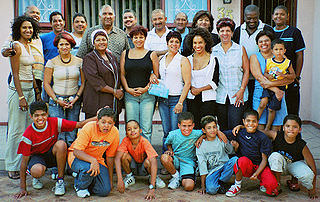5.13 非Mendelian遗产继承
章节大纲
-
Family Portrait
::家庭轮廓This photo of a South African family shows some of the variation in human skin color, which can range from very light to very dark, with every possible gradation in between. As you might expect, the skin color trait has a more complex genetic basis than just one gene with two , which is the type of simple trait that studied in . Like skin color, many other human traits have more complicated modes of inheritance than Mendelian traits. Such modes of inheritance are called non-Mendelian inheritance, and they include inheritance of , traits with codominance or incomplete dominance , and , among others. All of these modes are described below.
::南非家族的这张照片显示了人类肤色的某些差异,从非常光亮到非常暗的肤色,在两者之间可以有每一种可能的分层。 正如你可能预计的那样,肤色特征的遗传基础比两种基因(即研究的简单特征类型)更为复杂。与肤色一样,许多其他人类特征的继承模式比门德利特征更为复杂。这种继承模式被称为非门德利继承,包括继承、附着或不完全占支配地位的特征的继承,等等。Multiple Allele Traits
::多重全 allele 轨迹The majority of human genes are thought to have more than two normal versions, or alleles. Traits controlled by a single gene with more than two alleles are called multiple allele traits . An example is ABO blood type . Your refers to which of certain called antigens are found on your red blood cells . There are three common alleles for this trait, which are represented by the letters I A , I B , and i.
::大部分人类基因被认为具有两个以上正常的版本,或所有基因。由两个以上等同的单一基因控制的轨迹被称为多个等同特性。一个例子是ABO血型。您指的是在红血细胞上找到的哪种抗原。这个特性有三个常见的等同,由字母 IA、 IB 和 i 来表示。As shown in the table , there are six possible ABO genotypes , because the three alleles, taken two at a time, result in six possible combinations. The I A and I B alleles are dominant to the i allele . As a result, both I A I A and I A i genotypes have the same phenotype , with the A antigen in their (type A blood). Similarly, both I B I B and I B i genotypes have the same phenotype, with the B antigen in their blood (type B blood). No antigen is associated with the i allele, so people with the ii genotype have no antigens for ABO blood type in their blood (type O blood).
::如表所示,可能存在六种ABO基因型,因为三个异位数(一次两个)导致六种可能的组合。IA和IB异位数在ialle中占主导地位。结果,IAIA和IAi基因型都具有相同的苯型,其(A型血)中含有A抗原。同样,IBIB和IBI基因型都具有相同的苯型,其血液中含有B抗原(B型血 ) 。没有抗原与iele相关,因此二基因类人血液中没有ABO型血的抗原(O型血 )。ABO Blood Group Genotype Phenotype (blood type) I A I A A I A i
::爱爱社A I B I B B I B i B ii O I A I B AB Codominance
::共居情况Look at the genotype I A I B in the ABO blood group table. Alleles I A and I B for ABO blood type are neither dominant nor recessive to one another. Instead, they are codominant. Codominance occurs when two alleles for a gene are expressed equally in the phenotype of heterozygotes . In the case of ABO blood type, I A I B heterozygotes have a unique phenotype, with both A and B antigens in their blood (type AB blood).
::看看ABO血型表中的基因型 IAIB。 ABO血型的Aleles IA 和 IB 血型的Aleles IA 和 IB 并不具有主导性,也不是相互排斥性。相反,它们具有共占性。当一种基因的两个异体在异性锥体的血型中以等同的方式表达时,就会出现共占性。在ABO血型中,IABIB 异性锥体有独特的苯型,其血液中有A型和B型抗原(AB型血型)。Incomplete Dominance
::不完全占多数Another relationship that may occur between alleles for the same gene is incomplete dominance. This occurs when the dominant allele is not completely dominant. In this case, an intermediate phenotype results in heterozygotes who inherit both alleles. Generally, this happens when the two alleles for a given gene both produce proteins, but one protein is not functional. As a result, the heterozygote individual produces only half the amount of normal protein as is produced by an individual who is homozygous for the normal allele.
