15.2 呼吸系统的结构和功能
章节大纲
-
Seeing Your Breath
::看到你的呼吸Why can you “see your breath” on a cold day? The air you exhale through your nose and mouth is warm like the inside of your body. Exhaled air also contains a lot of vapor, because it passes over moist surfaces from the lungs to the nose or mouth. The water vapor in your breath cools suddenly when it reaches the much colder outside air. This causes the water vapor to condense into a fog of tiny droplets of liquid water. You release water vapor and other gases from your body through the process of respiration .
::为什么你能在寒冷的一天“看到你的呼吸 ” ? 你通过鼻子和嘴呼吸的空气和你的体内一样温暖。 吸入的空气中也含有大量的蒸气,因为它从肺部穿过湿润的表面,到鼻子或嘴部。 呼吸中的水蒸气在到达外面最冷的空气时突然冷却。 这导致水蒸气凝结成微小液态水滴的雾中。 你通过呼吸过程从身体中释放水蒸气和其他气体。What is Respiration?
::什么是呼吸?Respiration is the life-sustaining process in which gases are exchanged between the body and the outside atmosphere . Specifically, oxygen moves from the outside air into the body; and water vapor, carbon dioxide, and other waste gases move from inside the body to the outside air. Respiration is carried out mainly by the . It is important to note that respiration by the respiratory system is not the same process as —which occurs inside — although the two processes are closely connected. Cellular respiration is the metabolic process in which cells obtain energy , usually by “burning” glucose in the presence of oxygen. When cellular respiration is aerobic , it uses oxygen and releases carbon dioxide as a waste product. Respiration by the respiratory system supplies the oxygen needed by cells for aerobic cellular respiration, and removes the carbon dioxide produced by cells during cellular respiration.
::呼吸是身体和外部大气之间交换气体的维持生命的过程,具体来说,氧气从外部空气进入身体;水蒸气、二氧化碳和其他废气从身体内部转移到外部空气。呼吸主要由呼吸者进行。必须指出,呼吸系统呼吸的过程与呼吸系统的过程不同,而呼吸过程是内部发生的,尽管这两个过程是密切相连的。细胞呼吸是细胞获得能量的代谢过程,通常是在氧气面前“燃烧”葡萄糖。当细胞呼吸为有氧时,它使用氧,释放二氧化碳作为废料。呼吸系统呼吸提供细胞为有氧细胞呼吸所需的氧,并清除细胞呼吸期间产生的二氧化碳。Respiration by the respiratory system actually involves two subsidiary processes. One process is ventilation , or . Ventilation is the physical process of conducting air to and from the lungs. The other process is gas exchange . This is the biochemical process in which oxygen diffuses out of the air and into the , while carbon dioxide and other waste gases diffuse out of the blood and into the air. All of the organs of the respiratory system are involved in breathing, but only the lungs are involved in gas exchange.
::呼吸系统呼吸实际上涉及两个辅助过程:一个过程是通风,或.通风是肺中空气的物理过程;另一个过程是气体交换;这是生化过程,氧气从空气和气中扩散,而二氧化碳和其他废气则从血液和空气中扩散;呼吸系统的所有器官都参与呼吸,但只有肺部参与气体交换。Respiratory Organs
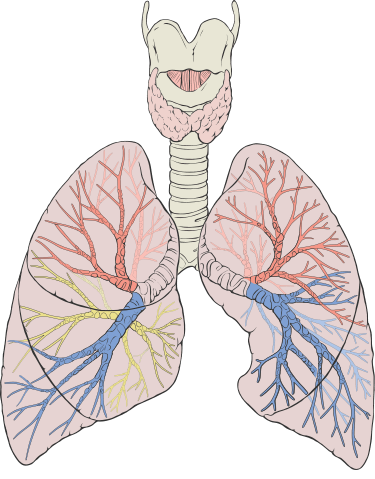
::呼吸器官The organs of the respiratory system form a continuous system of passages, called the respiratory tract , through which air flows into and out of the body. The respiratory tract has two major divisions: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract. The organs in each division are shown in the figure . In addition to these organs, certain of the thorax (body cavity that fills the chest) are also involved in respiration by enabling breathing. Most important is a large muscle called the diaphragm , which lies below the lungs and separates the thorax from the abdomen. Smaller muscles between the ribs also play a role in breathing. You can learn more about breathing muscles in the concept Breathing .
