14.3 肌肉组织类型
章节大纲
-
Work Those Eye Muscles!
::那些眼睛肌肉在工作!He turns his gray-blue in your direction—a very small movement , considering the conspicuously large and strong external eye muscles that control eyeball movements. These muscles have been called the strongest muscles in the relative to the work they do. However, the external eye muscles actually do a surprising amount of work. Eye movements occur almost constantly during waking hours, especially when we are scanning faces or reading. Eye muscles are also exercised nightly during the phase of sleep called rapid eye movement sleep. External eye muscles can move the eyes because they are made mainly of muscle tissue .
::他将灰蓝色转向你的方向——一个非常小的运动,考虑到控制眼球运动的外表肌肉明显巨大和强大的外表肌肉,这些肌肉被称为相对工作而言最强的肌肉,然而,外表肌肉实际上做大量工作,眼睛运动几乎在醒来时经常发生,特别是在我们扫描面孔或阅读时;眼肌肉也在睡眠阶段夜间进行,称为快速眼睛运动睡眠;外眼肌肉可以移动眼睛,因为它们主要是肌肉组织。What is Muscle Tissue?
::什么是肌肉组织?Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that makes up most of the tissues in the muscles of the human muscular system . Other tissues in muscles are connective tissues , such as tendons that attach to and sheaths of connective tissues that cover or line muscle tissues. Only muscle tissue per se, however, has with the ability to contract.
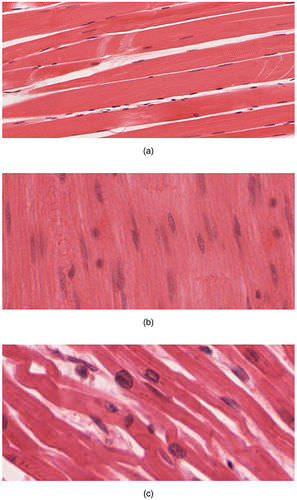
::肌肉组织是一种软组织,构成人体肌肉系统肌肉大部分组织,肌肉中的其他组织是连接组织,例如附着在肌肉组织或线性肌肉组织上的连接组织带和包层,但只有肌肉组织本身有能力缩缩。There are three major types of muscle tissues in the human body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle tissues. The figure shows how the three types of muscle tissues appear under magnification. When you read about each type below, you will learn why the three types appear as they do.
::人体的肌肉组织有三大类:骨骼组织、光滑组织、心肌组织。图中显示了三种肌肉组织在放大作用下出现的情况。当阅读下面每一种类型时,你会知道这三种类型为何出现。These magnified images show (a) skeletal muscle tissue, (b) smooth muscle tissue, and (c) cardiac muscle tissue.
::这些放大图像显示(a)骨骼肌肉组织,(b)光滑肌肉组织,(c)心脏肌肉组织。Skeletal Muscle Tissue
::骨骨肌肉组织Skeletal muscle is muscle tissue that is attached to bones by tendons, which are bundles of collagen fibers. Whether you are moving your eyes or running a marathon, you are using skeletal muscles. Contractions of skeletal muscles are voluntary, or under conscious control of the via the somatic nervous system . Skeletal muscle tissue is the most common type of muscle tissue in the human body. By weight, an average adult male is about 42 percent skeletal muscles, and the average adult female is about 36 percent skeletal muscles. Some of the major skeletal muscles in the human body are labeled in the two figures .
::骨骼肌肉是连接在骨骼上的肌肉组织,由圆锥形骨骼组成,这些圆形骨骼是捆绑的。无论你移动眼睛还是跑马拉松,你都会使用骨骼肌肉。骨骼肌肉的萎缩是自愿的,或者通过体质神经系统有意识地控制。骨骼肌肉组织是人体最常见的肌肉组织类型。按重量计算,平均成年男性大约为42%的骨骼肌肉,平均成年女性大约为36%的骨骼肌肉。人体的一些主要骨骼肌肉在两个数字中贴上标签。This figure shows major skeletal muscles in the front (anterior) of the body.
::该图显示身体前部(前部)的主要骨骼肌肉。This figure shows major skeletal muscles in the back (posterior) of the body.