::同一基因的异灵之间可能发生的另一种关系是不完全的支配地位。 当占支配地位的异灵并非完全占支配地位时, 就会发生这种情况。 在这种情况下, 中间的苯型导致两种异性人继承异性人。 一般来说, 当一个特定基因的两个异灵同时产生蛋白质, 但一个蛋白质不能发挥作用时, 就会发生这种情况。 结果, 异性人只产生正常蛋白量的一半, 而正常异性人所生产的正常蛋白是同质人生产的。An example of incomplete dominance in humans is Tay Sachs disease. The normal allele for the gene in this case produces an that is responsible for breaking down . A defective allele for the gene results in the production of a nonfunctional enzyme. Heterozygotes who have one normal and one defective allele produce half as much functional enzyme as the normal homozygote , and this is enough for normal . Homozygotes who have only defective allele, however, produce only nonfunctional enzyme. This leads to the accumulation of lipids in the brain starting in utero , which causes significant brain damage. Most individuals with Tay Sachs disease die at a young age, typically by the age of five years.
::在人类中不完全占支配地位的一个例子是Tay Sachs病。在这种情况下,基因的正常灵长类导致崩溃。基因有缺陷的灵长类导致产生一种不起作用的酶。一个正常的、一个有缺陷的异类会产出一半的功能性酶,这对正常人来说就足够了。只有缺陷的异类的同系物会只产生不起作用的酶。这导致从子宫开始的脑部脂肪积累,造成严重的脑损伤。大多数患有Tay Sachs病的人在幼年死亡,通常在5岁时死亡。Polygenic Traits
::多诱变轨数Many human traits are controlled by more than one gene. These traits are called polygenic traits . The alleles of each gene have a minor additive effect on the phenotype. There are many possible combinations of alleles, especially if each gene has multiple alleles. Therefore, a whole continuum of phenotypes is possible.
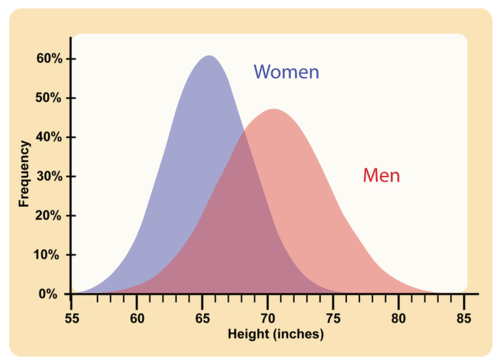
::许多人类特性由不止一个基因控制。 这些特性被称为多基因特性。 每种基因的异灵对苯型具有微小的添加效应。 可能有多种异灵组合, 特别是如果每个基因都有多个异灵。 因此, 整个苯型的连续体是可能的 。An example of a human polygenic trait is adult height. Several genes, each with more than one allele, contribute to this trait, so there are many possible adult heights. One adult’s height might be 1.655 m (5.430 feet), and another adult’s height might be 1.656 m (5.433 feet). Adult height ranges from less than 5 feet to more than 6 feet, with males, on average, being somewhat taller than females. The majority of people fall near the middle of the range of heights for their sex, as shown in the graph .
::人类多致性特征的一个例子是成人身高。 几个基因,每个基因有一个以上的异端,都促成了这一特征,因此有许多可能的成人身高。 一个成年人的身高可能为1.655米(5.430英尺),另一个成年人的身高可能为1.656米(5.433英尺 ) 。 成人身高从不到5英尺到6英尺不等,男性平均略高于女性。 绝大多数人的性别身高接近其身高的中间,如图所示 。Human Adult Height. Like many other polygenic traits, adult height has a bell-shaped distribution.
::与许多其他多致性特征一样,成年身高具有钟形分布。Environmental Effects on Phenotype
::对基因型的环境影响Many traits are affected by the environment, as well as by genes. This may be especially true for polygenic traits. A dult height, for example, might be negatively impacted by poor diet or childhood illness. Skin color is another polygenic trait. There is a wide range of skin colors in people worldwide. In addition to differences in genes, differences in exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light cause some variation. As shown in the photo , exposure to UV light darkens the skin.
::许多特征都受到环境以及基因的影响,对多致性特征来说尤其如此。例如,成人身高可能受到不良饮食或儿童疾病的负面影响。皮肤颜色是另一个多致性特征。全世界人民的皮肤颜色种类繁多。除了基因差异外,接触紫外线(UV)光的差别也造成一些差异。如照片所示,接触紫外线(UV)光使皮肤暗化。Due to the effects of UV radiation, the skin on the lower part of the arm is much darker in color than the protected skin near the top.
