13.8 案例研究结论:脚痛
章节大纲
-
Case Study Conclusion: A Pain in the Foot
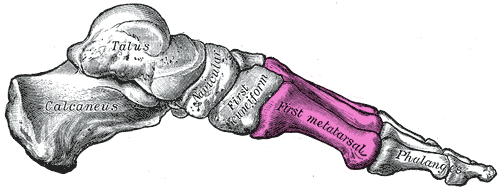
::案例研究结论:脚痛As Melissa discovered in the beginning of the chapter, wearing high heels can result in a condition called metatarsalgia. Metatarsalgia is named for the metatarsal bones, which are the five bones that run through the ball of the foot just behind the toes (highlighted in the illustration .) Wearing high heels causes excessive pressure on the ball of the foot, as described in the beginning of this chapter. Additionally, the toes are forced to pull upward in high heels, which moves the fleshy padding away from the ball of the foot and adds to the overall pressure placed on this region. Over time, this can cause inflammation and direct stress on the bones, resulting in the pain in the ball of the foot known as metatarsalgia. The pain occurs especially in weight-bearing positions, such as standing, walking, or running — which is what Melissa was experiencing. There may also be pain, numbness, or tingling in the toes associated with metatarsalgia.
::Melissa在本章开头发现,穿高跟鞋可导致一种叫“宫颈动脉”的状态。Metatarsalsgia被命名为“宫颈骨”,这是在脚趾后面的脚球中穿透五根骨骼的五根骨骼(插图中突出)。正如本章开头所描述的,穿高高跟鞋对脚球造成过度压力。此外,脚趾被迫高跟鞋向上拉,将肉身垫从脚球上移开,并增加给这个区域的总体压力。随着时间的推移,这可能导致骨骼的炎热和直接压力,导致被称为“宫颈动脉”的脚球疼痛。疼痛特别发生在有重量的姿势,例如站立、行走或跑动——梅丽莎正经历的姿势。在与宫颈相关的脚趾上也可能有疼痛、麻痹或麻痹动。Illustration of the bones of the foot, with the metatarsal bones highlighted in pink.
::以粉红色突出显示足部骨骼,Wearing high heels can also cause stress fractures in the feet, which are tiny breaks in bone that occur due to repeated mechanical stress. This is caused by the excessive pressure that high heels put on some of the bones of the feet. These fractures are somewhat similar to what occurs in osteoporosis when the bone mass decreases to the point where bones can fracture easily as a person goes about their daily activities. In both cases, a major noticeable injury is not necessary to create the tiny fractures. As you have learned, tiny fractures that accrue over time are the cause of dowager’s hump (or kyphosis), which is often seen in women with osteoporosis.
::高跟鞋穿高跟鞋还可能造成脚部的压力骨折,因为脚部骨折是因机械性压力反复造成的骨折,这是由高跟鞋对脚部骨骼施加的过度压力造成的。 这些骨折与骨质质下降到骨质容易骨折的程度时骨折的情况有些相似。 在这两种情况下,造成小骨折并不需要重大的明显伤害。 如你所知,随着时间推移而积累的小骨折是高压者腰部(或kyphosis)的原因,而骨质骨折通常出现在骨质疏松症妇女身上。Don’t think you are immune to stress fractures just because you don’t wear high heels! This injury also commonly occurs in people who participate in sports involving repetitive striking of the foot on the ground, such as running, tennis, basketball, or gymnastics. They may be avoided by taking preventative measures. You should ramp up any increase in activity slowly, cross-train by engaging in a variety of different sports or activities, rest if you experience pain, and wear well-cushioned and supportive running shoes.
::不要仅仅因为你没有穿高跟鞋而认为你不受压力骨折的影响。 这种伤害通常也发生在那些参加运动的人身上,这些运动涉及在地面上反复打脚,如跑步、网球、篮球或体操。 他们可以通过采取预防措施避免。 你应该通过参与各种不同的运动或活动来缓慢地增加活动,通过参加各种不同的运动或活动来增加交叉培训,如果你感到疼痛,休息,穿着精细的脚踏鞋和扶助性跑鞋。Melissa learned through her online research that wearing high heels can also lead to foot deformities, such as bunions and hammertoes. As you saw in the concept Disorders of the Skeletal System , a bunion is a protrusion on the side of the foot, most often at the base of the big toe. It can be caused by wearing shoes with a narrow, pointed toe box — a common shape for high heels (see picture ). The pressure of the shoes on the side of the foot causes an enlargement of bone or inflammation of other tissues in the region, which pushes the big toe toward the other toes.