::该图显示身体背部(前部)的主要骨骼肌肉。Skeletal Muscle Pairs
::骨骼肌肉皮To move bones in opposite directions, skeletal muscles often consist of muscle pairs that work in opposition to one another. For example, when the biceps muscle (on the front of the upper arm) contracts, it can cause the elbow joint to flex or bend the arm , as shown in the figure . When the triceps muscle (on the back of the upper arm) contracts, it can cause the elbow to extend or straighten the arm. The biceps and triceps muscles are an example of a muscle pair where the musc les work in opposition to each other.
::骨骼肌肉向相反方向移动时,骨骼肌肉往往由相互对立的肌肉成对组成。例如,如图所示,当(上臂前的)二头肌发生肌肉接触时,可以导致肘合,以伸展或弯曲手臂。当(上臂后)三头肌发生肌肉接触时,可以使肘伸展或伸直手臂。双头肌和三头肌是肌肉对立的肌肉一对例子。Triceps and biceps muscles in the upper arm are opposing muscles that move the arm at the elbow in opposite directions.
::上臂的三头肌和二头肌 与肌肉对立 手臂在肘部向相反方向移动Skeletal Muscle Structure
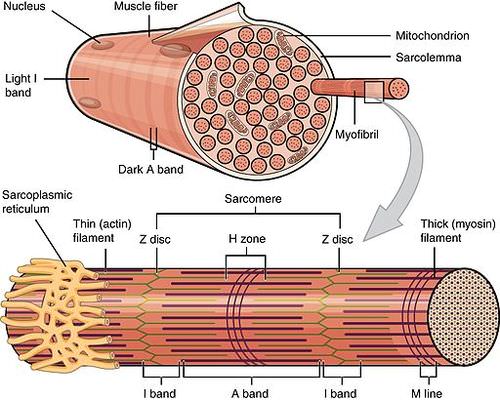
::骨骼肌肉结构Each skeletal muscle consists of hundreds — or even thousands — of skeletal muscle fibers, which are long, string-like cells. As shown in the figure , skeletal muscle fibers are individually wrapped in connective tissue called endomysium . The skeletal muscle fibers are bundled together in units called muscle fascicles , which are surrounded by sheaths of connective tissue called perimysium . Each fascicle contains between ten and 100 (or even more!) skeletal muscle fibers. Fascicles, in turn, are bundled together to form individual skeletal muscles, which are wrapped in connective tissue called epimysium . The connective tissues in skeletal muscles have a variety of functions. They support and protect muscle fibers , allowing them to withstand the forces of contraction by distributing the forces applied to the muscle. They also provide pathways for nerves and to reach the muscles. In addition, the epimysium anchors the muscles to tendons.
::每个骨骼肌肉由数百甚至数千个骨骼肌肉纤维组成,这些骨骼肌肉纤维是长的、类似于弦的细胞。如图所示,骨骼肌肉纤维单独包裹在称为内核的连接组织中。骨骼肌肉纤维被称作肌肉分册的单元捆绑在一起,这些单元被称为肌肉分册的连接组织包扎在一起。每个分册都包含10到100(甚至更多!)骨骼肌肉纤维。这些分册反过来被捆绑在一起,形成单独的骨骼肌肉,它们包扎在一起,被连结组织包扎在一起,称为缩膜。骨骼肌肉的连接组织有各种各样的功能。它们支持和保护肌肉纤维,通过对肌肉施压来抵抗收缩的力量。它们也提供神经和肌肉的路径。此外,肌肉的缩皮细胞固定着肌肉以调节。Each skeletal muscle has a structure of bundles within bundles. Bundles of muscle fibers make up a muscle fascicle, and bundles of fascicles make up a skeletal muscle. At each level of bundling, a connective tissue membrane surrounds the bundle.
