15.4 天然气交换
章节大纲
-
Oxygen Bar
::氧气列Belly up to the bar and get your favorite... oxygen? That’s right — in some cities, you can get a shot of pure oxygen, with or without your choice of added flavors. Bar patrons inhale oxygen through a plastic tube inserted into their nostrils, paying up to a dollar per minute to inhale the pure gas. Proponents of the practice claim that in extra oxygen will remove toxins from the body, strengthen the immune system , enhance concentration and alertness, increase energy , and even cure cancer! T hese claims, however, have not been substantiated by controlled scientific studies. Normally, leaving the lungs is almost completely saturated with oxygen, even without the use of extra oxygen, so i t ’s unlikely that a higher concentration of oxygen in air inside the lungs would lead to significantly greater oxygenation of the blood. Oxygen enters the blood in the lungs as part of the process of gas exchange.
::贝利到酒吧去,并得到你最喜欢的... 氧气? 是这样吗? 在某些城市,你可以得到一剂纯氧,无论你是否选择添加的口味。 酒吧老板通过插入鼻孔的塑料管吸入氧气,每分钟支付高达1美元用于吸入纯气。 这种做法的支持者声称,在额外的氧气中清除人体毒素,加强免疫系统,提高浓度和警觉性,增加能量,甚至治愈癌症。 然而,这些说法并没有通过受控制的科学研究得到证实。 通常,即使不使用额外的氧气,肺部中的氧气浓度也不太可能导致血液的氧化。 氧气进入肺中的血液是气体交换过程的一部分。What is Gas Exchange?
::什么是天然气交易所?Gas exchange is the biological process through which gases are transferred across to either enter or leave the blood. Oxygen is constantly needed by for aerobic , and the same process continually produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. Gas exchange takes place between the blood and cells throughout the body, with oxygen leaving the blood and entering the cells, and carbon dioxide leaving the cells and entering the blood. Gas exchange also takes place between the blood and the air in the lungs, with oxygen entering the blood from the inhaled air inside the lungs, and carbon dioxide leaving the blood and entering the air to be exhaled from the lungs.
::气体交换是一种生物过程,通过这种过程,气体被转移到进入或离开血液中。氧源是氧气不断需要的,而同一过程不断产生二氧化碳作为一种废物产品。血液和细胞之间发生气体交换,氧气离开血液进入细胞,二氧化碳离开细胞进入血液进入血液。肺部的血液和空气之间也发生气体交换,肺部吸入空气中的氧气进入血液中,二氧化碳离开血液进入空气,从肺部吸入空气中吸入呼吸。Gas Exchange in the Lungs
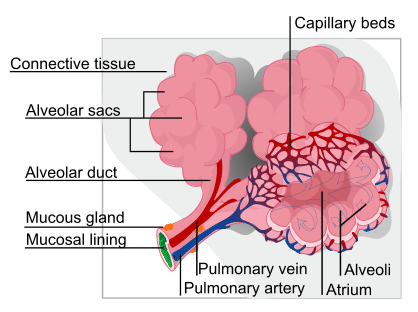
::肺肺气交换Alveoli are the basic functional units of the lungs where gas exchange takes place between the air and the blood. Alveoli (singular, alveolus) are tiny air sacs that consist of connective and epithelial tissues . The connective tissue includes elastic fibers that allow alveoli to stretch and expand as they fill with air during inhalation. During exhalation, the fibers allow the alveoli to spring back and expel the air. Special cells in the walls of the alveoli secrete a film of fatty substances called surfactant. This substance prevents the alveolar walls from collapsing and sticking together when air is expelled. Other cells in alveoli include macrophages, which are mobile scavengers that engulf and destroy foreign particles that manage to reach the lungs in inhaled air.
::Alveoli是肺部的基本功能单位,空气和血液之间发生气体交换。Alveoli(同卵、 alveolus)是小的空气囊,由连接和上皮骨组织组成。连接组织包括弹性纤维,在吸入过程中,允许阿勒维奥利在吸入空气时能够伸展和膨胀。在呼吸过程中,这些纤维允许阿勒维奥利回弹并排出空气。在阿尔维奥利的墙壁上,有特殊细胞,一个被称作表面活性剂的脂肪物质薄膜。这种物质防止高叶壁倒塌,在空气被排出时粘在一起。其他单叶细胞包括大型细胞,它们是移动的拾取者,吞噬并摧毁了在吸入空气中触及肺部的外国微粒子。As shown in the figure , alveoli are arranged in groups like clusters of grapes. Each alveolus is covered with epithelium that is just one cell thick. It is surrounded by a bed of pulmonary capillaries, each of which has a wall of epithelium just one cell thick. As a result, gases must cross through only two cells to pass between an alveolus and its surrounding capillaries.