::Melissa通过她的在线研究了解到,穿高跟鞋还会导致脚部畸形,如胸前刺和锤子。 正如你在骨骼系统概念中看到的那样,双胞胎是脚部侧,通常是大脚趾底部的刺伤,其原因可能是穿鞋用窄的、指尖的脚箱——高跟鞋的一种常见形状(见图 ) 。脚侧的鞋子压力导致骨骼膨胀或该地区其他组织发炎,将大脚趾推向其他脚趾部。High heels with a narrow, pointed toe box and thin stiletto heels
::高跟鞋,有窄窄的 尖尖的脚趾箱 和薄薄的丝质高跟鞋Hammertoes are an abnormal bend in the middle joint of the second, third, or fourth toe (with the big toe being the first toe), causing the toe to be shaped similarly to a hammer. The narrow, pointed toe box of many high heels — combined with the way the toes are squished into the front of the shoe as a result of the height of the heel — can cause the toes to become deformed this way . Treatments for bunions and hammertoe include wearing shoes with a roomy toe box, padding or taping the toes, and toe exercises and stretches. If the bunion or hammertoe does not respond to these treatments, surgery may be necessary to correct the deformity.
::锤子是第二个、第三个或第四个脚趾中间端的一个异常弯曲(大脚趾为第一个脚趾),使脚趾形状与锤子相似。许多高跟鞋的窄尖尖的指尖箱——加上脚趾因脚跟高度而冲入鞋前部的方式——可能导致脚趾如此畸形。 刺子和锤子的治疗方法包括穿鞋,带密脚趾箱,划踏或拍打脚趾,以及脚趾锻炼和伸展。如果两脚趾或锤子不对这些治疗作出反应,可能需要进行手术来纠正畸形。Because the bones of the skeleton are connected and work together with other systems to support the body, wearing high heels can also cause physical problems in areas other than the feet. Wearing high heels shifts a person’s posture and alignment, and can put strain on tendons, muscles, and other joints in the body. R esearch published in 2014 from a team at Stanford University suggests that wearing high heels — particularly if the person is overweight or the heels are very high — may increase the risk of osteoarthritis (OA) in the knee, due to added stress on the knee joint as the person walks. As you have learned, OA results from the breakdown of cartilage and bone at the joint. Because it can only be treated to minimize symptoms — and not for a cure — OA could be an unfortunate long-term consequence of wearing high heels.
::由于骨骼骨骼相互连接,并与其他系统一起支持身体,身高高跟鞋也会在除脚以外的地区造成身体问题。 身高高跟鞋会改变一个人的姿势和姿势,并会给身体内其他关节带来压力。 2014年斯坦福大学一个团队公布的研究表明,身高高高的鞋(尤其是当人超重或高跟鞋非常高时)可能会增加膝盖骨髓炎的风险,因为人们走路时膝盖关节会增加压力。 正如你们所了解的那样,手高高高高高跟鞋会导致骨骼骨折。 手高高跟鞋只能通过治疗来减少症状 — — 而不是治疗 — — 高跟鞋可能是一个不幸的长期后果。Melissa has decided that wearing high heels regularly is not worth the pain and potential long-term damage to her body. After consulting with her doctor, who confirmed she had metatarsalgia, she was able to successfully treat it with ice, rest, and wearing comfortable, supportive shoes instead of heels.
::Melissa认为,定期穿高跟鞋对她的身体来说不值得遭受痛苦和潜在的长期伤害。 在咨询了医生(医生证实她患有宫颈炎 ) 之后,她成功地用冰块、休息和穿着舒适、支持性鞋而不是高跟鞋来治疗了高跟鞋。High heels are not the only kind of shoes that can cause problems. Flip-flops, worn-out sneakers, and shoes that are too tight can all cause foot issues. To prevent future problems from her shoe choices, Melissa is following guidelines recommended by medical experts. The guidelines include:
::高跟鞋并非唯一能引起问题的鞋类。 短拖鞋、破旧的鞋和紧身鞋都会引起脚部问题。 为了防止鞋部未来出现问题,梅丽莎正在遵循医学专家建议的指导方针。 指导方针包括:-
Wearing shoes that fit well, have plenty of room in the toes, are supportive, and are comfortable right away. There should be no “break-in” period needed for shoes.