::每个骨骼肌肉在捆包内有一个捆包结构。肌肉纤维的捆包组成了一个肌肉分册,分册的捆包组成了骨骼肌肉。在捆绑的每一级,包包周围都有一个连接组织膜。The same bundles-within-bundles structure is replicated within each muscle fiber. As shown in the figure , a muscle fiber consists of a bundle of myofibrils, which are themselves bundles of filaments. These protein filaments consist of thin filaments of the protein actin — which are anchored to structures called Z discs — and thick filaments of the protein myosin . The filaments are arranged together within a myofibril in repeating units called sarcomeres , which run from one Z disc to the next. The sarcomere is the basic functional unit of skeletal (and cardiac) muscles. It contracts as actin and myosin filaments slide over one another. Skeletal muscle tissue is said to be striated , because it appears striped. It has this appearance because of the regular, alternating A (dark) and I (light) bands of filaments arranged in sarcomeres inside the muscle fibers. Other components of a skeletal muscle fiber include multiple and .
::如图所示,肌肉纤维是由一捆小青纤维组成的,它们本身是丝状的捆绑。这些蛋白丝包括蛋白外壳的细细丝丝,这些细丝被固定在称为Z盘的构造上,以及蛋白质髓灰质的厚丝质。丝状在一丝细细丝中排列在一起,在从一个Z盘一直运行到下一个盘的重复单元中,称为sarrcommeres。Sarcomere是骨骼(和心脏)肌肉的基本功能单元。它与外壳和肌膜的细细丝相连接,因为骨骼肌肉组织看起来有条纹。它之所以出现这种外观,是因为肌肉纤维中固定的、交替的A(dark)和I(light)的丝丝状,而肌肉肌肉肌肉纤维中的其他组成部分包括多种和多种。Bundles of protein filaments form a myofibril, and bundles of myofibrils make up a single muscle fiber. I and A bands refer to the positioning of myosin and actin fibers in a myofibril. Sarcoplasmic reticulum is a specialized type of endoplasmic reticulum that forms a network around each myofibril. It serves as a reservoir for calcium ions, which are needed for muscle contractions. H zones and Z discs are also involved in muscle contractions, which you can read about in the concept Muscle Contraction.
::蛋白丝的包条形成一个肌纤维,而肌膜的包包组成了一个肌肉纤维。I和A波段是指肌和活性纤维在肌纤维中的定位。Sarcoplasmic reticulum是一种特殊类型的内分光的内分光性内核,形成一个围绕每个肌的网络。它作为肌肉收缩所需的钙离子的库。H区和Z盘也涉及肌肉收缩,您可以从Muscle Contracion概念中读到这一点。Slow- and Fast-Twitch Skeletal Muscle Fibers
::慢速和快速开关 骨骼肌肉纤维Skeletal muscle fibers can be divided into two types, called slow-twitch (or type I) muscle fibers and fast-twitch (or type II) muscle fibers.
::骨骼肌肉纤维可分为两类,称为慢抽动(或I型)肌肉纤维和快抽动(或II型)肌肉纤维。-
Slow-twitch muscle fibers
are dense with capillaries and rich in mitochondria and myoglobin, which is a protein that stores oxygen until needed for muscle activity. Relative to fast-twitch fibers, slow-twitch fibers can carry more oxygen and sustain
aerobic
(oxygen-using) activity. Slow-twitch fibers can contract for long periods of time, but not with very much force. They are relied upon primarily in endurance events, such as distance running or cycling.
::慢开关肌肉纤维密度高,有刺青,并富含mitochondria 和 myoglobin, 这是一种蛋白质,在肌肉活动需要之前储存氧气。相对于快速开关纤维,慢开关纤维可以携带更多的氧气并保持有氧(使用氧)活性。 慢开关纤维可以长时间缩缩,但不会有很大的强度。 它们主要依靠耐力事件,如远程运行或循环运行。 -
Fast-twitch muscle fibers
contain fewer capillaries and mitochondria and less myoglobin. This type of muscle fiber can contract rapidly and powerfully, but it fatigues very quickly. Fast-twitch fibers can sustain only short,
anaerobic
(non-oxygen-using) bursts of activity. Relative to slow-twitch fibers, fast-twitch fibers contribute more to muscle strength and have a greater potential for increasing in mass. They are relied upon primarily in short, strenuous events, such as sprinting or weight lifting.
