13.7 骨骼系统紊乱
章节大纲
-
Dowager’s Hump
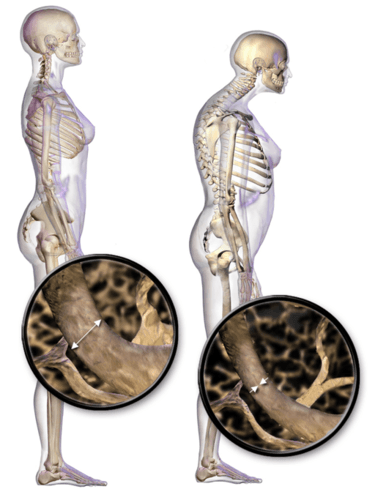
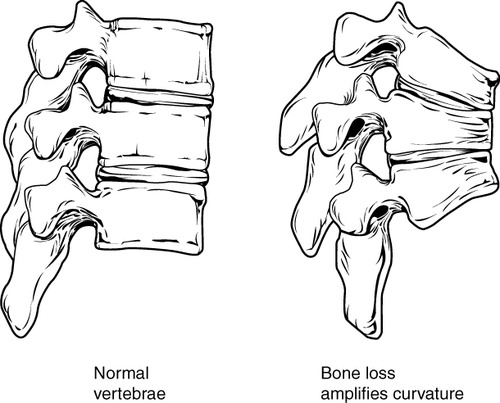
::下水道的重力The woman on the right in this image has a deformity in her back commonly called dowager’s (widow’s) hump, because it occurs most often in elderly women. Its medical name is kyphosis, and it is defined as excessive curvature of the spinal column in the thoracic region. The curvature generally results from fractures of thoracic vertebrae . As the inset drawings suggest, these fractures may occur due to a significant decrease in mass, which is called osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is one of the most prevalent disorders of the .
::在这张图中,右侧的妇女背部有畸形,通常被称为“大风”(Widow's)腰部,因为它最常发生在老年妇女身上。 其医学名称是kyphosis, 被定义为胸腔地区脊柱的过度弯曲。 曲线通常是由胸椎骨折造成的。 正如不固定的图画所显示的那样,这些骨折可能是由于质量的显著下降而发生,也就是骨质疏松症。 骨质疏松症是脑部骨质疏松症最普遍的疾病之一。Common Skeletal System Disorders
::常见骨骼系统疾病A number of disorders affect the skeletal system, including bone fractures and bone cancers. However, the two most common disorders of the skeletal system are osteoporosis and osteoarthritis . At least ten million people in the United States have osteoporosis, and more than 8 million of them are women. Osteoarthritis is even more common, affecting almost 30 million people in the United States. Because osteoporosis and osteoarthritis are so common, they are the focus of this concept. These two disorders are also good examples to illustrate the structure and function of the skeletal system.
::一些疾病影响到骨骼系统,包括骨折和骨癌,然而,骨骼系统的两种最常见的疾病是骨质疏松症和骨髓炎,美国至少有1 000万人患有骨质疏松症,其中超过800万人是妇女,骨质关节炎更为普遍,影响到美国近3 000万人,因为骨质疏松症和骨髓炎非常普遍,它们是这个概念的焦点,这两种疾病也是表明骨骼系统结构和功能的良好例子。Osteoporosis
::骨质疏松Osteoporosis is an age-related disorder in which bones lose mass, weaken, and break more easily than normal bones. Bones may weaken so much that a fracture can occur with minor stress — or even spontaneously, without any stress at all. Osteoporosis is the most common cause of broken bones in the elderly, but until a bone fracture occurs, it typically causes no symptoms. The bones that break most often include those in the wrist, hip, shoulder, and spine. When the thoracic vertebrae are affected, there can be a gradual collapse of the vertebrae due to compression fractures, as shown in the figure . This is what causes kyphosis, as pictured above.
::骨质疏松是一种与年龄有关的疾病,骨骼在这种疾病中失去质量、衰弱和断裂比正常骨骼更容易。骨骼可能会变弱,导致骨折在轻微压力下发生,甚至自发发生,没有任何压力。骨质疏松是老年人骨折的最常见原因,但在骨折发生之前,它通常不会造成症状。骨骼破裂的骨骼通常包括手腕、臀部、肩部和脊椎骨。当胸椎骨受到影响时,骨椎骨可能会因骨折而逐渐崩溃,如图所示。这就是造成脊椎骨折的原因,如上图所示。Compression fractures of thoracic vertebrae are relatively common in people with osteoporosis.