::鞋子穿得非常合身,脚趾有足够的空间,有支持性,而且马上舒适。 鞋不应有“破门而入”的“破门而入”期。 -
Avoiding high heels, especially those with heels over two inches
high, or those that
have narrow, pointed toe boxes or very thin heels. The heels pictured above are an example of a type that should be avoided.
::避免高跟鞋,特别是高两英寸高的高跟鞋,或窄、指尖箱或非常薄的高跟鞋。 上面的高跟鞋是应该避免的一种类型的例子。 -
If high heels
must
be worn, it should only be for a limited period of time.
::如果必须穿高跟鞋,则高跟鞋只应在有限的时间内穿。
As you have learned in this chapter, your skeletal system carries out a variety of important functions in your body, including physical support. But even though it is strong, your skeletal system can become damaged and deformed — even through such a seemingly innocuous act as wearing a certain type of shoe. Taking good care of your skeletal system is necessary to help it continue to take good care of the rest of you.
::正如你在本章中所学到的,你的骨骼系统在身体中履行着包括身体支持在内的各种重要功能,但是,即使身体坚固,你的骨骼系统也可能受损和畸形——即使穿着某种鞋这样看似无关紧要的行为,照顾好你的骨骼系统对于帮助它继续照顾你们其他人是必要的。Chapter Summary
::章次摘要In this chapter, you learned about the skeletal system. Specifically, you learned that:
::在本章中,你了解了骨骼系统。具体地说,你学到了:-
The skeletal system is the organ system that provides an internal framework for the human body. In adults, the skeletal system contains 206 bones.
::骨骼系统是人体内部框架的器官系统,在成人中,骨骼系统含有206根骨头。 -
Bones are organs made of dense connective tissues, mainly the tough protein collagen. Bones also contain blood vessels, nerves, and other tissues. Bones are hard and rigid, due to deposits of calcium and other mineral salts within their living tissues. Besides bones, the skeletal system includes cartilage and ligaments.
::骨骼是由稠密的连接组织构成的器官,主要是硬质蛋白质共聚物。骨骼还含有血管、神经和其他组织。骨骼硬硬硬,因为其活组织内存有钙和其他矿物盐。除了骨骼外,骨骼系统还包括软骨和颈部。 -
The skeletal system has many different functions, including supporting the body and giving it shape, protecting internal organs, providing attachment surfaces for skeletal muscles, allowing body movements, producing blood cells, storing minerals, helping to maintain mineral homeostasis, and producing endocrine hormones.
::骨骼系统有许多不同的功能,包括支持身体并给其形状,保护内脏器官,为骨骼肌肉提供依附面,允许身体运动,生产血细胞,储存矿物,帮助保持矿物质原状,以及生产内分泌激素。 -
There is relatively little sexual dimorphism in the human skeleton, although the female skeleton tends to be smaller and less robust than the male skeleton. The greatest sex difference is in the pelvis, which is adapted for childbirth in females.
::尽管女性骨骼往往小于男性骨骼,而且不那么强壮,但人体骨骼的性畸形相对较少。 最大的性别差异在于骨盆,因为骨盆适合女性分娩。 -
The skeleton is traditionally divided into two major parts: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton.
::骨骼传统上分为两大部分:轴心骨骼和附体骨骼。 -
The axial skeleton consists of a total of 80 bones. It includes the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage. It also includes the three tiny ossicles in the middle ear and the hyoid bone in the throat.
::轴骨骼由总共80个骨头组成,包括头骨、脊椎柱和肋骨笼,还包括中耳的3个小骨和喉咙的骨。 -
-
The skull provides a bony framework for the head. It consists of 22 different bones: eight in the cranium — which encloses the brain — and 14 in the face, which includes the upper and lower jaw.
::头骨为头骨提供了一个骨骼框架,由22个不同的骨头组成:头骨8个,上面和下下巴包括头骨14个。 -
The vertebral column is a flexible, S-shaped column of 33 vertebrae that connects the trunk with the skull and encloses the spinal cord. The vertebrae are divided into five regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal regions. The S shape of the vertebral column allows it to absorb shocks and distribute the weight of the body.
::脊椎柱是一个由33个脊椎组成的软体S型柱子,将脊椎骨与头骨连接起来,并附上脊髓,脊椎骨分为五个区域:宫颈、胸腔、腰椎、羊毛、羊毛和细胞细胞区域。脊椎柱的S型能吸收冲击并分配身体的重量。 -
The rib cage holds and protects the organs of the upper part of the trunk, including the heart and lungs. It includes the 12 thoracic vertebrae, the sternum, and 12 pairs of ribs.