::呼吸系统器官形成一个连续的通过系统,称为呼吸道,空气通过呼吸道流经身体,呼吸道有两个主要部分:上呼吸道和下呼吸道。每个部分的器官都显示在图中。除了这些器官外,某些胸腔(填充胸部的体腔)也通过呼吸进行呼吸。最重要的是一个大肌肉,叫做隔膜,位于肺下,将胸腔与腹部分开,肋骨之间的小肌肉也在呼吸中发挥作用。你可以更多地了解呼吸肌肉的概念。During breathing, inhaled air enters the body through the nose and passes through the respiratory tract to the lungs. Exhaled air travels from the lungs in the opposite direction.
::在呼吸期间,吸入的空气通过鼻子进入身体,通过呼吸道进入肺部,从肺部向相反方向呼气。Upper Respiratory Tract
::上呼吸管线All of the organs and other structures of the upper respiratory tract are involved in conduction , or the movement of air into and out of the body. Upper respiratory tract organs provide a route for air to move between the outside atmosphere and the lungs. They also clean, humidify, and warm the incoming air. N o gas exchange occurs in these organs, however,
::上呼吸道的所有器官和其他结构都参与了导电或空气进出身体的移动,上呼吸道器官为空气在外部大气和肺部之间移动提供了一条通道,它们也清洁、潮湿和温暖空气,但这些器官没有气体交换,但是,Nasal Cavity
::纳沙岩洞The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space in the skull above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. It is a continuation of the two nostrils. As inhaled air flows through the nasal cavity, it is warmed and humidified. Hairs in the nose help trap larger foreign particles in the air before they go deeper into the respiratory tract. In addition to its respiratory functions, the nasal cavity also contains chemoreceptors that are needed for the sense of smell , and that contribute to the sense of taste .
::鼻腔在头骨上和脸部中间的鼻子后面是一个巨大的空隙,充斥空气,是两个鼻孔的延续。吸入的空气通过鼻腔流动,温暖和潮湿。鼻部的毛发有助于在进入呼吸道更深处之前在空气中捕捉较大的外国粒子。鼻腔除了呼吸功能外,还含有嗅觉所需的和有助于品味感的乳房。Pharynx
::Pharynx 双环The pharynx is a tube-like structure that connects the nasal cavity and the back of the mouth to other structures lower in the throat, including the larynx . The pharynx has dual functions — both air and food (or other swallowed substances) pass through it, so it is part of both the respiratory and the digestive systems. Air passes from the nasal cavity through the pharynx to the larynx (as well as in the opposite direction). Food passes from the mouth through the pharynx to the esophagus .
::Pharynx是一种管状结构,将鼻腔和嘴后部连接到喉下部的其他结构,包括喉部。Pharynx具有双重功能——空气和食物(或其他吞咽的物质)通过它,因此它是呼吸系统和消化系统的一部分。空气从鼻腔通过pharynx到喉部(以及相反方向)。食物从口通过Pharynx到食道。Larynx
::拉ynxThe larynx connects the pharynx and trachea , and helps to conduct air through the respiratory tract. The larynx is also called the voice box, because it contains the vocal cords, which vibrate when air flows over them, thereby producing sound. You can see the vocal cords in the larynx in the figure . Certain muscles in the larynx move the vocal cords apart to allow breathing. Other muscles in the larynx move the vocal cords together to allow the production of vocal sounds. The latter muscles also control the pitch of sounds and help control their volume.