::快速开关肌肉纤维含有较少的辣椒和米托乔恩德里亚以及更少的红蛋白。 这种类型的肌肉纤维可以快速而有力地缩缩缩,但疲劳非常快。 快速开关纤维只能维持短时间、 厌氧( 非氧) 活动连发。 相对于慢开关纤维, 快速开关纤维有助于增加肌肉强度, 并具有更大的增加质量潜力。 它们主要依靠短、 艰苦的活动, 如冲刺或举重。
Proportions of fiber types vary considerabl y from muscle to muscle and from person to person. Individuals may be genetically predisposed to have a larger percentage of one type of muscle fiber than the other. Generally, an individual who has more slow-twitch fibers is better suited for activities requiring endurance, whereas an individual who has more fast-twitch fibers is better suited for activities requiring short bursts of power.
::纤维类型的比例因肌肉和肌肉而异,因人而异,个人在基因上可能倾向于拥有一种类型的肌肉比另一种类型的肌肉更大比例,一般而言,较慢抽动纤维的人更适合从事需要耐力的活动,而较快抽动纤维的人则更适合从事需要短电流的活动。Smooth Muscle
::平滑肌肉Smooth muscle is muscle tissue in the walls of internal organs and other internal structures such as blood vessels. When smooth muscles contract, they help the organs and vessels carry out their functions. W hen smooth muscles in the stomach wall contract, for example, they squeeze the food inside the stomach, helping to mix and churn the food and break it into smaller pieces. This is an important part of digestion . Contractions of smooth muscles are involuntary, so they are not under conscious control. Instead, they are controlled by the autonomic nervous system , , neurotransmitters , and other physiological factors.
::滑动肌肉是内脏和血管等其他内部结构的墙壁的肌肉组织; 当滑动肌肉收缩时,它们会帮助器官和血管发挥功能; 例如,当胃壁的滑动肌肉收缩时,它们会挤压腹部的食物,帮助混合和撕裂食物,把它碎成小块; 这是消化的一个重要部分; 滑动肌肉的缩缩是非自愿的,因此它们不会受到意识的控制; 相反,它们受到自主神经系统、神经传导器和其他生理因素的控制。Structure of Smooth Muscle
::平滑肌肉结构The cells that make up smooth muscle are generally called myocytes. Unlike the muscle fibers of striated muscle tissue, the myocytes of smooth muscle tissue do not have their filaments arranged in sarcomeres . Therefore, smooth tissue is not striated. However, the myocytes of smooth muscle do contain myofibrils, which in turn contain bundles of myosin and actin filaments. The filaments cause contractions when they slide over each other, as shown in the figure .
::形成光滑肌肉的细胞通常被称为骨。 与磨断肌肉组织肌肉纤维不同,光滑肌肉组织的细微骨细胞没有将丝丝排列在正方形内。 因此,光滑组织没有切除。 然而,光滑肌肉的细微骨细胞确实含有青蒿素,这反过来又含有麻黄素和丝状物的捆绑。 如图所示,丝状在它们滑过对方时会导致收缩。The basic mechanism of muscle contraction in smooth muscle is the same as that in other types of muscle tissue.
::在光滑肌肉中肌肉收缩的基本机制与其他类型的肌肉组织相同。Functions of Smooth Muscle
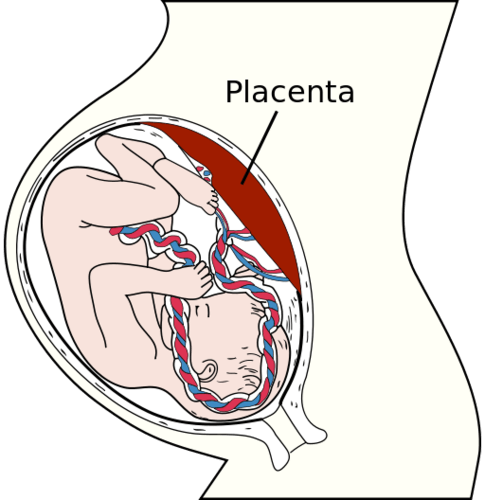
::平滑肌肉的功能Unlike striated muscle, smooth muscle can sustain very long-term contractions. Smooth muscle can also stretch and still maintain its contractile function, which striated muscle cannot. The elasticity of smooth muscle is enhanced by an extracellular matrix secreted by myocytes. The matrix consists of elastin, collagen, and other stretchy fibers. The ability to stretch and still contract is an important attribute of smooth muscle in organs such as the stomach and uterus (see the image ), both of which must stretch considerably as they perform their normal functions.
