11.5甲状腺
章节大纲
-
Too Much of a Good Thing
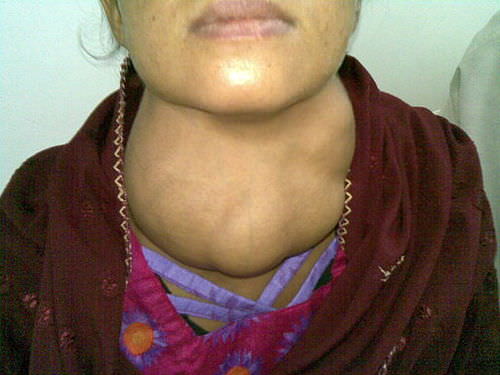
::太多好东西了The woman in this photo has a goiter , an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland, located in the neck. A goiter may form as a result of a number of different thyroid disorders. You’ll learn why in this concept.
::这张照片中的女人颈部有甲状腺异常膨胀的甲状腺。 甲状腺可能因不同的甲状腺紊乱而形成。 你会知道为什么这个概念。Thyroid Structure
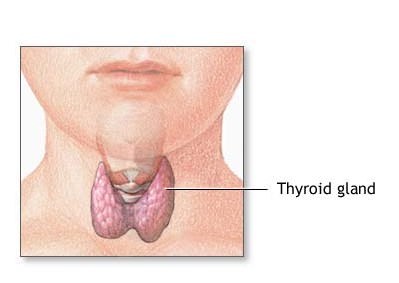
::甲状体结构The thyroid gland is one of the largest in the body. It is located in the front of the neck below the Adam’s apple (see figure ). The gland is butterfly shaped and composed of two lobes. The lobes are connected by a narrow band of thyroid tissue called an isthmus.
::甲状腺是身体中最大的腺体之一,位于亚当苹果下面的颈部前部(见图 ) 。 甲状腺是蝴蝶形状,由两叶组成。 甲状腺由狭窄的甲状腺组织组成,称为地峡。The thyroid gland is a two-lobed gland in the front of the neck.
::甲状腺在颈部前是两圈的腺。Internally, the thyroid gland is composed mainly of follicles . A follicle is a small cluster of surrounding a central cavity, which stores and other molecules made by the follicular cells. Thyroid follicular cells are unique in being highly specialized to absorb and use iodine. They absorb iodine as iodide ions (I - ) from the and use the iodide to produce thyroid hormones. The cells also use some of the iodide they absorb to form a called thyroglobulin , which serves to store iodide for later hormone synthesis. The outer layer of cells of each follicle secretes thyroid hormones as needed. Scattered among the follicles are another type of thyroid cells, called parafollicular cells (or C cells). These cells synthesize and secrete the hormone calcitonin.
::在内部,甲状腺腺主要由组成。一个浮冰是围绕一个中央腔层的一小部分,中央腔层储存着这个细胞和其他分子。甲状腺囊细胞具有独特的特性,非常专门吸收和使用碘。它们吸收碘化离子(I-)作为碘化离子(I-),并使用碘化离子产生甲状腺激素。这些细胞还使用一些吸收的碘化物形成一种称为甲状腺布林的甲状腺素,用来储存碘化物,供以后的荷尔蒙合成。每个浮球细胞的外层按需要储存甲状腺激素。在卵盘中散落为另一种甲状腺细胞,称为丙状腺细胞(或C细胞)。这些细胞合成并秘密了荷尔蒙的卡西通尼。Function of the Thyroid
::甲状体的功能Like all endocrine glands, the function of the thyroid is to synthesize hormones and secrete them into the bloodstream. Once in the blood, they can travel to cells throughout the body and influence their functions.
::与所有内分泌腺一样,甲状腺的作用是合成荷尔蒙并将激素分解到血液中,一旦进入血液中,它们就可以进入整个身体的细胞并影响其功能。Thyroid Hormones: T4 and T3
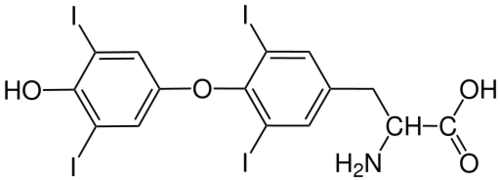
::甲状腺激素:T4和T3There are two main thyroid hormones produced by the follicles: thyroxine (T4) — which contains four iodide ions and is represented by the structural diagram — and triiodothyronine (T3), which contains three iodide ions. T3 is much more powerful than T4, but T4 makes up about 90 percent of circulating thyroid hormone, and T3 makes up only about ten percent. However, most of the T4 is converted to T3 by target tissues.
