9.3 人体细胞和组织
章节大纲
-
Dust Mop
::尘土摩托This photo looks like a close-up of an old fashioned dust mop, and the object it shows has a somewhat similar function. The object, however, is greatly enlarged in the photo. Can you guess what it is? The answer may surprise you.
::这张照片看起来像一个老式的灰尘拖把的特写, 它所显示的物体有相似的功能。 但是, 该对象在照片中放大很大。 你能猜到它是什么吗? 答案可能会令你吃惊 。It is a scanning-electron micrograph of human epithelial that line the bronchial passages. The floppy, dust-mop-like extensions are actually microscopic structures called cilia projecting from the outer surface of the epithelial cells. The function of the cilia is to trap dust, , and other particles in the air before it enters the lungs . The cilia also sway back and forth to sweep the trapped particles upward toward the throat, from which they can be expelled from the body.
::这是支气管通道线上的人类上皮细胞扫描-电子显微镜。软盘、粉尘和粉尘一样的扩展体实际上是被称为从上皮细胞外表面投射的显微形结构。 硅的功能是捕捉灰尘, 以及空气中进入肺部的其他颗粒。 仙子还前后摇摆, 将被困的粒子向上扫向喉咙, 从身体上将它们驱离。Human Cells
::人体细胞Like the ciliated bronchial cells in the micrograph above, many other cells in the are very distinctive and well-suited for special functions. To perform their special functions, cells may vary in a number of ways.
::与上述显微镜中的接合支气管细胞一样,其他许多细胞非常独特,适合特殊功能。 为了履行特殊功能,细胞可能以多种方式不同。Variation in Human Cells
::人体细胞的变异Some cells act as individual cells and are not attached to one another. Red blood cells are a good example. Their main function is to transport oxygen to other cells throughout the body, so they must be able to move freely through the . Many other cells, in contrast, act together with other similar cells as part of the same tissue , so they are attached to one another and cannot move freely. For example, epithelial cells lining the respiratory tract are attached to each other to form a continuous surface that protects the from particles and other hazards in the air.
::红细胞是一个很好的例子,它们的主要功能是将氧气输送到整个身体的其他细胞中,因此它们必须能够自由穿透。相比之下,许多其他细胞与其他类似的细胞一起作为同一组织的一部分活动,因此它们彼此相连,不能自由移动。例如,连接呼吸道的上皮细胞相互连接,形成一个连续的表面,保护空气中免受粒子和其他危害。Many cells can divide readily and form new cells. Skin cells are constantly dying and being shed from the body and replaced by new skin cells, and cells can divide to form new bone for growth or repair. On the other hand, some other cells — like certain nerve cells — can divide and form new cells only under exceptional circumstances. N ervous system injuries (such as a severed spinal cord) generally cannot heal by the production of new cells, which results in a permanent loss of function.
::许多细胞可以很容易地分裂并形成新的细胞。皮肤细胞不断死亡,从身体中流出,被新的皮肤细胞取代,细胞可以分裂形成新的骨骼以供生长或修复;另一方面,其他一些细胞,如某些神经细胞,只有在例外情况下才能分裂和形成新的细胞。 神经系统创伤(如断裂的脊髓)一般无法通过新细胞的产生而愈合,从而导致功能的永久丧失。Many human cells have the primary job of producing and secreting a particular substance, such as a or an . For example, special cells in the pancreas produce and secrete the hormone insulin , which regulates the level of glucose in the . Some of the epithelial cells that line the bronchial passages produce mucus , a sticky substance that helps trap particles in the air before it passes into the lungs.
::许多人类细胞的主要工作是生产和分泌某种物质,例如一种或一种。例如,胰腺中的特殊细胞生产一种或一种,并分泌激素胰岛素,以调节葡萄糖在肺中的含量。一些支气管通道线上的上皮细胞会产生粘粘性物质粘性物质,有助于在进入肺前在空气中捕捉粒子。Different, but Identical
::不同,但一模一样All the different cell types within an individual human organism are genetically identical, so no matter how different the cells are, they all have the same genes . How can such different types of cells arise? The answer is differential regulation of genes. Cells with the same genes can be very different because different genes are expressed depending on the cell type.
