15.7 案例研究结论:咳嗽不休
章节大纲
-
Case Study Conclusion: Cough That Won't Quit
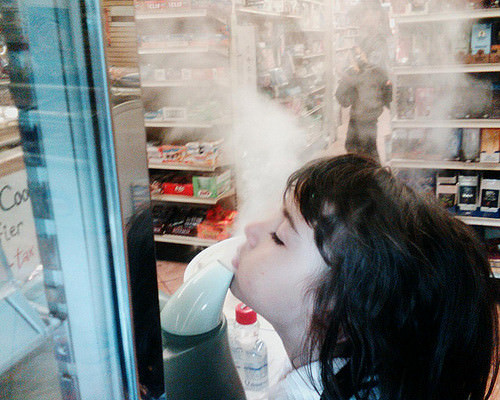
::案例研究结论:不放弃的咳嗽The little girl shown above seems to be enjoying the air coming out of a humidifier. Inhaling the moist air from a humidifier or steamy shower can feel particularly good if you have a respiratory system infection, such as bronchitis. The moist air helps to loosen and thin mucus in the respiratory system, allowing you to breathe easier.
::上面显示的小女孩似乎正在享受来自湿润器的空气。 如果呼吸系统感染,比如支气管炎,从湿润器或蒸汽淋浴中吸入潮湿空气会感觉特别好。 潮湿空气有助于呼吸系统放松和稀薄的肌肉,使呼吸更容易呼吸。In the beginning of this chapter, you learned about Erica, who developed acute bronchitis after getting a cold. She had a worsening cough, a sore throat due to coughing, and chest congestion. She was also coughing up thick mucus.
::埃丽卡在感冒后患了急性支气管炎。她咳嗽越来越严重,喉咙因为咳嗽而痛,胸腔堵塞。她还咳嗽着厚厚的黏液。Acute bronchitis usually occurs after a cold or flu, usually due to the same viruses that cause cold or flu. Because bronchitis is not usually caused by bacteria (although it can be), in most cases, antibiotics are not an effective treatment.
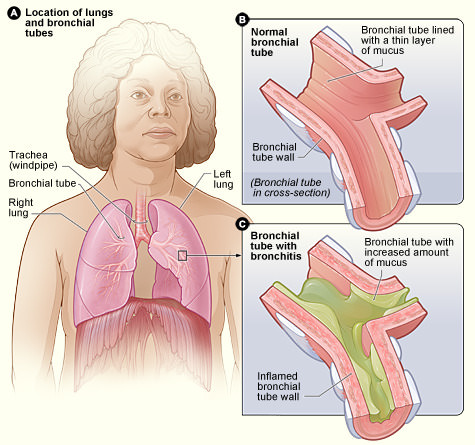
::急性支气管炎通常发生于感冒或流感之后,通常因为同一种病毒导致感冒或流感,因为支气管炎通常不是细菌引起的(尽管可能是细菌造成的),在大多数情况下,抗生素不是有效的治疗方法。Bronchitis affects the bronchial tubes, which, as you have learned, are air passages in the lower respiratory tract. The main bronchi branch off of the trachea and then branch into smaller bronchi, and then bronchioles. In bronchitis, the walls of the bronchi become inflamed, which makes them narrower. T here is also excessive production of mucus in the bronchi, which further narrows the pathway where air can flow through. The illustration shows how bronchitis affects the bronchial tubes.
::支气管受到支气管的影响,如你所知,支气管是下呼吸道的空气通道。气管的主要支气管是气管的支气管,然后是小支气管,然后是支气管,然后是支气管。在支气管中,支气管的墙壁开始发炎,使其更加狭窄。在支气管中,还过度生产粘液,进一步缩小了空气流经的通道。插图说明支气管如何影响支气管。The function of mucus is to trap pathogens and other potentially dangerous particles that enter the respiratory system from the air. However, when too much mucus is produced in response to an infection (as in the case of bronchitis), it can interfere with normal airflow. The body responds by coughing as it tries to rid itself of the pathogen-laden mucus.
