a , and the other is a .
::有两种非常有用的工具来研究特征如何从一代传到下一代。 一种是工具,另一种是工具。 一种是工具,另一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具,一种是工具。Pedigree
::集水地The chart is called a pedigree . A pedigree shows how a trait is passed from generation to generation within a family. A pedigree can show, for example, whether a Mendelian trait is an autosomal or X-linked trait .
::图表被称为“ 单位” 。 单位表示一个特性如何在家庭中代代相传。 单位表示一个特性是如何在家庭中代代相传的。 比如, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位表示, 单位的特性是自动的或X相联的特性 。The trait represented by this chart is a hypothetical autosomal trait controlled by a dominant allele . At the top of the pedigree, you can see symbols representing a married couple. The husband has the trait (affected male), but the wife does not (unaffected female). The next row of the pedigree shows the couple's children, as well as the spouses of three of the children. For example, the first child on the left is an affected male married to an unaffected female. The third row of the pedigree shows the next generation (the grandchildren of the couple at the top of the pedigree). One child in this generation — the affected female on the left — is married to an unaffected male. The other children are not married.
::该图所呈现的特征是假设的自体细胞特征,由占支配地位的异性人控制。在幼虫的顶部,您可以看到代表已婚夫妇的符号。丈夫有这个特征(受影响的男性),妻子没有(受影响的女性)。下排小鼠显示的是夫妇的子女以及三个孩子的配偶。例如,左边的第一个孩子是受影响的男性,与未受影响的女性结婚。小鼠的第三排显示的是下一代(在幼虫顶部的夫妇的孙子)。这一代中,有一个孩子——受影响的女性——嫁给了未受影响的男性。其他孩子没有结婚。A pedigree chart is similar to a family tree. It shows how a trait is passed from parents to offspring in a family. The trait represented by this pedigree is an autosomal dominant trait.
::幼虫图与一棵家庭树相似,它显示一个特性是如何从父母传给家庭中的后代的。这个小虫图所代表的特征是一种自给性主性特征。Punnett Square
::Punnett 广场A Punnett square is a chart that allows you to easily determine the expected ratios of possible genotypes in the offspring of two parents. You can see a hypothetical example In this case, the gene is autosomal, and both parents are heterozygotes (Aa) for the gene. Half of the gametes produced by each parent will have the A allele, and half will have the a allele. That's because the two alleles are on homologous chromosomes , which always separate and go to separate gametes during . The alleles in the gametes from each parent are written down the side and across the top of the Punnett square. Filling in the of the Punnett square gives the possible genotypes of their children. It also shows the most likely ratios of the genotypes, which in this case is 25 percent AA, 50 percent Aa, and 25 percent aa.
::Punnett 方块是一个图表, 便于您确定双亲后代中可能的基因型的预期比率。 您可以看到一个假设的例子。 在此情况下, 基因是自动的, 双亲都是基因的异体性球( Aa) 。 每父子所产的配方中的一半将具有Aalle, 另一半将具有Aele 。 这是因为两个异体在同族染色体上, 它们在 相同染色体中总是分离, 并在 期间去到不同的调子。 每个父子的配方在Punnett 方形的侧面和上方写下来。 在 Punnett 方形填满时, 提供了他们孩子可能具有的基因型。 它也显示了最有可能的基因型比, 在本案中, 25% AA, 50% Aa 和 25% aa 。A Punnett square shows the most likely proportions of offspring by genotype for a particular mating type.
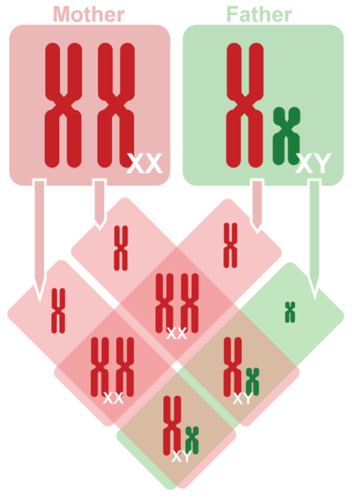
::Punnett 方形显示特定交配类型按基因型分列的最有可能的后代比例。A Punnett square can also be used to show how the X and Y chromosomes are passed from parents to their children. This is illustrated in the Punnett square . It may help you understand the inheritance pattern of sex-linked traits.
