10.5 中央神经系统
章节大纲
-
Homunculus
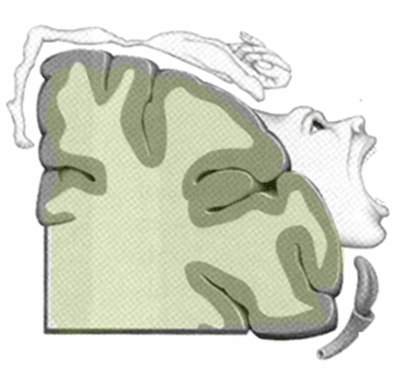
::Homunculus( 双细胞)This very odd-looking drawing is called a homunculus. The greenish mass represents a cross-sectional wedge of the human brain , and the drawing shows some areas of the brain associated with different parts of the body. As you can see, larger areas of the brain in this region are associated with the hands, face, and tongue, as compared to the areas associated with the legs and feet. Given the importance of speech, manual dexterity, and face-to-face social interactions in human beings, it is not surprising that relatively large areas of the brain are needed to control these body parts. The brain is the most complex organ in the and part of the central nervous system.
::这幅奇特的图画被称为“homunculus ” 。 绿色质量代表着人类大脑的交叉部位,图画显示了与身体不同部位相关的部分。 正如你可以看到的,与与腿和脚相关的部分相比,这个区域的大脑大面积与手、脸和舌头相关。鉴于语言、手动灵活性和面对面的社会互动在人类中的重要性,要控制这些身体部分需要大脑的相对较大部分并不奇怪。大脑是中枢神经系统中最复杂的器官。What Is the Central Nervous System?
::中央神经系统是什么?The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the that includes the brain and spinal cord . The drawing shows the central nervous system as one of two main divisions of the total nervous system. The other main division is the (PNS). The CNS and PNS work together to control virtually all body functions. You can read much more about the PNS in the concept Peripheral Nervous System .
::中枢神经系统(CNS)是包含大脑和脊髓的部分。绘图显示中枢神经系统是整个神经系统的两个主要部分之一。另一个主要部分是(PNS)。中枢神经系统和PNS共同控制几乎所有身体功能。您可以在 Peripheral Nervous System 的概念中读更多关于 PNS 的信息。The two main parts of the central nervous system are the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system makes up all of the rest of the nervous system.
::中枢神经系统的两个主要部分是大脑和脊髓,外围神经系统构成神经系统的其他部分。The delicate nervous tissues of the central nervous system are protected by major physical and chemical barriers . Physically, the brain and spinal cord are surrounded by tough meninges, a three-layer protective sheath that also contains cushioning cerebrospinal fluid. The of the skull and spinal vertebrae also contribute to physically protecting the brain and spinal cord. Chemically, the brain and spinal cord are isolated from the circulation — and most toxins or in the — by the blood-brain barrier. The blood-brain barrier is a highly selective membrane formed of endothelial that separates the circulating blood from extracellular fluid in the CNS. The barrier allows , certain gases, glucose , and some other molecules needed by the brain and spinal cord to cross from the blood into the CNS, while keeping out potentially harmful substances. These physical and chemical barriers make the CNS less susceptible to injury than the PNS. However, damage to the CNS is likely to have more serious consequences.
::中枢神经系统的敏感神经组织受到主要的物理和化学屏障的保护,从身体上看,大脑和脊髓绳环绕着坚硬的阴茎,一种三层保护层的包层,其中含有缓冲性脑脊椎液,头骨和脊椎脊椎骨也有助于对大脑和脊髓进行人身保护,从化学上看,大脑和脊髓绳与循环隔绝,大多数毒素或是在血液-脑屏障下隔绝,血液-脑屏障是一种选择性很强的膜,它把循环血液与CNS的外细胞液分离。屏障允许某些气体、葡萄糖和大脑所需的其他分子从血液中穿透到CNS,同时保持潜在有害物质。这些物理和化学屏障使得CNS比PNS更容易受伤。但是,CNS的损害很可能产生更严重的后果。The Brain
::大脑The brain is the control center not only of the rest of the nervous system, but of the entire organism . The adult brain makes up only about two percent of the body’s weight, but it uses about 20 percent of the body’s total energy . The brain contains an estimated one hundred billion , and each neuron has thousands of synaptic connections to other neurons. The brain also has about the same number of glial cells as neurons. No wonder the brain uses so much energy! In addition, the brain uses mostly glucose for energy. As a result, if the brain is deprived of glucose, it can lead to unconsciousness. The brain is able to store some glucose in the form of glycogen, but in much smaller amounts than are found in the liver and .