::由于紫外线辐射的影响,手臂下部的皮肤颜色比顶部附近受保护的皮肤更暗。Pleiotropy
::颗粒Some genes affect more than one phenotypic trait. This is called pleiotropy . There are numerous examples of pleiotropy in humans. They generally involve important proteins that are needed for the normal development or functioning of more than one organ system . An example of pleiotropy in humans occurs with the gene that codes for the main protein in collagen , a substance that helps form . This protein is also important in the ears and . in the gene result in problems not only in bones, but also in these sensory organs , which is how the gene's pleiotropic effects were discovered.
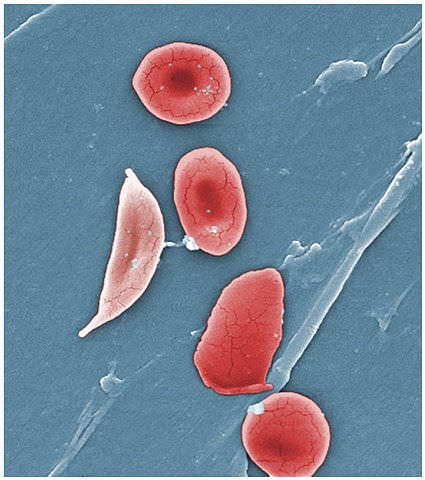
::有些基因影响到不止一种胎儿特征。 这叫脾气。 有许多人类的脾气的例子。 它们一般涉及重要的蛋白质, 这对于一个以上的器官系统的正常发育或功能来说是必要的。 人体的蛋白质有一个例子, 基因编码了主要的蛋白质, 这是一种有助于形成形态的物质。 这种蛋白在耳朵和... 基因中也是很重要的, 不仅在骨头中, 而且在感官器官中都会产生问题, 这就是基因的细胞效应是如何被发现的。Another example of pleiotropy occurs with sickle anemia. This recessive occurs when there is a mutation in the gene that normally encodes the red blood cell protein called hemoglobin . People with the disorder have two alleles for sickle cell hemoglobin, so named for the sickle shape (pictured ) that their red blood cells take on under certain conditions (like physical exertion). The sickle-shaped red blood cells clog small , causing multiple phenotypic effects, including stunting of physical growth, certain bone deformities, kidney failure , and strokes.
::骨髓炎的另一个例子是镰状贫血。这种休眠发生在通常将红血细胞蛋白编码为血红蛋白的基因发生突变时。 患有这种紊乱症的人有两种细胞细胞血红蛋白的同源物,以红细胞在某种条件下(如身体施压)的镰状(图象)命名为镰状(图象 ) 。 镰状红血细胞在小处塞,造成多种胎儿影响,包括身体发育障碍、某些骨骼畸形、肾衰竭和中风。For comparison, the sickle-shaped red blood cell on the left is shown next to several normal red blood cells.
::相比之下,左侧的镰状红血细胞在几个正常的红血细胞旁边显示。Epistasis
::动画Some genes affect the expression of other genes. This is called epistasis . Epistasis is similar to dominance, except that it occurs between different genes, rather than between different alleles for the same gene.
::某些基因会影响其他基因的表达方式。 这叫“粘附 ” 。 Epistasis 类似于支配地位,只是发生在不同的基因之间,而不是发生在同一基因的不同等同基因之间。Albinism is an example of epistasis. A person with albinism has virtually no pigment in the skin. The condition occurs due to an entirely different gene than the genes that encode skin color. Albinism occurs because a protein called tyrosinase, which is needed for the production of normal skin pigment, is not produced, due to a gene mutation. If an individual has the albinism mutation, he or she will not have any skin pigment, regardless of the skin color genes that were inherited.
::白化病是上瘾的一个例子。白化病患者在皮肤上几乎没有色素。这种病因的基因与皮肤编码的基因完全不同。白化病是因为生产正常皮肤色素需要一种叫作甲状腺素的蛋白质,但因基因突变而没有产生。如果一个人有白化突变,他(或她)将没有任何皮肤色素,不管继承的肤色基因如何。Feature: My Human Body
::特质:我的人体Do you know your ABO blood type? In an emergency, knowing this valuable piece of information could possibly save your life. If you ever need a blood transfusion, it is vital that you receive blood that matches your own blood type. Why? If the blood transfused into your body contains an antigen that your own blood does not contain, antibodies in your blood plasma (the liquid part of your blood) will recognize the antigen as foreign to your body and cause a reaction called agglutination. In this reaction, the transfused red blood cells will clump together, as shown in the image below. The agglutination reaction is serious and potentially fatal.