::肋骨笼包住并保护内衣上部的器官,包括心脏和肺部,包括12胸脊椎、胸骨和12对肋骨。
::头骨为头骨提供了一个骨骼框架。骨骼由22个不同的骨骼组成:8个在头顶上,它包含大脑,14个在脸部,它包括上下下巴。脊椎柱是一个灵活、S形的33个脊椎柱,将脊椎与头骨连接起来,并包含脊椎。脊椎分为5个区域:宫颈、胸椎、腰部、腰栏、羊角和骨囊区域。脊椎柱的S形状允许它吸收冲击并分配身体的重量。肋骨笼关押并保护脊椎上部的器官,包括心脏和肺部。它包括12个胸脊椎、胸骨和12对肋骨。 -
The skull provides a bony framework for the head. It consists of 22 different bones: eight in the cranium — which encloses the brain — and 14 in the face, which includes the upper and lower jaw.
-
The appendicular skeleton consists of a total of 126 bones. It includes the bones of the four limbs, shoulder girdle, and pelvic girdle. The girdles attach the appendages to the axial skeleton.
::外形骨骼由总共126根骨骼组成,包括四肢、肩带和骨盆骨骼的骨骼。臂带将附着物附在轴骨骼上。 -
-
Each upper limb consists of 30 bones. There is one bone (called the humerus) in the upper arm, and two bones (called the ulna and radius) in the lower arm. The wrist contains eight carpal bones, the hand contains five metacarpals, and the fingers consist of 14 phalanges. The thumb is opposable to the palm and fingers of the same hand.
::每个上肢由30个骨骼组成。上臂有一个骨头(称为humerus),下臂有两个骨头(称为ulna和半径 ) 。手腕有8个骨骼,手部有5个形骨,手指有14个长颈骨。拇指对手掌和手指是可抵抗的。 -
Each lower limb also consists of 30 bones. There is one bone (called the femur) in the upper leg, and two bones (called the tibia and fibula) in the lower leg. The patella covers the knee joint. The ankle contains seven tarsal bones, and the foot contains five metatarsals. The tarsals and metatarsals form the heel and arch of the foot. The bones in the toes consist of 14 phalanges.
::下肢各有30根骨头,上腿有1根骨头(称为大腿骨),下腿有2根骨头(称为小腿骨和纤维骨),膝盖盖盖有2根骨头(称为小腿骨和纤维骨),膝盖盖盖盖有2根骨头,脚踝有7根沥青骨头,脚部有5根大脚骨,头部和头部有2根骨,脚部有14根长腿骨。 -
The shoulder girdle attaches the upper limbs to the trunk of the body. It is connected to the axial skeleton only by muscles, allowing mobility of the upper limbs. Bones of the shoulder girdle include a right and left clavicle, and a right and left scapula.
::肩臂将上肢绑在身体的后备箱上,只有肌肉才能连接到轴骨,允许上肢运动。 肩臂臂的骨骼包括左、右和左锁骨,以及左和右骨骨。 -
The pelvic girdle attaches the legs to the trunk of the body and supports the organs of the abdomen. It is connected to the axial skeleton by ligaments. The pelvic girdle consists of two halves that are fused together in adults. Each half consists of three bones: the ilium, pubis, and ischium.
::骨盆盖将双腿绑在骨干上,支撑腹部的器官,用颈部与轴骨相连,骨盆盖由两根半部分组成,两根半在成人体内结合,每半由三根骨头组成:、和。
::每个上肢由30个骨骼组成。 上臂有1个骨骼( 称为humerus ) , 下臂有2个骨骼( 叫做 humerus ) 。 手腕有8个骨骼, 手有5个骨质, 手指有14个长颈。 拇指可以对同一手的手掌和手指有抵抗力。 每个下肢也由30个骨骼组成。 上腿有1个骨骼( 称为 humerus ) , 下腿有2个骨骼( 称为 tubea 和 fibula ) 。 膝盖盖盖盖盖盖盖有2个骨骼。 脚踝有7个焦骨, 脚部有5个骨质。 手表和头有5个长颈部, 头部的骨骼由14个phalangs组成。 肩部将上肢部的骨部与骨部连接到骨部。 脊部的骨部和脊部是1个骨部。 脊部的骨部和脊部。 脊部的脊部是骨部和脊部的脊部。 。 骨部的骨部和脊部。 骨部、 骨部的骨部和脊部的骨部和脊部的脊部的骨部和脊部的脊部。 骨部和脊部。 -
Each upper limb consists of 30 bones. There is one bone (called the humerus) in the upper arm, and two bones (called the ulna and radius) in the lower arm. The wrist contains eight carpal bones, the hand contains five metacarpals, and the fingers consist of 14 phalanges. The thumb is opposable to the palm and fingers of the same hand.