::larynx 连接 pharynx 和 气管, 帮助通过呼吸道进行空气。 larynx 也被称为声音盒, 因为它包含声带, 当空气流过时会振动, 从而产生声音 。 您可以在图中看到 larynx 中的声带 。 喉部的某些肌肉将声带分开, 以便呼吸。 喉部的其他肌肉将声带一起移动, 以便产生声音。 后者的肌肉也控制声音的声道, 并帮助控制声音的音量 。The larynx as viewed from the top
::从顶部查看的喉角A very important function of the larynx is protecting the trachea from aspirated food. When swallowing occurs, the backward motion of the tongue forces a flap called the epiglottis to close over the entrance to the larynx. (You can see the epiglottis in the figure above.) This prevents swallowed material from entering the larynx and moving deeper into the respiratory tract. If swallowed material does start to enter the larynx, it irritates the larynx and stimulates a strong cough reflex . This generally expels the material out of the larynx, and into the throat.
::喉咙的一个非常重要的功能是防止气管被吸入食物。当吞咽时,舌头的后向运动迫使一个叫上皮球的扇子关闭喉咙的入口。 (你可以看到上图中的皮球球子。 )这阻止了吞咽的物质进入喉咙,更深入地进入呼吸道。 如果吞咽的物质开始进入喉咙,它就会刺激喉咙,刺激强烈的咳嗽反应。 这通常会将这种物质从喉咙中排出,并排入喉咙。Lower Respiratory Tract
::下部呼吸轨迹The trachea and other passages of the lower respiratory tract conduct air between the upper respiratory tract and the lungs. These passages form an inverted tree-like shape (see figure ), with repeated branching as they move deeper into the lungs. All told, there are an astonishing 1,500 miles of airways conducting air through the human respiratory tract! It is only in the lungs, however, that gas exchange occurs between the air and the bloodstream.
::呼吸道下部的气管和其他通道在上呼吸道和肺之间进行空气流通。这些通道形成树形反向形状(见图 ) , 在进入肺部的深处反复延伸。 全部说,有惊人的1,500英里的气道通过人类呼吸道进行空气流通。 然而,只有在肺中,空气和血液之间才会发生气体交换。This diagram illustrates the tree-like branching of the passages of the lower respiratory tract within the lungs.
::该图显示了肺部下呼吸道通道的树形分支。Trachea
::拖车NameThe trachea, or windpipe, is the widest passageway in the respiratory tract. It is about 2.5 cm (1 in.) wide and 10-15 cm (4-6 in.) long. It is formed by rings of cartilage , which make it relatively strong and resilient. The trachea connects the larynx to the lungs for the passage of air through the respiratory tract. The trachea branches at the bottom to form two bronchial tubes.
::气管,即风管,是呼吸道中最宽的通道,宽约2.5厘米(1英寸)宽,长约10-15厘米(4-6英寸),由软骨环组成,使其相对坚固和耐受力较强,气管将喉和肺连接,通过呼吸道通过空气。底部的气管枝形成两个支气管。Bronchi and Bronchioles
::Bronchi和Bronchioles 地区There are two main bronchial tubes, or bronchi (singular, bronchus) , called the right and left bronchi. The bronchi carry air between the trachea and lungs. Each bronchus branches into smaller, secondary bronchi; and secondary bronchi branch into still smaller tertiary bronchi. The smallest bronchi branch into very small tubules called bronchioles . The tiniest bronchioles end in alveolar ducts, which terminate in clusters of minuscule air sacs , called alveoli (singular, alveolus), in the lungs.
::支气管或支气管(支气管、支气管)称为左支气管。支气管在气管和肺间传播空气。支气管和肺间传播空气。支气管的每一个支气管都分小于二支支支支气管;支气管的第二支支支气管都分小于第三支支支支气管。小支气管的最小支气管被称作支气管。小支气管的最小支气管端在长肺中,以微小的气囊(气管、高压管)结束。Lungs
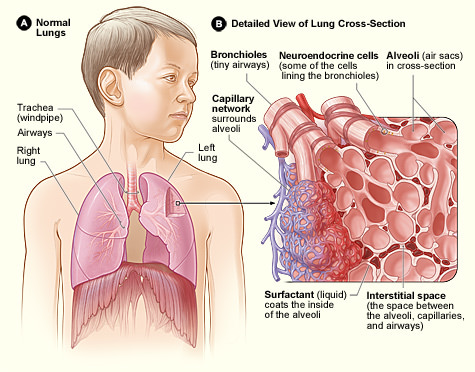
::肺肺The lungs are the largest organs of the respiratory tract. They are suspended within the pleural cavity of the thorax. The lungs are surrounded by two thin membranes called pleura , which secrete fluid that allows the lungs to move freely within the pleural cavity. This is necessary so the lungs can expand and contract during breathing. In the diagram , you can see that each of the two lungs is divided into sections. These are called lobes, and they are separated from each other by connective tissues . The right lung is larger and contains three lobes. The left lung is smaller and contains only two lobes. The smaller left lung allows room for the heart, which is just left of the center of the chest.