::有两种主要甲状腺荷尔蒙,一种是甲状腺激素(T4),其中含有4种碘离子,结构图代表了这些激素),另一种是三碘甲状腺激素(T3),其中含有3种碘离子。T3比T4强得多,但T4占甲状腺流动激素的90%左右,T3仅占10%左右。然而,大多数T4通过目标组织转换为T3。This structural model represents a single molecule of thyroxine (T4). The I’s represent the four iodide ions it contains. The rings consist mainly of carbon atoms.
::这个结构模型代表了甲状腺素(T4)的单一分子。 我代表着它所含的四种碘离子。 环主要由碳原子组成。Like steroid hormones , T3 and T4 cross everywhere in the body and bind to intracellular receptors to regulate . U nlike steroid hormones, however, thyroid hormones can cross cell membranes only with the help of special transporter proteins. Once inside the of cells, T3 and T4 turn on genes that control . Thyroid hormones increase the rate of metabolism in cells, allowing them to absorb more , use more energy , and produce more heat. Thyroid hormones also increase the rate and force of the heartbeat. In addition, they increase the sensitivity of cells to fight-or- flight hormones (that is, catecholamine hormones, such as adrenaline).
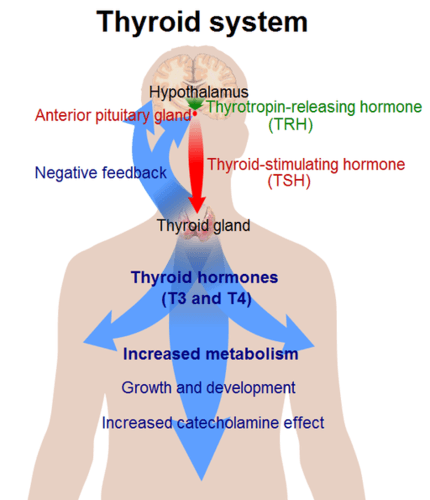
::甲状腺荷尔蒙只有在特殊传送蛋白的帮助下才能跨过细胞膜。一旦进入细胞,T3和T4就会转向控制基因。甲状腺荷尔蒙会增加细胞中新陈代谢的速率,允许细胞吸收更多、使用更多能量和产生更多热量。甲状腺荷尔蒙也会增加心跳的速率和强度。此外,它们也会增加细胞对抗争或飞动激素(如肾上腺素)的敏感度。The production of both T4 and T3 is regulated primarily by thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted by the anterior pituitary gland (see the diagram ). TSH production, in turn, is regulated by thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH), which is produced by the hypothalamus . The thyroid gland, pituitary gland, and hypothalamus form a negative feedback loop to keep thyroid hormone secretion within a normal range. TRH and TSH production is suppressed when T4 levels start to become too high. The opposite occurs when T4 levels start to become too low.
::T4和T3的生产主要受甲状腺刺激激素(TSH)管制,甲状腺刺激激素(TSH)由前脑腺秘密(见图)管理。TSH的生产则由甲状腺释放激素(TRH)管理,后者由低丘脑生成。甲状腺、无脊椎腺和下脑瘤形成负面反馈循环,将甲状腺激素分泌在正常范围内。当T4水平开始过高时,TRH和TSH的生产就会受到抑制。相反,当T4水平开始过低时,T4水平会变得过低。The thyroid system is a negative feedback loop that includes the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and thyroid gland. As this diagram shows, thyroid hormones increase the effect of catecholamines such as adrenaline, a fight-or-flight hormone.
