13.5 骨增长、改造和修理
章节大纲
-
Break A Leg
::断断腿Did you ever break a leg or other , like the man looking longingly at the in this swimming pool? Having a broken bone can really restrict your activity. Bones are very hard, but they will break (or fracture) if enough force is applied to them. Fortunately, bones are highly active organs that can repair themselves if they break. Bones can also remodel themselves and grow. You’ll learn how bones can do all of these things in this concept.
::你有没有像那个在游泳池里望望望的人那样摔断一条腿或其他东西?骨折确实会限制你的活动。骨骼非常硬,但如果有足够的力力力,它们就会断裂(或断裂 ) 。 幸运的是,骨骼是高度活跃的器官,一旦断裂,可以修复自己。骨骼也可以改造自己,成长。你会知道骨骼如何在这个概念下完成所有这些事情。Bone Growth
::Bone 增长Early in the of a human fetus , the skeleton is made almost entirely of cartilage . The relatively soft cartilage gradually turns into hard bone through ossification . Ossification is a process in which bone tissue is created from cartilage. The steps in which bones of the skeleton form from cartilage are illustrated in the figure . The steps are as follows:
::人体胚胎早期,骨骼几乎完全由软骨骼组成,相对软的软骨骼通过骨化逐渐变成硬骨。骨骼组织从骨骼组织形成的过程。骨骼骨骼骨骼的骨骼形状在图中显示了步骤。步骤如下:-
C
artilage “model” of bone forms. This
model
continues to grow as ossification takes place.
::骨质形态的软骨“模型”,随着骨质化的发生,这一模型继续增长。 -
Ossification begins at a primary ossification center in the middle of bone.
::骨质化从骨骼中间的 一级骨质化中心开始 -
Ossification then starts to occur at secondary ossification centers at the ends of bone.
::然后在骨骨端的二级骨质化中心开始发生骨质化。 -
The medullary cavity forms. This cavity will contain red
bone marrow
.
::体积腔表,这个腔将包含红骨髓 -
Areas of ossification meet at epiphyseal plates, and articular cartilage forms. Bone growth ends.
::骨质化区与验血板和手动骨骼形式相交。骨骼生长结束。
The ossification of cartilage in the human skeleton is a process that lasts throughout childhood in some bones.
::人体骨骼骨骼骨骼的骨刻化过程 持续到整个童年 在某些骨头里Primary and Secondary Ossification Centers
::初级和中级观测中心When bone forms from cartilage, ossification begins with a point in the cartilage called the primary ossification center . This generally appears during fetal development, although a few short bones begin their primary ossification after birth. Ossification happens toward both ends of the bone from the primary ossification center, and — in the case of long bones — it eventually forms the shaft of the bone.
::当骨骼骨质形成时,骨质化从软骨中取一个点开始,称为主骨质化中心,这通常出现在胎儿发育期间,尽管一些短骨在出生后开始初步骨质化,骨质化从主骨质化中心发生于骨骼两端,如果是长骨质,则最终形成骨质轴。Secondary ossification centers form after birth. Ossification from secondary centers eventually forms the ends of the bones. The shaft and ends of the bone are separated by a growing zone of cartilage until the individual reaches skeletal maturity.
::产后形成二级骨化中心,从二级中心进行植入最终会形成骨骼的端端端。骨的轴部和端部被不断增长的软骨区隔开,直到个人骨骼发育成熟为止。Skeletal Maturity
::骨骼成熟期Throughout childhood , the cartilage remaining in the skeleton keeps growing, and allows for bones to grow in size. O nce all of the cartilage has been replaced by bone, and fusion has taken place at epiphyseal plates, bones can no longer keep growing in length. At this point, skeletal maturity has been reached. It generally takes place by age 18 to 25.
::在整个童年时期,骨骼中残留的骨骼不断生长,骨骼得以生长,骨骼得以生长。 一旦骨骼全部被骨骼取代,骨骼的聚变已经发生,骨骼已经无法再长长。此时,骨骼已经达到骨骼成熟程度,通常在18至25岁之前发生。The use of anabolic steroids by teens can speed up the process of skeletal maturity, resulting in a shorter period of cartilage growth before fusion takes place. This means that teens who use steroids are likely to end up shorter as adults than they would otherwise have been.