::Punnett广场也可以用来显示X和Y染色体是如何从父母传给孩子的。Punnett广场就说明了这一点。它可以帮助你理解与性有关特性的继承模式。Inheritance of Sex Chromosomes. Mothers pass only X chromosomes to their children. Fathers always pass their X chromosome to their daughters, and their Y chromosome to their sons. Can you explain why fathers always determine the sex of the offspring?
::性染色体继承:母亲只把X染色体传给子女;父亲总是把X染色体传给女儿,Y染色体传给儿子。你能解释为什么父亲总是决定后代的性别吗?Autosomal Mendelian Traits in Humans
::人类中自动的门德利人悲剧Not many human autosomal traits are controlled by a single gene with two alleles, but they are a good starting point for understanding human heredity . As discussed in the beginning of this concept, most forms of albinism in humans ha ve a Mendelian inheritance pattern. Albinism is usually controlled by a single autosomal gene with two alleles . The allele for normal pigmentation (let's call it R ) is dominant to the allele for albinism ( r ) . Individuals with either an RR or Rr genotype will not have albinism, because the R allele is dominant over the recessive r allele.
::并非许多人类的自生细胞特征都由具有两种异变的单一基因控制,但它们是了解人类遗传性的良好起点。 正如在这一概念的开头所讨论的,人类大多数白化病患形式都有门德尔遗传模式。白化病通常由具有两种异变的单一自生细胞基因控制。正常色素(我们称为R)的异种在白化病(r)的异种中占主导地位。有RR或Rr基因型的人不会患白化症,因为Rele是优于绝缘变异种的。However, consider what happens if two individuals with the Rr genotype reproduce with each other. The outcome would be similar to the example shown in the Punnett square for two hypothetical Aa individuals. Their possible offspring c ould be RR (normal pigmentation), Rr (normal pigmentation), or rr (albinism). This explains why a child with albinism ( rr ), can have two parents that do not have albinism. Both unaffected parents must be a carrier of the recessive r allele, but they also have a dominant R allele that prevents them from having the condition themselves.
::但是,请考虑一下,如果两个使用Rr基因型的人相互繁殖,结果会怎样。结果与Punnett广场上两个假设Aa人的例子相似。他们的后代可能是RR(正常色素 ) 、 Rr(正常色素 ) 、 rr(白化病 ) 、 rr(白化病 ) 。 这解释了白化病 (rr) 儿童有两个没有白化病的父母的原因。 双不受影响的父母都必须是休眠短发体的载体,但他们也有主要的Ralle, 阻止他们有病症。Some other human traits that have a Mendelian inheritance pattern are Huntington's disease and wet versus dry ear wax. You may have heard about other human traits that were previously thought to be Mendelian, such as dimples, a widow's peak hairline, hitchiker's thumb, and the ability to roll your tongue . As science has progressed, it is now understood that these are not actually Mendelian traits. In fact, most human traits are actually controlled by multiple genes, or otherwise have more than two alleles, which means they do not have a simple Mendelian inheritance pattern.
::具有曼德利继承模式的其他人类特征是亨廷顿的疾病和湿与干耳蜡。你可能听说过以前被认为是门德利人的其他人类特征,如酒窝、遗孀的顶部发线、打字机的拇指和摇动舌头的能力。随着科学的进步,现在人们已经认识到这些并不是曼德利人的特征。 事实上,大多数人类特征实际上由多种基因控制,或者有两种以上的异性,这意味着它们没有简单的门德利人的继承模式。X-Linked Mendelian Traits in Humans
::人类中X连锁的门德利安悲剧Because males have just one X chromosome, they have only one allele for any X-linked trait. Therefore, a recessive X-linked allele is always expressed in males. Because females have two X chromosomes, they have two alleles for any X-linked trait. Therefore, they must inherit two copies of the recessive allele to express an X-linked recessive trait. This explains why X-linked recessive traits are less common in females than males, and why they show a different pattern of inheritance than autosomal traits.
