13.2 骨骼系统介绍
章节大纲
-
Skull and Cross-Bones
::骨骨和交叉骨The skull and cross- symbol has been used for a very long time to represent death, perhaps because after death and decomposition, bones are all that remain. Many people think of bones as dead, dry, and brittle. These adjectives may correctly describe the bones of a preserved skeleton, but the bones of a living human being are very much alive. Living bones are also strong and flexible. Bones are the major organs of the skeletal system.
::头骨和交叉符号用来代表死亡的时间已经很长了,或许是因为在死亡和腐烂之后,骨头就只剩下了。许多人认为骨头是死亡、干燥和易碎的。这些形容词可以正确地描述保存的骨骼的骨骼,但活人的骨骼非常活生生。活骨头也是坚固和灵活的。骨骼是骨骼系统的主要器官。Overview of the Skeleton System
::Skeleton系统概览The skeletal system is the organ system that provides an internal framework for the . Why do you need a skeletal system? Try to imagine what you would look like without it. You would be a soft, wobbly pile of skin containing and internal organs, but no bones. You might look something like a very large slug. Not that you would be able to see yourself — folds of skin would droop down over your and block your , because of your lack of skull bones. You could push the skin out of the way, if you could only move your arms, but you need bones for that, as well!
::骨骼系统是提供内部框架的器官系统。为什么你需要一个骨骼系统?试想一下没有骨骼系统,你会是什么样子。你会是一块柔软的、摇摆的皮肤和内脏,但没有骨头。你可能看起来像一个非常大的子弹。不是因为你能够看见自己——因为你缺乏头骨,皮肤的折叠会滑倒在你的头上,堵住你的头骨。你可以把皮肤推开,如果你能动手臂,但你也需要骨头。Components of the Skeletal System
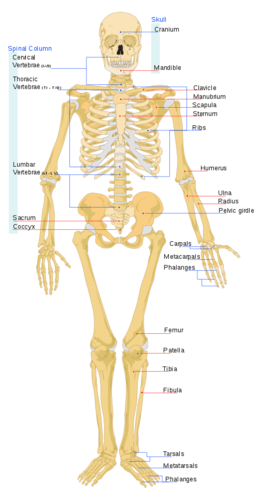
::骨骼系统组成部分In adults, the skeletal system includes 206 bones, many of which are shown in the figure . Bones are organs made of dense connective tissues , mainly the tough collagen . Bones contain , nerves , and other tissues , and they are hard and rigid, due to deposits of calcium and other mineral salts within their living tissues. Spots where two or more bones meet are called . Many joints allow bones to move like levers. Y our elbow, for example, is a joint that allows you to bend and straighten your arm.
::在成人中,骨骼系统包括206个骨头,其中许多在图中显示。骨骼是由密闭的结结结组织组成的器官,主要是硬的凝固的凝固的凝结组织。骨骼含有、神经和其他组织,并且由于在活组织内存有钙和其他矿物盐,骨骼系统坚硬僵硬。两个或两个以上骨骼相交的点被称作“。许多关节允许骨头像杆子一样移动。例如,你的肘部是一个可以弯曲和伸直手臂的连接点。The adult skeleton contains 206 bones. A newborn infant has 270 bones, but many of them fuse together by adulthood.
::成人骨骼有206具骨头,新生婴儿有270具骨头,但其中许多在成年前融为一体。Besides bones, the skeletal system includes cartilage and ligaments .
::除骨头外,骨骼系统还包括软骨和颈部。-
Cartilage
is a type of dense connective tissue, made of tough protein fibers. It is strong, but flexible and very smooth. It covers the ends of bones at joints, providing a smooth surface for bones to move over.
::陶瓷是一种由坚硬蛋白纤维组成的密度稠密的连接组织,它很坚固,但很灵活,很光滑。它覆盖了关节骨的端端,为骨头移动提供了光滑的表面。 -
Ligaments
are bands of fibrous connective tissue that hold bones together. They keep the bones of the skeleton in place.
::粘结是将骨骼凝结在一起的纤维结结组织带,它们把骨骼的骨骼固定在原地。
Axial and Appendicular Skeletons
::轴心和辅助骨骼The skeleton is traditionally divided into two major parts: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton, both of which are pictured below.
::骨骼传统上分为两大部分:轴心骨骼和天体骨骼,这两部分都如下图所示。-
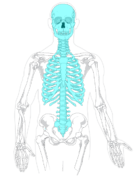
The
axial skeleton
forms the axis of the body. It includes the skull,
vertebral column
(spine), and rib cage. The bones of the axial skeleton — along with ligaments and muscles — allow the human body to maintain its upright posture. The axial skeleton also transmits weight from the head, trunk, and upper extremities down the back to the lower extremities. In addition, the bones protect the
brain
and organs in the chest.