::肺部是呼吸道中最大的器官。 肺部在胸腔中悬浮。 肺部周围有两块薄薄膜, 叫做胸膜, 内分泌液可以让肺在胸腔中自由移动。 这是必需的, 这样肺部可以在呼吸期间膨胀和收缩。 在图表中, 您可以看到两个肺部的每一个被分割成几个部分。 这些称为叶状, 它们通过连接组织相互分离。 右肺更大, 含有三个叶状。 左肺较小, 仅含有两个叶状。 左肺允许心脏有空间, 心脏位于胸中左侧。The cross-section of lung tissue on the right in this diagram shows the alveoli, in which gas exchange takes place with the capillary network that surrounds them. Neuroendocrine cells lining the bronchioles control their diameter and the flow of air through them. Surfactant is a liquid that covers the inside of the alveoli and prevents them from collapsing and sticking together when air empties out of them during exhalation.
::本图右侧的肺组织横截面显示了气交换与周围毛细网的气交换的阿尔维奥利藻;支气管内衬的神经内分泌细胞控制着它们的直径和空气流。表面活性剂是一种液体,覆盖了藻利的内部,防止它们在呼气时倒塌并粘在一起。Lung tissue consists mainly of alveoli (see the diagram above). These tiny air sacs are the functional units of the lungs where gas exchange takes place. The two lungs may contain as many as 700 million alveoli, providing a huge total surface area for gas exchange to take place. In fact, alveoli in the two lungs provide as much surface area as half a tennis court! Each time you breathe in, the alveoli fill with air, making the lungs expand. Oxygen in the air inside the alveoli is absorbed by the blood in the mesh-like network of tiny capillaries that surrounds each alveolus. The blood in these capillaries also releases carbon dioxide into the air inside the alveoli. Each time you breathe out, air leaves the alveoli and rushes into the outside atmosphere, carrying waste gases with it.
::肺部组织主要由alveoli组成(见上图)。这些微小的空气囊是气体交换的肺部的功能单位。两个肺部可能含有多达7亿 alveoli,为气体交换提供了巨大的整个表面面积。事实上,两个肺部的Alveoli提供了相当于半个网球场的表面积。每次呼吸,气泡中都含有气泡,使肺部膨胀。在空气中的氧气被每只 alveolus周围的微小的毛细血管网状网状的血液吸收。这些血管中的血液也将二氧化碳释放到螺旋内的空气中。每次呼吸时,空气中都会释放出气泡,并用废气冲进外面的大气中。The lungs receive blood from two major sources. They receive deoxygenated blood from the heart. This blood absorbs oxygen in the lungs and carries it back to the heart to be pumped to cells throughout the body. The lungs also receive oxygenated blood from the heart that provides oxygen to the cells of the lungs for cellular respiration.
::肺部从两个主要来源获得血液,它们从心脏获得脱氧血液。这种血液吸收了肺部氧气,然后将氧气带回心脏,然后抽到全身的细胞中。肺部还从心脏获得氧化血液,为肺部细胞呼吸提供氧气。Protecting the Respiratory System
::保护呼吸系统You may be able to survive for weeks without food and for days without water, but you can survive without oxygen for only a matter of minutes — except under exceptional circumstances — so protecting the respiratory system is vital. Ensuring that a patient has an open airway is the first step in treating many medical emergencies. Fortunately, the respiratory system is well protected by the ribcage of the . T he extensive surface area of the respiratory system, however, is directly exposed to the outside world and all its potential dangers in inhaled air. It should come as no surprise that the respiratory system has a variety of ways to protect itself from harmful substances, such as dust and in the air.