::大脑不仅是神经系统其余部分的控制中心,而且是整个生物体的控制中心。 成人大脑只占身体重量的2%左右,但使用身体总能量的20%左右。 大脑中大约有1000亿个,每个神经元与其他神经元有数千个合成连接。 大脑的细微细胞与神经元的数量大致相同。 难怪大脑使用如此多的能量。 此外,大脑大多使用葡萄糖作为能量。 因此,如果大脑没有葡萄糖,它就会导致失去知觉。 大脑可以储存一些以甘油为形式的葡萄糖,但数量比肝脏和肝脏中发现的要小得多。The brain controls such mental processes as reasoning, imagination, memory, and language. It also interprets information from the and commands the body how to respond. It controls basic physical processes (such as and heartbeat), as well as voluntary activities (such as walking and writing). The brain has three major parts: the cerebrum , cerebellum , and brain stem . These parts are shown in the following figure and described .
::大脑控制着理性、想象力、记忆力和语言等心理过程。它也解释来自身体的信息并命令身体如何应对。它控制着基本的物理过程(如心跳)以及自愿活动(如行走和写作)。大脑有三个主要部分:大脑、小脑和脑干。这些部分见下图并描述。This drawing shows the brain from the left side of the head. It shows how the brain would appear if the skull and meninges were removed.
::这张图显示大脑从头部左侧的大脑。 它显示如果头骨和脑膜被切除, 大脑会如何出现 。Brain Stem
::脑干The brain stem is the lowest part of the brain. It resembles a stalk on which the cerebrum is perched. The brain stem connects the rest of the brain with the spinal cord and passes between the brain and spinal cord. It also controls unconscious vital functions of the body, such as heart rate and breathing. The uppermost part of the brain stem controls some reflex actions (described below) and is involved in the control of eye movements and certain other voluntary motions.
::脑干是大脑中最底层的部分。 它类似于大脑被粘住的尾部。 脑干将大脑的其余部分与脊髓连接, 并在大脑和脊髓之间传递。 它还控制着身体的无意识关键功能, 如心率和呼吸。 大脑最上层部分控制着一些反射动作( 见下文描述) , 并参与控制眼睛运动和某些其他自愿运动。Cerebellum
::The cerebellum is just below the cerebrum and at the back of the brain behind the brain stem. It coordinates body movements and is involved in movements that are learned with repeated practice. Wh en you hit a softball with a bat or touch type on a keyboard, for example, you are using the cerebellum. Many nerve pathways link the cerebellum with motor neurons throughout the body.
::小脑在脑部下部和脑干后面的大脑后部。 它协调身体运动, 并参与通过反复练习学到的运动。 例如, 当你用蝙蝠击打软球或键盘上的触摸类型时, 您正在使用小脑。 许多神经路径将小脑与全身的动脉神经连接在一起。Cerebrum
::脑叶The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. It controls conscious, intellectual functions. Among other things, it controls reasoning, language, memory, sight , touch, and hearing . When you read a book, play a video game, or recognize a classmate, you are using your cerebrum.
::脑部是大脑中最大的部分。 它控制意识、 智力功能。 除其他外, 它控制理性、 语言、 记忆、 视觉、 触摸和听力。 当你读书、 玩电子游戏或识别同学时, 您正在使用大脑 。Hemispheres and Lateralization of the Cerebrum
::脑积分的半球和横向化The cerebrum is divided from front to back into two halves called the left and right hemispheres. The two hemispheres are connected by a thick bundle of axons , known as the corpus callosum, which lies deep within the brain. The corpus callosum is the main avenue of between the two hemispheres. It connects each point in the cerebrum to the mirror-image point in the opposite hemisphere.