::轴骨骼构成身体的轴心,包括头骨、脊椎柱(松)和肋骨笼;轴骨的骨骼,连同颈部和肌肉,使人体保持直立的姿势;轴骨也从头部、后部和上部向后部向下部传递重量;此外,骨骼保护胸部的大脑和器官。 -
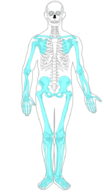
The
appendicular skeleton
forms the
appendages
and their attachments to the axial skeleton. It includes the bones of the arms and legs, hands and feet, and shoulder and pelvic girdles. The bones of the appendicular skeleton make possible
and other
movements
of the appendages. They also protect the major organs of
digestion
,
excretion
, and
.
::外形骨骼形成附着物及其附着物,包括胳膊和腿、手和脚、肩和骨盆骨的骨骼。外形骨骼的骨骼使外形骨骼和其他运动成为可能。它们还保护消化、排泄和排泄的主要器官。
Axial skeleton
::轴骨架Appendicular skeleton
::外形骨架Functions of the Skeletal System
::骨骼系统功能The skeletal system has many different functions that are necessary for human survival. Some of the functions, such as supporting the body, are relatively obvious. Other functions are less obvious but no less important. T hree tiny bones (hammer, anvil, and stirrup) inside the middle ear, for example, transfer sound waves into the inner ear.
::骨骼系统有许多人类生存所必需的不同功能,有些功能,如支持身体,比较明显。其他功能不那么明显,但同样重要。例如,中耳的三根小骨头(锤子、子和子)将声波移入内耳。Support, Shape, and Protection
::支助、形状和保护The skeleton supports the body and gives it shape. Without the rigid bones of the skeletal system, the human body would be just a bag of soft tissues, as described above. The bones of the skeleton are very hard and provide protection to the delicate tissues of internal organs. For example, the skull encloses and protects the soft tissues of the brain, and the vertebral column protects the nervous tissues of the spinal cord . The vertebral column, ribs, and sternum (breast bone) protect the heart, lungs , and major blood vessels. Providing protection to these latter internal organs requires the bones to be able to expand and contract. The ribs and the cartilage that connects them to the sternum and vertebrae are capable of small shifts that allow and other internal organ movements.
::骨骼支撑身体并形成形状。没有骨骼系统的僵硬骨骼,人体将只是一袋如上文所述的软组织。骨骼的骨骼非常硬,为内部器官的微妙组织提供了保护。例如,头骨围住并保护了大脑的软组织,脊椎柱保护了脊椎的神经组织。脊椎柱、肋骨和胸骨(胸骨)保护了心脏、肺和主要血管。保护这些骨骼的骨骼需要骨骼能够膨胀和缩缩缩。骨骼和骨骼与骨质和脊椎相连的骨骼能够进行小的转变,允许其他器官运动。Movement
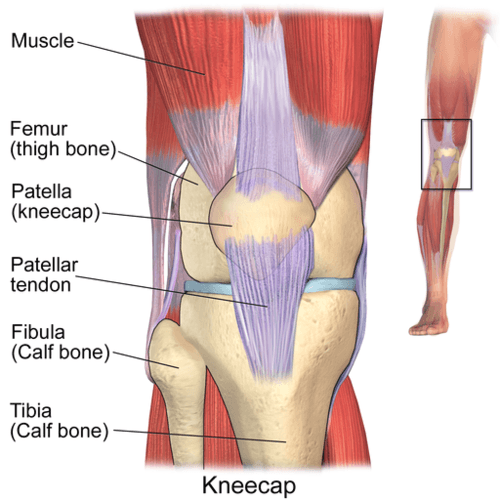
::动 动The bones of the skeleton provide attachment surfaces for . When the muscles contract, they pull on and move the bones. The figure , for example, shows the muscles attached to the bones at the knee. They help stabilize the joint and allow the leg to bend at the knee. The bones at joints act like levers moving at a fulcrum point, and the muscles attached to the bones apply the force needed for movement.
::骨骼骨骼为骨骼提供了依附表层。当肌肉收缩时,它们拉起并移动骨骼。例如,图中显示了与膝盖骨头相连的肌肉。它们帮助稳定关节,使腿弯曲到膝盖。关节的骨骼举止就像在支架点上移动的杆子,而骨骼上的肌肉则施加了运动所需的力力。Bones that meet at the knee joint include the tibia and fibula in the lower leg, the femur in the upper leg, and the kneecap at the front of the knee. These bones provide attachment surfaces for muscles that move the bones at the joint.