::你可以在没有食物的情况下生存数周,在没有水的情况下生存数天,但除了特殊情况之外,没有氧气只能生存几分钟,因此,保护呼吸系统至关重要,确保病人有一个开阔的空气道是治疗许多医疗紧急情况的第一步,幸运的是,呼吸系统受到肋骨的妥善保护,但呼吸系统广泛的表面积直接暴露于外部世界及其在吸入空气中的所有潜在危险,呼吸系统有各种方法保护自己免受诸如灰尘和空气等有害物质的危害,这不足为奇。The main way the respiratory system protects itself is called the mucociliary escalator . From the nose through the bronchi, the respiratory tract is covered in epithelium that contains mucus-secreting goblet cells. The mucus traps particles and pathogens in the incoming air. The epithelium of the respiratory tract is also covered with tiny cell projections called cilia (singular, cilium), as shown in the figure . The cilia constantly move in a sweeping motion upward toward the throat, moving the mucus and trapped particles and pathogens away from the lungs and toward the outside of the body.
::呼吸系统保护自身的主要方式称为粘结扶梯。从鼻部到支气管,呼吸道覆盖在包含粘结绝缘细胞的粘膜中。粘结在进入空气的空气中捕捉颗粒和病原体。呼吸道的粘结也包含微小细胞投影,如图所示,称为硅(硅、)。硅在向喉咙的扫荡中不断向上移动,将粘结和被困颗粒和病原体从肺向外移动。The upward sweeping motion of cilia lining the respiratory tract helps keep it free from dust, pathogens, and other harmful substances.
::呼吸道的西里子衬衬向上倾斜运动有助于保持呼吸道没有尘埃、病原体和其他有害物质。What happens to the material that moves up the mucociliary escalator to the throat? It is generally removed from the respiratory tract by clearing the throat or coughing. Coughing is a largely involuntary response of the respiratory system that occurs when nerves lining the airways are irritated. The response causes air to be expelled forcefully from the trachea, helping to remove mucus and any debris it contains (called phlegm) from the upper respiratory tract to the mouth. The phlegm may be spit out (expectorated), or it may be swallowed and destroyed by stomach acids.
::将肌肉扶梯升到喉咙的物质会怎么样?通常通过清除喉咙或咳嗽从呼吸道中取出;咳嗽是呼吸系统的一种基本上非自愿的反应,当神经内衬气道受到刺激时,呼吸系统就会发生这种情况;这种反应导致空气从气管中被强行排出,帮助将上呼吸道的粘结和任何碎片(称为phlegm)从上呼吸道中移到嘴部;呼吸道可能会被吐出来(稀释),或者被胃酸吞咽和摧毁。Sneezing is a similar involuntary response that occurs when nerves lining the nasal passage are irritated. It results in forceful expulsion of air from the mouth, which sprays millions of tiny droplets of mucus and other debris out of the mouth and into the air, as shown in the photo . This explains why it is so important to sneeze into a tissue (rather than the air) if we are to prevent the transmission of respiratory pathogens.
::喷嚏是一种类似的非自愿反应,当鼻腔通过神经内衬受到刺激时,也会发生这种反应,其结果是将空气强行从嘴里排出,如照片所示,口中喷出数百万微小微粒的微缩糖浆和其他碎片,从嘴里和空气中喷出。 这就解释了为什么如果我们要防止呼吸道病原体的传播,在组织(而不是空气)中打喷嚏如此重要。Sneezing results in tiny particles from the mouth being forcefully ejected into the air.