::青少年使用新陈代谢类固醇可以加速骨骼成熟过程,从而导致在聚变发生前的软体生长期缩短。 这意味着使用类固醇的青少年在成年后可能会比其他情况下更短。Bone Remodeling
::B. 骨骨改造改造Even after skeletal maturity has been attained, bone is constantly being resorbed and replaced with new bone in a process called bone remodeling . In this lifelong process, mature bone tissue is continually turned over, with about ten percent of the skeletal mass of an adult being remodeled each year. Bone remodeling is carried out through the work of osteoclasts — which are bone that resorb bone and dissolve its minerals — and osteoblasts , which are bone cells that make new bone matrix .
::即使在骨骼成熟后,骨骼也不断被转基因,并在一个称为骨骼改造的过程中被新骨头取代。在这一终生过程中,成熟的骨组织不断被翻转,每年对成年人骨骼质量的大约10%进行改造。骨骼改造是通过骨骼细胞的工程进行的,骨骼骨骼是骨骼骨骼的骨骼,是骨骼骨骼骨骼的骨骼细胞,是骨骼细胞的骨骼细胞,是新的骨骼矩阵。Bone remodeling serves several functions. It shapes the bones of the skeleton as a child grows, and it repairs tiny flaws in bone that result from everyday movements . Remodeling also makes bones thicker at points where place the most stress on them. In addition, remodeling helps regulate mineral homeostasis , because it either releases mineral from bones into the or absorbs mineral from the blood into bones. The figure shows how osteoclasts in bones are involved in calcium regulation.
::骨骨改造有几个功能。 它在孩子成长时塑造骨骼的骨骼, 修复日常运动造成的骨骼小缺陷。 改造还使得骨骼在压力最大的地方变得更厚。 此外, 改造有助于调节矿物质恒定状态, 因为它要么将矿物从骨头中释放出来, 要么将矿物质从血液中吸收到骨头中。 图表显示了骨骼中的骨骼是如何参与钙的调节的。Keeping the calcium level in homeostasis involves the work of osteoclasts, the bone cells that resorb bone and release calcium into the blood.
::将钙水平保持在足压状态中涉及骨骼细胞的工作,骨骼细胞是骨骼细胞,骨骼细胞是骨骼,将钙释放到血液中。The action of osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone remodeling and calcium is controlled by a number of , , and other substances that either promote or inhibit the activity of the cells. In this way, these substances control the rate at which bone is made, destroyed, and changed in shape. For example, the rate at which osteoclasts resorb bone and release calcium into the blood is promoted by parathyroid hormone (PTH) and inhibited by calcitonin, which is produced by the thyroid gland (see the diagram above). The rate at which osteoblasts create new bone is stimulated by growth hormone, which is produced by the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland . Thyroid hormone and sex hormones (estrogens and androgens) also stimulate osteoblasts to create new bone.
::骨骼改造和钙中骨质激素和骨质激素的动作由若干促进或抑制细胞活动的物质和其他物质控制。以这种方式,这些物质控制骨质制造、破坏和形状改变的速度。例如,骨质激素反应骨和将钙释放到血液中的速率由对流体激素(PTH)推动,由甲状腺腺生成的卡西通宁抑制(见以上图表)。骨质激素刺激骨质生成新骨头的速度是生长激素,生长激素是由垂状腺前叶产生的。甲状腺激素和性激素(激素和激素)也刺激骨质生成。Bone Repair
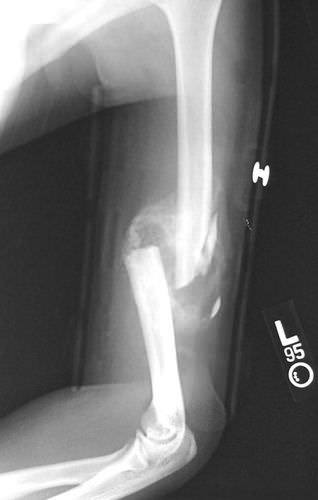
::骨骨修理Bone repair (or healing) is the process in which a bone repairs itself following a bone fracture . You can see an X-ray of a bone fracture . In this fracture, the humerus in the upper arm has been completely broken through its shaft. Before this fracture heals, a physician must push the displaced bone parts back into their correct positions. Then, the bone must be stabilized — with a cast and/or pins surgically inserted into the bone, for example — until the bone’s natural healing process is complete. This process may take several weeks.