::你知不知道你的ABO血型?在紧急情况下,知道这个有价值的信息可以拯救你的生命。如果你需要输血,那么获得与你自己的血型相匹配的血液至关重要。为什么?如果输入你身体的血液中含有一种你自己的血液不含有的抗原,那么血液血浆中的抗体(你的血液中的液体部分)将承认抗原与你的身体无关,并导致一种称为混合反应的反应。在这种反应中,转基因的红血细胞将聚集在一起,如下图所示。浸泡反应是严重和可能致命的。Two samples of the same blood are shown here. The sample on the left is mixed with anti-B antibodies. The sample on the right is mixed with anti-A antibodies. Agglutination by the anti-A antibodies on the right shows that the sample is type A blood.
::这里显示的是同一血迹的两个样本。左边的样本与抗B抗体混合。右边的样本与抗A抗体混合。右边的抗A抗体浸泡表明样本是A型血液。Knowing the antigens and antibodies present in each of the ABO blood types will help you understand which type(s) of blood you can safely receive if you ever need a transfusion. This information is shown in the table for all of the ABO blood types. If you have blood type A, this means that your red blood cells have the A antigen and that your blood plasma contains anti-B antibodies. If you were to receive a transfusion of type B or type AB blood, both of which have the B antigen, your anti-B antibodies would attack the transfused red blood cells, causing agglutination.
::了解ABO血型中存在的抗原和抗体将帮助您了解如果需要输血,您可以安全地接收哪种类型的血液。表格中列出了所有ABO血型的这些信息。如果您有A型血型,这意味着您的红血细胞有A型抗原,而您的血浆含有抗B型血型抗体。如果您获得B型或AB型血型的输血,而B型血型或AB型血型血液都有B型抗血型,那么您的抗B型血型血型将袭击被移植的红血型血型,导致浸泡。Antigens and antibodies in ABO blood types
::ABO血型中的抗原和抗体You may have heard that people with blood type O are called " universal donors ," and that people with blood type AB are called universal recipients . People with type O blood have neither A nor B antigens in their blood, so if their blood is transfused into someone with a different ABO blood type, it causes no immune reaction, meaning they can donate blood to anyone. On the other hand, people with type AB blood have no anti-A or anti-B antibodies in their blood, so they can receive a transfusion of blood from anyone. Which blood type(s) can safely receive a transfusion of type AB blood, and which blood type(s) can be safely received by those with type O blood?
::你可能听说过,O型血类人被称为“普遍捐献者 ” , AB型血类人被称为“普遍接受者 ” 。 O型血类人在其血液中没有A型和B型抗原,因此,如果他们的血液被移植到不同ABO型血型的人身上,就不会造成免疫反应,这意味着他们可以向任何人捐赠血液。另一方面,AB型血类人血液中没有抗A型或B型抗体,因此他们可以从任何人那里获得输血。哪类血类人可以安全地接受AB型血的输血,而O型血类人可以安全地接收哪种血型?Summary
::摘要-
Non-Mendelian inheritance refers to the inheritance of traits that have a more complex genetic basis than one gene with two alleles and complete dominance.
::非endelian继承是指具有比一个基因更复杂的遗传基础的遗传特征的继承,该基因有两个异系和完全占支配地位。 -
Multiple allele traits are controlled by a single gene with more than two alleles. An example of a human multiple allele trait is ABO blood type, for which there are three common alleles: I
A
, I
B
, and i.
::多重异变特性由两个以上异变基因的单一基因控制。 人类多个异变特性的一个例子是ABO血型,对ABO血型有三种常见异变:IA、IB和i。 -
Codominance occurs when two alleles for a gene are expressed equally in the phenotype of heterozygotes. A human example of codominance also occurs in the ABO blood type, in which the I
A
and I
B
alleles are codominant.
::当一种基因的两个异狄氏元素在异体zygotes的苯型中以等同的表达方式表示时,就会出现共性。 在ABO血型中,也会出现人类的共性例子,在这种血型中,IA和IB等异灵是共性。 -
Incomplete dominance is the case in which the dominant allele for a gene is not completely dominant to a recessive allele for the gene, so an intermediate phenotype occurs in heterozygotes who inherit both alleles. A human example of incomplete dominance is Tay Sachs disease, in which heterozygotes produce half as much functional enzyme as normal homozygotes.