::喷嚏导致嘴部微小微粒被强行喷射到空气中。How the Respiratory System Works with Other Organ Systems
::呼吸系统如何与其他器官系统一起工作The amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood must be maintained within a limited range for survival of the organism . Cells cannot survive for long without oxygen, and if there is too much carbon dioxide in the blood, the blood becomes dangerously acidic (pH is too low). Conversely, it there is too little carbon dioxide in the blood, the blood becomes too basic (pH is too high). The respiratory system works hand-in-hand with the nervous and cardiovascular systems to maintain in blood gases and pH.
::血液中的氧和二氧化碳含量必须保持在有限的范围内,以维持有机体的生存。 细胞没有氧气就无法长期生存,如果血液中二氧化碳过多,血液就会变成危险的酸性(pH太低 ) 。 相反,血液中的二氧化碳太少,血液变得太基本(pH太高 ) 。 呼吸系统与神经和心血管系统并肩工作,以保持血液气体和pH。It is the level of carbon dioxide — rather than the level of oxygen — that is most closely monitored to maintain blood gas and pH homeostasis. The level of carbon dioxide in the blood is detected by cells in the brain , which speed up or slow down the rate of breathing through the autonomic nervous system as needed to bring the carbon dioxide level within the normal range. Faster breathing lowers the carbon dioxide level (and raises the oxygen level and pH), while slower breathing has the opposite effects. In this way, the levels of carbon dioxide, oxygen, and pH are maintained within normal limits.
::二氧化碳水平(而不是氧水平)受到最严密的监测,以保持血液气和pH基本保持。 血液中的二氧化碳水平由大脑细胞检测,通过自主神经系统加快或减缓呼吸速度,以将二氧化碳水平纳入正常范围。 呼吸速度加快降低二氧化碳水平(提高氧水平和pH水平 ) , 而呼吸速度放慢则产生相反的效果。 以这种方式,二氧化碳、氧和pH水平保持在正常限度内。The respiratory system also works closely with the to maintain homeostasis. The respiratory system exchanges gases with the outside air, but it needs the cardiovascular system to carry them to and from . Oxygen is absorbed by the blood in the lungs and then transported through a vast network of to cells throughout the body, where it is needed for aerobic cellular respiration. The same system absorbs carbon dioxide from cells and carries it to the respiratory system for removal from the body.
::呼吸系统也与保持软体保持密切配合,呼吸系统与外部空气交换气体,但需要心血管系统将气体运入和运出。 氧由肺中的血液吸收,然后通过一个庞大的细胞网络运到整个身体的细胞,供有氧细胞呼吸之用,同一系统从细胞中吸收二氧化碳,并携带到呼吸系统,以便从身体中取出。Feature: My Human Body
::特质:我的人体Choking due to a foreign object becoming lodged in the airway results in nearly 200 thousand deaths each year. For the sake of your own , as well as those of loved ones, you should be aware of choking risks, signs, and treatments.
::由于一个外国物体被放置在气道上,因此,每年有近20万人死亡。 为了你自己和亲人的利益,你应该意识到窒息的风险、迹象和治疗方法。Choking is the mechanical obstruction of the flow of air from the atmosphere into the lungs. It prevents breathing, and may be partial or complete. Partial choking allows some — though inadequate — air flow into the lungs. Prolonged or complete choking results in asphyxia, or suffocation, which is potentially fatal.
::窒息是机械阻碍空气从大气进入肺部,妨碍呼吸,可能是局部或完全的,部分窒息使部分空气(尽管不够充分)进入肺部,窒息或窒息的长时间或完全窒息会导致窒息或窒息,可能致命。Obstruction of the airway typically occurs in the pharynx or trachea. Young children are more prone to choking than are older people, in part because they often put small objects in their mouth and do not understand the risk of choking that they pose. Young children may choke on small toys or parts of toys, or on household objects, in addition to food. Foods that can adapt their shape to that of the pharynx, such as bananas and marshmallows, are especially dangerous, and may cause choking in adults, as well as children.