::个体人类机体中所有不同的细胞类型在基因上都是相同的, 所以无论细胞有多么不同, 它们都有相同的基因。 如何产生这种不同类型的细胞? 答案是基因的不同调节。 具有相同基因的细胞可能非常不同, 因为不同的基因会根据细胞类型来表达。Examples of Human Cell Types
::人体细胞类型实例Many common types of human cells — such as bone cells and white blood cells — actually consist of several subtypes of cells. Each subtype, in turn, has a special structure and function. A closer look at these cell types will give you a better appreciation for the diversity of structures and functions of human cells.
::人体细胞的许多常见类型——例如骨细胞和白血细胞——实际上由若干次型细胞组成,而每个子型细胞都有特殊的结构和功能,仔细研究这些细胞类型将使你更好地认识人类细胞结构和功能的多样性。Bone Cells
::骨头单元格There are four main subtypes of bone cells, as shown in the diagram . Each type has a different form and function:
::如图所示,骨细胞有四种主要的子类型。每种类型都有不同的形态和功能:-
Osteogenic cells
are undifferentiated
cells that differentiate to form osteoblasts in the tissue that covers the outside of bone.
::定型细胞是无差异的细胞,在覆盖骨骼外部的组织内形成骨质激素。 -
Osteoblasts
are immature bone cells that are involved in synthesizing new bone. They develop into osteocytes, or mature bone cells.
::骨质激素是参与合成新骨头的不成熟的骨细胞。它们发展成骨质素,或成熟的骨细胞。 -
Osteocytes
are star-shaped bone cells that make up the majority of bone tissue. They are the most common cells in mature bone.
::骨细胞系恒星形骨细胞,构成骨骼组织的大多数。它们是成熟骨骼中最常见的细胞。 -
Osteoclasts
are very large, multinucleated cells responsible for the breakdown of bones through resorption. The breakdown of bone is very important in
, because it allows for bone remodeling.
::骨骼细胞非常大,多核细胞导致骨骼通过再吸附破裂。骨骼破裂非常重要,因为它允许骨骼改造。
Four subtypes of bone cells in the human skeletal system
::人体骨骼系统中骨细胞的四个子类型White Blood Cells
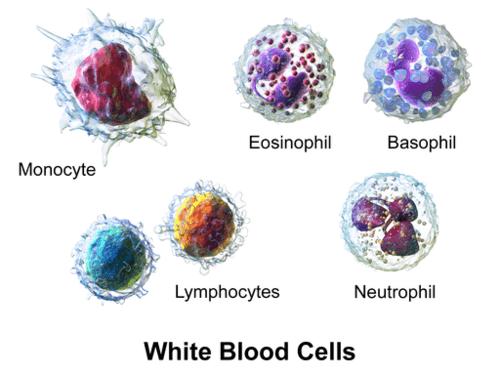
::白血细胞White blood cells (also called leukocytes) are even more variable than bone cells. Five subtypes of white blood cells are shown in the figure . All of them are immune system cells involved in defending the body, but each subtype has a different function. They also differ in the normal proportion of all leukocytes they make up.
::白血细胞(也称为白血球)比骨细胞更具有变异性。图中显示的是五种亚型白血细胞。所有白血细胞都是用于保护身体的免疫系统细胞,但每种子类型都有不同的功能。它们构成的所有白血球细胞的正常比例也各不相同。-
Monocytes
make up about five percent of leukocytes. They engulf and destroy (phagocytize) pathogens in tissues.
::单细胞占白鲸的5%左右,它们吞没并摧毁组织中的病原体(气态化)。 -
Eosinophils
compose
about two percent of leukocytes. They attack larger
parasites
and set off allergic responses.