::骨骨修复(或愈合)是骨骨折后骨骼修复过程本身的过程。 你可以看到骨折的X光。 在这一骨折中,上臂的骨完全断裂。 在骨折愈合之前,医生必须把骨折的骨部分推回到正确的位置。 然后,骨骼必须稳定下来 — — 比如用手术将石膏和(或)针插进骨头中 — — 直到骨骼的自然愈合过程完成。 这一过程可能需要几周时间。A bone fracture does not always involve a complete break in the bone, as in this X-ray. Sometimes, a fracture is just a crack in the bone. In other cases, the bone not only breaks all the way through, but also breaks through the soft tissues around it so it protrudes from the skin. This is called an open fracture.
::骨折并不总是与骨骼完全断裂有关,就像X光一样。有时,骨折只是骨裂。在另一些情况下,骨折不仅穿透了整个骨折,还穿透了周围的软组织,从皮肤中穿透。这被称为开放骨折。Although bone repair is a natural physiological process, it may be promoted or inhibited by several factors. F racture repair is more likely to be successful with adequate nutrient intake. Age, bone type, drug therapy, and pre-existing bone disease are additional factors that may affect healing. Bones that are weakened by disease (such as osteoporosis or bone cancer) are not only likely to heal more slowly, but are also more likely to fracture in the first place.
::骨骼修复虽然是一种自然生理过程,但可能受到若干因素的推动或抑制。骨骼修复如果有足够的营养摄入,就更有可能取得成功。年龄、骨型、药物治疗和先前存在的骨骼疾病是可能影响愈合的其他因素。 被疾病(如骨质疏松症或骨癌)削弱的骨骼不仅可能更慢地愈合,而且首先更有可能骨折。Feature: Myth vs. Reality
::特征:神话对现实Bone fractures are fairly common, and there are many myths about them. Knowing the facts is important, because fractures generally require emergency medical treatment.
::骨骨骨骨折相当常见,关于骨骨骨骨骨折的神话也很多。 了解事实很重要,因为骨骨骨骨折通常需要紧急医疗治疗。Myth: A bone fracture is a milder injury than a broken bone.
::传说:骨折比骨折轻伤。Reality: A bone fracture is the same thing as a broken bone.
::现实:骨折和骨折是一样的Myth: If you still have full range of motion in a limb, then it must not be fractured.
::传说:如果你的四肢仍有完全的运动, 那它就不能断裂。Reality: Even if a bone is fractured, the muscles and tendons attached to it may still be able to move the bone normally. This is especially likely if the bone is cracked — but not broken — into two pieces. Even if a bone is broken all the way through, range of motion may not be affected if the bones on either side of the fracture remain properly aligned.
::现实:即使骨头骨折,但骨骼上的肌肉和护带仍能正常移动。如果骨骼破碎(但没有折断)成两块,这尤其可能。即使骨骼一直断裂,骨骼两侧的骨骼保持正轨,运动范围可能不会受到影响。Myth: A fracture always produces a bruise.
::神话:骨折总是产生瘀伤。Reality: Many — but not all — fractures produce a bruise. If a fracture does produce a bruise, it may take several hours (or even a day or more!) for the bruise to appear.
::真实情况:许多(但并非全部)骨折造成瘀伤,如果骨折确实造成瘀伤,可能需要几个小时(甚至一天或更长时间! )才能出现瘀伤。Myth: Fractures are so painful that you will immediately know if you break a bone.
::神话:断裂是如此痛苦, 你就会立刻知道,如果你骨折了。Reality: Ligament sprains and muscle strains are also very painful, sometimes more painful than fractures. Additionally, every person has a different pain tolerance. People with a high pain tolerance may continue using a broken bone in spite of the pain.
::现实:拉链扭扭和肌肉紧张也非常痛苦,有时比骨折更痛苦。 此外,每个人都有不同的止痛耐痛能力。 高耐痛能力的人尽管有疼痛,仍可以继续使用断骨。Myth: You can tell when a bone is fractured because there will be very localized pain over the break.
::传说:你可以看到骨折是什么时候, 因为休息时会有局部的疼痛。Reality: A broken bone is often accompanied by injuries to surrounding muscles or ligaments. As a result, the pain may extend far beyond the location of the fracture. The pain may be greater directly over the fracture, but the intensity of the pain may make it difficult to pinpoint exactly where the pain originates.
::真实性:骨折时,周围肌肉或颈部经常受伤。结果,疼痛可能远远超出骨折的位置。疼痛可能直接大于骨折,但疼痛的强度可能使得很难准确确定疼痛的发源地。Summary
::摘要-
Bone is very active tissue. Its cells are constantly forming and resorbing bone matrix.