-
Bones are organs that consist mainly of bone (or osseous) tissue. Osseous tissue is a type of connective tissue consisting of a collagen matrix that is mineralized with calcium and phosphorus crystals. The combination of flexible collagen and minerals makes bone hard, without making it brittle.
::骨骼是主要由骨骼组织(或骨骼组织)组成的器官。骨骼组织是一种连接组织,由用钙和磷晶体进行矿化的钴基体组成。软钴和矿物的结合使骨骼硬化,而不会使骨骼硬化。 -
-
There are two types of osseous tissues: cortical bone tissue and spongy bone tissue. Cortical bone tissue is smooth and dense. It forms the outer layer of bones. Spongy bone tissue is porous and light, and it is found inside many bones.
::骨骼组织分为两类:皮质骨骼组织和海绵骨组织;骨质骨质组织平滑而稠密;骨质骨质组织构成骨骼外层;海绵骨质组织多孔和光亮,许多骨骼中都发现了这种组织。
::骨骼组织分为两类:皮质骨骼组织和海绵骨组织;骨质骨质组织平滑而稠密;骨质骨质组织构成骨骼外层;海绵骨质组织多孔和光亮,许多骨骼中都发现了这种组织。 -
There are two types of osseous tissues: cortical bone tissue and spongy bone tissue. Cortical bone tissue is smooth and dense. It forms the outer layer of bones. Spongy bone tissue is porous and light, and it is found inside many bones.
-
Besides osseous tissues, bones also contain nerves, blood vessels, bone marrow, and periosteum.
::除了骨骼组织之外,骨骼还含有神经、血管、骨髓和骨髓。 -
Bone tissue is composed of four different types of bone cells: osteoblasts, osteocytes, osteoclasts, and osteogenic cells. Osteoblasts form new collagen matrix and mineralize it, osteoclasts break down bone, osteocytes regulate the formation and breakdown of bone, and osteogenic cells divide and differentiate to form new osteoblasts. Bone is a very active tissue, constantly being remodeled by the work of osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
::骨骼组织由四种不同类型的骨细胞组成:骨质激素、骨质激素、骨质激素和骨质细胞。骨质激素形成新的科兰基质并进行矿物化,骨质激素分解骨质,骨质激素调节骨质形成和分解,骨质细胞分化并区分形成新的骨质激素。骨质是一种非常活跃的组织,不断通过骨质激素和骨质激素的工作进行改造。 -
There are six types of bones in the human body: long bones (such as the limb bones), short bones (such as the wrist bones), sesamoid bones (such as the patella), sutural bones in the skull, and irregular bones (such as the vertebrae).
::人体有六种骨骼:长骨骼(如肢体骨骼)、短骨骼(如手腕骨骼)、骨骼骨骼(如手腕骨)、骨骼骨骼(如板骨)、头骨和不固定骨骼(如脊椎骨)。 -
Early in the development of a human fetus, the skeleton is made almost entirely of cartilage. The relatively soft cartilage gradually turns into hard bone — a process that is called ossification. It begins at a primary ossification center in the middle of bone, and later also occurs at secondary ossification centers in the ends of bone. The bone can no longer grow in length after the areas of ossification meet and fuse at the time of skeletal maturity.
::人体胎儿早期发育时,骨骼几乎完全由软软软的骨骼组成,逐渐变成硬骨头,这一过程被称为骨质化过程,开始于骨质中间的主要骨质化中心,后来也发生在骨骼端的二级骨质化中心,骨骼在骨骼成熟时骨质化领域相遇和引信后,骨骼不再长。 -
Throughout life, bone is constantly being replaced in the process of bone remodeling. In this process, osteoclasts resorb bone and osteoblasts make new bone to replace it. Bone remodeling shapes the skeleton, repairs tiny flaws in bones, and helps maintain mineral homeostasis in the blood.