::脑部从前向后分裂为两半块,称为左半球和右半球。两个半球由一块厚厚的斧子连接起来,这些斧子被称作骨架,它位于大脑的深处。细胞骨架是两个半球之间的主要途径。它把大脑中的每个点连接到相反半球的镜像点。The right and left hemispheres of the cerebrum are similar in shape, and most areas of cerebrum are found in both hemispheres. Some areas, however, show lateralization, or a concentration in one hemisphere or the other. I n most people, for example, language functions are more concentrated in the left hemisphere, whereas abstract reasoning and visual-spatial abilities are more concentrated in the right hemisphere.
::大脑的右半球和左半球的形状相似,脑部的多数区域都存在于两个半球。然而,有些区域表现出横向化,或者集中在一个半球或另一个半球。 例如,在大多数人中,语言功能更集中在左半球,而抽象推理和视觉空间能力则更集中在右半球。For reasons that are not yet clear, each hemisphere of the brain interacts primarily with the opposite side of the body. The left side of the brain receives messages from and sends commands to the right side of the body, and the right side of the brain receives messages from and sends commands to the left side of the body. Sensory nerves from the spinal cord to the brain and motor nerves from the brain to the spinal cord both cross the midline of the body at the level of the brain stem.
::由于尚不清楚的原因,大脑的每个半球主要与身体的对面相互作用。大脑的左侧接收来自身体右侧的信息并向右侧发出指令,而大脑右侧接收来自身体左侧的信息并向左侧发出指令。脊髓神经从脊髓到脑部以及脑部到脊髓的运动神经都横跨身体中间线。Lobes of the Cerebrum
::脑细胞的卵巢Each hemisphere of the cerebrum is further divided into the four lobes shown in the following figure and described .
::下图所示并描述的大脑每个半球进一步分为四个叶子。Each hemisphere of the cerebrum consists of four parts, called lobes. Each lobe is associated with particular brain functions. Just one function of each lobe is listed here.
::每个脑半球由四个部分组成, 称为叶。 每个叶子都与特定的脑功能相关。 这里仅列出每个叶子的一个函数 。-
The
frontal lobes
are located at the front of the brain behind the forehead. The frontal lobes are associated with executive functions, such as attention, self-control, planning, problem solving, reasoning, abstract thought, language, and personality.
::前额叶位于前额的大脑前部。 前额叶与行政功能有关,如注意力、自我控制、规划、解决问题、推理、抽象思想、语言和个性。 -
The
parietal lobes
are located behind the frontal lobes at the top of the head. The parietal lobes are involved in sensation — including temperature, touch, and
taste
. Reading and arithmetic are also functions of the parietal lobes.
::Parietal 叶子位于头顶前叶后面,有感性,包括温度、触摸和口味,阅读和算术也是Parietal 叶子的功能。 -
The
temporal lobes
are located at the sides of the head below the frontal and parietal lobes. The temporal lobes enable hearing, the formation and retrieval of memories, and the integration of memories and sensations.
::时间叶位于头部的两侧,前部和顶部叶的两侧,时间叶使听力、记忆的形成和检索以及记忆和感知的融合成为可能。 -
The
occipital lobes
are located at the back of the head below the parietal lobes. The occipital lobes are the smallest of the four pairs of lobes. They are dedicated almost solely to
.
::叶位于脊椎叶下部头部的后部。 叶是四对叶子中最小的。 它们几乎完全用于。
Cerebral Cortex
::脑骨架Most of the information processing in the brain actually takes place in the cerebral cortex , a rind of gray matter and other tissues just a few millimeters thick that makes up the outer surface of the cerebrum in both hemispheres of the brain. The cerebral cortex has many folds in it, greatly increasing the amount of surface area of the brain that can fit within the skull. Because of all the folds in the human cerebral cortex, it has a surface area of about 2,500 cm 2 (2.5 ft 2 ). The size and importance of the cerebral cortex is far greater in the human brain than the brains of any other vertebrates , including nonhuman .