::在膝盖关节相遇的骨骼包括下腿的提比亚和纤维、上腿的股骨和膝盖前的膝盖骨。这些骨骼为在关节移动骨头的肌肉提供了依附面。Hematopoiesis
::血蛋白Hematopoiesis is the process by which are produced. This process occurs in a tissue called red marrow, which is found inside some bones, including the pelvis, ribs, and vertebrae. Red marrow synthesizes red blood cells , white blood cells , and platelets . Billions of these blood cells are produced inside the bones every day.
::血压是产生血压的过程。这个过程发生在一个被称为红骨髓的组织中,它存在于一些骨头中,包括骨盆、肋骨和脊椎。红骨是红血细胞、白血细胞和小板的合成体。这些血细胞中有数十亿个每天都在骨头中产生。Mineral Storage and Homeostasis
::矿物储存和保持原状Another function of the skeletal system is storing minerals, especially calcium and phosphorus. This storage function is related to the role of bones in maintaining mineral homeostasis . Just the right levels of calcium and other minerals are needed in the blood for normal functioning of the body. When mineral levels in the blood are too high, bones absorb some of the minerals and store them as mineral salts, which is why bones are so hard. When blood levels of minerals are too low, bones release some of the minerals back into the blood. Bone minerals are alkaline (basic), so their release into the blood buffers the blood against excessive acidity (low pH), whereas their absorption back into bones buffers the blood against excessive alkalinity (high pH). In this way, bones help maintain acid-base in the blood.
::骨骼系统的另一个功能是储存矿物,特别是钙和磷,这种储存功能与骨骼在维持矿物原状方面的作用有关。血液中只需要正确的钙和其他矿物含量,身体才能正常运转。当血液中的矿物含量太高时,骨骼吸收一些矿物,作为矿盐储存起来,这就是骨骼如此坚硬的原因。当矿物的血液含量太低时,骨骼将一些矿物释放回血液中。骨骼矿物是碱性(基质),因此它们释放到血液缓冲物中,血液与过度酸性(低pH)抗争,而它们吸收到骨骼中会缓冲血液与过度碱性(高pH)抗争。这样,骨骼有助于保持血液中的酸基。Another way that bones help maintain homeostasis is by acting as an endocrine organ. One endocrine secreted by bone cells is osteocalcin, which helps regulate blood glucose and fat deposition. It increases insulin secretion, as well as cell's sensitivity to insulin . In addition, it boosts the number of insulin-producing cells and reduces fat stores.
::骨骼有助于保持家庭耐久的另一个方式是作为内分泌器官发挥作用。骨骼细胞隐藏的一个内分泌是骨骼癌,它有助于调节血糖和脂肪沉积。它增加了胰岛素分泌以及细胞对胰岛素的敏感性。此外,它增加了胰岛素生产细胞的数量并减少了脂肪商店。Sexual Dimorphism of the Human Skeleton
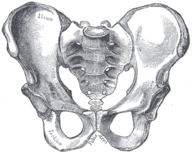
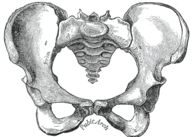
::人类骨骼的性变性The human skeleton is not as sexually dimorphic as that of many other primate , although human female skeletons tend to be smaller and less robust than human male skeletons within a given . There are also subtle differences between males and females in the morphology of the skull, teeth, longs bones, and pelvis. The greatest difference is in the pelvis, because the female pelvis is adapted for child birth.
::人类骨骼不像其他许多灵长类动物一样具有性畸形性,尽管人类女性骨骼往往比人类男性骨骼小,而且不那么强大。 在头骨、牙齿、长骨和骨盆的形态方面,男性和女性之间也存在细微的差异。 最大的差异在于骨盆,因为女性骨盆适合生育。Male pelvis
::男性骨盆Female pelvis
::女性骨盆Summary
::摘要-
The skeletal system is the organ system that provides an internal framework for the human body. In adults, the skeletal system contains 206 bones.
::骨骼系统是人体内部框架的器官系统,在成人中,骨骼系统含有206根骨头。 -
Bones are organs made of dense connective tissues, mainly the tough protein collagen. Bones also contain blood vessels, nerves, and other tissues. Bones are hard and rigid, due to deposits of calcium and other mineral salts within their living tissues. Besides bones, the skeletal system includes cartilage and ligaments.