::骨骼在整个生命中在骨骼改造过程中不断被替换。 在这一过程中,骨骼恢复骨骼和骨骼骨骼制造了新的骨骼来替换骨骼。骨骼改造塑造骨骼,修复骨骼的细小缺陷,并帮助保持血液中的矿物质恒定。 -
Bone repair is the natural process in which a bone repairs itself following a bone fracture. This process may take several weeks. In the process, periosteum produces cells that develop into osteoblasts, and the osteoblasts form new bone matrix to heal the fracture. Bone repair may be affected by diet, age, pre-existing bone disease, or other factors.
::骨骼修复是骨折后骨骼修复本身的自然过程,这一过程可能需要数周时间。在这一过程中,皮下骨骼生成细胞,形成骨质突变,骨质突变形成新的骨质矩阵以治愈骨折。骨骨骼修复可能受到饮食、年龄、先前存在的骨骼疾病或其他因素的影响。 -
Joints are locations at which bones of the skeleton connect with one another.
::关节是骨骼骨骼相互连接的地点 -
Joints can be classified structurally or functionally, and there is significant overlap between the two types of classifications.
::联合体可按结构或功能进行分类,这两类分类之间有很大的重叠。 -
The structural classification of joints depends on the type of tissue that binds the bones to each other at the joint. There are three types of joints in the structural classification: fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints.
::关节的结构分类取决于在关节将骨骼捆绑在一起的组织类型。 在结构分类中,有三种类型的关节:纤维性关节、卷骨性关节和修复性关节。 -
The functional classification of joints is based on the type and degree of movement that they allow. There are three types of joints in the functional classification: immovable, partly movable, and movable joints.
::联合体的功能分类以其允许的移动类型和程度为基础,功能分类有三类联合体:不动产、部分动产和动产联合体。 -
-
Movable joints can be classified further according to the type of movement they allow. There are six classes of movable joints: pivot, hinge, saddle, plane, condyloid, and ball-and-socket joints.
::流动关节可以根据其允许的移动类型进一步分类。 有六类可移动关节:轴线、链条、马鞍、平面、锥形和球和小接合。
::流动关节可以根据其允许的移动类型进一步分类。 有六类可移动关节:轴线、链条、马鞍、平面、锥形和球和小接合。 -
Movable joints can be classified further according to the type of movement they allow. There are six classes of movable joints: pivot, hinge, saddle, plane, condyloid, and ball-and-socket joints.
-
A number of disorders affect the skeletal system, including bone fractures and bone cancers. The two most common disorders of the skeletal system are osteoporosis and osteoarthritis.
::一些疾病影响到骨骼系统,包括骨折和骨癌,骨骼系统最常见的两种疾病是骨质疏松症和骨髓炎。 -
Osteoporosis is an age-related disorder in which bones lose mass, weaken, and break more easily than normal bones. The underlying mechanism in all cases of osteoporosis is an imbalance between bone formation and bone resorption in bone remodeling. Osteoporosis may also occur as a side effect of other disorders or certain medications.
::骨质疏松是一种与年龄有关的紊乱,骨质疏松比正常骨骼更容易失去质量、衰弱和断裂。 骨质疏松的所有情况下,骨质疏松的基本机制是骨骼形成和骨质再吸附之间的不平衡,骨质疏松也可能是其他紊乱或某些药物的副作用。 -
-
Osteoporosis is diagnosed by measuring a patient’s bone density and comparing it with the normal level of peak bone density. Fractures are the most dangerous aspect of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is rarely fatal, but complications of fractures often are.
::骨质疏松症的诊断方法是测量病人的骨头密度,并与正常的峰骨密度水平进行比较。 骨折是骨质疏松症最危险的方面。 骨质疏松症很少致命,但骨折的并发症往往是。 -
Risk factors for osteoporosis include older age, female sex, European or Asian ancestry, family history of osteoporosis, short stature and small bones, smoking, alcohol consumption, lack of exercise, vitamin D deficiency, poor nutrition, and consumption of soft drinks.
::骨质疏松症的风险因素包括年龄较大、女性性别、欧洲或亚洲血统、骨质疏松症的家庭史、身材矮小的骨骼、吸烟、酒精消费、缺乏锻炼、维生素D缺乏、营养不良和喝软饮料。 -
Osteoporosis is often treated with medications (such as bisphosphonates) that may slow or even reverse bone loss. Preventing osteoporosis includes eliminating any risk factors that can be controlled through changes of behavior, such as undertaking weight-bearing exercise.