::甲状腺系统是一个负面反馈循环,包括低丘体、低脑腺和甲状腺。 如本图所示,甲状腺荷尔蒙增加了肾上腺素(如肾上腺素 ) , 即抗争或飞行荷尔蒙的影响。Calcitonin
::卡尔西托宁NameThe calcitonin produced by the parafollicular cells of the thyroid gland has the role of helping to regulate blood calcium levels by stimulating the movement of calcium into . Calcitonin is secreted in response to rising blood calcium levels. It decreases blood calcium levels by enhancing calcium absorption and deposition in bone. Calcitonin works hand-in-hand with parathyroid hormone, which is secreted by the parathyroid glands and has the opposite effects as calcitonin. Together, these two hormones maintain calcium .
::甲状腺光谱细胞生成的钙素通过刺激钙进入 . Calcitonin 因血液钙含量上升而秘而不宣,它通过增加钙吸收和骨头沉积而降低钙含量。 Calcitonin 与类固醇激素并肩工作,该激素由除虫菊酯的腺体所隐蔽,其影响与卡西托宁截然相反。这两种荷尔蒙加在一起保持了钙含量。Thyroid Disorders
::甲状腺病As with other endocrine disorders, thyroid disorders are generally associated with either over- or under-secretion of hormones. Abnormal secretion of thyroid hormones may occur for a variety of reasons.
::与其他内分泌紊乱一样,甲状腺紊乱通常与荷尔蒙过度或不足有关,甲状腺荷尔蒙的异常分泌可能出于各种原因发生。Hyperthyroidism
::超超体机器人病Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves’ disease. Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder in which abnormal antibodies produced by the immune system stimulate the thyroid to secrete excessive quantities of its hormones. This stimulation overrides the usual negative feedback mechanism that normally controls thyroid hormone output. Graves’ disease often results in the formation of an enlarged thyroid (goiter) because of the continued stimulation to produce more hormones.
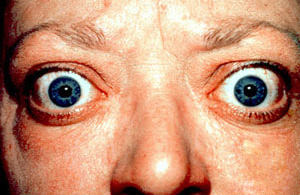
::当甲状腺产生过多甲状腺荷尔蒙时,就会出现超超固醇。超固醇最常见的原因是格雷夫斯病。重力病是一种自动免疫紊乱,免疫系统产生的异常抗体刺激甲状腺分泌过多的荷尔蒙。这种刺激超越了通常控制甲状腺荷尔蒙产出的通常负面反馈机制。格雷夫的病因持续刺激产生更多的荷尔蒙,导致甲状腺(甲状腺)膨胀。Besides a goiter, other signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include protruding (see photo ), heart palpitations, excessive sweating, diarrhea, weight loss despite increased appetite, muscle weakness, and unusual sensitivity to heat. Medications can be prescribed to mitigate the symptoms of the disease. Anti-thyroid drugs can also be given to decrease the production of thyroid hormones. If the drugs are ineffective, the gland can be partially or entirely removed. This can be done surgically or with the administration of radioactive iodine. Removal of the thyroid produces hypothyroidism.
::除了甲状腺病外,其他超甲状腺病的迹象和症状可能包括:甲状腺突变(见照片)、心动、过度出汗、腹泻、体重下降(尽管胃口增加)、肌肉疲软和对热异常敏感;可以开药缓解该疾病的症状;抗甲状腺药物也可以用于减少甲状腺激素的生产;如果药物不起作用,可以部分或完全去除腺;可以通过外科手术或通过放射性碘的施用进行;甲状腺除去会导致甲状腺机能丧失。Protruding eyes are one sign of hyperthyroidism, such as Graves’ disease.
::眼神引人入胜是超机器人病的一种症状,如格雷夫病。Hypothyroidism
::环甲体环环甲体Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces insufficient amounts of thyroid hormones. It can result from surgical removal of the thyroid. However, worldwide, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is dietary iodine deficiency. In cases of iodine deficiency, the negative feedback loop controlling the release of thyroid hormone causes repeated stimulation of the thyroid, resulting in the thyroid gland growing in size and producing a goiter. Although the gland gets larger, it cannot increase hormone output because of the lack of iodine in the diet.
::当甲状腺产生甲状腺激素数量不足时,就会出现甲状腺环状体环状腺炎,而甲状腺激素的外科切除则会造成甲状腺激素的不足;然而,在世界范围内,甲状腺缺碘是甲状腺缺碘的最常见原因;在缺碘的情况下,控制甲状腺激素释放的负面反馈循环导致甲状腺的反复刺激,导致甲状腺腺腺的体积和甲状腺的生长。 虽然甲状腺的体积变大,但由于饮食缺乏碘,它不能增加荷尔蒙的产值。Iodine deficiency is uncommon in the Western world because iodine is added to salt. In places like this where iodine deficiency isn't a problem, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. This is another , but in this case, the immune system destroys the thyroid gland, producing hypothyroidism. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis tends to run in families, so it is likely to have a genetic component. It usually appears after the age of 30, and is more common in females than males.