::蛋白质大约占白血球的2%,它们攻击较大的寄生虫,引发过敏反应。 -
Basophils
make up less than one percent of leukocytes. They release
called
histamines
that are involved in inflammation.
::巴索菲人只占白血球的不到1%。 他们释放了被称作有炎症的异丙胺。 -
Lymphocytes
make up about 30 percent of leukocytes. They include
B cells
and
T cells
. B cells produce
antibodies
against nonself
antigens
, and T cells destroy virus-infected cells and
cells.
::淋巴细胞约占白血球的30%,包括B细胞和T细胞,B细胞产生抗体抗非自我抗原,T细胞摧毁受病毒感染的细胞和细胞。 -
Neutrophils
are the most numerous white blood cells, making up about 62 percent of leukocytes. They phagocytize single-celled
and
in the blood.
::中微子是数量最多的白细胞,占白血球的62%左右。它们将单细胞和血液中分裂成一个细胞。
Five subtypes of human white blood cells in the human immune system
::人类免疫系统中5种亚型人类白血细胞Tissues
::组织组织Groups of connected cells form tissues. The cells in a tissue may all be the same type, or they may be of multiple types. In either case, the cells in the tissue work together to carry out a specific function. There are four main types of human tissues: connective, epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissues .
::连接的细胞组构成组织。组织内的细胞可能是同一类型,也可能是多种类型。在这两种情况下,组织内的细胞都一起工作,以发挥特定功能。人类组织有四种主要类型:连接、上皮、肌肉和神经组织。Connective Tissue
::连连组织Bone and blood are e xamples of connective tissue . Connective tissue is very diverse. In general, it forms a framework and support structure for and organs . It's made up of living cells separated by non-living material, called extracellular matrix, which can be solid or liquid. T he extracellular matrix of bone, for example, is a rigid mineral framework. The extracellular matrix of blood is liquid plasma. Connective tissues such as bone and cartilage generally form the body's structure.
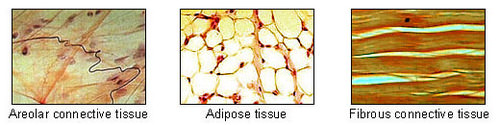
::骨和血液是连接组织的例子。 连接组织是多种多样的。 一般来说, 它构成一个框架和支撑结构以及器官。 它由非生物物质( 称为外细胞矩阵)分离的活细胞组成, 叫做细胞外矩阵, 可以是固体的, 也可以是液体的。 例如, 骨头的外细胞矩阵是一个硬质的矿物质框架。 血液的外细胞矩阵是液体等离子。 骨骼和软骨等连接组织通常构成身体的结构 。Three other types of connective tissue are shown in the figure . They look very different from one another, which is a reflection of their different functions:
::图中显示了另外三种类型的连接组织。它们看起来彼此差异很大,这反映了它们的不同功能:-
Areolar connective tissue
is a common form of loose connective tissue. It is found in the skin and mucous membranes, where it binds the skin or membrane to underlying tissues, such as
. It is also found around
and internal organs, where it links and supports them.
::骨髓连接组织是松散连接组织的一种常见形式,存在于皮肤和粘膜膜中,将皮肤或膜与底部组织(如.)捆绑在一起。在周围和内部器官中也发现,将皮肤或膜与底部组织(如.)联系起来并支撑它们。 -
Adipose tissue
is body fat. It is composed mainly of fat-storage cells called adipocytes. Its main role is to store
energy
in the form of
. Adipose tissue also cushions and insulates the body and produces hormones.
::脂肪组织是身体脂肪,主要由脂肪储存细胞组成,称为二细胞,其主要作用是储存能量,其形式是.脂肪组织还有衬垫,隔绝身体和产生荷尔蒙。 -
Fibrous connective
tissue
is composed of parallel bundles of
collagen
fibers, making it tough and elastic. It is found in skin,
tendons
, and
ligaments
.