::阻塞呼吸道的情况通常发生在Pharynx或气管中,幼儿比老人更容易被窒息,部分原因是他们经常把小东西放在嘴里,不理解自己造成的窒息风险; 幼儿可能会被小玩具或玩具部件或家用物品,以及食物窒息; 能够使其形状适应Pharynx的形状的食物,例如香蕉和棉花糖,特别危险,在成人和儿童中可能造成窒息。How can you tell if a loved one is choking? The person cannot speak or cry out, or has great difficulty doing so. Breathing, if possible, is labored, producing gasping or wheezing. The person may desperately clutch at his or her throat or mouth. If breathing is not soon restored, the person’s face will start to turn blue from lack of oxygen. This will be followed by unconsciousness, if oxygen deprivation continues beyond a few minutes.
::你怎能知道被爱的人是否窒息了呢?他不能说话,也不能大喊大叫,或很难这样做。如果可能的话,呼吸是劳累的,可以造成喘气或颤抖。他可能急切地抓住自己的喉咙或口腔。如果呼吸很快恢复不了,他的脸就会开始从缺氧中变蓝。接下来是昏迷,如果缺氧持续超过几分钟,就会失去氧气。If an infant is choking, turning the baby upside down and slapping him on the back may dislodge the obstructing object. To help an older person who is choking, first encourage the person to cough. Give them a few hard back slaps to help force the lodged object out of the airway. If these steps fail, perform the Heimlich maneuver on the person. You can easily find instructional videos online to learn how to do it. If the Heimlich maneuver also fails, call for emergency medical care immediately.
::如果婴儿窒息,把婴儿翻倒倒倒在背部扇他一巴掌,可能会将阻塞的物体移开。为了帮助已窒息的老人,首先鼓励咳嗽者。给他们几下后耳光,帮助他们把上方的物体推出气道。如果这些步骤失败,请对人进行海姆利希操纵。你可以很容易地在网上找到教学视频,学习如何做到这一点。如果海姆利希的动作失败了,请立刻要求紧急医疗。The Heimlich maneuver may be needed to help force an aspirated object out of the respiratory tract.
::可能需要进行海姆利希操作,以帮助将被浸透的物体从呼吸道中推出。Summary
::摘要-
Respiration is the process in which oxygen moves from the outside air into the body, and in which carbon dioxide and other waste gases move from inside the body into the outside air. It involves two subsidiary processes: ventilation and gas exchange. Respiration is carried out mainly by the respiratory system.
::呼吸是氧气从外部空气进入身体的过程,二氧化碳和其他废气从身体内部进入外部空气的过程,它涉及两个辅助过程:通风和气体交换,呼吸主要由呼吸系统进行。 -
The organs of the respiratory system form a continuous system of passages, called the respiratory tract. It has two major divisions: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract.
::呼吸道系统的器官形成一个称为呼吸道的连续通过系统,主要分为两个部分:上呼吸道和下呼吸道。 -
The upper respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx. All of these organs are involved in conduction, or the movement of air into and out of the body. Incoming air is also cleaned, humidified, and warmed as it passes through the upper respiratory tract. The larynx is also called the voice box, because it contains the vocal cords, which are needed to produce vocal sounds.
::上呼吸道包括鼻腔、 pharynx 和 lalynx。 所有这些器官都与导电或空气进出身体有关。 进入的空气也经过上呼吸道时被清洁、潮湿和暖化。 喉咙也被称为语音盒, 因为它包含声带, 需要它们来产生声响。 -
The lower respiratory tract includes the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles, and the lungs. The trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles are involved in conduction. Gas exchange takes place only in the lungs, which are the largest organs of the respiratory tract. Lung tissue consists mainly of tiny air sacs called alveoli, which is where gas exchange takes place between air in the alveoli and the blood in capillaries surrounding them.
::下呼吸道包括气管、支气管和支气管以及肺部;气管、支气管和支气管都与导管有关;气体交换只在肺部进行,肺部是呼吸道最大的器官;肺组织主要包括小气囊,叫做Alveoli,这是在藻类空气中和周围血管血液中进行气体交换的地方。 -
The respiratory system protects itself from potentially harmful substances in the air by the mucociliary escalator. This includes mucus-producing cells, which trap particles and pathogens in incoming air. It also includes tiny hair-like cilia that continually move to sweep the mucus and trapped debris away from the lungs and toward the outside of the body.