::与割裂的肌肉不同,光滑的肌肉可以维持非常长期的收缩。光滑的肌肉也可以伸展,并且仍然保持其紧凑的功能,而这种功能是割裂的肌肉不能维持的。光滑的肌肉的弹性通过由近视细胞隔离的外细胞矩阵而增强。矩阵由弹性体、科拉根和其他伸展纤维组成。伸展和仍然缩缩缩的能力是胃和子宫等器官中滑动肌肉的一个重要属性(见图象),这两个器官在正常功能上必须相当伸展。The muscular uterine wall stretches to a great extent to accommodate a growing fetus, yet it can still contract with great force during the labor that precedes childbirth. At that time, it can exert up to 100 pounds of force.
::肌肉子宫墙在很大程度上可以容纳不断增长的胎儿,但是在分娩前的劳动期间仍然可以用巨大的力量收缩。 那时,它可以产生100磅的强度。The following list indicates where many smooth muscles are found, along with some of their specific functions.
::下表列出了发现许多光滑肌肉的地方及其某些具体功能。-
Walls of organs of the
gastrointestinal tract
(such as the
esophagus
, stomach, and intestines), moving food through the tract by
peristalsis
::胃肠道器官(如食道、胃和肠道)的壁壁,食物通过阴道穿行。 -
Walls of air passages of the
respiratory tract
(such as the bronchi), controlling the diameter of the passages and the volume of air that can pass through them
::呼吸道呼吸道(如支气管)气道墙壁(如支气管),控制气道的直径和能够穿过气道的空气量 -
Walls of organs of the male and female reproductive tracts; in the uterus, for example, pushing a baby out of the uterus and into the birth canal
::男女生殖器官的墙壁;例如,在子宫中,将婴儿从子宫中推出,推入出生的运河 -
Walls of structures of the
, including the
urinary bladder
, allowing the
bladder
to expand so it can hold more
urine
, and then contract as urine is released
::包括尿囊在内的阴囊结构墙壁,使膀胱能够膨胀,以便能保持更多的尿液,然后在尿液释放后保持收缩。 -
Walls of blood vessels, controlling the diameter of the vessels and thereby affecting
flow and
::血管壁壁,控制船只直径,从而影响流动和流动 -
Walls of lymphatic vessels, squeezing the fluid called
lymph
through the vessels
::淋巴船只的墙壁,通过船只挤压称为淋巴体的液体 -
Iris of the eyes, controlling the size of the pupils and thereby the amount of light entering the eyes
::眼睛的Iris 控制学生的体积 从而控制进入眼睛的光量 -
Arrector pili in the skin, raising hairs in
hair follicles
in the
dermis
::皮肤皮质亚氏 皮肤皮质皮质皮质 皮肤皮质下毛发的毛发毛发
Cardiac Muscle
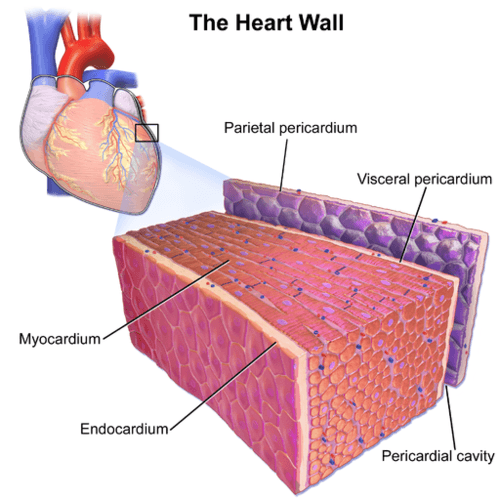
::心脏肌肉Cardiac muscle is found only in the wall of the heart. It is also called myocardium. As shown in the figure , myocardium is enclosed within connective tissues, including the endocardium on the inside of the heart and pericardium on the outside of the heart. When cardiac muscle contracts, the heart beats and pumps blood. Contractions of cardiac muscle are involuntary, like those of smooth muscles. They are controlled by electrical impulses from specialized cardiac muscle cells in an area of the heart muscle called the sinoatrial node.