::骨质疏松症经常用药物(如二磷酸酯)治疗,这些药物可能会减慢甚至逆转骨骼流失。 预防骨质疏松症包括消除任何可以通过行为变化(如承担载重锻炼)加以控制的危险因素。
::骨质疏松症的诊断方法是测量病人的骨头密度,并将其与正常的峰值骨密度进行比较。骨折是骨质疏松症的最危险方面。骨质疏松症很少致命,但骨折的并发症往往是。骨质疏松症的风险因素包括老年、女性、欧洲或亚洲血统、骨质疏松症的家庭史、骨质疏松症和小骨骼、吸烟、酒精消费、缺乏锻炼、维生素D缺乏、营养不良和软饮料消费。骨质疏松症经常用药物治疗(如二磷酸等),这些药物可能会减慢甚至扭转骨质流失。 预防骨质疏松症包括消除通过行为变化可以控制的任何风险因素,比如承担体重锻炼。 -
Osteoporosis is diagnosed by measuring a patient’s bone density and comparing it with the normal level of peak bone density. Fractures are the most dangerous aspect of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is rarely fatal, but complications of fractures often are.
-
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a joint disease that results from the breakdown of joint cartilage and bone. The most common symptoms are joint pain and stiffness. OA is thought to be caused by mechanical stress on the joints with insufficient self-repair of cartilage, coupled with low-grade inflammation of the joints.
::骨髓炎(OA)是联合软骨和骨骼破裂导致的一种共同疾病,最常见的症状是共同疼痛和僵硬,据认为,OA是关节机械压力造成的,因为软骨的自我修复不足,关节的发炎程度低。 -
-
Diagnosis of OA is typically made on the basis of signs and symptoms, such as joint deformities, pain, and stiffness. X-rays or other tests are sometimes used to either support the diagnosis or rule out other disorders. Age is the chief risk factor for OA. Other risk factors include joint injury, excess body weight, and a family history of OA.
::对OA的诊断通常基于症状和症状,如共同畸形、疼痛和僵硬,有时使用X光或其他测试来支持诊断或排除其他疾病,年龄是OA的主要风险因素。 其他风险因素包括共同受伤、体重过重以及OA的家庭历史。 -
OA cannot be cured, but the symptoms can often be treated successfully. Treatments may include exercise, efforts to decrease stress on joints, pain medications, and surgery to replace affected hip or knee joints.
::治疗方法可能包括锻炼、努力减轻关节压力、止痛药和手术以取代受感染的臀部或膝关节。
::对OA的诊断通常基于症状和症状,如共同畸形、疼痛和僵硬,有时使用X光或其他测试来支持诊断或排除其他疾病,年龄是OA的主要风险因素。其他风险因素包括共同受伤、体重过重和OA的家庭史。 OA的家庭史无法治愈,但症状往往可以成功治疗。治疗可包括锻炼、努力减轻关节压力、止痛药物和手术以取代受到影响的臀部或膝关节。 -
Diagnosis of OA is typically made on the basis of signs and symptoms, such as joint deformities, pain, and stiffness. X-rays or other tests are sometimes used to either support the diagnosis or rule out other disorders. Age is the chief risk factor for OA. Other risk factors include joint injury, excess body weight, and a family history of OA.
As you have learned in this chapter, one of the important functions of the skeletal system is to allow movement of the body. But it doesn’t do it alone. Movement is caused by the contraction of muscles, which pull on the bones, causing them to move. Read the next chapter to learn about this and other important functions of the muscular system.
::正如你们在本章中所学到的,骨骼系统的重要功能之一是允许身体移动。但它不能单枪匹马地进行。 运动是由肌肉收缩造成的,肌肉收缩拉动骨骼,导致骨骼移动。 阅读下一章了解肌肉系统的这个功能和其他重要功能。Chapter Summary Review
::" 概述 " 章次1. Hematopoiesis is carried out by _____________________.
::1. 血蛋白由___________________ 实施。a. spongy bone tissue
::a. 海绵骨组织b. periosteum
::b. periosteum (千兆赫)c. yellow bone marrow
::c. 黄骨髓d. red bone marrow
::d. 红骨髓2. Which aspect of the skeleton is different between women and men?
::2. 男女骨骼的哪个方面不同?a. Women have fewer ribs than men.
::a. 妇女的肋骨比男子少。b. Men have fewer ribs than women.
::b. 男子的肋骨比妇女少。c. Women have a differently shaped pelvis than men.