::纤维连接组织由平行的科兰纤维捆绑组成,使其坚硬和弹性。 它存在于皮肤、和长颈中。
Three specialized subtypes of connective tissues in the human organism
::人体有机体中连接组织的三个专门子类型Epithelial Tissue
::环境组织Epithelial tissue is made up of cells that line inner and outer body surfaces, such as the skin and the inner surface of the digestive tract. Epithelial tissue that lines inner body surfaces and body openings is called mucous membrane . This type of epithelial tissue produces mucus , a slimy substance that coats mucous membranes and traps pathogens, particles, and debris. Epithelial tissue protects the body and its internal organs, secretes substances (such as hormones) in addition to mucus, and absorbs substances (such as nutrients). The table provides additional details on many specific types of epithelial tissues.
::细胞组织由细胞组成,其内外部表面和外体表面,如消化道的皮肤和内表面; 内部组织,其内部表面和身体开口称为粘膜; 这种上皮组织产生粘结,一种粘粘物质,涂上粘结膜,并捕捉病原体、颗粒和碎片; 下皮组织保护身体及其内器官,除粘结外还有隐蔽物质(如荷尔蒙)和吸收物质(如营养素); 表格提供了许多特定类型的上皮组织的其他细节。Types of human epithelial tissues, including their locations and functions
::人类上皮组织类型,包括其位置和功能Muscle Tissue
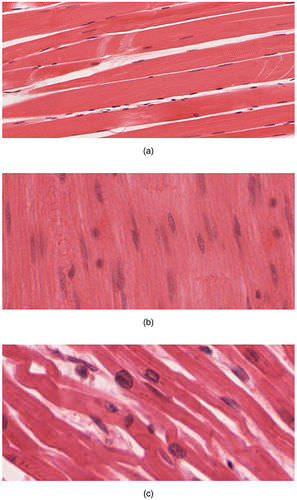
::肌肉组织Muscle tissue is made up of cells that have the unique ability to contract. There are three major types of muscle tissue, as pictured : skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissues.
::肌肉组织由细胞组成,细胞具有独特的收缩能力。 肌肉组织有三种主要类型,如图象所示:骨骼、光滑和心肌组织。-
are
striated
(or striped) in appearance, because of their internal structure. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones by tendons, a type of connective tissue. When they pull on the bones, they enable the body to move. Skeletal muscles are under voluntary control.
::骨骼肌肉因内部结构而与骨骼相连,这是一种连接组织,在骨骼上拉动时,可以使身体运动,骨骼肌肉处于自愿控制之下。 -
Smooth muscles
are nonstriated muscles. They are found in the walls of blood vessels and in the reproductive, gastrointestinal, and respiratory tracts. Smooth muscles are not under voluntary control.
::滑动肌肉是非裂变肌肉,在血管的墙壁和生殖、胃肠和呼吸道中发现,滑动肌肉不受自愿控制。 -
Cardiac muscles
are striated and found only in the heart. Their contractions cause the heart to pump blood. Cardiac muscles are not under voluntary control.
::心血管肌肉被割裂,只存在于心脏中,它们的收缩导致心脏抽血,心血管肌肉不受自愿控制。
Types of muscle tissues: (a) skeletal muscle, (b) smooth muscle, (c) cardiac muscle
::肌肉组织类型a) 骨骼肌肉,(b) 光滑肌肉,(c) 心脏肌肉
Nervous Tissue
::神经组织Nervous tissue is made up of and other types of cells, generally called glial cells (see the figure ). Neurons transmit messages — usually through an electrochemical process — with support from the other cells . Nervous tissue makes up the (mainly the brain and spinal cord) and (the network of nerves that runs throughout the rest of the body).
::神经组织由神经组织和其他种类的细胞组成,一般称为螺旋细胞(见图)。 神经组织通常通过电化学过程,在其他细胞的支持下传递信息。 神经组织组成(主要是大脑和脊髓)和(神经网络,在身体其余部分运行)。This diagram shows some of the cell types that make up nervous tissues. Microglial cells, oligodendrocytes, and astrocytes are all types of glial cells.