::在骨质疏松症患者中,胸椎骨折的压缩骨折相对常见。Changes in Bone Mass with Age
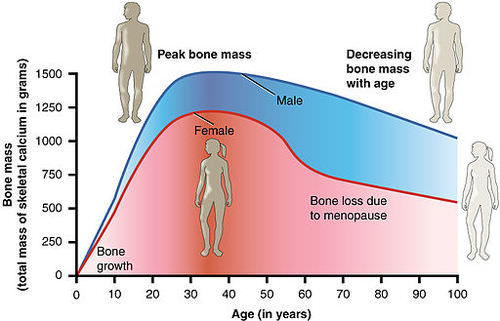
::随年龄变化的骨质质量的变化As shown in the graph , bone mass in both males and females generally peaks when people are in their thirties , with males typically attaining a higher peak mass than females. In both sexes, bone mass usually decreases after that , and this tends to occur more rapidly in females, especially after menopause . The greater decrease in females is generally attributable to low levels of estrogen in the post-menopausal years.
::如图所示,男性与女性的骨质通常在30多岁时达到峰值,男性通常达到高于女性的峰值,此后,男性的骨质通常会下降,女性的骨质往往会更快,特别是在更年期后,女性的骨质下降幅度较大,一般是由于绝经后女性的雌激素水平较低。Bone mass is a measure of the total mass of calcium in the bones of the skeleton. As bone mass decreases, the risk of fractures increases.
::骨质是骨头骨骼中钙的总质量的量度,骨质下降,骨折的风险增加。What Causes Osteoporosis?
::导致骨质疏松的原因是什么?The underlying mechanism in all cases of osteoporosis is an imbalance between bone formation by osteoblasts and bone resorption by osteoclasts. Normally, bones are constantly being remodeled by these two processes, with up to ten percent of all bone mass undergoing remodeling at any point in time. As long as these two processes are in balance , no net loss of bone occurs. There are three main ways that an imbalance between bone formation and bone resorption can occur and lead to a net loss of bone. All three ways may occur in the same individual. The three ways are described below:
::在骨质疏松的所有情况下,骨质疏松的基本机制都是骨骼形成与骨骼重新吸附之间的不平衡。通常,骨骼不断被这两个过程改造,所有骨质中多达10%的骨质随时在改造中。只要这两个过程是平衡的,就不会出现骨骼净流失。骨骼形成与骨骼再吸附之间的不平衡可以发生并导致骨骼净流失的三个主要方式。所有三种方式都可能发生在同一个人身上。三种方式如下:-
An individual never develops normal peak bone mass during the young adult years:
If the peak level is lower than normal, then there is less bone mass to begin with, making osteoporosis more likely to develop.
::如果峰值水平低于正常水平,那么开始的骨质就会减少,使骨质疏松症更有可能发展。 -
There is greater than normal bone resorption:
Bone resorption normally increases after peak bone mass is reached, but age-related bone resorption may be greater than normal for a variety of reasons. One possible reason is
calcium
or
vitamin D
deficiency, which causes the parathyroid gland to release PTH, the
that promotes resorption by osteoclasts.
::骨吸附大于正常的骨吸附:骨质峰值达到后骨吸附通常会增加,但由于各种原因,与年龄有关的骨吸附可能大于正常值,其中一个可能的原因是钙或维生素D缺乏,导致对硫菊酯腺释放PTH,这促使骨骼细胞重新吸附。 -
There is inadequate formation of new bone by osteoblasts during remodeling:
Lack of estrogen may decrease the normal deposition of new bone. Inadequate levels of calcium and vitamin D also lead to impaired bone formation by osteoblasts.
::在改造过程中,骨质激素新骨头的形成不足:缺乏雌激素可能会减少新骨头的正常沉积,钙和维生素D的含量不足也会导致卵质骨质的形成受损。
An imbalance between bone building and bone destruction leading to bone loss may also occur as a side effect of other disorders. For example, people with alcoholism, anorexia nervosa, or hyperthyroidism have an increased rate of bone loss. Some medications — including anti-seizure medications, chemotherapy drugs , steroid medications, and some antidepressants — also increase the rate of bone loss.
::骨骼构造与导致骨骼流失的骨骼破坏之间的不平衡也可能是其他紊乱的副作用,例如,有酗酒、厌食狂或甲状腺炎的人或超甲状腺病的人的骨骼损失率上升,一些药物——包括抗震素药物、化疗药物、类固醇药物和一些抗抑郁药物——也增加了骨骼损失率。Diagnosing Osteoporosis
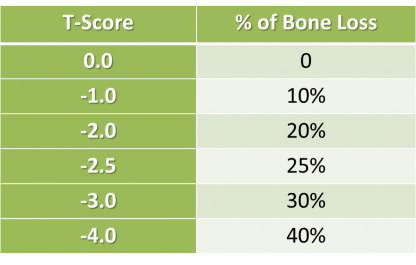
::骨质疏松症Osteoporosis is diagnosed by measuring a patient’s bone density and comparing it with the normal level of peak bone density in a young adult reference of the same sex as the patient. If the patient’s bone density is too far below the normal peak level (as measured by a statistic called a T-score), then osteoporosis is diagnosed (see figure below). Bone density is usually measured by a type of X-ray called dual- energy X-ray absorptiometry (or DEXA). Typically, the density is measured at the hip. Sometimes, other areas are also measured, because there may be variation in bone density in different parts of the skeleton. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that all women 65 years of age and older be screened with DEXA for bone density. Screening may be recommended at younger ages in people with risk factors for osteoporosis (see Risk Factors for Osteoporosis below).