::粘液的作用是捕捉病原体和其他从空气进入呼吸系统的潜在危险微粒,然而,当由于感染(如支气管炎)而产生过多的粘液时,它会干扰正常的空气流,身体在试图摆脱病原体粘液时咳嗽,从而作出反应。The treatment for most cases of bronchitis involves thinning and loosening the mucus so that it can be effectively coughed out of the airways. This can be done by drinking plenty of fluids, using humidifiers or steam, and — in some cases — using over-the-counter medications (such as expectorants). Dr. Johnson recommended some of these treatments to Erica, and also warned against using cough suppressants. Cough suppressants work on the nervous system to suppress the cough reflex. When a patient has a “productive” cough (which means they are coughing up mucus), doctors generally advise them not to take cough suppressants, so that they can cough the mucus out of their bodies.
::对大部分支气管炎病例的治疗涉及消瘦和松绑肌肉,从而能够有效地从空气中咳出,这可以通过大量饮用液体、使用湿润剂或蒸汽,以及在某些情况下,使用场外药物(如孕妇)来实现。约翰逊博士建议Erica使用其中一些治疗方法,并警告不要使用咳嗽抑制剂。咳嗽抑制剂在神经系统进行抑制咳嗽反应的工作。当病人有“生产性”咳嗽(这意味着咳嗽)时,医生通常建议他们不要服用咳嗽抑制剂,这样他们就可以从身体上咳嗽。When Dr. Johnson was examining Erica, she used a pulse oximeter to measure the oxygen level in her blood. Why did she do this? As you have learned, the bronchial tubes branch into bronchioles, which ultimately branch into the alveoli of the lungs. The alveoli are where gas exchange occurs between the air and the blood to take in oxygen and remove carbon dioxide and other wastes. By checking Erica’s blood oxygen level, Dr. Johnson was making sure that her clogged airways were not impacting her level of much-needed oxygen.
::当强生生医生检查埃丽卡时,她用脉冲氧量计测量血液中的氧气水平。为什么她这样做?正如你所知道的那样,支气管支管插进支气管,最终将支气管插入肺的肺泡中。 气流是空气和血液之间交换气体以吸收氧气并清除二氧化碳和其他废物的地方。 通过检查埃丽卡的血液氧气水平,约翰逊博士正在确保她堵塞的气道不会影响她急需的氧气水平。Erica has acute bronchitis, but you may recall that chronic bronchitis was discussed earlier in this chapter as term that describes the symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). COPD is often due to tobacco smoking, and it causes damage to the walls of the alveoli. Acute bronchitis, on the other hand, typically occurs after a cold or flu, and involves inflammation and mucus build-up in the bronchial tubes. As implied by the difference in their names, chronic bronchitis is an ongoing, long-term condition, while acute bronchitis is likely to resolve relatively quickly with proper rest and treatment.
::Erica患有急性支气管炎,但你可能记得,慢性支气管炎在本章早些时候曾作为描述慢性阻塞性肺病症状(COPD)的术语讨论过。 CPD经常是吸烟造成的,对肺壁造成破坏。 另一方面,急性支气管炎通常发生在感冒或流感之后,并涉及支气管的炎和粘结。 慢性支气管炎的名称不同,表明慢性支气管炎是一个持续和长期的状况,而急性支气管炎则很可能在适当的休息和治疗下较快地得到解决。Erica smokes cigarettes, so she is more likely to develop chronic respiratory conditions, such as COPD. As you have learned, smoking damages the respiratory system, along with many other systems of the body. Smoking increases the risk of respiratory infections, including bronchitis and flu, due to its damaging effects on the respiratory and immune systems. Dr. Johnson strongly encouraged Erica to quit smoking, not only so that her acute bronchitis resolves, but so that she can avoid future infections and other negative health outcomes associated with smoking, including COPD and lung cancer.
::Erica 医生强烈鼓励Erica戒烟,这不仅是为了让她的急性支气管炎得以治愈,而且是为了避免今后感染和与吸烟相关的其他不良健康后果,包括肺癌和肺癌。As you have learned in this chapter, the respiratory system is critical to carry out the gas exchange necessary for life’s functions, and to protect the body from pathogens and other potentially harmful substances in the air. But this ability to interface with the outside air has a cost. The respiratory system is prone to infections, as well as damage and other negative effects from allergens, mold, air pollution, and cigarette smoke. While exposure to most of these things cannot be avoided, not smoking is an important step you can take to protect this organ system — as well as many other systems of your body.