::心肌只存在于心脏的墙壁中, 也称为心肌。 如图所示, 心肌被封闭在连接组织中, 包括心脏内部的心肌, 心脏外的心肌外的心肌。 当心脏肌肉收缩时, 心脏跳动和抽动血液。 心肌的缩放是非自愿的, 和光滑的肌肉一样。 它们受被称为神经节点的心脏肌肉区域中特殊心脏肌肉细胞的电脉冲控制。The thick wall of the heart consists mainly of cardiac muscle tissue called myocardium.
::心脏厚厚的墙壁主要由心肌组织组成,叫做心肌瘤。Like skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated because its filaments are arranged in sarcomeres inside the muscle fibers. However, in cardiac muscle, the myofibrils are branched at irregular angles rather than arranged in parallel rows (as they are in skeletal muscle). This explains why cardiac and skeletal muscle tissues look different from one another.
::与骨骼肌肉一样,心脏肌肉也因为其丝状在肌肉纤维内以正红体排列而变形,但是,在心脏肌肉中,肌膜的切片是非正常的,而不是平行的(在骨骼肌肉中)排列。这解释了心脏和骨骼肌肉组织为何看起来不同的原因。The cells of cardiac muscle tissue are arranged in interconnected networks. This arrangement allows rapid transmission of electrical impulses, which stimulate virtually simultaneous contractions of the cells. This enables the cells to coordinate contractions of the heart muscle.
::心脏肌肉组织细胞在相互连接的网络中排列。这种安排可以快速传输电脉冲,这几乎可以同时刺激细胞的收缩,使细胞能够协调心脏肌肉的收缩。The heart is the muscle that performs the greatest amount of physical work in the course of a lifetime. Although the power output of the heart is much less than the maximum power output of some other muscles in the human body, the heart does its work continuously over an entire lifetime without rest. Cardiac muscle contains a great many mitochondria, which produce ATP for energy and help the heart resist fatigue.
::心脏是一生中进行最大体力锻炼的肌肉。 虽然心脏的能量输出远远低于人体中某些其他肌肉的最大能量输出,但心脏在整个一生中不休息地持续工作。 心肌包含大量微小孔晶体,产生能量ATP,帮助心脏抵抗疲劳。Feature: Human Biology in the News
::特著:《新闻》中的人类生物学The human heart develops in a sequence of events that are controlled by among different types of cells, including cells that will become myocardium (cardiac muscle that forms the wall of the heart) and cells that will become endocardium (the connective tissue that covers the inside surface of the myocardium). If communication among the cells is abnormal, it can lead to a variety of heart defects, such as cardiac hypertrophy, or abnormal enlargement of the heart muscle. Cardiac hypertrophy causes the heart to thicken and weaken over time, so it is less able to pump blood. Eventually, heart failure may develop, causing fluid to build up in the lungs and extremities.
::人类心脏在一系列由不同种类细胞控制的事件中发展,包括成为心肌细胞(心肌构成心脏的墙壁)和心心细胞(覆盖心心肌内表面的连接组织)。如果细胞之间的交流不正常,可能导致各种心脏缺陷,如心脏超肥或心脏肌肉异常膨胀。心肌超肥导致心脏变厚和变弱,因此无法抽血。最终,心脏衰竭可能会发展,导致液体在肺部和体外积聚。Abnormal is the mechanism by which a called PTPN11 leads to cardiac hypertrophy in a disorder referred to as NSML (Noonan Syndrome with Multiple Lentigines). New research by scientists at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston has determined in which type of cells abnormalities occur that lead to NSML. In the research, the scientists engineered mouse models to express the PTPN11 mutation as they developed. The researchers manipulated the mouse models so that in some of the mice, the mutation was expressed only in cells that would develop into myocardium, whereas in other mice, the mutation was expressed only in cells that would develop into endocardium. Unexpectedly, hypertrophy of the heart occurred only in the mice that expressed the mutation in endocardial cells, not in myocardial cells, which had long been assumed to be the cells affected. The results of the research suggest potential targets for treatment of NSML. They may also help scientists understand causes of other types of cardiac disorders that are much more common than NSML.