::由于男性只有一个X染色体,因此他们只有一个与X有关特性的异差。因此,一个与休眠的X相联的异差总是用男性表示。由于女性有两个X染色体,因此他们有两个异差来表示任何与X相联的特性。因此,他们必须继承两张休眠异差,以表达与X相联的异差。这解释了为什么与X相联的顺差在女性中比男性要少,以及为什么她们表现出的继承模式不同于自动休眠特征。An example of a recessive X-linked trait is red-green color blindness . People with this trait cannot distinguish between the colors red and green. More than one recessive gene on the X chromosome codes for this trait, which is fairly common in males, but relatively rare in females. The figure shows a simple pedigree for this trait. A female with one of the recessive alleles for the trait does not have the trait herself, but can pass it on to her children. In this case, she is called a carrier of the trait. Half of any sons she has can be expected to have the trait, because there is a 50 percent chance that they will inherit the X chromosome with the color-blindness allele. Having only one X chromosome, the recessive allele will be expressed in the sons who inherit it. However, as long as the father is not affected, none of the woman's daughters will have the trait. The daughters have a 50 percent chance of inheriting the X chromosome with the color-blindness allele, but it won't be expressed because it is recessive to the normal allele they inherit from their father.
::与休眠X相关特性的一个例子是红绿色失明。 具有这种特性的人无法区分颜色红色和绿色。 X染色体代码上有一个以上的隐性基因, 这个特性在男性中相当常见, 但在女性中相对少见。 图表显示了一种简单的血清, 这个特性的简单血清。 一个具有消亡性色谱的雌性女性, 本身没有这种特性, 但是可以把它传给孩子。 在这种情况下, 她被称为性特征的载体。 半数她拥有这种特性的子孙, 因为有50%的机率会继承X染色体, 并带有色盲等色。 只有一种X染色体, 沉睡的血缘关系将表现在继承该特性的子中。 但是, 只要父亲没有受到影响, 女性的女儿就没有一个有这种特性。 女儿有50% 继承X染色体和色盲色色色体的可能性, 但它不会被表达, 因为它是来自父亲的正常继承。
Another example of a recessive X-linked Mendelian trait is hemophilia, which is a disorder characterized by the blood's inability to clot normally. England's Queen Victoria (pictured ) carried the disorder . Two of her five daughters inherited the hemophilia allele from their mother and were carriers. When they married royalty in other European countries, they spread the allele across Europe, including to the royal families of Spain, Germany, and Russia. Victoria's son Prince Leopold also inherited the hemophilia allele from his mother, and he actually suffered from the disease. Understandably , hemophilia was once popularly called "the royal disease."
::与休眠X联系的孟德尔人性特征的另一个例子是血友病。血友病是一种以血液无法正常凝固为特征的疾病。英格兰女王维多利亚(Victoria Queen of Victoria)携带了这种疾病。她的五个女儿中有两个从母亲那里继承了血友病,她们是携带者。当她们在其他欧洲国家结婚时,她们把血友病传播到整个欧洲,包括西班牙、德国和俄罗斯的皇室家庭。维多利亚王子利奥波德也从母亲那里继承了血友病,而且他实际上患有这种疾病。可以理解,血友病曾经被流行称为“皇室病 ” 。Queen Victoria carried hemophilia, and she passed the hemophilia allele to two of her daughters and one of her sons. This portrait of her was painted in the 1840s.
::Victoria王后怀着血友病,她把血友病传染给两个女儿和一个儿子,1840年代她画的这幅肖像画是1840年代画的。Feature: My Human Body
::特质:我的人体Are you color blind, or do you think you might be? If you inherited this X-linked recessive disorder, a world without clear differences between certain colors seems normal to you. It's all you have ever known! Some people who are color blind are not even aware of it. Simple tests have been devised to determine whether a person is color blind, and to what degree . An example of such a test is pictured . What do you see when you look at this circle? Can you clearly perceive the number 74? If so, you probably have normal red-green color . If you cannot see the number, you may have red-green color blindness.