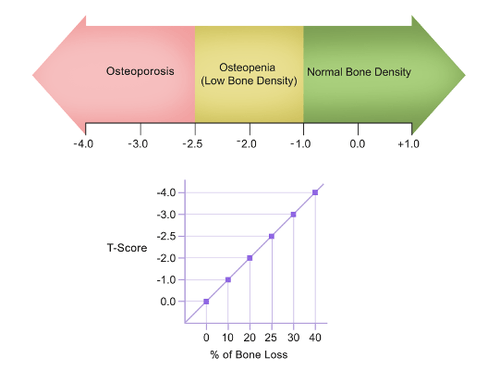
::骨质疏松症的诊断方法是测量病人的骨头密度,并将它与与与病人同性同性年轻成人参考的正常峰值骨密度进行比较。如果病人的骨头密度远远低于正常峰值水平(以称为T-score的统计数字衡量),那么骨质疏松症的诊断(见下文图 ) 。 骨质疏松症的密度通常用一种叫作双能X-射线吸收测量(或DEXA ) 的X射线进行测量。 通常在臀部测量其密度。 有时,也测量其他地区,因为骨骼不同部分的骨密度可能存在差异。 美国预防服务工作队建议,所有65岁和65岁以上的妇女都要接受DEXA的骨密度检查。 在具有骨质疏松症风险因素的年轻人中,可以建议进行筛查(见下面骨质疏松症的风险因素 ) 。The result of a patient’s DEXA scan is used to compute a T-score, which shows how significant the patient’s loss of bone density is relative to the normal level of peak bone density. As shown in the diagram on the left, a T-score of -2.5 or lower indicates osteoporosis, whereas a T-score between -1.0 and -2.5 indicates osteopenia (low bone density). A patient’s T-score can also be correlated with the percentage of bone loss that has occurred, as shown in the table.
::病人的DEXA扫描结果被用于计算T - Score, 这表明病人骨密度损失与峰值骨密度的正常水平相比有多严重。 如左侧图表所示, T-score为-2.5或更低,表示骨质疏松,而T-score介于-1.0和-2.5之间,表示骨质疏松(低骨头密度 ) 。 病人的T-score也可能与表所示的骨质流失百分比相关。Osteoporotic Fractures
::骨质疏松性断裂Fractures are the most dangerous aspect of osteoporosis, and osteoporosis is responsible for millions of fractures annually. Debilitating pain among the elderly is often caused by fractures from osteoporosis, and it can lead to further disability and early mortality. Fractures of the long bones (such as the femur) can impair mobility and may require surgery. Hip fracture usually requires immediate surgery, as well. The immobility associated with fractures — especially of the hip — increases the risk of deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and pneumonia . Osteoporosis is rarely fatal, but these complications of fractures often are. Older people tend to have more falls than younger people, due to such factors as poor eyesight and balance problems, increasing their risk of fractures even more. The likelihood of falls can be reduced by removing obstacles and loose carpets or rugs in the living environment.
::骨质疏松症是骨质疏松症的最危险方面,骨质疏松症是每年成百上千万人骨折的原因。老年人的消化疼痛往往由骨质疏松症造成的骨折造成,并可能导致进一步的残疾和过早死亡。长骨头的骨折(如股骨)会损害行动能力,可能需要手术。臀骨折通常需要立即进行手术。骨折——特别是臀部骨折——导致的不活动增加了心血管疏松、肺栓塞和肺炎的风险。骨质疏松很少致命,但骨折的并发症经常是。由于视力和平衡问题等因素,老年人的跌落率往往高于年轻人,从而增加了他们骨折的风险。通过在生活环境中排除障碍和松散的地毯或地毯,可以减少坠落的可能性。Risk Factors for Osteoporosis
::骨质疏松症风险因素There are a number of factors that increase the risk of osteoporosis. Eleven of them are listed below. The first five factors cannot be controlled, but the remaining factors generally can be controlled by changing behaviors.