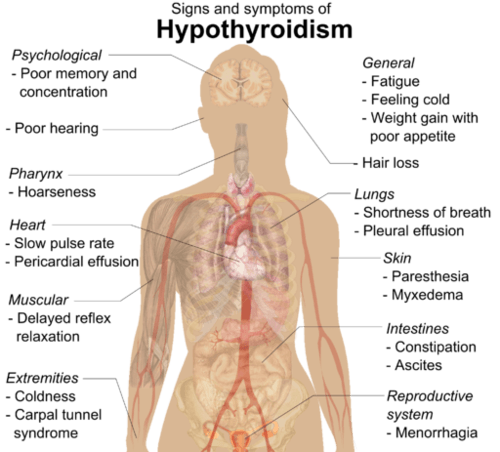
::碘缺乏症在西方世界并不常见,因为碘会添加到盐中。 在像这里这样的缺碘症没有问题的地方,甲本甲状腺炎是甲状腺缺碘最常见的原因。 这是另一个原因,但在这种情况下,免疫系统摧毁甲状腺,造成甲状腺缺碘症。 桥本甲状腺炎往往在家庭中流行,因此可能具有遗传成分。 通常在30岁以后出现,女性比男性更常见。Hypothyroidism produces many signs and symptoms, as shown in the figure . These may include abnormal weight gain, tiredness, baldness, cold intolerance, and slow heart rate. Hypothyroidism is generally treated with thyroid hormone replacement therapy. This may be needed for the rest of a person’s life.
::如图所示,甲状腺环球病产生了许多征兆和症状。 这可能包括超常体重增量、疲劳、秃头、冷漠和心率缓慢。 甲状腺环球病一般都通过甲状腺激素替代疗法治疗。 这或许是个人余生需要的。Hypothyroidism generally causes symptoms that are the opposite of those caused by hyperthyroidism.
::甲状腺环球体环球病通常造成与超甲状腺病相反的症状。Hypothyroidism in a pregnant woman can have serious adverse consequences for the fetus . During the fetal period, cells of the developing brain are a major target for thyroid hormones, which play a crucial role in brain maturation. When levels of thyroid hormones are too low, the fetus may suffer permanent deficits in cognitive abilities. Deafness is also a potential outcome of hypothyroidism in utero .
::在胎儿期,发育中的大脑细胞是甲状腺激素的主要对象,这些激素在大脑成熟过程中起着关键作用。当甲状腺激素水平过低时,胎儿可能会在认知能力方面遭受永久性的缺陷。耳聋也是子宫内甲状腺机能不足的潜在结果。Feature: Myth vs. Reality
::特征:神话对现实Thyroid disorders are relatively common, affecting as many as 20 million people in the United States. Because the disorders are common, there are also many common myths about them.
::甲状腺病相对常见,影响美国多达2 000万人。 由于这种病症很常见,因此也有许多关于他们的常见神话。Myth: If you have a thyroid problem, you will know something is wrong because you will have obvious symptoms.
::传说:如果你有一个甲状腺问题, 你会知道什么是错的,因为你会有明显的症状。Reality: The majority of people with a thyroid disorder are not aware they have it, because the symptoms are often mild, nonspecific, and easy to ignore. Generally, blood tests of thyroid hormone levels are needed to make a conclusive diagnosis.
::现实:大多数甲状腺紊乱症患者并不知道他们是否患有甲状腺紊乱症,因为症状往往温和、不具体、容易忽略。 一般来说,要做出结论性诊断,需要甲状腺激素水平的血液测试。Myth: If you are diagnosed with a thyroid disorder, you will have to take medication for the rest of your life.
::神话:如果你被诊断患有甲状腺紊乱,你将不得不终生服药。Reality: Whether you need to continue thyroid medication for life depends on the cause of the disorder. For example, some women develop hypothyroidism during but no longer need medication after the pregnancy is over and hormone levels return to normal.