::正如你们在本章中所了解到的,呼吸系统对于进行生命功能所必需的气体交换以及保护身体不受病原体和其他潜在有害物质的危害至关重要。但是,与外部空气接触的能力是有代价的。呼吸系统容易感染,以及过敏基因、霉菌、空气污染和烟雾的损害和其他负面影响。 虽然无法避免接触大多数这些物质,但吸烟是你能采取的一个重要步骤来保护这个器官系统——以及你身体的许多其他系统。Chapter Summary
::章次摘要In this chapter, you learned about the respiratory system. Specifically, you learned that:
::在本章中,你学到了呼吸系统。具体地说,你学到了:-
Respiration is the process in which oxygen moves from the outside air into the body, and carbon dioxide and other waste gases move from inside the body to the outside air. It involves two subsidiary processes: ventilation and gas exchange.
::呼吸是氧气从外部空气进入身体的过程,二氧化碳和其他废气从身体内部转移到外部空气的过程,涉及两个辅助过程:通风和气体交换。 -
The organs of the respiratory system form a continuous system of passages, called the respiratory tract. It has two major divisions: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract.
::呼吸道系统的器官形成一个称为呼吸道的连续通过系统,主要分为两个部分:上呼吸道和下呼吸道。 -
-
The upper respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx. All of these organs are involved in conduction, or the movement of air into and out of the body. Incoming air is also cleaned, humidified, and warmed as it passes through the upper respiratory tract. The larynx is also called the voice box, because it contains the vocal cords, which are needed to produce vocal sounds.
::上呼吸道包括鼻腔、 pharynx 和 lalynx。 所有这些器官都与导电或空气进出身体有关。 进入的空气也经过上呼吸道时被清洁、潮湿和暖化。 喉咙也被称为语音盒, 因为它包含声带, 需要它们来产生声响。 -
The lower respiratory tract includes the trachea, bronchi and bronchioles, and the lungs. The trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles are involved in conduction. Gas exchange takes place only in the lungs, which are the largest organs of the respiratory tract. Lung tissue consists mainly of tiny air sacs called alveoli, which is where gas exchange takes place between air in the alveoli and the blood in capillaries surrounding them.
::下呼吸道包括气管、支气管和支气管以及肺部;气管、支气管和支气管都与导管有关;气体交换只在肺部进行,肺部是呼吸道最大的器官;肺组织主要包括小气囊,叫做Alveoli,这是在藻类空气中和周围血管血液中进行气体交换的地方。
::上呼吸道包括鼻腔、 pharynx 和 lalynx。 所有这些器官都与导电或空气进出身体有关。 进入的空气在通过上呼吸道时也经过清洁、 湿化和温暖。 喉也称为声音盒, 因为它含有声带, 产生声音所需的声带; 下呼吸道包括气管、 支气管、 支气管和支气管以及肺。 气管、 支气管和支气管都与导电有关。 气管交换只在肺部进行, 肺部是呼吸道中最大的器官。 肺部组织主要由微小的气囊组成, 叫做藻类, 这是藻类空气中空气与周围的血管血液之间交换气体的地方。 -
The upper respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx. All of these organs are involved in conduction, or the movement of air into and out of the body. Incoming air is also cleaned, humidified, and warmed as it passes through the upper respiratory tract. The larynx is also called the voice box, because it contains the vocal cords, which are needed to produce vocal sounds.
-
The respiratory system protects itself from potentially harmful substances in the air by the mucociliary escalator. This includes mucus-producing cells, which trap particles and pathogens in incoming air. It also includes tiny hair-like cilia that continually move to sweep the mucus and trapped debris away from the lungs and toward the outside of the body.
::呼吸系统保护自己免受肌肉扶梯在空气中可能有害的物质的影响,其中包括诱发微粒和病原体进入空气的粘结细胞,还包括微小的发型相似的硅球,它不断移动,从肺部向身体外扫去,从肺部向外扫去粘结和碎片。 -
The level of carbon dioxide in the blood is monitored by cells in the brain. If the level becomes too high, it triggers a faster rate of breathing, which lowers the level to the normal range. The opposite occurs if the level becomes too low. The respiratory system exchanges gases with the outside air, but it needs the cardiovascular system to carry the gases to and from cells throughout the body.