::大脑中大部分信息处理实际上都发生在大脑皮层中, 灰质和其他组织被冲洗后只有几毫米厚, 构成大脑两半球大脑外表。 大脑皮层中有许多折叠, 大大增加了大脑骨骼中可以容纳的表层面积。 由于人类大脑皮层中的所有折叠, 它的表面面积约为2 500厘米( 2.5英尺)。 脑皮层在人类大脑中的规模和重要性远远大于任何其他脊椎动物的大脑, 包括非人类的大脑。Inner Structures of the Brain
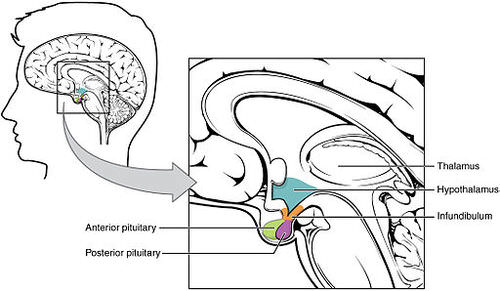
::脑内结构Several structures are located deep within the brain and are important for communication between the brain and spinal cord (or the rest of the body). These structures include the hypothalamus and thalamus. The diagram shows where these structures are located in the brain. Like the two halves of the cerebrum, the hypothalamus and thalamus exist in two halves, one in each hemisphere.
::有几个结构位于大脑深处,对于大脑和脊髓(或身体的其他部分)之间的沟通很重要。这些结构包括下丘脑和骨。图表显示了这些结构在大脑中的位置。和大脑的两半一样,下丘脑和骨存在于两半之间,每个半球各一个。Structures deep within the brain include the hypothalamus and thalamus.
::大脑深处的结构包括下脑膜和脑膜Hypothalamus
::假子脑The hypothalamus is located just above the brain stem, and is about the size of an almond. The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system , including body temperature, heart rate, hunger, thirst, fatigue, sleep, wakefulness, and circadian (24-hour) rhythms. The hypothalamus is also an important emotional center of the brain. The hypothalamus can regulate so many body functions because it responds to many different internal and external signals, including messages from the brain, light, steroid hormones , stress, and invading pathogens, among others.
::脑膜下脑膜位于大脑干叶上方,与杏仁的大小差不多。脑膜下脑膜下脑系统负责某些代谢过程和自主神经系统的其他活动,包括身体温度、心率、饥饿、口渴、疲劳、睡眠、觉醒和环礁(24小时)节律。脑下脑膜下脑也是一个重要的情感中心。下脑膜下脑膜可以调节如此多的身体功能,因为它响应了许多不同的内部和外部信号,包括来自大脑、灯光、类固醇、压力和入侵病原体等的信息。One way the hypothalamus influences body functions is by synthesizing that directly influence body processes. It synthesizes the hormone oxytocin , which stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth and the letdown of milk during lactation . It also synthesizes the hormone vasopressin (also called antidiuretic hormone), which stimulates the to reabsorb more water and excrete more concentrated urine . These two hormones are sent from the hypothalamus via a stalk-like structure called the infundibulum (see diagram above) directly to the posterior (back) portion of the pituitary gland , which secretes them into the blood.
::一种方式是将直接影响身体过程的激素催产素合成为激素催产素,激素催产素在分娩期间刺激子宫萎缩,哺乳期间牛奶衰竭。它还合成激素血管抑制素(也称为抗亚尿素激素),刺激重新吸收更多的水和排出更集中的尿液。这两种激素通过一种类似跟踪的结构,即所谓的内基布卢(见上文图)直接从下基腺的后部(后部)输送到血液中。The main way the hypothalamus influences body functions is by controlling the pituitary gland, known as the master gland of the . The hypothalamus synthesizes neurohormones called releasing factors that travel through the infundibulum directly to the anterior (front) part of the pituitary gland. The releasing factors generally either stimulate or inhibit the secretion of anterior pituitary hormones, most of which control other glands of the endocrine system.
::脑下腺影响身体功能的主要方式是控制脑下腺,即所谓的“主腺 ” 。 脑下腺合成神经激素,称为释放因素,直接穿透脑下膜直接进入脑下腺的前部(前部)部分。释放因素通常刺激或抑制前脑下荷尔蒙的分泌,其中多数控制内分泌系统的其他腺。Thalamus
::撒拉穆斯The thalamus, which is located near the hypothalamus (see diagram ), is a major hub for information traveling back and forth between the spinal cord and cerebrum. It relays sensory signals to the cerebral cortex and motor signals to the spinal cord. It is also involved in the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness.