::超自然是一种机制,即所谓的PTPN11在被称为NSML(诺南综合症与多锥体)的疾病中导致心脏肥大;波士顿Beth Israel Deaconess医疗中心科学家的新研究确定了哪些类型的细胞异常导致NSML。在研究中,科学家设计了鼠模型,以表达PTPN11突变。研究人员操纵了鼠模型,使某些小鼠的变异表现在将发展成心肌的细胞中,而在其他小鼠中,变异只表现在会发展成内心细胞的细胞中。出乎意料的是,心脏富营养只出现在表示内心细胞突变的老鼠身上,而不是心肌细胞中,它们早就被假定是受到影响的细胞。研究结果表明,该细胞的治疗目标可能是NSML。他们还可能帮助科学家了解比NSML更常见的其他类型心血管紊乱的原因。Summary
::摘要-
Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that makes up most of the tissues in the muscles of the human muscular system. It is the only type of tissue that has cells with the ability to contract.
::肌肉组织是一种软组织,构成人体肌肉系统肌肉组织的大多数组织,是唯一一类组织,其细胞有能力缩缩。 -
Skeletal muscle tissue is attached to bones by tendons. It allows voluntary body movements.
::骨骼肌肉组织通过管子附在骨头上,允许自愿的身体运动。 -
Skeletal muscle
is the most common type of muscle tissue in the human body. To move bones in opposite directions, skeletal muscles often consist of pairs of muscles that work in opposition to one another to move bones in different directions at joints.
::骨骼肌肉是人体最常见的肌肉组织类型。 要将骨骼向相反方向移动,骨骼肌肉通常由两对肌肉组成,它们相互对立,在关节上将骨骼向不同方向移动。 -
Skeletal muscle fibers are bundled together in units called muscle fascicles, which are bundled together to form individual skeletal muscles. Skeletal muscles also have connective tissue supporting and protecting the muscle tissue.
::骨骼肌肉纤维以称为肌肉分册的单元捆绑在一起,这些单元被捆绑在一起形成个体骨骼肌肉,骨骼肌肉也有连接组织支持和保护肌肉组织。 -
Each skeletal muscle fiber consists of a bundle of myofibrils, which are bundles of protein filaments. The filaments are arranged in repeating units called sarcomeres, which are the basic functional units of skeletal muscles. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated because of the pattern of sarcomeres in its fibers.
::每根骨骼肌肉纤维都由一捆骨髓纤维组成,这是一捆蛋白丝的捆包。这些丝丝被安排在称为沙红的重复单元中,这些单元是骨骼肌肉的基本功能单位。骨骼肌肉组织由于其纤维中的沙红的形态而被撕裂。 -
Skeletal muscle fibers can be divided into two types, called slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers. Slow-twitch fibers are used mainly in aerobic endurance activities, such as long-distance running. Fast-twitch fibers are used mainly for non-aerobic, strenuous activities, such as sprinting. Proportions of the two types of fibers vary from muscle to muscle and person to person.
::骨骼肌肉纤维可分为两类,称为慢动和快动纤维;慢动纤维主要用于有氧耐力活动,如长距离运行;快动纤维主要用于无氧、强力活动,如冲刺;两种纤维的比例因肌肉和人而异。 -
Smooth muscle tissue is found in the walls of internal organs and vessels. When smooth muscles contract, they help the organs and vessels carry out their functions. Contractions of smooth muscles are involuntary and controlled by the autonomic nervous system, hormones, and other substances.
::在内脏器官和容器的墙壁上发现了肌肉组织,在肌肉组织松动时,它们会帮助器官和容器发挥功能,肌肉肌肉的腐蚀是非自愿的,由自主神经系统、荷尔蒙和其他物质控制。 -
Cells of smooth muscle tissue are not striated because they lack sarcomeres, but the cells contract in the same basic way as striated muscle cells. Unlike striated muscle, smooth muscle can sustain very long-term contractions and maintain its contractile function, even when stretched.