::您是盲目的, 还是你认为自己是盲的? 如果您继承了这个与 X 相关的休眠障碍, 一个在特定颜色之间没有明显差异的世界对你来说是正常的。 这是你所知道的。 一些色盲的人甚至不知道它。 已经设计了简单的测试来确定一个人是否是盲的, 以及程度如何。 这样的测试的一个实例被描绘出来。 当您看到这个圆时, 您看到什么? 您可以清楚地看到数字74 吗? 如果是这样, 您可能拥有普通的红绿色颜色 。 如果您看不到数字, 您可能会看到红绿色盲 。This circle of colors containing the number 74 is part of the Ishihara color blindness test.
::包含74号的颜色圆 是石原色盲测试的一部分Being color blind can cause a number of problems. These may range from minor frustrations to outright dangers. Here are a few examples:
::色盲可能造成一些问题,从轻微的挫折到直接的危险。-
If you are color blind, it may be difficult to color-coordinate clothing and furnishings. You may end up wearing color combinations that people with normal color vision think are odd or clashing.
::如果您是色盲, 可能很难使用颜色协调的衣物和家具。 您可能最终会使用颜色组合, 而有正常颜色视力的人认为这些组合是奇异或冲突 。 -
Many LED indicator lights are red or green.
P
ower strips and electronic devices, for example, may have indicator lights to show whether they are on (green) or off (red).
::许多LED指示灯是红灯或绿灯,例如,电源条和电子装置可能有指示灯,显示是开(绿)灯还是关(红)灯。 -
Test strips for pH, hard
, swimming pool chemicals, and other common tests are also often color coded. Litmus paper for testing pH, for example, turns red in the presence of an acid, but if you are color blind, you may not be able to read the test result.
::PH、硬体、游泳池化学剂和其他常见试验的测试条也经常使用颜色编码。例如,用于测试pH的Litmus纸在有酸的情况下会变红,但如果是色盲,你可能无法读取测试结果。 -
Do you like your steak well done? If you are color blind, you may not be able to tell if the meat is still undercooked (red) or grilled just right. You also may not be able to distinguish ripe (red) from unripe (green)
fruits
and vegetables, such as tomatoes. And some foods, such as dark green spinach, may look more like mud than
food
, making them totally unappetizing.
::你喜不喜欢你的牛排吗?如果你是色盲,你也许无法辨别肉类是煮不足的(红的)还是烤得恰到好处的。你也许也无法辨别熟熟的(红的)水果和蔬菜,比如西红柿。有些食物,比如深绿色的菠菜,可能比食物更像泥,使它们完全不开胃。 -
Weather
maps often are color coded. Is that rain (green) in your forecast, or a wintry mix of sleet and freezing rain (pink or red)? If you can't tell the difference, you may go out on the roads when you shouldn't, putting yourself in danger.
::天气图通常使用彩色编码。 预报中的雨( 绿色) , 或雨( 粉或红色) 和冰冷的雨( 喷雾或红的) 的圆边组合吗? 如果您无法辨别差异, 您可以在路边走出去, 使自己处于危险之中 。 -
Being able to distinguish red from green traffic lights may be a matter of life or death. This can be very difficult for someone with red-green color blindness. In some countries, people with this vision defect are not allowed to drive.
::能够区分红色和绿色交通灯可能是一个生死攸关的问题。 对于红绿色失明的人来说,这可能非常困难。 在一些国家,有这种视力缺陷的人不允许开车。
Summary
::摘要-
Mendelian inheritance refers to the inheritance of traits controlled by a single gene with two alleles, one of which may be completely dominant to the other. The pattern of inheritance of Mendelian traits depends on whether the traits are controlled by genes on autosomes, or by genes on sex chromosomes.
::门德利人继承指的是由两种异系基因的单一基因控制的特性的继承,其中一种可能完全主导另一种。 门德利人的继承模式取决于这些特性是由异体基因控制,还是由性染色体基因控制。 -
Two tools for studying inheritance are pedigrees and Punnett squares. A pedigree is a chart that shows how a trait is passed from generation to generation within a family. A Punnett square is a chart that shows the expected ratios of possible genotypes in the offspring of two parents.
