10.4 神经障碍
章节大纲
-
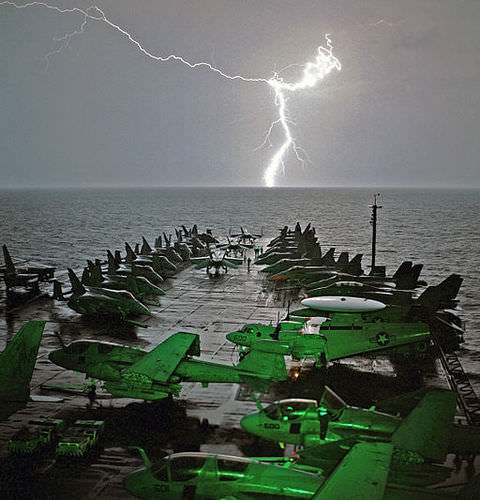
When Lightning Strikes
::闪亮罢工时This amazing cloud-to-surface lightning occurred when a difference in electrical charge built up in a cloud relative to the ground. When the buildup of charge was great enough, a sudden discharge of electricity occurred. A nerve impulse is similar to a lightning strike. Both a nerve impulse and a lightning strike occur because of differences in electrical charge, and both result in an electric current.
::这种惊人的云对地闪电发生时,电荷在云中与地面相对形成差异。当电荷积累足够大时,突然释放了电力。神经冲动类似于闪电。神经冲动和闪电打击都因电荷差异而发生,两者都导致电流。Generating Nerve Impulses
::正在生成神经元件A nerve impulse , like a lightning strike, is an electrical phenomenon. A nerve impulse occurs because of a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a . How does this difference in electrical charge come about? The answer involves ions , which are electrically-charged atoms or molecules.
::神经脉冲,如闪电打击,是一种电子现象。神经脉冲的产生是由于血浆膜之间的电荷差异。电荷的这种差异是如何产生的?答案涉及离子,这些离子是充电原子或分子。Resting Potential
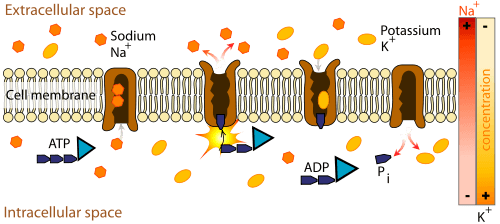
::恢复潜力When a neuron is not actively transmitting a nerve impulse, it is in a resting state, ready to transmit a nerve impulse. During the resting state, the maintains a difference in charge across the of the neuron. The sodium-potassium pump is a mechanism of that moves sodium ions out of and potassium ions into cells. The sodium-potassium pump moves both ions from areas of lower to higher concentration, using energy in ATP and carrier proteins in the cell membrane. The figure shows in greater detail how the sodium-potassium pump works. Sodium is the principal ion in the fluid outside of cells, and potassium is the principal ion in the fluid inside of cells. These differences in concentration create an electrical gradient across the cell membrane, called resting potential . Tightly controlling membrane resting potential is critical for the transmission of nerve impulses.
::当神经元没有积极传播神经脉冲时,它处于休眠状态,可以传输神经脉冲。在休眠状态期间,它保持了神经元各部分的能量差异。钠-钾泵是将钠离子从钠离子移出并将钾离子移入细胞的一种机制。钠-钾泵将离子从低浓度地区移到高浓度地区,使用ATP的能量和细胞膜中的载体蛋白。该图更详细地显示了钠-钾泵是如何工作的。钠是细胞外液体中的主要离子,钾是细胞内液体中的主要离子。这些浓度差异在细胞膜上产生电梯度,称为休息潜力。对神经脉冲的传播至关重要。The sodium-potassium pump maintains the resting potential of a neuron. There is more negative charge inside than outside the cell membrane.
::钠-钾泵保持神经元的休息潜力,其内负电荷大于细胞膜外的负电荷。Action Potential
::行动潜力A nerve impulse is a sudden reversal of the electrical gradient across the plasma membrane of a resting neuron. The reversal of charge is called an action potential . It begins when the neuron receives a chemical signal from another cell or some other type of stimulus . The signal causes gates in sodium ion channels to open, allowing positive sodium ions to flow into the neuron. As a result, the inside of the neuron becomes positively charged, compared to the outside of the neuron. This reversal of charges ripples down the axon of the neuron very rapidly as an electric current, which is illustrated in the diagram . A nerve impulse is an all-or-nothing response. If a neuron responds at all, it responds completely. A greater stimulation does not produce a stronger impulse.