::如图所示, alveoli 被排列成像葡萄团那样的一组。 每一个 alveolus 都被一个厚的细胞内膜所覆盖, 周围是一块肺部毛毛虫的床, 每张上面只有一块薄膜的墙。 因此, 气体必须穿过两个细胞, 才能穿过 alveolus 及其周围的毛细虫。Clusters of alveolar sacs make up most of the functional tissue of the lungs. Note that in this and subsequent illustrations, arteries, which carry oxygenated blood, are colored red; and veins, which carry deoxygenated blood, are colored blue.
::肺部大部分功能组织都包含长长长的肺囊。请注意,在这一插图和随后的插图中,含有氧化血液的动脉是红色的;含有脱氧化血液的血管是蓝色的。The pulmonary artery (also shown in the figure above) carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. Then, the blood travels through the pulmonary capillary beds, where it picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. The oxygenated blood then leaves the lungs and travels back to the heart through pulmonary veins . There are four pulmonary veins (two for each lung), and all four carry oxygenated blood to the heart. From the heart, the oxygenated blood is then pumped to cells throughout the body.
::肺动脉(亦如上图所示)含有从心脏到肺部的脱氧血液。然后,血液通过肺部毛虫病床穿透肺部,在那里吸收氧气并释放二氧化碳。氧血液然后离开肺部,通过肺血管回心。有四条肺血管(每条肺两条),所有四条都携带氧血液到心脏。从心脏,氧血液被抽到整个身体的细胞。Mechanism of Gas Exchange
::天然气交换机制机制Gas exchange occurs by across cell membranes. Gas molecules naturally move down a concentration gradient from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This is a passive process that requires no energy. To diffuse across cell membranes, gases must first be dissolved in a liquid. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported around the body dissolved in blood. Both gases bind to the hemoglobin in red blood cells , although oxygen does so more effectively than carbon dioxide. Some carbon dioxide also dissolves in blood plasma.
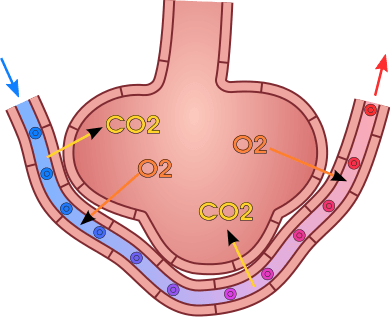
::气体交换发生于细胞膜之间。 气体分子自然会从高浓度地区向低浓度地区移动浓度梯度。 这是一个无能量的被动过程。 要在细胞膜之间扩散, 气体必须首先溶解在液体中。 氧和二氧化碳在血液中溶解的身体周围迁移。 这两种气体都与红细胞中的血红蛋白结合, 尽管氧比二氧化碳更有效。 有些二氧化碳也在血浆中溶解。As shown in the diagram , oxygen in inhaled air diffuses into a pulmonary capillary from the alveolus. Carbon dioxide in the blood diffuses in the opposite direction. The carbon dioxide can then be exhaled from the body.
::如图所示,吸入空气中的氧气会从阿尔韦勒斯扩散到肺部的毛虫中,血液中的二氧化碳会向相反的方向扩散,然后从身体中排放二氧化碳。A single alveolus is a tiny structure that is specialized for gas exchange between inhaled air and the blood in pulmonary capillaries.
::单 alveolus 是一种微小的结构,专门用于吸入空气和肺毛细血管中的血液之间的气体交换。Gas exchange by diffusion depends on having a large surface area through which gases can pass. Although each alveolus is tiny, there are hundreds of millions of them in the lungs of a healthy adult, so the total surface area for gas exchange is huge. It is estimated that this surface area may be as great as 100 m 2 .
::气体扩散的气体交换取决于气体能够穿过的广阔面积。 虽然每个藻类很小,但是在健康的成年人的肺里却有数亿颗,因此气体交换的总面积是巨大的。 据估计,这个面积可能高达100平方米。Gas exchange by diffusion also depends on maintaining a steep concentration gradient for oxygen and carbon dioxide. Continuous blood flow in the capillaries and constant breathing maintain this gradient.
::气体扩散交换还取决于氧气和二氧化碳保持一个陡峭的浓度梯度。-
Each time you inhale, there is a greater concentration of oxygen in the air in the alveoli than there is in the blood in the pulmonary capillaries. As a result, oxygen diffuses from the air inside the alveoli into the blood in the capillaries. Carbon dioxide, in contrast, is more concentrated in the blood in the pulmonary capillaries than it is in the air inside the alveoli.
As a result
, carbon dioxide diffuses in the opposite direction.
::每次吸入时,藻类中空气中的氧浓度都比肺毛毛毛毛血管中的血液中氧浓度高。结果,藻类中的氧扩散到毛细血管中的血液中。相比之下,二氧化碳在肺部毛细血管中的血液中的浓度要比在肺毛毛毛的空气中的浓度高。结果,二氧化碳向相反的方向扩散。 -
The cells of the body have a much lower concentration of oxygen than does the oxygenated blood that reaches them in
peripheral capillaries
, which are the capillaries that supply
tissues
throughout the body. As a result, oxygen diffuses from the peripheral capillaries into
. The opposite is true of carbon dioxide. It has a much higher concentration in body cells than it does in the blood of the peripheral capillaries. Thus, carbon dioxide diffuses from body cells into the peripheral capillaries.