::骨骼是由稠密的连接组织构成的器官,主要是硬质蛋白质共聚物。骨骼还含有血管、神经和其他组织。骨骼硬硬硬,因为其活组织内存有钙和其他矿物盐。除了骨骼外,骨骼系统还包括软骨和颈部。 -
The skeleton is traditionally divided into two major parts: the axial skeleton (which includes the skull, spine, and rib cage) and the appendicular skeleton (which includes the appendages and the girdles that attach them to the axial skeleton).
::骨骼传统上分为两大部分:轴骨骼(包括头骨、脊椎和肋骨笼)和附肢骨骼(包括附着在轴骨上的附肢和刺带)。 -
The skeletal system has many different functions, including supporting the body and giving it shape, protecting internal organs, providing attachment surfaces for skeletal muscles, allowing body movements, producing blood cells, storing minerals, helping to maintain mineral homeostasis, and producing endocrine hormones.
::骨骼系统有许多不同的功能,包括支持身体并给其形状,保护内脏器官,为骨骼肌肉提供依附面,允许身体运动,生产血细胞,储存矿物,帮助保持矿物质原状,以及生产内分泌激素。 -
There is relatively little sexual dimorphism in the human skeleton, although the female skeleton tends to be smaller and less robust than the male skeleton. The greatest sex difference is in the pelvis, which is adapted for childbirth in females.
::尽管女性骨骼往往小于男性骨骼,而且不那么强壮,但人体骨骼的性畸形相对较少。 最大的性别差异在于骨盆,因为骨盆适合女性分娩。
Review
::回顾1. What is the skeletal system? How many bones are there in the adult skeleton?
::1. 什么是骨骼系统?成人骨骼中有多少骨头?2. Describe the composition of bones.
::2. 描述骨头的构成。3. Besides bones, what other organs are included in the skeletal system?
::3. 除骨骼外,骨骼系统还包括哪些其他器官?4. Identify the two major divisions of the skeleton.
::4. 查明骨骼的两个主要部分。5. List several functions of the skeletal system.
::5. 列出骨骼系统的若干功能。6. Discuss sexual dimorphism in the human skeleton.
::6. 讨论人体骨骼中的性畸形。7. Bones, cartilage, and ligaments are all made of types of ____________ tissue.
::7. 骨骼、软骨和颈部都是由组织类型组成的。8. True or False: Bones contain living tissue and can affect processes in other parts of the body.
::8. 真实或假的:骨骼含有活组织,可能影响身体其他部分的过程。9. True or False: Bone cells contract to pull on muscles in order to initiate a movement.
::9. 真实或假:骨细胞合同,拉肌肉以发起运动。10. If a person has a problem with blood cell production, what type of bone tissue is most likely involved? Explain your answer.
::10. 如果一个人对血细胞生产有问题,最可能涉及哪类骨骼组织?11. Are the pelvic girdles part of the axial or appendicular skeleton?
::11. 骨盆刺骨是轴骨或附体骨骼的一部分吗?12. What are three forms of homeostasis that the skeletal system regulates? Briefly explain how each one is regulated by the skeletal system.
::12. 骨骼系统调节的三种形式的自足状态是什么?简要地解释每个形式的自足状态如何受骨骼系统的制约。13. What do you think would happen to us if we did not have ligaments? Explain your answer.
::13. 如果我们没有长袍,你认为我们会发生什么?解释你的答复。14. What is a joint? How is cartilage related to joints? Identify one joint in the human body and describe its function.
::14. 什么是联合体?软体与联合体的关系如何?在人体中找出一个联合体并说明其功能。Explore More
::探索更多Did you ever watch the popular TV series Bones ? It’s about a forensic anthropologist who uses her expert knowledge of the human skeleton to solve murder mysteries. In the video below, you can listen to the brains behind Bones — forensic anthropologist and award-winning fiction writer Dr. Kathy Reichs — as she talks about the real world of forensic anthropology and the realistic fictional world she has created.
::你看过流行的电视系列《骨头》吗?这是关于一名法医人类学家,她利用她对人类骨骼的专业知识解决谋杀奥秘。 在下面的视频中,你可以聆听Bones背后的大脑 — — 法医人类学家和获奖小说作家凯西·里奇斯博士 — — 当她谈论法医人类学和她所创造的现实虚构世界的真实世界时。Most primates are sexually dimorphic . T o learn more, check out this video:
::多数灵长类是性畸形的。 -
Cartilage
is a type of dense connective tissue, made of tough protein fibers. It is strong, but flexible and very smooth. It covers the ends of bones at joints, providing a smooth surface for bones to move over.