::研究继承的两个工具是小儿科和Punnett广场。小儿科是一张图表,显示一个特征如何在家庭中代代相传。Punnett广场是一张图表,显示双亲后代中可能基因型的预期比率。 -
Examples of human autosomal Mendelian traits include
albinism and
Huntington's disease
. Examples of human X-linked traits include red-green color blindness and hemophilia.
::人类蛋白质蛋白质和亨廷顿病等人类蛋白质的个体蛋白质包括白化病和亨廷顿病,与人类X相关的特征包括红绿色失明和血友病。
Review
::回顾1. Define genetic traits and Mendelian inheritance.
::1. 界定遗传特征和门德利继承。2. Explain why autosomal and X-linked Mendelian traits have different patterns of inheritance.
::2. 解释为什么自动溶液和与X相连的门德利特质有不同的继承模式。3. What is a pedigree, and why is it useful for studying how traits are passed from one generation to the next?
::3. 什么是血统,为什么有助于研究特征如何代代相传?4. What is a Punnett square? What does it show?
::4. 什么是Punnett广场?它显示什么?5. Identify examples of human autosomal and X-linked Mendelian traits.
::5. 查明人类自给和与X相连的门德勒特征的例子。6. Imagine a hypothetical human gene that has two alleles, Q and q . Q is dominant to q and the inheritance of this gene is Mendelian. Answer the following questions about this gene.
::6. 想象一个假想的人类基因,它有两个异灵,Q和Q。 Q占Q的主导地位,而这个基因的继承人是Mendelian。回答关于这个基因的以下问题。a. If a woman has the genotype Qq and her husband has the genotype QQ , list each of their possible gametes. What proportion of their gametes will have each allele?
::a. 如果妇女有基因型Qq,而其丈夫有基因型Qq,请列出每个可能的复方位数。b. What are the likely proportions of their offspring being QQ , Qq , or qq ?
::b. 其后代的 、 Qq 或 qq 的可能比例是多少?c. Is this an autosomal trait or an X-linked trait? How do you know?
:c) 这是自给性格还是X相关性格?
d. What are the chances of their offspring exhibiting the dominant Q trait? Explain your answer.
::d. 他们的后代表现出主要Q特性的可能性有多大?解释你的答复。7. Explain why fathers always pass their X chromosome down to their daughters.
::7. 解释为什么父亲总是把X染色体传给女儿。8. True or False: Women are more likely than men to have X-linked diseases.
::8. 真实或假:妇女比男子更有可能患与X有关的疾病。9. True or False: Most human autosomal traits are controlled by a single gene with two alleles, similar to Mendel’s pea plants.
::9. 真实或假:大多数人类自豆质特征都由一个单基因控制,有两个异形,类似于门德尔的豆类植物。10. For each of the scenarios below, choose whether you would use a Punnett square or a pedigree. Choose only the one that best fits the scenario.
::10. 对于以下每一种情况,请选择使用Punnett广场还是pedigree,只选择最符合设想情况的方案。a. A man and a woman have known genotypes, and you want to predict the possible genotypes of their offspring.
::a. 男人和女人有已知的基因型,你想预测他们的后代可能的基因型。b. You want to document which members of your family had or have breast cancer.
::b. 想要记录贵国家庭哪些成员患有或患有乳腺癌。Explore More
::探索更多Hemophilia is a rare genetic disorder that causes uncontrolled bleeding . Learn more about the genetic inheritance of this disease here:
::血友病是一种罕见的遗传疾病,造成无节制的出血。Explore more about inheritance and sex-linked traits here:
::以下是更多关于继承和与性别相关特性的探讨: -
Autosomal traits
are controlled by genes on one of the 22 pairs of human autosomes. Autosomes are all the
except the X or
Y chromosome
, and they do not differ between males and females, so autosomal traits are inherited in the same way, regardless of the sex of the parent or offspring.