::Telamus位于下脑膜附近(见图),是脊髓和脑脑之间往返信息的主要枢纽,向脑皮层传递感官信号,向脊髓传递运动信号,并参与意识、睡眠和警觉的调节。Spinal Cord
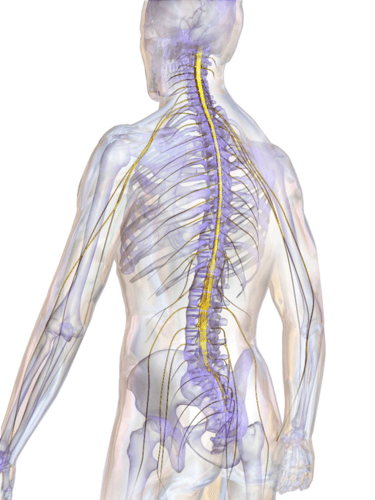
::脊柱状The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissues that extends from the brain stem and continues down the center of the back to the pelvis. It is highlighted in yellow in the diagram . The spinal cord is enclosed within, but is shorter than, the vertebral column .
::脊髓是一个长、薄、管状的神经组织捆绑,从脑干延伸至脑干,一直从背部中心一直到骨盆。在图表中以黄色突出显示。脊髓嵌在脊椎内,但短于脊椎柱。The spinal cord (yellow) runs from the bottom of the brain to the lower back.
::脊髓(黄线)从大脑底部跑到下背部。Structure of the Spinal Cord
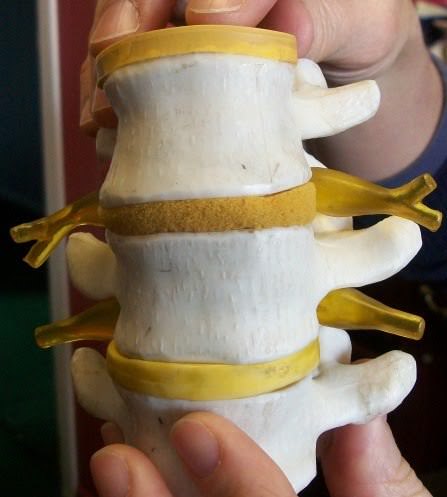
::脊柱骨结构结构The center of the spinal cord consists of gray matter, which is made up mainly of cell bodies of neurons, including interneurons and motor neurons. The gray matter is surrounded by white matter that consists mainly of myelinated axons of motor and sensory neurons . Spinal nerves, which connect the spinal cord to the PNS, exit from the spinal cord between vertebrae (see illustration ).
::脊髓的中心是由灰质组成的灰质,主要由神经元细胞组成,包括中中子和运动神经元。灰质周围是白物质,主要由运动和感官神经元的近距离轴组成。脊髓神经将脊髓连接到 PNS,从脊椎之间的脊髓离开(见插图)。This model shows three vertebrae (white) with branching spinal nerves (yellow) emerging from the either side of the spinal cord between vertebrae.
::这个模型显示三个脊椎骨(白),脊椎脊椎两侧脊椎脊椎脊髓(黄)的脊椎神经(黄)从脊椎两侧脊椎脊髓两侧出现。Functions of the Spinal Cord
::脊柱锥体的功能The spinal cord serves as an information superhighway. It passes messages from the body to the brain and from the brain to the body. Sensory (afferent) nerves carry nerve impulses to the brain from sensory receptor cells everywhere in and on the body. Motor (efferent) nerves carry nerve impulses away from the brain to glands, organs, or throughout the body.