::有一些因素增加了骨质疏松的风险,下面列出了其中11个因素,前5个因素无法控制,但其余因素一般可以通过改变行为加以控制。-
older age
::年龄(岁以上) -
female sex
::女性性别 女性性别 女性性别 -
European or Asian ancestry
::欧洲或亚洲血统 -
family history of osteoporosis
::骨质疏松症家族史 -
short stature and small bones
::身材短短,骨瘦骨瘦骨 -
smoking
::吸烟 -
alcohol consumption
::酒精消费 -
lack of
::缺乏 -
vitamin D deficiency
::缺乏维生素D -
poor nutrition
::营养不良 -
consumption of soft drinks
::消费软饮料
Treatment and Prevention of Osteoporosis
::治疗和预防骨质疏松症Osteoporosis is often treated with medications that may slow or even reverse bone loss. Medications called bisphosphonates, for example, are commonly prescribed. Bisphosphonates slow down the breakdown of bone, allowing bone rebuilding during remodeling to keep pace. This helps maintain bone density and decreases the risk of fractures. The medications may be more effective in patients who have already broken bones than in those who have not, significantly reducing their risk of another fracture. Generally, patients are not recommended to stay on bisphosphonates for more than three or four years. There is no evidence for continued benefit after this time — in fact, there is a potential for adverse side effects.
::骨质疏松症的治疗往往采用可能会减慢甚至逆转骨骼流失的药物,例如,通常使用称为二磷酸的药物,例如,通常使用二磷酸盐,减缓骨折速度,允许在改造期间进行骨骼重建以跟上步伐,这有助于保持骨密度和减少骨折风险,这些药物对已经骨折的病人可能比没有骨折的病人更有效,大大降低了再次骨折的风险。一般而言,不建议病人在二磷酸盐上停留三、四年以上。没有证据表明此后继续受益,事实上,可能会产生不良副作用。Preventing osteoporosis includes eliminating any risk factors that can be controlled through changes of behavior. If you smoke, stop. If you drink, reduce your alcohol consumption — or cut it out altogether. Eat a nutritious diet and make sure you are getting adequate amounts of vitamin D. You should also avoid drinking carbonated beverages.
::预防骨质疏松包括消除通过行为变化可以控制的任何风险因素。如果吸烟、戒烟、戒烟、戒酒、饮酒、减少酒精消费或完全戒除酒精。吃有营养的饮食,确保获得足够的维生素D。你也应该避免饮用碳酸饮料。If you’re a couch potato, get involved in regular exercise. Aerobic , weight-bearing, and resistance exercises can all help maintain or increase bone mineral density. Exercise puts stress on bones, which stimulates bone building. Good weight-bearing exercises for bone building include weight training, dancing, stair climbing, running, and hiking (see photo ). Biking and swimming are less beneficial, because they don’t stress the bones. Ideally, you should exercise for at least 30 minutes a day most days of the week.
::如果你是沙发马铃薯,请参与常规锻炼。 有氧、有重力和抗力练习都有助于保持或提高骨质矿藏密度。 锻炼会给骨骼造成压力,刺激骨骼建设。 良好的骨质锻炼包括体重训练、舞蹈、攀登楼梯、跑步和徒步(见照片 ) 。 赛车和游泳没有多大好处,因为它们不会给骨头造成压力。 理想的情况是,你应该每周大部分时间每天至少锻炼30分钟。Hiking is an enjoyable way to help keep bones strong and reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
::远足是一种令人愉快的方式,有助于保持骨骼坚固,减少骨质疏松症的风险。Osteoarthritis
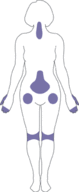
::骨髓炎Osteoarthritis (OA) is a joint disease that results from the breakdown of joint cartilage and bone. The most common symptoms are joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include joint swelling and decreased range of motion. Initially, symptoms may occur only after exercise or prolonged activity, but over time, they may become constant, negatively affecting work and normal daily activities. As shown in the figure , the most commonly involved are those near the ends of the fingers, at the bases of the thumbs, and in the neck, lower back, hips, and knees. Often, joints on one side of the body are affected more than those on the other side.
::骨髓炎(OA)是联合软骨和骨骼破裂导致的一种共同疾病,最常见的症状是共同疼痛和僵硬,其他症状可能包括联合肿胀和运动范围缩小。最初,症状只有在锻炼或长期活动后才会发生,但随着时间的推移,它们可能会变得持续,对工作和正常的日常活动产生不利影响。如图所示,最经常涉及的是手指端、拇指底部、颈部、背部、臀部和膝盖。通常,身体一侧的关节比另一侧的关节受影响更大。The areas shaded in blue indicate the joints most commonly affected by OA.
::蓝色区域表示受有机农业影响最严重的接合点。What Causes Osteoarthritis?
::导致骨髓炎的原因是什么?OA is thought to be caused by mechanical stress on the joints with insufficient self-repair of cartilage. The stress may be exacerbated by low-grade inflammation of the joints, as lining the joint attempt to remove breakdown products from cartilage in the synovial space. OA develops over decades as stress and inflammation cause increasing loss of articular cartilage. Eventually, bones may have no cartilage to separate them, so bones rub against one another at joints. This damages the articular surfaces of the bones and contributes to the pain and other symptoms of OA. Because of the pain, movement may be curtailed, leading to loss of muscle, as well.