::呼吸系统保护自己免受肌肉扶梯在空气中可能有害的物质的影响,其中包括诱发微粒和病原体进入空气的粘结细胞,还包括微小的发型相似的硅球,它不断移动,从肺部向身体外扫去,从肺部向外扫去粘结和碎片。 -
The level of carbon dioxide in the blood is monitored by cells in the brain. If the level becomes too high, it triggers a faster rate of breathing, which lowers the level to the normal range. The opposite occurs if the level becomes too
low
. The respiratory system exchanges gases with the outside air, but it needs the cardiovascular system to carry the gases to and from cells throughout the body.
::血液中的二氧化碳水平由大脑中的细胞监测。如果水平太高,就会触发更快的呼吸速度,从而将水平降低到正常范围。相反,如果水平太低,就会发生相反的情况。呼吸系统与外部空气交换气体,但它需要心血管系统将气体携带到整个身体的细胞之间。
Review
::回顾1. What is respiration, as carried out by the respiratory system? Name the two subsidiary processes it involves.
::1. 呼吸系统进行的呼吸是什么? 说明呼吸系统所涉及的两个辅助过程。2. Describe the respiratory tract.
::2. 描述呼吸道。3. Identify the organs of the upper respiratory tract. What are their functions?
::3. 查明上呼吸道的器官,其功能是什么?4. List the organs of the lower respiratory tract. Which organs are involved only in conduction?
::4. 列出下呼吸道器官清单:哪些器官只涉及导导?5. Where does gas exchange take place?
::5. 在哪里进行天然气交换?6. How does the respiratory system protect itself from potentially harmful substances in the air?
::6. 呼吸系统如何保护自己不受空气中潜在有害物质的影响?7. Explain how the rate of breathing is controlled.
::7. 解释如何控制呼吸率。8. Why does the respiratory system need the cardiovascular system to help it perform its main function of gas exchange?
::8. 为什么呼吸系统需要心血管系统来帮助它履行其气体交换的主要功能?9. Place the following organs/structures of the respiratory system in order of when they are encountered by air entering the body, from earliest to latest:
::9. 将呼吸系统下列器官/结构按通过空气进入身体时遇到的顺序排列,最早至最晚:trachea; nasal cavity; alveoli; bronchioles; larynx; bronchi; pharynx
::气管;鼻腔;阿勒维奥利;支气管;喉管;支气管;支气管;支气管;支气管;支气管;支气管10. Which organ is part of both the digestive and respiratory systems?
::10. 哪个器官是消化系统和呼吸系统的一部分?a. larynx
::a. 喉b. trachea
::b. 气管(气管)ac. pharynx
::c. pharynxd. bronchus
::d. 支气管11. Describe two ways in which the body prevents food from entering the lungs.
::11. 描述身体防止食物进入肺部的两种方式。12. True or False: The lungs receive some oxygenated blood.
::12. 真实或假:肺部获得一些氧化血液。13. True or False: Gas exchange occurs in both the upper and lower respiratory tracts.
::13. 真实或虚假:气体交换发生在上呼吸道和下呼吸道。14. Coughing can expel ___________ from the body.
::14. 咳嗽可驱离身体。a. mucus
::a. 粘液b. food particles
::b. 食物颗粒c. phlegm
::c. 残疾人d. All of the above
::d. 以上所有情况15. What is the relationship between respiration and cellular respiration?
::15. 呼吸和细胞呼吸之间的关系是什么?Explore More
::探索更多Learn why premature infants can have respiratory distress syndrome — and how the problem is treated — by watching this video:
::了解早产婴儿为什么会患呼吸困难综合症,Check out this video to learn about how boys' voices change during puberty:
::学习男孩在青春期的声音如何改变: -
Respiration is the process in which oxygen moves from the outside air into the body, and in which carbon dioxide and other waste gases move from inside the body into the outside air. It involves two subsidiary processes: ventilation and gas exchange. Respiration is carried out mainly by the respiratory system.