::脊髓起到信息高速公路的作用,它将信息从身体传递到大脑,从大脑传递到身体;感官(后发)神经将神经冲动从感官受体细胞从身体内和体内的任何地方传递到大脑;运动(后发)神经将神经冲动从大脑转移到腺、器官或全身。The spinal cord also independently controls certain rapid responses called reflexes without any input from the brain. You can see how this may happen in the diagram . A sensory receptor responds to a sensation and sends a nerve impulse along a sensory nerve to the spinal cord. In the spinal cord, the message passes to an interneuron and from the interneuron to a motor nerve, which carries the impulse to a muscle. The muscle contracts in response. These neuron connections form a reflex arc , which requires no input from the brain. No doubt you have experienced such reflex actions yourself. For example, you may have reached out to touch a pot on the stove, not realizing that it was very hot. Virtually at the same moment that you feel the burning heat, you jerk your arm back and remove your hand from the pot.
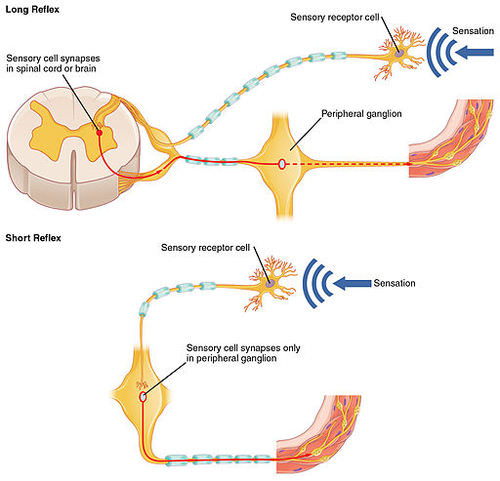
::脊髓独立地控制了某些叫反射的快速反应,即没有大脑输入的反射。 您可以在图表中看到这种情况的发生。 感官受体对感官反应, 并沿着感官神经向脊髓发出神经冲动。 在脊髓中, 电文传递到中中中枢, 从中中中枢传到运动神经, 将脉冲传到肌肉。 肌肉相互配合。 这些神经连接形成反射弧, 不需要大脑输入。 毫无疑问, 您自己也经历过这样的反射动作 。 比如, 您可能已经伸出手去触摸炉子上的锅子, 没有意识到它非常热 。 几乎就在你感受到燃烧的热量的那一刻, 您就把手往后拉, 把你的手从锅中移开 。This diagram shows what happens in a long reflex (top), in which sensory nerves carry the message all the way to the spinal cord; and in a short reflex (bottom), in which sensory nerves travel only to a ganglion outside the spinal cord. Note that interneurons are involved in reflexes, connecting sensory and motor neurons, but they are not actually shown in the diagram.
::此图显示在长反射( 上方) 中发生的情况, 感官神经将信息一直传送到脊髓; 在短反射( 下方) 中, 感官神经只传到脊髓外的交织处。 请注意, 中中子与反射、 连接感官和运动神经元有关, 但是在图表中并没有显示它们 。Injuries to the Spinal Cord
::脊柱骨受伤Physical damage to the spinal cord may result in paralysis, which is loss of sensation and movement in part of the body. Paralysis generally affects all the areas of the body below the level of the injury, because nerve impulses are interrupted and can no longer travel back and forth between the brain and body beyond that point. If an injury to the spinal cord produces nothing more than swelling, the symptoms may be transient. However, if nerve fibers (axons) in the spinal cord are badly damaged, the loss of function may be permanent. Experimental studies have shown that spinal nerve fibers attempt to regrow, but tissue destruction usually produces scar tissue that cannot be penetrated by the regrowing nerves, as well other factors that inhibit nerve fiber regrowth in the central nervous system.
::脊髓的物理损伤可能导致麻痹,即身体部分部分失去感觉和运动,瘫痪一般会影响身体内所有部位,伤害程度低于受伤水平,因为神经脉冲被打断,不能再在大脑与身体之间自来自去。如果脊髓的损伤造成的只是肿胀,症状可能是短暂的。但是,如果脊髓神经纤维(轴)受到严重破坏,功能的丧失可能是永久性的。实验研究表明,脊髓神经纤维试图重新生长,但组织破坏通常会产生骨骼组织,而这种组织不会被再生长的神经神经系统以及抑制神经神经系统神经纤维再生长的其他因素所渗透。Feature: My Human Body
::特质:我的人体Each year, many millions of people have a stroke , and stroke is the second leading cause of death in adults. Stroke, also known as cerebrovascular accident, occurs when poor blood flow to the brain results in the death of brain cells. There are two main types of strokes:
::每年有数百万人中风,而中风是成人死亡的第二大原因。 脑血管事故也被称为脑血管事故,当血液流入脑部时,血液不全导致脑细胞死亡。 中风主要有两种类型:-
Ischemic strokes occur due to lack of blood flow because of a blood clot in an
artery
going to the brain.