::有机体被认为是由关节的机械压力造成的,而软骨的自修不足,这种压力可能因关节的低等级炎症而加剧,因为合力试图将断裂产物从修复空间的软骨中去除。有机体随着压力和炎症的加剧而发展了几十年。最终,骨骼可能没有骨骼可以分离,因此骨骼在关节上相互摩擦。这损害了骨骼的动脉表面,加剧了有机体的痛苦和其他症状。由于疼痛,行动可能会被削减,导致肌肉丧失。Diagnosing Osteoarthritis
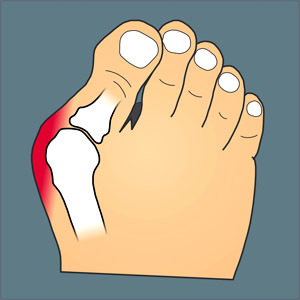
::诊断骨髓炎Diagnosis of OA is typically made on the basis of signs and symptoms. Signs include joint deformities, such as bony nodules on the finger joints or bunions on the feet (as illustrated in the figure ). Symptoms include joint pain and stiffness. The pain is usually described as a sharp ache or burning sensation, which may be in the and tendons around the affected joints, as well as in the joints themselves. The pain is usually made worse by prolonged activity, and it typically improves with rest. Stiffness is most common when first arising in the morning, and it usually improves quickly as daily activities are undertaken.
::对OA的诊断通常是根据迹象和症状进行的,迹象包括联合畸形,例如手指关节或脚部的骨质结核(如图所示),症状包括联合疼痛和僵硬,疼痛通常被描述为尖锐的疼痛或灼痛,这可能是在受影响的关节周围以及关节周围和关节周围,通常疼痛会因长时间的活动而更加严重,而且通常会随着休息而改善。在早上第一次出现时,紧张最为常见,通常随着日常活动的开展而迅速改善。A bunion is a common sign of osteoarthritis. It is typically located at the base of the big toe.
::双胞胎是骨髓炎的常见症状,通常位于大脚趾底部。X-rays or other tests are sometimes used to either support the diagnosis of OA or to rule out other disorders. B lood tests might be done, for example, to look for factors that indicate rheumatoid arthritis (RA), an in which the immune system attacks the body’s joints. If these factors are not present in the , then RA is unlikely, and a diagnosis of OA is more likely to be correct.
::X光片或其他测试有时被用于支持对 OA 的诊断或排除其他疾病。 比如,可以进行血液检测,以寻找显示风湿性关节炎(RA)的因素,即免疫系统攻击身体关节的风湿性关节炎(RA ) 。 如果这些因素没有出现,RA就不太可能存在,对 OA 的诊断更可能正确。Risk Factors for Osteoarthritis
::骨髓炎风险因素Age is the chief risk factor for osteoarthritis. By age 65, as many as 80 percent of all people have evidence of osteoarthritis. However, people are more likely to develop OA — especially at younger ages — if they have had a joint injury. A high school football player might have a bad knee injury that damages the joint, leading to OA in the knee by the time he is in his thirties. If people have joints that are misaligned due to congenital malformations or disease, they are also more likely to develop OA. Excess body weight is another factor that increases the risk of OA, because of the added stress it places on weight-bearing joints.
::年龄是骨髓炎的主要风险因素。到65岁时,多达80%的人有骨髓炎的证据。然而,如果有共同损伤,人们更有可能发展骨髓炎,特别是较年幼的人。高中足球运动员的膝盖受伤可能很严重,导致关节损伤,在30岁时导致膝盖骨折。如果人们有先天畸形或疾病导致关节错位,他们也更有可能发展骨髓炎。过重的身体重量是增加骨髓炎风险的另一个因素,因为它给有体重的关节增加了压力。Researchers have found that people with a family history of OA have a heightened risk of developing the disorder, which suggests that genetic factors are also involved in OA. It is likely that many different genes are needed for normal cartilage and cartilage repair. If such genes are defective and cartilage is abnormal or not normally repaired, OA is more likely to result.
::研究人员发现,有家庭经历的OA的人患上这种疾病的风险较高,这表明OA也涉及遗传因素。 正常的软骨和软骨修复可能需要许多不同的基因。 如果这种基因有缺陷,软骨不正常或通常没有修复,OA就更有可能产生这种基因。Treatment and Prevention of Osteoarthritis
::治疗和预防骨髓炎OA cannot be cured, but the symptoms — especially the pain — can often be treated successfully to maintain good quality of life for people with OA. Treatments include exercise, efforts to decrease stress on joints, pain medications, and surgery.
::助产手术无法治愈,但症状——特别是疼痛——往往可以成功地治疗,以维持受助者的良好生活质量。 治疗包括锻炼、努力减轻关节压力、止痛药和手术。Exercise
::演习演习 演习Exercise helps maintain joint mobility and also increases muscle strength. Stronger muscles may help keep the bones in joints correctly aligned, and this can reduce joint stress. Good exercises for OA include swimming, aerobics (see picture ), and biking. These activities are recommended for OA, because they put relatively little stress on the joints.