::神经脉冲是休息神经元的等离子膜上的电梯度的突然逆转。 电荷的逆转被称为行动潜力。 当神经元从另一个细胞或其它种类的刺激中收到化学信号时, 电源的逆转即开始。 信号使离子钠通道的门打开, 允许正钠离子流入神经。 结果, 神经元的内部与神经元的外侧相比, 变得正电。 这种电源的逆转会迅速将神经元的轴反转为电流, 图表中说明了这一点。 神经脉冲是一种全无反应。 如果神经元做出反应, 它会完全反应。 更大的刺激不会产生更强烈的脉冲 。An action potential speeds along an axon in milliseconds. Sodium ions flow in and cause the action potential, and then potassium ions flow out to reset the resting potential.
::行动潜力在毫秒内沿着xon加速。 钠离子流进并导致行动潜力, 然后钾离子流出以重置休息潜力。In neurons with a myelin sheath on their axon, ions flow across the membrane only at the nodes between sections of myelin. As a result, the action potential appears to jump along the axon membrane from node to node, rather than spreading smoothly along the entire membrane. This increases the speed at which the action potential travels.
::在轴轴上带有髓髓灰质树脂的神经元中,离子只在髓林各节点之间流过膜。 结果,行动潜力似乎在轴膜从节点跳到节点,而不是在整个膜上顺利扩散。 这增加了行动可能行进的速度。Transmitting Nerve Impulses
::传送神经元件The place where an axon terminal meets another cell is called a . This is where the transmission of a nerve impulse to another cell occurs. T he cell that sends the nerve impulse is called the presynaptic cell , and the cell that receives the nerve impulse is called the postsynaptic cell .
::轴终端遇到另一个细胞的地方被称为 a 。 这是神经脉冲传输到另一个细胞的地方 。 发送神经脉冲的细胞被称为预发性神经细胞, 接收神经脉冲的细胞被称为后发性细胞 。Some synapses are purely electrical and make direct electrical connections between neurons. Most synapses, however, are chemical synapses. Transmission of nerve impulses across chemical synapses is more complex.
::有些突触纯粹是电子突触,在神经元之间直接连接电路,但大多数突触是化学突触,神经冲动通过化学突触传播更为复杂。Chemical Synapses
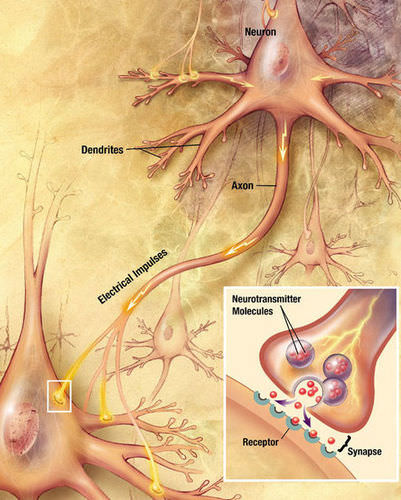
::化学合成At a chemical synapse, both the presynaptic and postsynaptic areas of the cells are full of molecular machinery that is involved in the transmission of nerve impulses. As shown in the diagram , the presynaptic area contains many tiny spherical vessels called synaptic vesicles that are packed with chemicals called neurotransmitters . When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of the presynaptic cell, it opens channels that allow calcium to enter the terminal. Calcium causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with the membrane, releasing their contents into the narrow space between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes. This area is called the synaptic cleft . The neurotransmitter molecules travel across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors , which are embedded in the membrane of the postsynaptic cell.
::在化学突触中,先发性细胞和后发性突触中,细胞的预发性细胞和后发性细胞都充斥着与神经脉冲的传播有关的分子机械。如图所示,预发性细胞包含许多微小球体,称为神经传导器。当行动潜力到达预发性细胞的轴终端时,它打开了通道,允许钙进入终端。钙导致合成性囊与膜结合,将其内装物释放到预发性神经与后发性膜之间的狭窄空间。这个区域称为突发性脊椎。神经飘移分子穿过突触器左侧,并粘附在后发性膜细胞的膜内。This diagram shows how an action potential transmits a signal across a synapse to another cell by neurotransmitter molecules. The inset diagram shows in detail the structures and processes occurring at a single axon terminal and synapse.