::这个图表显示了构成神经组织的一些细胞类型。 微晶体细胞、寡头催化细胞和天体细胞都是各种细球细胞。Feature: My Human Body
::特质:我的人体If you are a blood donor, then you have donated tissue. Blood is a tissue that you can donate when you are alive. You may have indicated on your driver’s license application that you wish to be a tissue donor in the event of your death. Deceased people can donate many different tissues, including skin, bone, heart valves, and the corneas of the . If you are not already registered as a tissue donor, the information below may help you decide if you would like to register.
::如果您是献血者,那么您已经捐赠了组织。血液是一种组织,在您活着时可以捐赠。您可能在驾照申请中表示,您在死亡时希望成为组织捐赠者。死者可以捐赠许多不同的组织,包括皮肤、骨头、心脏阀门和角膜。如果您尚未注册为组织捐赠者,以下信息可能会帮助您决定您是否愿意注册。Each year, approximately 30 thousand people donate tissues, which supplies tissues for up to one million tissue transplants. One tissue donor can enhance or save the life of more than 50 people! Unlike organs — which generally must be transplanted immediately after the donor dies — donated tissues can be processed and stored for a long time for later use. Donated tissues can be used to replace burned skin and damaged bone, and to repair ligaments. Corneal tissues can be used for corneal transplants that restore sight in blind people. In fact, each year 48 thousand patients have their sight restored with corneal transplants. Unfortunately, there are not enough tissues to go around, and the need for donated tissues keeps rising.
::每年约有30 000人捐赠组织,为多达100万个组织移植提供组织,一个组织捐赠者可以提升或拯救50多人的生命。 与器官不同,捐赠组织通常在捐赠者死后立即进行移植。 捐赠组织可以长期处理和储存,供以后使用。捐赠组织可以用来替代烧伤的皮肤和受损的骨头,修复颈部。 角组织可以用于角形移植,恢复盲人的视力。 事实上,每年有48 000名病人的视力通过角形移植得到恢复。 不幸的是,没有足够的组织可以到处活动,对捐赠组织的需求也在增加。Summary
::摘要-
Cells of the human body show a lot of variation. Some cells are unattached to other cells and can move freely, while others are attached to each other and cannot move freely. Some cells can divide readily and form new cells, and others can divide only under exceptional circumstances. Many cells are specialized to produce and secrete particular substances.
::人体细胞存在许多差异。 有些细胞不与其他细胞相连,可以自由移动,而另一些细胞彼此相连,不能自由移动。 有些细胞可以随意分裂,形成新的细胞,而另一些细胞只能在特殊情况下才能分裂。 许多细胞专门生产并分泌特定物质。 -
All the different cell types within an individual have the same genes. Cells can vary because different genes are expressed depending on the cell type.
::个人内所有不同的细胞类型都有相同的基因。 细胞可以不同,因为不同的基因因细胞类型而不同。 -
Many common types of human cells actually consist of several subtypes of cells, each of which has a special structure and function.
S
ubtypes of bone cells, for example, include osteocytes, osteoblasts, osteogenic cells, and osteoclasts.
::许多常见类型的人类细胞实际上由几种子型细胞组成,其中每种细胞都有特殊的结构和功能。 例如,骨骼细胞的子类型包括骨质素、骨质激素、骨质细胞和骨质激素。 -
There are four major types of human tissues: connective, epithelial, muscle, and nervous tissues.
::人体组织有四种主要类型:连接、上皮、肌肉和神经组织。 -
Connective tissues, such as bone and blood, are made up of living cells that are separated by non-living material, called extracellular matrix.
::骨骼和血液等连接组织由活细胞组成,由非生物物质(称为外细胞基体)分离。 -
Epithelial tissues, such as skin and mucous membranes, protect the body and its internal organs. They also secrete or absorb substances.