::现实:你是否需要在生命中继续使用甲状腺药物取决于病因。例如,有些妇女在妊娠期结束、荷尔蒙水平恢复正常后,在出现甲状腺机能减退后,就不再需要药物了。Myth: As soon as you start taking thyroid medication, your symptoms will resolve.
::神话:一旦你开始服用甲状腺药物, 你的症状就会得到解决。Reality: It often takes weeks — or even months — for thyroid hormone levels to return to normal and for symptoms to disappear.
::现实:甲状腺激素水平恢复正常和症状消失往往需要几周甚至几个月的时间。Myth: You can take an over-the-counter iodine supplement to correct hypothyroidism.
::传说:你可以接受一种超额抗碘补充剂 来纠正甲状腺机能机能缺陷。Reality: In the United States, where dietary iodine is almost always adequate, iodine deficiency is unlikely to be the cause of hypothyroidism. Therefore, taking supplemental iodine is not likely to correct the problem.
::现实:在美国,饮食碘几乎总是充足,缺碘不大可能是甲状腺机能不足的原因。 因此,补充碘不可能纠正问题。Myth: If thyroid symptoms are mild, you don’t need to take medication.
::传说:如果甲状腺症状不严重,Reality: Because thyroid hormones are responsible for so many vital body functions, failing to treat even a mild thyroid disorder may lead to a range of other problems, such as osteoporosis or infertility.
::现实:由于甲状腺激素是造成如此众多重要身体功能的原因,即使轻微甲状腺紊乱不治,也可能导致诸如骨质疏松症或不育等一系列其他问题。Myth: Goiter may be caused by eating “goitrogenic” vegetables, such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and spinach.
::传说:戈蒂尔可能是因食用花椰菜、布鲁塞尔芽菜和菠菜等 " 雌性 " 蔬菜引起的。Reality: Although these foods can interfere with the thyroid’s ability to process iodide, you would have to eat huge amounts of them to cause a goiter.
::现实:尽管这些食物可以干扰甲状腺处理碘化的能力,Myth: Thyroid disorders occur only after middle age and only in women.
::传说:甲状腺紊乱仅在中年后才发生,仅在妇女中发生。Reality: Thyroid disorders may occur at any age and in any sex. Hypothyroidism occurs more commonly in older adults, but hyperthyroidism occurs more commonly in younger adults. Although women are more likely to develop thyroid disorders, about 20 percent of cases occur in men.
::现实:甲状腺紊乱可能发生在任何年龄和任何性别。在老年人中,甲状腺环状腺环状腺炎更为常见,而超甲状腺环状腺病则更常见于较年轻的成年人。尽管妇女更有可能患甲状腺紊乱,但大约20%的病例发生在男性。Summary
::摘要-
The thyroid gland is a large endocrine gland in the front of the neck. It is composed mainly of clusters of cells called follicles, which are specialized to absorb iodine and use it to make thyroid hormones. Parafollicular cells among the follicles synthesize the hormone calcitonin.
::甲状腺是颈部前方的大型内分泌腺,主要由称为卵囊的细胞群组成,这些细胞群专门吸收碘,并用来制造甲状腺激素。 -
Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) cross cell membranes and regulate gene expression to control the rate of metabolism in cells body-wide, among other functions. The production of T4 and T3 is regulated by thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) from the pituitary, which is regulated, in turn, by thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) from the hypothalamus.
::甲状腺素(T4)和三碘二甲苯丙胺(T3)交叉细胞膜,并管制基因表达,以控制整个细胞体中新陈代谢率,除其他功能外,T4和T3的生产由垂体甲状腺刺激激素(TSH)调节,而垂体甲状腺激素(TSH)则由下脑脑膜的甲状腺释放激素(TRH)调节。 -
Calcitonin helps regulate blood calcium levels by stimulating the movement of calcium into bone. It works in conjunction with parathyroid hormone to maintain calcium homeostasis.
::Calcitonin通过刺激钙进入骨骼,帮助调节血钙水平,它与除虫菊激素一起保持钙的均匀。 -
Abnormal secretion of thyroid hormones may occur for a variety of reasons, and it may lead to the development of a goiter. The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder. Iodine deficiency is a common cause of hypothyroidism worldwide. In the United States, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, another autoimmune disorder. Hypothyroidism in pregnant women may cause permanent cognitive deficits in children.