::光滑肌肉组织细胞不会因为缺乏正丙烯而减缩,而是细胞以与减速肌肉细胞相同的基本方式收缩。 与减速肌肉不同的是,光滑肌肉可以保持非常长期的收缩并保持其内脏功能,即使拉伸时也是如此。 -
Cardiac muscle tissue is found only in the wall of the heart. When cardiac muscle contracts, the heart beats and pumps blood. Contractions of cardiac muscle are involuntary, like those of smooth muscles. They are controlled by electrical impulses from specialized cardiac cells.
::心肌组织只能在心脏的墙壁中找到。当心脏肌肉收缩时,心脏会跳动,抽动血液。心肌的萎缩是非自愿的,就像光滑肌肉一样。它们受特殊心脏细胞的电脉冲控制。 -
Like skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is striated because its filaments are arranged in sarcomeres inside the muscle fibers. However, the myofibrils are branched instead of arranged in parallel rows, making cardiac and skeletal muscle tissues look different from one another.
::与骨骼肌肉一样,心脏肌肉也因为其丝状在肌肉纤维内以正红体排列而变形。然而,肌膜的细细枝状与平行的直排不同,使心脏和骨骼肌肉组织看起来不同。 -
The heart is the muscle that performs the greatest amount of physical work in the course of a lifetime. Its cells contain a great many mitochondria to produce ATP for energy and help the heart resist fatigue.
::心脏是肌肉,在一生中做体力工作的数量最大。细胞中含有大量细胞细胞,可以产生能量ATP,帮助心脏抵御疲劳。
Review
::回顾1. What is muscle tissue?
::1. 什么是肌肉组织?2. Where is skeletal muscle found, and what is its general function?
::2. 骨骼肌肉在哪里被发现,其一般功能是什么?3. Why do many skeletal muscles work in pairs?
::3. 为什么许多骨骼肌肉是成对的?4. Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle.
::4. 描述骨骼肌肉的结构。5. Relate muscle fiber structure to the functional units of muscles.
::5. 将肌肉纤维结构与肌肉功能单元联系起来。6. Why is skeletal muscle tissue striated?
::6. 为什么骨骼肌肉组织被撕裂?7. Compare and contrast slow-twitch and fast-twitch skeletal muscle fibers.
::7. 比较和对比慢动和快动骨骼肌肉纤维。8. Where is smooth muscle found? What controls the contraction of smooth muscle?
::8. 哪里找到光滑肌肉?什么控制光滑肌肉的收缩?9. Compare and contrast smooth muscle and striated muscle (such as skeletal muscle).
::9. 比较和对比光滑的肌肉和断裂的肌肉(如骨骼肌肉)。10. Where is cardiac muscle found? What controls its contractions?
::10. 心肌在哪里发现?什么控制其收缩?11. Both cardiac and skeletal muscle tissues are striated, but they look different from one another. Why?
::11. 心肌和骨骼肌肉组织都分解了,但看起来不同,为什么?12. The heart muscle is smaller and less powerful than some other muscles in the body. Why is the heart the muscle that performs the greatest amount of physical work in the course of a lifetime? How does the heart resist fatigue?
::12. 心脏肌肉比身体中其他肌肉小,力量小,为什么心脏肌肉是一生中从事最大体力工作的肌肉?心脏如何抗拒疲劳?13. Arrange the following units within a skeletal muscle in order, from smallest to largest:
::13. 在骨骼肌肉内排列以下单元,从最小到最大顺序:fascicle; sarcomere; muscle fiber; myofibril
::分册; sacremere; 肌肉纤维; 近光膜14. Give one example of connective tissue that is found in muscles. Describe one of its functions.
::14. 举一个在肌肉中发现的连接组织的例子,说明其功能之一。15. True or False: Muscle fibers are cells with multiple nuclei.
::15. 真实或假:肌肉纤维是多核细胞。Explore More
::探索更多You can learn more about the three types of muscle tissues by watching this Khan Academy video:
::更多关于三种肌肉组织, -
Slow-twitch muscle fibers
are dense with capillaries and rich in mitochondria and myoglobin, which is a protein that stores oxygen until needed for muscle activity. Relative to fast-twitch fibers, slow-twitch fibers can carry more oxygen and sustain
aerobic
(oxygen-using) activity. Slow-twitch fibers can contract for long periods of time, but not with very much force. They are relied upon primarily in endurance events, such as distance running or cycling.