::锻炼有助于保持联合运动,并增加肌肉强度。 更强壮的肌肉可以帮助骨骼在关节中保持正确的对齐,这可以减少联合压力。 良好的锻炼包括游泳、有氧运动(见图 ) 、 骑自行车。 这些活动被推荐给OA, 因为它们对关节造成的压力相对较小。Exercising in water provides buoyancy that places less stress on joints than the same exercises would on the ground or other hard surface.
::在水中施展水能提供浮力,比在地面或其他硬表面进行的同样的作业对接合点造成的压力小一些。Destressing Joints
::装修接点Efforts to decrease stress on joints include resting and using mobility devices such as canes, which reduce the weight placed on weight-bearing joints and also improve stability. In people who are overweight, losing weight may also reduce joint stress.
::降低关节压力的努力包括休息和使用诸如拐杖等移动装置,这些装置可以减少对有重量关节的重量,也可以改善稳定性。 在超重人群中,减重也可以减少联合压力。Pain Medications
::止痛药品The first type of pain medication likely to be prescribed for OA is acetaminophen (e.g., Tylenol). When taken as prescribed, it has a relatively low risk of serious side effects. If this medication is inadequate to relieve the pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen) may be prescribed. NSAIDs, however, are more likely to cause serious side effects, such as gastrointestinal bleeding, elevated , and increased risk of stroke . Opioids usually are reserved for patients who have suffered serious side effects or for whom other medications have failed to relieve pain. Due to the risk of addiction, short-term use of opioids is generally recommended.
::可能为OA处方的第一种止痛药物是乙酰胺芬(如Tylenool),按处方服用时,其严重的副作用风险相对较低,如果这种药物不足以减轻疼痛,则可以处方非类固醇抗炎药物(如ibuprofen),但非类固醇抗炎药物更可能造成严重副作用,如胃肠出血、高血和中风风险增加,类阿片通常留给已经严重副作用或其他药物未能减轻疼痛的病人,由于上瘾的危险,一般建议短期使用类阿片。Surgery
::外科Joint-replacement surgery is the most common treatment for serious OA in the knee or hip. In fact, knee and hip replacement surgeries are among the most common of all surgeries. Although they require a long period of healing and physical rehabilitation, the results are usually worth it. The replacement “parts” are usually pain-free and fully functional for at least a couple of decades. Quality, durability, and customization of artificial joints are constantly improving.
::联合替换手术是严重膝部或臀部助产手术最常见的治疗方法,事实上,膝部和臀部替换手术是所有手术中最常见的治疗方法,虽然需要长期的愈合和身体康复,但结果通常值得。替代“部分”通常没有疼痛,至少可以完全运作几十年。 人工关节的质量、耐久性和定制正在不断改善。Feature: Myth vs. Reality
::特征:神话对现实About one out of every two Americans will develop osteoarthritis in his or her lifetime. The more you know about this disease, the more you can do to avoid it or slow its progression. That means knowing the facts, rather than believing the myths about osteoarthritis.
::大约每两位美国人中就有一人会在一生中患上骨髓炎。 你越了解这种疾病,就越能避免或减缓其发展速度。 这意味着了解事实,而不是相信有关骨髓炎的神话。Myth: Cracking my knuckles will cause osteoarthritis.
::我的指关节断裂会导致骨关节炎Reality: Cracking your knuckles may lead to inflammation of your tendons, but it will not cause osteoarthritis.
::现实:扭断你的指关节可能导致你的发炎, 但不会引起骨髓炎。Myth: My diet has no effect on my joints.
::传说:我的饮食对我的关节没有任何影响。Reality: What and how much you eat does affect your body weight, and every pound you gain translates into an additional four pounds (or more!) of stress on your knees. B eing overweight, therefore, increases the chances of developing osteoarthritis — and also the rate at which it progresses.
::现实:你吃什么和吃多少会影响你的体重,你每增加一磅就会变成膝盖上额外的四磅(或更多! )的压力。 因此,超重会增加发展骨髓炎的可能性 — — 以及其发展速度。Myth: Exercise causes osteoarthritis or makes it worse, so I should avoid it.
::传说:运动引起骨髓炎或使其恶化,所以我应避免。Reality: This is one of the biggest myths about osteoarthritis. Low-impact exercise can actually lessen the pain and improve other symptoms of osteoarthritis. If you don’t have osteoarthritis, exercise can reduce your risk of developing it. Low-impact exercise helps keep the muscles around joints strong and flexible, so they can help stabilize and protect the joints.