::皮肤和粘膜等环境组织保护身体及其内部器官,并秘密或吸收物质。 -
Muscle tissues are made up of cells that have the unique ability to contract. They include skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissues.
::肌肉组织由具有独特能力的细胞组成,包括骨骼、光滑和心脏肌肉组织。 -
Nervous tissues are made up of neurons — which transmit messages — and glial cells of various types, which play supporting roles.
::神经组织由神经元组成——它们传递信息——和各种类型的滑翔细胞组成,发挥辅助作用。
Review
::回顾1. Give an example of cells that function individually and move freely. Additionally, give an example of cells that act together and are attached to other cells of the same type.
::1. 举例说明单独运作并自由移动的细胞;此外,举例说明同时行动并附于同类其他细胞的细胞。2. What is an example of cells that can readily divide? What is an example of cells that can divide only under rare circumstances?
::2. 可轻易分割的细胞的例子是什么?只能在特殊情况下分割的细胞的例子是什么?3. Identify a type of cell that secretes an important substance. Name the substance it secretes.
::3. 确定一种秘密重要物质的细胞类型,列出其秘密物质的名称。4. Explain how different cell types come about when all the cells in an individual human being are genetically identical.
::4. 解释当一个人的所有细胞在基因上完全相同时,不同的细胞类型是如何产生的。5. Compare and contrast four subtypes of human bone cells.
::5. 比较和对比人类骨细胞的四个亚型。6. Identify three types of human white blood cells. State their functions.
::6. 确定三种人类白血细胞,说明其功能。7. Why are bone and blood both classified as connective tissues?
::7. 为什么骨骼和血液都被列为连接组织?8. Name another type of connective tissue. Describe its role in the human body.
::8. 指出另一类连接组织,说明其在人体中的作用。9. Based on the information in the table above about types of epithelial tissues, list four general ways this type of tissue functions in the human body.
::9. 根据上表关于上表关于上皮组织类型的资料,列出这种组织在人体中的四种一般功能方式。10. Compare and contrast the three types of muscle tissues.
::10. 比较和比较三类肌肉组织。11. Identify the two main types of cells that make up nervous tissue. Compare their general functions.
::11. 确定构成神经组织的两种主要细胞类型,比较其一般功能。12. Of the main types of human tissue, name two that can secrete hormones.
::12. 在主要的人体组织类型中,列出可以隐匿荷尔蒙的两种。13. Cells in a particular tissue...
::13. 特定组织中的细胞...a. are all of the same type
::a. 均为同一类型。b. have different genes from cells in other tissues
::b. 与其他组织中的细胞有不同的基因。c. work together to carry out a function
::c. 共同努力履行一项职能d. are always connected physically to each other
::d. 始终相互之间有实际联系;14. Why are mucus membranes often located in regions that interface between the body and the outside world?
::14. 为什么粘膜往往位于身体与外界交接的区域?15. Skin is a type of _____________ tissue.
::15. 皮肤是一种组织。16. Body fat is a type of ____________ tissue.
::16. 身体脂肪是一种组织类型。Explore More
::探索更多Each person’s body is unique, which means that everyone reacts differently to drugs and other medical treatments. In the TED talk below, tissue engineer Nina Tandon talks about a possible solution to this problem — making artificial tissues engineered to be the same as the patient’s, and then using the tissues to test the effectiveness of specific drugs or other treatments.
::每个人的身体都是独一无二的,这意味着每个人对药物和其他医疗反应都不同。 在TED下面的演讲中,组织工程师尼娜·坦登(Nina Tandon)谈论了解决这一问题的可能办法 — — 使人工组织与病人组织设计成相同,然后用组织测试特定药物或其他治疗的效果。Check out this video of a whole face transplant procedure here:
::看看这段视频 整个面部移植手术 -
Osteogenic cells
are undifferentiated
cells that differentiate to form osteoblasts in the tissue that covers the outside of bone.