::此图表显示了一个行动潜力如何通过神经感应分子将一个信号通过突触传递到另一个单元格。 内置图详细显示了单个轴终端和突触中的结构和过程。Neurotransmitters and Receptors
::神经传送器和受体There are more than a hundred known neurotransmitters, and more than one type of neurotransmitter may be released at a given synapse by a presynaptic cell . For example, it is common for a faster-acting neurotransmitter to be released, along with a slower-acting neurotransmitter. Many neurotransmitters also have multiple types of receptors to which they can bind. Receptors, in turn, can be divided into two general groups: chemically gated ion channels and second messenger systems.
::已知的神经传送器有100多种已知的神经传送器,一种以上的神经传送器可能通过预先合成细胞在特定突触中释放出来。例如,较快反应的神经传送器和较慢反应的神经传送器通常都会释放出来。许多神经传送器也有多种可与之结合的受体。反过来,受体可以分为两大类:化学封闭离子通道和第二信使系统。-
When a chemically gated ion channel is activated, it forms a passage that allows specific types of ions to flow across the cell membrane. Depending on the type of ion, the effect on the
target cell
may be excitatory or inhibitory.
::当化学封闭的离子信道被激活时,它将形成一个通道,允许特定种类的离子穿过细胞膜,视离子类型而定,对目标细胞的影响可能是刺激性或抑制性。 -
When a second messenger system is activated, it starts a cascade of molecular interactions inside the target cell. This may ultimately produce a wide variety of complex effects, such as increasing or decreasing the sensitivity of the cell to stimuli, or even altering
gene
.
::当第二个信使系统被激活时,它会在目标细胞内部开始一系列分子互动。 这最终可能会产生各种各样的复杂效应,比如提高或降低细胞对刺激的敏感度,甚至改变基因。
The effect of a neurotransmitter on a postsynaptic cell depends mainly on the type of receptors that it activates, making it possible for a particular neurotransmitter to have different effects on various target cells. A neurotransmitter might excite one set of target cells, inhibit others, and have complex modulatory effects on still others, depending on the type of receptors. However, some neurotransmitters have relatively consistent effects on other cells. Consider the two most widely used neurotransmitters, glutamate and GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid). Glutamate receptors are either excitatory or modulatory in their effects, whereas GABA receptors are all inhibitory in their effects in adults.
::神经分解器对后合成细胞的影响主要取决于它激活的受体类型,使特定的神经分解器有可能对不同的目标细胞产生不同的影响。 神经分解器可能会刺激一组目标细胞,抑制其他细胞,并对其他细胞产生复杂的调节效应,视受体类型而定。然而,一些神经分解器对其他细胞具有相对一致的影响。考虑到两种最广泛使用的神经分解器,即谷类和伽马-氨基丁酸(伽马-氨基丁酸 ) , 凝聚受体的效果要么是显性,要么是调节性,而GABA受体在成人的效果中都是抑制性的。Problems with neurotransmitters or their receptors can cause neurological disorders. The disease myasthenia gravis, for example, is caused by antibodies from the immune system blocking receptors for the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in postsynaptic muscle cells. This inhibits the effects of acetylcholine on muscle contractions, producing symptoms, such as muscle weakness and excessive fatigue during simple activities. Some mental illnesses (including depression) are caused, at least in part, by imbalances of certain neurotransmitters in the brain . One of the neurotransmitters involved in depression is thought to be serotonin, which normally helps regulate mood, among many other functions. Some antidepressant drugs are thought to help alleviate depression in many patients by normalizing the activity of serotonin in the brain.
::神经传导器或其受体的问题可能导致神经系统紊乱。例如,这种疾病是免疫系统阻塞后合成肌肉细胞神经传感性乙酰胆碱的抗体造成的。这抑制了乙酰胆碱酯酶对肌肉萎缩的影响,产生症状,如肌肉虚弱和在简单活动期间过度疲劳等。某些精神疾病(包括抑郁症)至少部分是由于某些神经传导器在大脑中的不平衡造成的。忧郁症中的神经传导器之一被认为是血清素,通常有助于调控情绪和其他许多功能。一些抗抑郁药物被认为有助于通过大脑中血清素活动的正常化来缓解许多病人的抑郁症。Summary
::摘要-
A nerve impulse is an electrical phenomenon that occurs because of a difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron.
::神经冲动是一种电子现象,由于神经元等离子膜的电荷差异而出现。 -
The sodium-potassium pump maintains an electrical gradient across the plasma membrane of a neuron when it is not actively transmitting a nerve impulse. This gradient is called the resting potential of the neuron.
::钠-钾泵在神经元的等离子膜上保持电子梯度,当它不积极传播神经脉冲时。这个梯度被称为神经元的休息潜力。 -
An action potential is a sudden reversal of the electrical gradient across the plasma membrane of a resting neuron. It begins when the neuron receives a chemical signal from another cell or some other type of stimulus. The action potential travels rapidly down the neuron’s axon as an electric current.