::现实:这是有关骨髓炎的最大神话之一。 低影响练习实际上可以减轻疼痛,改善其他骨髓炎症状。 如果没有骨髓炎,运动可以降低发育风险。 低影响练习有助于将肌肉维持在关节周围的坚固和灵活,从而帮助稳定并保护关节。Myth: If my mom or dad has osteoarthritis, I will also develop it.
::传说:如果我爸妈有骨髓炎,Reality: It is true that you are more likely to develop osteoarthritis if a parent has it, but it isn’t a sure thing. There are several things you can do to decrease your risk, such as getting regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight.
::现实:确实,如果父母有,你更可能患骨髓炎,但这不能肯定。 你可以做一些事情来降低风险,比如定期锻炼和保持健康体重。Myth: Bad weather causes osteoarthritis.
::传说:坏天气导致骨髓炎。Reality: Weather conditions do not cause osteoarthritis, although in some people who already have osteoarthritis, bad weather seems to make the symptoms worse. It is primarily low barometric pressure that increases osteoarthritis pain, probably because it leads to greater pressure inside the joints relative to the outside air pressure. Some people think their osteoarthritis pain is worse in cold weather, but systematic studies have not found convincing evidence for this.
::现实:天气状况不会引起骨髓炎,尽管在已经患有骨髓炎的一些人中,坏天气似乎使症状更加严重。 主要是低气压增加了骨髓炎疼痛,这可能是因为它导致关节内的压力比外部空气压力更大。 有些人认为他们的骨髓炎疼痛在寒冷天气中更严重,但系统性研究并没有找到令人信服的证据。Myth: Joint pain is unavoidable as you get older, so there is no need to see a doctor for it.
::传说:共同痛苦是不可避免的,因为你长大了,所以没有必要去看医生。Reality: Many people with osteoarthritis think there is nothing that can be done for the pain of osteoarthritis, or that surgery is the only treatment option. In reality, osteoarthritis symptoms often can be improved with a combination of exercise, weight loss, pain management techniques, and pain medications. If osteoarthritis pain interferes with daily life and lasts more than a few days, you should see your doctor.
::现实:许多患有骨髓炎的人认为对骨髓炎的疼痛无能为力,或者说手术是唯一的治疗选择。 事实上,骨髓炎症状通常可以通过锻炼、减重、止痛管理技术和止痛药物相结合来改善。 如果骨髓炎疼痛干扰日常生活,持续超过几天,你应该去看医生。Myth: Osteoarthritis is inevitable in seniors.
::传说:骨髓炎在老年人中是不可避免的。Reality: Although many people over 65 develop osteoarthritis, there are many people who never develop it, no matter how old they live to be. You can reduce your risk of developing osteoarthritis in later life by protecting your joints throughout life.
::现实:尽管许多65岁以上的人患上骨髓炎,但许多人从未患上骨髓炎,不管他们活到多大年纪。 你可以通过保护一生的关节来降低在晚年患上骨髓炎的风险。Summary
::摘要-
A number of disorders affect the skeletal system, including bone fractures and bone cancers. The two most common disorders of the skeletal system are osteoporosis and osteoarthritis.
::一些疾病影响到骨骼系统,包括骨折和骨癌,骨骼系统最常见的两种疾病是骨质疏松症和骨髓炎。 -
Osteoporosis is an age-related disorder in which bones lose mass, weaken, and break more easily than normal bones. The underlying mechanism in all cases of osteoporosis is an imbalance between bone formation and bone resorption in bone remodeling. Osteoporosis may also occur as a side effect of other disorders or certain medications.
::骨质疏松是一种与年龄有关的紊乱,骨质疏松比正常骨骼更容易失去质量、衰弱和断裂。 骨质疏松的所有情况下,骨质疏松的基本机制是骨骼形成和骨质再吸附之间的不平衡,骨质疏松也可能是其他紊乱或某些药物的副作用。 -
Osteoporosis is diagnosed by measuring a patient’s bone density and comparing it with the normal level of peak bone density. Fractures are the most dangerous aspect of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is rarely fatal, but complications of fractures often are.
::骨质疏松症的诊断方法是测量病人的骨头密度,并与正常的峰骨密度水平进行比较。 骨折是骨质疏松症最危险的方面。 骨质疏松症很少致命,但骨折的并发症往往是。 -
Risk factors for osteoporosis include older age, female sex, European or Asian ancestry, family history of osteoporosis, short stature and small bones, smoking, alcohol consumption, lack of exercise, vitamin D deficiency, poor nutrition, and consumption of soft drinks.
::骨质疏松症的风险因素包括年龄较大、女性性别、欧洲或亚洲血统、骨质疏松症的家庭史、身材矮小的骨骼、吸烟、酒精消费、缺乏锻炼、维生素D缺乏、营养不良和喝软饮料。 -
Osteoporosis is often treated with medications — such as bisphosphonates — that may slow or even reverse bone loss. Preventing osteoporosis includes eliminating any risk factors that can be controlled through changes of behavior, such as undertaking weight-bearing exercise.