::血液中的二氧化碳水平由大脑中的细胞监测。如果水平太高,就会触发更快的呼吸速度,从而将水平降低到正常范围。相反,如果水平太低,就会发生相反的情况。呼吸系统与外部空气交换气体,但它需要心血管系统将气体携带到整个身体的细胞之间。 -
Breathing, or ventilation, is the two-step process of drawing air into the lungs (inhaling) and letting air out of the lungs (exhaling). Inhaling is an active process that results mainly from contraction of a muscle called the diaphragm. Exhaling is typically a passive process that occurs mainly due to the elasticity of the lungs when the diaphragm relaxes.
::呼吸或通风是将空气吸入肺部(吸入)和释放出肺部(吸入)的两步过程,吸入是一个活性过程,主要来自称为隔膜的肌肉收缩。 吸入一般是一种被动过程,主要由于隔膜放松时肺的弹性。 -
-
Breathing is one of the few vital bodily functions that can be controlled consciously, as well as unconsciously. Conscious control of breathing is common in many activities, including swimming and singing. However, there are limits on the conscious control of breathing. If you try to hold your breath, for example, you will soon have an irrepressible urge to breathe.
::呼吸是少数可以有意识和无意识地控制的重要身体功能之一。 有意识地控制呼吸在很多活动中是常见的,包括游泳和唱歌。然而,有意识地控制呼吸是有限度的。例如,如果你试图屏住呼吸,你很快就会有一种不可抑制的呼吸冲动。 -
Unconscious breathing is controlled by respiratory centers in the medulla and pons of the brainstem. They respond to variations in blood pH by either increasing or decreasing the rate of breathing as needed to return the pH level to the normal range.
::无意识的呼吸由脑激素的中风和脉搏的呼吸中心控制,它们通过增加或降低将pH水平恢复到正常范围所需的呼吸速度,对血液pH值的变化作出反应。 -
Nasal breathing is generally considered to be superior to mouth breathing, because it does a better job of filtering, warming, and moistening incoming air. It also results in slower emptying of the lungs, which allows more oxygen to be extracted from the air.
::鼻呼吸通常被认为优于口腔呼吸,因为它更适合过滤、变暖和潮湿空气流入。 它还导致肺部的排空速度放慢,从而可以从空气中提取更多的氧气。
::呼吸是少数可以自觉和无意识控制的重要身体功能之一。 呼吸的自觉控制在很多活动中是常见的, 包括游泳和唱歌。 但是, 呼吸的自觉控制是有限制的。 例如, 如果您试图屏住呼吸, 很快就会有不可抑制的呼吸冲动。 呼吸由呼吸中心控制, 在脑细胞的呼吸器和脉搏中。 它们通过增加或降低将pH水平恢复到正常水平所需的呼吸速度来应对血液pH的变化。 呼吸一般被认为优于口腔呼吸, 因为它在过滤、 变暖和运动进入空气方面效果更好。 它还导致肺部的呼吸变慢, 从而使得更多的氧能从空气中提取出来。 -
Breathing is one of the few vital bodily functions that can be controlled consciously, as well as unconsciously. Conscious control of breathing is common in many activities, including swimming and singing. However, there are limits on the conscious control of breathing. If you try to hold your breath, for example, you will soon have an irrepressible urge to breathe.
-
Gas exchange is the biological process through which gases are transferred across cell membranes to either enter or leave the blood. Gas exchange takes place continuously between the blood and cells throughout the body, and also between the blood and the air inside the lungs.
::气体交换是一种生物过程,通过这种过程,气体通过细胞膜转移进入或流出血液。 气体交换在全身血液和细胞之间以及肺内的血液和空气之间持续进行。 -
-
Gas exchange in the lungs takes place in alveoli. The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it travels through pulmonary capillaries, picking up oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. The oxygenated blood then leaves the lungs through pulmonary veins.