::骨是活性组织 细胞不断形成和重组骨质矩阵 -
Early in the development of a human fetus, the skeleton is made almost entirely of cartilage. The relatively soft cartilage gradually turns into hard bone. This is called ossification. It begins at a primary ossification center in the middle of bone, and later also occurs at secondary ossification centers in the ends of bone. The bone can no longer grow in length after the areas of ossification meet and fuse at the time of skeletal maturity.
::人体胎儿早期发育时,骨骼几乎完全由软软的骨骼组成。相对软的骨骼逐渐变成硬骨头。这被称为骨质化。它始于骨骼中间的主要骨质化中心,后来也发生在骨骼端的二级骨质化中心。骨骼在骨骼成熟时骨质化领域相遇和发炎后,骨骼不能再长长。 -
Throughout life, bone is constantly being replaced in the process of bone remodeling. In this process, osteoclasts resorb bone, and osteoblasts make new bone to replace it. Bone remodeling shapes the skeleton, repairs tiny flaws in bones, and helps maintain mineral homeostasis in the blood.
::整个生命中,骨骼在骨骼改造过程中不断被替换。 在这一过程中,骨骼还原骨骼和骨骼造新骨骼来替换骨骼。骨骼改造塑造骨骼,修复骨骼的微小缺陷,并帮助保持血液中的矿物质自久不衰。 -
Bone repair is the natural process in which a bone repairs itself following a bone fracture. This process may take several weeks. In the process, periosteum produces cells that develop into osteoblasts, and the osteoblasts form new bone matrix to heal the fracture. Bone repair may be affected by diet, age, pre-existing bone disease, or other factors.
::骨骼修复是骨折后骨骼修复本身的自然过程,这一过程可能需要数周时间。在这一过程中,皮下骨骼生成细胞,形成骨质突变,骨质突变形成新的骨质矩阵以治愈骨折。骨骨骼修复可能受到饮食、年龄、先前存在的骨骼疾病或其他因素的影响。
Review
::回顾1. Outline how bone develops starting early in the fetal stage, and through the age of skeletal maturity.
::1. 概述骨骼从胎儿阶段早期开始,直至骨骼发育成熟期是如何发育的。2. Describe the process of bone remodeling. When does it occur?
::2. 描述骨骼改造过程:何时发生?3. What purposes does bone remodeling serve?
::3. 骨骼改造的目的是什么?4. Define bone repair. How long does this process take?
::4. 界定骨骼修补:这一过程需要多长时间?5. Explain how bone repair occurs.
::5. 解释如何修复骨骼。6. Identify factors that may affect bone repair.
::6. 查明可能影响骨骼修复的因素。7. Parts of bone that have not yet become ossified are made of _________ .
::7. 骨骼尚未骨化的部分由______ 制成。8. If there is a large region between the primary and secondary ossification centers in a bone, is the person young or old? Explain your answer.
::8. 如果骨质中初级和二级骨质化中心之间有较大的区域,是年轻人还是老人?请解释您的答复。9. The region where the primary and secondary ossification centers meet is called the ________ ________ .
::9. 初级和二级骨化中心聚会的区域称为__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________10. True or False: Most bones are made entirely of cartilage at birth.
::10. 真实或假的:大多数骨头都是在出生时完全用软骨制成的。11. True or False: A broken bone is the same as a bone fracture.
::11. 真实或假:骨折与骨折相同。12. If bones can repair themselves, why are casts and pins sometimes necessary in the process ?
::12. 如果骨骼可以自我修复,为什么在过程中有时需要石膏和钉子?13. When calcium levels are low, which type of bone cell causes the release of calcium to the bloodstream?
::13. 当钙含量低时,哪种骨细胞导致钙释放到血液中?14. Which tissue and bone cell type are primarily involved in bone repair after a fracture?
::14. 骨折后,哪些组织和骨骼细胞类型主要用于骨骼修复?15. Describe one way in which hormones are involved in bone remodeling.
::15. 描述荷尔蒙参与骨骼改造的一种方式。Explore More
::探索更多Watch this short video to see how and why a newborn’s skeleton differs from an adult’s skeleton.
::观察这段短片, 以了解新生儿骨骼与成人骨骼有何不同,For a better appreciation of how fractured bones heal themselves, watch this interesting animated video about the healing process:
::为了更好地了解骨折如何愈合自己, 观看关于愈合过程的这段有趣的动画影片: -
C
artilage “model” of bone forms. This
model
continues to grow as ossification takes place.