::脑动脉中的血凝块导致血液缺乏流动,导致心血管中出现中风。 -
Hemorrhagic strokes occur due to bleeding from a broken
in the brain.
::脑破裂导致出血,导致出血。
Either type of stroke may result in paralysis, loss of the ability to speak or comprehend speech, loss of bladder control, personality changes, and many other potential effects, depending on the part of the brain that is injured. The effects of a stroke may be mild and transient or more severe and permanent. A stroke may even be fatal. It generally depends on the type of stroke and how extensive it is.
::任何一种中风都可能导致瘫痪、失去说话或理解语言的能力、失去膀胱控制、人格改变和许多其他潜在影响,这取决于受伤的大脑部分。 中风的影响可能是温和的、短暂的或更严重和永久的。 中风甚至可能是致命的。 它一般取决于中风的类型和范围。Are you at risk of stroke? The main risk factor for stroke is age — about two-thirds of strokes occur in people over the age of 65. There is nothing you can do about your age, but most other stroke risk factors can be reduced with lifestyle changes or medications. The risk factors include high , tobacco smoking, obesity , high blood cholesterol, mellitus, and atrial fibrillation.
::你是否面临中风风险?中风的主要风险因素是年龄 — — 大约三分之二的中风发生在65岁以上的人群中 — — 您对自己的年龄无能为力,但大多数其他中风风险因素可以通过改变生活方式或药物来降低。 风险因素包括高发、吸烟、肥胖、高血胆固醇、宫颈和小发性纤维化。Chances are good that you or someone you know is at risk of a stroke, so it is important to recognize a stroke if one occurs. A stroke is a medical emergency, and the more quickly treatment is given, the better the outcome is likely to be. In the case of ischemic strokes, the use of clot-busting drugs may prevent permanent brain damage if administered within three or four hours of the stroke. Remembering the signs of a stroke is easy. They are summed up by the acronym FAST.
::如果您或您认识的人面临中风风险,您或某个人的机会是好的,因此,如果发生中风,必须识别中风。中风是医疗紧急情况,而且治疗越快,结果可能越好。在缺血性中风的情况下,使用断流药物如果在中风三或四小时内进行,可能会防止永久性脑损伤。记住中风的症状很容易。它们被缩略语FAST所概括。Summary
::摘要-
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that includes the brain and spinal cord. It is physically protected by bones, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid. It is chemically protected by the blood-brain barrier.
::中枢神经系统是包括大脑和脊髓在内的神经系统的一部分,受到骨头、脑膜和脑脊髓液的实物保护,受到血液脑屏障的化学保护。 -
The brain is the control center of the nervous system and of the entire organism. The brain uses a relatively large proportion of the body’s energy, primarily in the form of glucose.
::大脑是神经系统和整个生物体的控制中心。 大脑使用身体能量的相对较大比例,主要是葡萄糖。 -
The brain is divided into three major parts, each with different functions: brain stem, cerebellum, and cerebrum. The cerebrum is further divided into left and right hemispheres. Each hemisphere has four lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital. Each lobe is associated with specific senses or other functions.
::大脑分为三个主要部分,每个部分的功能不同:脑干、小脑和大脑。大脑进一步分为左半球和右半球。每个半球有四个叶子:前叶、双叶、时间叶和食堂。每个叶子都与特定感官或其他功能有关。 -
The cerebrum has a thin outer layer called the cerebral cortex. Its many folds give it a large surface area. This is where most information processing takes place.
::大脑外层薄薄,叫做脑皮层。它的很多折叠给它提供了大面积的表面积。这是大部分信息处理的地方。 -
Inner structures of the brain include the hypothalamus — which controls the endocrine system via the pituitary gland — and the thalamus, which has several involuntary functions.