::肺部的气体交换在 alveoli 中发生。肺动脉从心脏到肺部携带脱氧血液,通过肺部毛细血管穿行,采集氧气并释放二氧化碳。氧血液然后通过肺血管将肺部留在肺部。 -
Gas exchange occurs by diffusion across cell membranes. Gas molecules naturally move down a concentration gradient from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This is a passive process that requires no energy.
::气体交换通过细胞膜之间的扩散进行。气体分子自然会从高浓度地区向低浓度地区移动浓度梯度。这是一个不需要能量的被动过程。 -
Gas exchange by diffusion depends on the large surface area provided by the hundreds of millions of alveoli in the lungs. It also depends on a steep concentration gradient for oxygen and carbon dioxide. This gradient is maintained by continuous blood flow and constant breathing.
::气体扩散的气体交换取决于肺部数亿叶子提供的大面积表面积,还取决于氧气和二氧化碳的陡峭浓度梯度,这种梯度由持续的血液流动和持续呼吸维持。
::肺部的气体交换在alveoli中进行。肺动脉从心脏到肺部携带脱氧血液,在肺部中通过肺部松动,采集氧气,释放二氧化碳。氧化血液然后通过肺血管离开肺部。气体交换通过细胞膜的传播进行。气体分子自然从高浓度地区向低浓度地区移动浓度梯度。这是一个无能量的被动过程。气体的传播取决于肺部数亿亿苏维奥提供的大面积表面积。它也取决于氧气和二氧化碳的陡峭的浓度梯度。这种梯度通过持续的血液流动和持续呼吸维持。 -
Gas exchange in the lungs takes place in alveoli. The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it travels through pulmonary capillaries, picking up oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. The oxygenated blood then leaves the lungs through pulmonary veins.
-
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways in the lungs, in which the airways periodically become inflamed. This causes swelling and narrowing of the airways, often with excessive mucus production, leading to difficulty breathing and other symptoms. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Asthma attacks are triggered by allergens, air pollution, or other factors.
::哮喘是肺气道中一种慢性炎症,气道定期发炎,造成气道膨胀和缩小,经常产生过度的粘结,导致呼吸困难和其他症状,据认为,气喘是遗传和环境因素综合作用造成的,哮喘袭击是由过敏、空气污染或其他因素引起的。 -
Pneumonia is a common inflammatory disease of the respiratory tract in which inflammation affects primarily the alveoli, which become filled with fluid that inhibits gas exchange. Most cases of pneumonia are caused by viral or bacterial infections. Vaccines are available to prevent pneumonia. Treatment often includes prescription antibiotics.
::肺炎是呼吸道一种常见的发炎性疾病,其发炎主要影响阿尔维奥利,它含有抑制气体交换的液体,大部分肺炎病例是由病毒或细菌感染引起的,疫苗可用于预防肺炎,治疗通常包括处方抗生素。 -
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a lung disease characterized by chronic poor airflow, which causes shortness of breath and a productive cough. It is caused most often by tobacco smoking, which leads to breakdown of connective tissues in the lungs. Alveoli are reduced in number and elasticity, making it impossible to fully exhale air from the lungs. There is no cure for COPD, but stopping smoking may reduce the rate at which COPD worsens.
::慢性阻塞性肺病(COPD)是一种肺病,其特点是长期空气流动不良,造成呼吸短促和有生产力的咳嗽,其最常见的原因是吸烟,导致肺部连接组织破裂,Alveoli数量和弹性减少,无法从肺部全面排出空气,没有治疗COPD的药方,但戒烟可能会降低CPD恶化的速度。 -
Lung cancer is a malignant tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. It results from accumulated DNA damage, most often caused by tobacco smoking. Lung cancer is typically diagnosed late, so most cases cannot be cured. It may be treated with surgery, chemotherapy, and/or radiation therapy.
::肺癌是一种恶性肿瘤,其特征是肺组织细胞不受控制地生长,其原因是累积的DNA损伤,最常见的是吸烟造成的DNA损伤,肺癌通常被诊断为晚期,因此大多数病例无法治愈,可以通过手术、化疗和(或)放射治疗进行治疗。 -
Smoking is the single greatest cause of preventable death worldwide. It has adverse effects on just about every body system and organ. Tobacco smoke affects not only smokers, but also non-smokers who are exposed to secondhand smoke. The nicotine in tobacco is highly addictive, making it very difficult to quit smoking.