::骨质疏松症经常用药物治疗,例如二磷酸二酯,这种药物可能减缓甚至扭转骨骼流失,预防骨质疏松症包括消除任何可以通过行为变化(如进行计重锻炼)加以控制的危险因素。 -
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a joint disease that results from the breakdown of joint cartilage and bone. The most common symptoms are joint pain and stiffness. OA is thought to be caused by mechanical stress on the joints with insufficient self-repair of cartilage, coupled with low-grade inflammation of the joints.
::骨髓炎(OA)是联合软骨和骨骼破裂导致的一种共同疾病,最常见的症状是共同疼痛和僵硬,据认为,OA是关节机械压力造成的,因为软骨的自我修复不足,关节的发炎程度低。 -
Diagnosis of OA is typically made on the basis of signs and symptoms, such as joint deformities, pain, and stiffness. X-rays or other tests are sometimes used to either support the diagnosis or rule out other disorders. Age is the chief risk factor for OA. Other risk factors include joint injury, excess body weight, and a family history of OA.
::对OA的诊断通常基于症状和症状,如共同畸形、疼痛和僵硬,有时使用X光或其他测试来支持诊断或排除其他疾病,年龄是OA的主要风险因素。 其他风险因素包括共同受伤、体重过重以及OA的家庭历史。 -
OA cannot be cured, but the symptoms can often be treated successfully. Treatments may include exercise, efforts to decrease stress on joints, pain medications, and surgery to replace affected hip or knee joints.
::治疗方法可能包括锻炼、努力减轻关节压力、止痛药和手术以取代受感染的臀部或膝关节。
Review
::回顾1. Name the two most common disorders of the skeletal system.
::1. 列出骨骼系统最常见的两种疾病。2. What is osteoporosis? What causes it?
::2. 什么是骨质疏松症?是什么原因?3. How is osteoporosis diagnosed?
::3. 骨质疏松症是如何诊断的?4. Why is osteoporosis dangerous?
::4. 为什么骨质疏松症有危险?5. Identify risk factors for osteoporosis.
::5. 查明骨质疏松症的风险因素。6. How is osteoporosis treated? What can be done to prevent it?
::6. 骨质疏松症是如何治疗的?可以做些什么来预防?7. What is OA? What are its chief symptoms?
::7. 什么是OA?其主要症状是什么?8. What causes OA?
::8. 是什么导致OA?9. Describe how OA is diagnosed.
::9. 说明如何诊断有机农业。10. Identify risk factors for OA.
::10. 查明有机农业的风险因素。11. How is OA treated?
::11. 有机农业的待遇如何?12. Why is it important to build sufficient bone mass in your young adult years?
::12. 为什么在你的年轻成人岁月中必须建立足够的骨质骨质?13. Explain the difference in cause between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
::13. 解释风湿性关节炎和风湿性关节炎之间的区别。14. True or False: Osteoarthritis is caused by physical activity, so people who are equally active are equally susceptible to it.
::14. 真实的或假的:骨髓炎是由身体活动引起的,因此,同样活跃的人同样容易染上这种疾病。15. True or False: Estrogen generally promotes production of new bone.
::15. 真实或假:雌激素通常促进新骨头的生产。Explore More
::探索更多Osteoarthritis grinds down millions of joints. Many people find relief from hip or knee pain and disability by having one or more joints replaced with artificial joints made of metal and plastic. In the U.S. alone, more than a million knee and hip joint replacements are performed each year. However, the best remedy for worn out, painful joints is replacement with real biological tissue from a tissue donor rather than replacement with artificial joints. Unfortunately, using human donor tissues to repair joints is very costly. There is also a severe shortage of donor tissues. Orthopedic surgeon and researcher Kevin Stone is developing a treatment that could avoid these drawbacks of human tissue transplants by using specially developed animal tissues. Watch his TED talk to learn more:
::骨髓炎导致数百万关节衰竭。 许多人通过用金属和塑料制造的人工关节取代一个或多个关节,从臀部或膝部疼痛和残疾中解脱出来。 仅在美国,每年就有超过100万个膝部和臀部联合替换。 然而,对破损的最佳补救是用组织捐献者的真正生物组织代替疼痛关节,而不是用人工关节替代。 不幸的是,使用人体捐赠组织修复关节的费用非常昂贵。 捐赠组织也严重短缺。 矫形外科医生和研究家凯文·斯通正在开发一种治疗方法,通过使用特别开发的动物组织避免人体组织移植的这些缺陷。 观看他的TED演讲以学习更多:Check out this video to learn about Primordial Dwarfism here:
::校对:Portnoy -
An individual never develops normal peak bone mass during the young adult years:
If the peak level is lower than normal, then there is less bone mass to begin with, making osteoporosis more likely to develop.