::人体细胞的氧浓度远低于在周围毛细血管中接触的氧化血液,这些血液是整个身体组织供应的毛细血管。结果,氧气从周围毛细血管扩散到里面。二氧化碳的情况正好相反。人体细胞中的浓度远远高于周围毛细血管中的浓度。因此,二氧化碳从身体细胞扩散到周围毛细血管中。
Summary
::摘要-
Gas exchange is the biological process through which gases are transferred across cell membranes to either enter or leave the blood. Gas exchange takes place continuously between the blood and cells throughout the body, and also between the blood and the air inside the lungs.
::气体交换是一种生物过程,通过这种过程,气体通过细胞膜转移进入或流出血液。 气体交换在全身血液和细胞之间以及肺内的血液和空气之间持续进行。 -
Gas exchange in the lungs takes place in alveoli, which are tiny air sacs surrounded by networks of capillaries. The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it travels through pulmonary capillaries, picking up oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. The oxygenated blood then leaves the lungs through pulmonary veins.
::肺部的气体交换在alveoli中进行,这些肺部是被刺青网络环绕的微小空气囊。 肺动脉携带脱氧血液,从心脏到肺部,穿过肺部的心血管,吸收氧气和释放二氧化碳。 氧化血液然后通过肺血管将肺部留在肺部。 -
Gas exchange occurs by diffusion across cell membranes. Gas molecules naturally move down a concentration gradient from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This is a passive process that requires no energy.
::气体交换通过细胞膜之间的扩散进行。气体分子自然会从高浓度地区向低浓度地区移动浓度梯度。这是一个不需要能量的被动过程。 -
Gas exchange by diffusion depends on the large surface area provided by the hundreds of millions of alveoli in the lungs. It also depends on a steep concentration gradient for oxygen and carbon dioxide. This gradient is maintained by continuous blood flow and constant breathing.
::气体扩散的气体交换取决于肺部数亿叶子提供的大面积表面积,还取决于氧气和二氧化碳的陡峭浓度梯度,这种梯度由持续的血液流动和持续呼吸维持。
Review
::回顾1. What is gas exchange?
::1. 什么是天然气交换?2. Where in the human body does gas exchange take place?
::2. 气体交换在人体中在何处发生?3. What are alveoli, and what is their function?
::3. " 代谢 " 是什么,其功能是什么?4. Summarize the flow of blood into and out of the lungs for gas exchange.
::4. 为交换气体对进出肺部的血液进行抽查。5. Describe the mechanism by which gas exchange takes place.
::5. 说明进行天然气交换的机制。6. Identify the two main factors upon which gas exchange by diffusion depends.
::6. 查明通过扩散进行气体交换所依赖的两个主要因素。7. What is the purpose of surfactant in the lungs?
::7. 肺部表面活性剂的目的何在?8. Why are there macrophages in the alveoli?
::8. 藻类中为什么有大型植物?9. True or False: The pulmonary vein carries deoxygenated blood.
::9. 真实或假:肺血管含有脱氧血液。10. True or False: Gas exchange occurs because of a protein pump on lung cell membranes known as the oxygen-carbon dioxide pump.
::10. 真实或假:气体交换是因为肺细胞膜上的蛋白质泵,即氧-二氧化碳泵。11. If the concentration of oxygen were higher inside of a cell than outside of it, which way would the oxygen flow? Explain your answer.
::11. 如果一个细胞内部的氧浓度高于其外表,那么氧的流量会如何?解释你的答复。12. Gas exchange takes place between the alveoli and the pulmonary ____________ .
::12. Alveoli和肺部之间发生气体交换。a. artery
::a.动脉b. vein
::b. 血管c. capillaries
::c. 毛膜d. all of the above
::d. 以上所有情况13. Why is it important that the walls of the alveoli are only one cell thick?
::13. 为什么高温室的墙只厚一个牢房呢?14. Why are there so many alveoli in the lungs?
::14. 为什么肺里有这么多叶子?15. How many pulmonary veins are there in each lung?
::15. 每个肺部有多少肺静脉?a. two
::a. 2个b. four
::b. 4个c. one
::c. 1个d. five
::d. 5个Explore More
::探索更多Watch this Khan Academy video to see in greater detail how a molecule of oxygen makes its way from an alveolus into the blood:
::看这段汗学院录像, 更详细地看一股氧分子如何从阿尔韦勒斯流入血液:Learn about the "silent killer" that is carbon monoxide poisoning here:
::了解“沉默杀手”是一氧化碳中毒: -
Each time you inhale, there is a greater concentration of oxygen in the air in the alveoli than there is in the blood in the pulmonary capillaries. As a result, oxygen diffuses from the air inside the alveoli into the blood in the capillaries. Carbon dioxide, in contrast, is more concentrated in the blood in the pulmonary capillaries than it is in the air inside the alveoli.
As a result
, carbon dioxide diffuses in the opposite direction.