::吸烟是全世界可预防死亡的最主要原因之一。 它对每个身体系统和器官都有不利影响。 烟草烟雾不仅影响吸烟者,而且影响接触二手烟的非吸烟者。 烟草中的尼古丁具有很高的上瘾性,因此很难戒烟。 -
-
A major health risk of smoking is
lung cancer
. Smoking also increases the risk of many other types of cancer. Tobacco smoke contains dozens of chemicals that are known carcinogens.
::吸烟的主要健康风险是肺癌,吸烟也增加了其他许多类型癌症的风险,吸烟含有数十种已知致癌化学品。 -
Smoking is the primary cause of COPD. Chemicals — such as carbon monoxide and cyanide in tobacco smoke — reduce the elasticity of alveoli so the lungs can no longer fully exhale air.
::吸烟是可口可乐的主要原因。 化学品——如烟草烟雾中的一氧化碳和氰化物——减少了 alveoli的弹性,使肺不再能够完全吸入空气。 -
Smoking damages the cardiovascular system and increases the risk of high blood pressure, blood clots, heart attack, and stroke. Smoking also has a negative impact on blood lipid levels.
::吸烟会损害心血管系统,增加高血压、血块、心脏病发作和中风的风险。 吸烟也会对血脂水平产生负面影响。 -
A wide diversity of additional adverse health effects — such as erectile dysfunction, female infertility, and slow wound healing — are attributable to smoking.
::吸烟对健康造成多种其他不利影响,如勃起功能障碍、女性不孕症和伤口愈合缓慢。
::吸烟还增加了其他许多类型癌症的风险; 烟草烟雾中含有数十种已知的致癌化学品; 吸烟是丙烯丙烯酸二氧化碳和烟雾中的氰化物等主要致因; 化学品——如烟雾中的一氧化碳和氰化物——减少了肺泡的弹性,使肺部无法再全面呼吸空气; 吸烟损害心血管系统,增加高血压、血块、心脏病发作和中风的风险; 吸烟也对血脂水平产生负面影响; 吸烟造成多种其他不良健康影响,如立体功能障碍、女性不孕症和慢性伤口愈合。 -
A major health risk of smoking is
lung cancer
. Smoking also increases the risk of many other types of cancer. Tobacco smoke contains dozens of chemicals that are known carcinogens.
As you have learned, the respiratory system brings in oxygen to the body and removes waste gases to the atmosphere — but these molecules wouldn’t get to where they need to go without the cardiovascular system to transport them via the bloodstream. Read the next chapter to learn about how the cardiovascular system carries out these critical functions.
::正如你们所学到的,呼吸系统给身体带来氧气,并将废气清除到大气中,但这些分子不会在没有心血管系统的情况下到达他们需要去的地方,通过血液输送。 阅读下一章了解心血管系统是如何发挥这些关键功能的。Chapter Summary Review
::" 概述 " 章次1. Describe the relationship between the bronchi, secondary bronchi, tertiary bronchi, and bronchioles.
::1. 说明支气管、第二支支气管、第三支气管和支气管之间的关系。2. What is the uppermost structure in the lower respiratory tract?
::2. 下呼吸道的最高结构是什么?a. bronchus
::a. 支气管b. lung
::b. 肺部c. alveolus
::c. alveolusd. trachea
::d. 气管3. Deoxygenated and oxygenated blood both travel to the lungs. Describe what happens to each there.
::3. 脱氧和脱氧血液均流向肺部,说明那里发生的情况。4. True or False: There are radioactive isotopes in cigarette smoke.
::4. 真实或假:烟雾中含有放射性同位素。5. True or False: The right and left lungs are identical in structure.
::5. 真实或假:右肺和左肺结构相同。6. Explain the difference between ventilation and gas exchange.
::6. 解释通风和气体交换之间的区别。7. Which way do oxygen and carbon dioxide flow during gas exchange in the lungs, and why? Which way do oxygen and carbon dioxide flow during gas exchange between the blood and the body’s cells, and why?
::7. 肺气交换期间氧气和二氧化碳以何种方式流出,为什么?血液和身体细胞之间气体交换期间氧气和二氧化碳以何种方式流出,为什么?8. Why does the body require oxygen, and why does it emit carbon dioxide as a waste product?