::大脑的内部结构包括通过垂垂状腺控制内分泌系统的下丘脑和具有若干非自愿功能的下丘脑。 -
The spinal cord is a tubular bundle of nervous tissues that extends from the head down the middle of the back to the pelvis. It functions mainly to connect the brain with the peripheral nervous system. It also controls certain rapid responses called reflexes without any input from the brain.
::脊髓是由神经组织组成的管状捆绑,从头部向下从背部中间延伸至骨盆,主要功能是连接大脑与外围神经系统。它控制着一些叫作反射的快速反应,而大脑却没有任何输入。 -
A spinal cord injury may lead to paralysis (loss of sensation and movement) of the body below the level of the injury, because nerve impulses can no longer travel up and down the spinal cord beyond that point.
::脊髓损伤可能导致身体瘫痪(失去感觉和运动),低于受伤水平,因为神经脉冲不能再在脊髓上下移动超过该点。
Review
::回顾1. What is the central nervous system?
::1. 中枢神经系统是什么?2. How is the central nervous system protected?
::2. 中央神经系统如何受到保护?3. What is the overall function of the brain?
::3. 大脑的总体功能是什么?4. Identify the three main parts of the brain and one function of each part.
::4. 确定大脑的三个主要部分和每个部分的一个功能。5. Describe the hemispheres of the brain.
::5. 描述大脑的半球。6. Explain and give examples of lateralization of the brain.
::6. 解释和举例说明大脑的横向平衡。7. Identify one function of each of the f our lobes of the cerebrum.
::7. 确定脑部四个叶的每个叶的功能。8. Summarize the structure and function of the cerebral cortex. Explain how the hypothalamus controls the endocrine system.
::8. 概述大脑皮层的结构和功能,解释下丘脑如何控制内分泌系统。9. Describe the spinal cord.
::9. 描述脊髓。10. What is the main function of the spinal cord?
::10. 脊髓的主要功能是什么?11. Explain how reflex actions occur.
::11. 解释反射行动是如何发生的。12. Why do severe spinal cord injuries usually cause paralysis?
::12. 为什么严重的脊髓损伤通常导致瘫痪?13. What do you think are some possible consequences of severe damage to the brain stem? How might this compare to the consequences of severe damage to the frontal lobe? Explain your answer.
::13. 你认为脑干受到严重损害的后果是什么?这如何与前额叶受到严重损害的后果相比较?解释你的答复。14. Information travels very quickly in the nervous system, but generally, the longer the path between areas, the longer it takes. Based on this, explain why you think reflexes often occur at the spinal cord level, and do not require input from the brain.
::14. 信息在神经系统中流动非常迅速,但一般而言,区域之间的路径越长,需要的时间就越长,根据这一点,可以解释为什么你认为反应经常发生在脊髓水平上,不需要大脑输入。Explore More
::探索更多More than 40 million people worldwide suffer from the brain disorder Alzheimer’s disease, and the number is expected to grow dramatically in the coming decades. The disease was discovered more than a century ago, but little progress has been made in finding a cure. Watch this exciting TED talk in which scientist Samuel Cohen shares a new breakthrough in Alzheimer's research, as well as a message of hope that a cure for Alzheimer’s will be found.
::全世界有4000多万人患有脑疾病阿尔茨海默氏病,预计在未来几十年中,该疾病的数量会急剧增长。 该疾病在一个多世纪前就已经发现,但在找到治愈方法方面进展甚微。 观看这一令人振奋的TED演讲,科学家塞缪尔·科恩在演讲中分享了阿尔茨海默氏病研究的新突破,并传递了希望的信息,希望能够找到治疗阿尔茨海默氏病的良药。To reduce the severity of his seizures, Joe had the bridge between his left and right cerebral hemispheres (the corpus callosum) severed. As a result, his left and right brains no longer communicate through that pathway. Here's what happened as a result:
::为了降低他的癫痫严重程度,Joe将左脑和右脑半球之间的桥梁切断。结果,他的左脑和右脑不再通过这条路径交流。结果如下: -
The
frontal lobes
are located at the front of the brain behind the forehead. The frontal lobes are associated with executive functions, such as attention, self-control, planning, problem solving, reasoning, abstract thought, language, and personality.