::完全占支配地位的情况是,基因的主宰异端并不完全主导基因的休眠异端,因此在继承这两种异端的异体中会出现中间苯型。 人类不完全占支配地位的一个例子是Tay Sachs病,在这种情况下,异构异端会产生功能性酶,其数量相当于正常同系物的一半。 -
Polygenic traits are controlled by more than one gene, each of which has a minor additive effect on the phenotype. This results in a whole continuum of phenotypes. Examples of human polygenic traits include skin color and adult
height
.
::多基因特性由一个以上基因控制,其中每种基因对苯型具有微小的添加效应,从而产生整个苯型的连续体,人类多基因特性的例子包括肤色和成人身高。 -
Many traits are affected by the environment, as well as by genes. This may be especially true for polygenic traits.
S
kin color, for example, may be affected by exposure to UV light, and adult stature may be affected by diet or
childhood disease.
::许多特征都受到环境以及基因的影响,对于多基因特征来说尤其如此,例如皮肤颜色可能受到紫外线光的影响,成人可能受到饮食或儿童疾病的影响。 -
Pleiotropy refers to the situation in which a gene affects more than one phenotypic trait. A human example of pleiotropy occurs with sickle cell anemia. People who inherit two recessive alleles for this disorder have abnormal red blood cells and may exhibit multiple other phenotypic effects, such as stunting of physical growth, kidney failure, and strokes.
::Pleiotropy指的是基因影响不止一个胎儿特征的情况,一个人类的脾性激素例子发生在镰状细胞贫血中。 继承两种间歇性血管的人患有异常的红细胞,并可能表现出其他多种胎儿影响,如身体发育发育迟缓、肾衰竭和中风。 -
Epistasis is the situation in which one gene affects the expression of other genes. An example of epistasis is albinism, in which the albinism mutation negates the expression of skin color genes.
::白化病是一种基因影响其他基因表达方式的情况。 癫痫的一个例子是白化病,白化病突变否定了肤色基因表达方式。
Review
::回顾1. What is non-Mendelian inheritance?
::1. 什么是非黑山继承?2. Explain why the human ABO blood group is an example of a multiple allele trait with codominance.
::2. 解释为什么人类ABO血族是多重异长特征与共占优势的一个例子。3. What is incomplete dominance? Give an example of this type of non-Mendelian inheritance in humans.
::3. 什么是不完全的主导地位?举一个例子说明人类中这种非黑山人的继承。4. Explain the genetic basis of human skin color.
::4. 解释人类肤色的遗传基础。5. How can the human trait of adult height be influenced by the environment?
::5. 成年身高的人类特征如何能受到环境的影响?6. Define pleiotropy, and give a human example.
::6. 定义胸膜,并举人类为例。7. Compare and contrast epistasis and dominance.
::7. 比较和对比上下文和支配地位。8. What is the difference between pleiotropy and epistasis?
::8. 脾炎与上瘾之间有什么区别?9. Which of the following terms best matches each trait description? Choose only the one term that best fits each trait.
::9. 以下哪些术语最符合每个特征说明?只选择一个最符合每个特征的术语。codominance; multiple allele trait; Mendelian trait; polygenic trait
::共位;多重异长特性; 门德勒特性; 多源特性a. a trait controlled by four genes
::a. 受四种基因控制的特性b. a trait for which each allele of a heterozygote makes an equal contribution to the phenotype
::b. 异血体zygote的每个所有物对苯型作出同等贡献的特性c. a trait controlled by a single gene that has three different versions
::c. 由三种不同版本的单一基因控制的特性d. a trait controlled by a single gene where one allele is fully dominant to the only other allele
::d. 由单一基因控制的特性,其中一人完全支配于唯一的另一人;10. People with type AB blood have:
::10. 患有AB型血的人有:a. anti-O antibodies
::a. 抗氧抗体b. anti-A and anti-B antibodies
::b. 抗A和抗B抗体c. A and B antigens
::c. A和B抗原d. both A and C
::d. A 和 C 两者11. True or False: People with type O blood cannot receive a blood transfusion from anyone besides others with type O blood.
::11. 真实或假:O型血的人除O型血之外,不能接受任何其他人输血。12. True or False: People with type O blood can be heterozygous for this trait.
::12. 真实或假的:O型血的人可能因这一特征而成为异体阳性人。Explore More
::探索更多Check out these videos t o learn more about non-Mendelian i nheritance:
::校对:Portnoy -
Non-Mendelian inheritance refers to the inheritance of traits that have a more complex genetic basis than one gene with two alleles and complete dominance.