::8. 为什么身体需要氧气,为什么作为废物排放二氧化碳?9. True or False: Conduction refers to the movement of gases across cell membranes.
::9. 真实或虚假:行为指气体跨细胞膜的移动。10. True or False: Gas exchange does not require energy.
::10. 真实或虚假:天然气交换不需要能源。11. What do coughing and sneezing have in common?
::11. 咳嗽和打喷嚏有什么共同点?12. The _______________ escalator protects the respiratory system.
::12. 扶梯保护呼吸系统。a. phlegmociliary
::a. 单子体b. mucociliary
::b. 粘合剂c. mucoflagellar
::c. 混旗器d. surfactociliary
::d. 表面活性13. COPD can cause too much carbon dioxide in the blood. Answer the following questions about this:
::13. 氯丁二烯会在血液中造成过多的二氧化碳。a. Why does COPD cause there to be too much carbon dioxide in the blood?
::a. 为什么COPD导致血液中二氧化碳过多?b. What does this do to the blood pH?
::b. 这对血液pH值有何影响?c. How does the body respond to this change in blood pH?
::c. 身体如何应对血液pH值的这一变化?14. From the following list of diseases, choose which one best fits each description. Each disease is used only once.
::14. 从下面的疾病清单中,选择哪种疾病最适合每种疾病,每种疾病只使用一次。Diseases: asthma, pneumonia, COPD, lung cancer
::疾病:哮喘、肺炎、肺癌、肺癌a. Alveoli become inflamed and fill with fluid.
::a. Alveoli被发炎并装满液体。b. This disease can be caused by exposure to inhaled carcinogens.
::b. 这种疾病可能由接触吸入致癌物引起。c. There is a reduction in the number of alveoli.
::c. 代谢剂数量有所减少。d. Airways periodically narrow and fill with mucus.
::d. 航空公司定期收缩,装满粘液。15. True or False: Pneumonia can be caused by fungi.
::15. 真或假:肺炎可能由真菌引起。16. True or False: The diaphragm contracts during exhalation.
::16. 真实或假:呼气期间隔膜合同。17. What are three different types of things that can enter the respiratory system and cause illness or injury? Describe the negative health effects of each in your answer.
::17. 可以进入呼吸系统并造成疾病或伤害的三种不同类型的物质有哪些?在回答中说明每种物质对健康的消极影响。18. Where are the respiratory centers of the brain located? What is the main function of the respiratory centers of the brain?
::18. 大脑呼吸道中心位于何处?大脑呼吸道中心的主要功能是什么?19. Smoking increases the risk of getting influenza, commonly known as the flu. Explain why this could lead to a greater risk of pneumonia.
::19. 吸烟增加了流行性流感(俗称流感)的风险,解释为什么这会导致肺炎风险增加。20. If a person has a gene that caused them to get asthma, could changes to their environment (such as more frequent cleaning) help their asthma? Why or why not?
::20. 如果一个人有导致哮喘发作的基因,那么改变其环境(如更经常的清洁)可以帮助其哮喘?为什么或为什么不能?21. What does the term bronchodilator refer to?
::21. " 支气管 " 一词指的是什么?a. the largest bronchial tube
::a. 最大的支气管b. an area of the brain that increases breathing rate
::b. 大脑中可增加呼吸率的一个区域c. a medication that opens constricted airways
::c. 开放收缩气道的药物d. a medication that clears the nasal cavity
::d. 清除鼻腔的药物22. Explain why nasal breathing generally stops particles from entering the body at an earlier stage than mouth breathing does.
::22. 解释为什么鼻腔呼吸通常比口呼吸更早的阶段阻止颗粒进入身体。23. Which structure is also called the “voice box?”
::23. 哪个结构也称为 " 语音信箱? " ?a. larynx
::a. 喉b. pharynx
::b. 光环c. epiglottis
::c. 上皮蛋白d. trachea
::d. 气管 -
Respiration is the process in which oxygen moves from the outside air into the body, and carbon dioxide and other waste gases move from inside the body to the outside air. It involves two subsidiary processes: ventilation and gas exchange.