::c. 妇女的骨盆与男子的骨盆形状不同。d. Women have more vertebrae then men.
::d. 女性的脊椎比男性多。3. True or False: Osteocalcin is a hormone produced by bone cells.
::3. 真实或假:骨质硬化素是骨细胞产生的荷尔蒙。4. True or False: Vertebrae make up part of the rib cage.
::4. 真实或假:骨髓癌构成肋骨笼的一部分。5. For each of the following bones, indicate whether they are part of the axial or appendicular skeleton.
::5. 对于以下每一块骨头,请说明它们是轴骨还是附骨的一部分。a. the ossicles of the middle ear
::a. 中耳的卵蛋b. the femur
::b. 股骨c. the phalanges
::c. 长喉d. the bones of the cranium
::d. 头盖骨的骨头e. the ilium
::e.6. Why does the rib cage need to be flexible? Why can it be flexible?
::6. 为什么肋骨笼需要灵活,为什么可以灵活?7. In general, what do “girdles” in the skeletal system do?
::7. 一般而言,骨骼系统中的 " 外壳 " 有何作用?8. Which protein does bone mainly consist of?
::8. 骨骼主要包括哪一种蛋白质?a. keratin
::a. 氯丙烯b. collagen
::b. 科林c. cellulose
::c. 纤维素d. elastin
::d. 弹性体9. For each of the descriptions below, identify which process best fits the description. Use each process only once.
::9. 对于下文的每一项说明,确定哪一种程序最符合说明,每个程序只使用一次。Processes: bone growth; bone repair; bone remodeling
::工艺:骨骼生长;骨骨修补;骨骼改造a. New osteoblasts form from periosteum and produce new bone tissue.
::a. 来自近地点的新骨质素,产生新的骨质组织。b. Cartilage grows, and the primary and secondary ossification centers move toward each other.
::b. 陶瓷生长,初级和二级骨化中心相互靠近。c. Osteoclasts break down bone tissue and osteoblasts build new bone tissue.
::c. 骨骼组织破裂,骨骼组织形成新的骨骼组织。10. D escribe when each of the following processes occurs.
::10. 描述以下每个过程何时发生。a. bone growth
::a. 骨头生长b. bone repair
::b. 骨骨修理c. bone remodeling
::c. 骨骼改造11. Would swimming be more effective as an exercise for preventing osteoporosis or as a treatment for osteoarthritis? Explain your answer.
::11. 游泳作为预防骨质疏松或治疗骨质关节炎的一种方法是否更有效?12. True or False: Use of anabolic steroids in the teenage years generally makes people taller.
::12. 真实或假:在青少年时期使用新陈代谢类固醇通常使人高一些。13. True or False: The largest joint in the human body is the knee joint.
::13. 真实或假:人体中最大的关节是膝关节。14. How much of an adult’s skeletal mass is broken down and rebuilt each year?
::14. 每年有多少成人骨骼被分解和重建?a. none
::a. 无b. five percent
::b. 5%c. ten percent
::c. 10%d. 30 percent
::d. 30%15. Explain why some of the vertebrae become misshapen in the condition called dowager’s hump (or kyphosis).
::15. 解释为什么有些脊椎骨变成误差,其状况被称为“双层顶部”(或kyphosis)。16. Explain why osteoarthritis often involves inflammation in the joints.
::16. 解释为什么骨髓炎经常涉及关节炎。17. Osteoporosis can involve excess bone resorption, as well as insufficient production of new bone tissue. What are the two main bone cell types that carry out these processes, respectively?
::17. 骨质疏松可能涉及过量的骨吸附,以及新骨组织生产不足。18 . True or False: Bone mass does not decrease as men age.
::18. 真实或假:骨质不会像男子年龄一样减少。19. True or False: Ideally, a person’s spine would be perfectly straight and rigid.
::19. 真实或假:理想的情况是,一个人的脊椎是完全直的和僵硬的。20. Compare and contrast a tendon and a ligament.
::20. 比较和对比一个圆形和一个长带。21. Describe two roles that calcium in bones play in the body.
::21. 描述骨头中的钙在身体中扮演的两个角色。22. How many bones are in the adult human skeleton?
::22. 成人骨骼中有多少骨头?a. 80
::a. a. 80b. 126
::b. 126c. 206
::c. 206d. 270
::d. 270 -
Wearing shoes that fit well, have plenty of room in the toes, are supportive, and are comfortable right away. There should be no “break-in” period needed for shoes.