::甲状腺激素的异常分泌可能因多种原因而发生,并可能导致甲状腺病的形成。 超甲状腺病的最常见原因是格雷夫斯病(Graves ) , 一种自体免疫紊乱。 碘缺乏症是全世界甲状腺机能不足的常见原因。 在美国,甲状腺机能不足的最常见原因是哈本甲状腺炎,这是另一种自体免疫紊乱。 孕妇的甲状腺类固醇可能导致儿童长期认知缺陷。
Review
::回顾1. Describe the structure and location of the thyroid gland.
::1. 描述甲状腺的结构和位置。2. Identify the types of cells within the thyroid gland that produce hormones.
::2. 查明甲状腺内产生荷尔蒙的细胞类型。3. Compare and contrast T4 and T3.
::3. 比较和对比T4和T3。4. How do T4 and T3 affect body cells?
::4. T4和T3如何影响身体细胞?5. Explain how T4 and T3 production is regulated.
::5. 解释如何管制T4和T3生产。6. What is calcitonin's function?
::6. 卡尔西托宁的作用是什么?7. Identify the chief cause and effects of hyperthyroidism.
::7. 查明超甲状腺病的主要原因和影响。8. What are two possible causes of hypothyroidism?
::8. 甲状腺机能失常的两种可能原因是什么?9. List signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism.
::9. 列出甲状腺机能失常的迹象和症状。10. Why is it that both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism cause goiters?
::10. 为什么高超机器人主义和机能甲状腺主义都会引起甲状腺病?11. Choose one symptom each for hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Based on the functions of thyroid hormones, explain why each symptom occurs.
::11. 对超甲状腺和甲状腺缺甲状腺分别选择一种症状,根据甲状腺激素的功能,解释每一种症状为何出现。12. Which hormone is produced by the thyroid gland?
::12. 甲状腺产生何种荷尔蒙?a. T3
::a. T3b. calcitonin
::b. 卡西通宁c. parathyroid hormone
::c. 甲状腺素激素激素d. TSH
::d. TSHe. A and B
::e. A和B13. In cases of hypothyroidism caused by Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or removal of the thyroid gland to treat hyperthyroidism, patients are often given medication to replace the missing thyroid hormone. Explain why the level of replacement thyroid hormone must be carefully monitored and adjusted if needed.
::13. 对于由桥本甲状腺炎引起的甲状腺炎或为治疗超甲状腺病而去除甲状腺而导致的甲状腺机能不足的情况,经常向病人提供药物,以取代缺失的甲状腺激素,解释为什么必须在必要时仔细监测和调整替代甲状腺激素的水平。14. True or False: T3 and T4 bind to receptors on the plasma membrane of target cells.
::14. 真实或假:T3和T4与目标细胞等离子膜上的受体捆绑在一起。15. Which of the below diseases causes the production of too much thyroid hormone?
::15. 以下哪些疾病造成甲状腺激素过多?a. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
::a. 桥本甲状腺炎b. Graves’ disease
::b. 坟墓病c. goiter
::c. 甲极d. iodine deficiency
::d. 缺碘Explore More
::探索更多You can learn more about Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis by watching this video, which compares and contrasts these two autoimmune thyroid disorders:
::你可以通过观看这段视频了解更多关于格雷夫斯病和桥本甲状腺炎的知识,The thyroid gland, especially in children, is extremely sensitive to the damaging effects of nuclear radiation. There has been a recent spike in thyroid cancer in Japanese children. Did the 2011 Fukushima nuclear accident cause the spike? Watch this documentary and then form your own opinion.
::甲状腺,特别是儿童甲状腺,对核辐射的破坏性影响极为敏感。 最近日本儿童甲状腺癌的发病率呈上升趋势。 2011年福岛核事故是否引发了这一上升趋势? 观看这部纪录片,然后形成你自己的观点。 -
The thyroid gland is a large endocrine gland in the front of the neck. It is composed mainly of clusters of cells called follicles, which are specialized to absorb iodine and use it to make thyroid hormones. Parafollicular cells among the follicles synthesize the hormone calcitonin.