::行动潜力是休息神经元等离子膜的电梯度突如其来的逆转。 当神经元从另一个细胞或某种其他类型的刺激中收到化学信号时,行动潜力就开始了。 行动潜力会以电流的形式迅速从神经元的斧子上流下来。 -
A nerve impulse is transmitted to another cell at either an electrical or a chemical synapse. At a chemical synapse, neurotransmitter chemicals are released from the presynaptic cell into the synaptic cleft between cells. The chemicals travel across the cleft to the postsynaptic cell and bind to receptors embedded in its membrane.
::神经脉冲在电气或化学突触时被传送到另一个细胞,在化学突触时,神经传感化学物质从预先合成细胞释放到细胞之间的合成裂缝中,化学品穿过裂缝进入后合成细胞,并与嵌入其膜内的受体捆绑在一起。 -
There are many different types of neurotransmitters. Their effects on the postsynaptic cell generally depend on the type of receptor they bind to. The effects may be excitatory, inhibitory, or modulatory in more complex ways. Both physical and mental disorders may occur if there are problems with neurotransmitters or their receptors.
::神经传导器种类多种多样,对后合成细胞的影响一般取决于它们所捆绑的受体类型,其影响可能是刺激性、抑制性或调节性更复杂,如果神经传导器或其受体有问题,则可能出现身体和精神紊乱。
Review
::回顾1. Define nerve impulse.
::1. 界定神经冲动。2. What is the resting potential of a neuron, and how is it maintained?
::2. 神经元的休息潜力是什么? 如何保持这种潜力?3. Explain how and why an action potential occurs.
::3. 解释行动潜力如何和为何出现。4. Outline how a signal is transmitted from a presynaptic cell to a postsynaptic cell at a chemical synapse.
::4. 概述信号如何从预合成细胞传输到化学突触中的后合成细胞。5. What generally determines the effects of a neurotransmitter on a postsynaptic cell?
::5. 通常由什么因素决定神经传播器对后合成细胞的影响?6. Identify three general types of effects that neurotransmitters may have on postsynaptic cells.
::6. 查明神经传送器可能对后合成细胞产生的三种一般影响类型。7. Explain how an electrical signal in a presynaptic neuron causes the transmission of a chemical signal at the synapse.
::7. 解释预发性神经元中的电子信号如何导致在突触时传送化学信号。8. The flow of which type of ion into a neuron results in an action potential? How do these ions get into the cell? What does this flow of ions do to the relative charge inside the neuron compared to the outside?
::8. 哪种类型的离子流入神经元会产生作用潜力?这些离子如何进入细胞?这些离子流对神经元内相对电荷的影响如何?相对于外表而言,这些离子流对神经元内相对电荷的影响如何?9. The sodium-potassium pump...
::9. 钠-钾泵...a. is activated by an action potential
::a. 被行动潜力所激活b. requires energy
::b. 需要能源c. does not require energy
::c. 不需要能源d. pumps potassium ions out of cells
::d. 抽出细胞中的钾离子10. True or False: Some action potentials are larger than others, depending on the amount of stimulation.
::10. 真实或虚假:某些行动潜力大于其他行动潜力,视刺激程度而定。11. True or False: Synaptic vesicles from the presynaptic cell enter the postsynaptic cell.
::11. 真实或假的:先发性合成细胞的神经囊进入后发性细胞。12. True or False: An action potential in a presynaptic cell can ultimately cause the postsynaptic cell to become inhibited.
::12. 真实或假的:预先合成细胞中的行动潜力最终会导致后合成细胞受到抑制。13. Name three neurotransmitters.
::13. 列出三个神经传送器。Explore More
::探索更多You can watch an animation showing in detail how a nerve impulse is transmitted across a synapse here:
::您可以观看动画, 详细展示神经脉冲是如何通过突触传播的:Antidepressants are the third most commonly prescribed therapeutic drugs in the United States. Watch the following video to learn how antidepressants called SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) change the levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin in the brain.
::抗抑郁药物是美国第三大最常用处方治疗药物。 观看以下视频了解所谓的抗抑郁药物SSRI(选择性血清素再摄入抑制剂)如何改变大脑神经质素血清素水平。 -
When a chemically gated ion channel is activated, it forms a passage that allows specific types of ions to flow across the cell membrane. Depending on the type of ion, the effect on the
target cell
may be excitatory or inhibitory.