17.4 上肠胃肠道
章节大纲
-
Head Stand
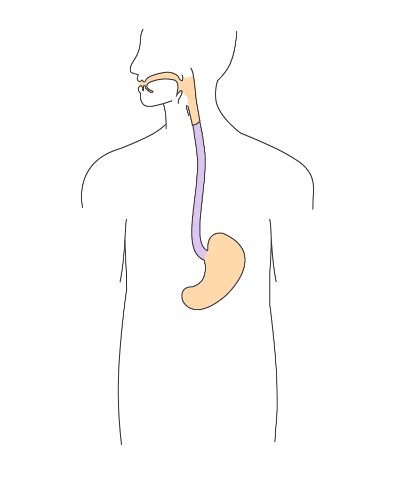
::头起Did you ever wonder what would happen if you tried to swallow food while standing on your head like this boy? Many people think that food travels down the gullet from the mouth by the force of gravity. If that were the case, then food you swallowed would stay in your throat while you were standing on your head. In reality, your position doesn’t have much to do with your ability to swallow. Food will travel from your mouth to your stomach whether you are standing upright or upside down. That’s because the tube the food travels through — the esophagus — moves the food along via muscular contractions known as peristalsis . The esophagus is one of several organs that make up the upper gastrointestinal tract .
::你有没有想过,如果你像这个男孩那样站在头顶上吞食食物,会有什么后果?许多人认为食物会从嘴里用重力从嘴里流下来。如果是这样的话,那么在你的头上吞食的食物就会留在喉咙里。在现实中,你的立场与吞咽的能力没有多大关系。无论你是站立还是颠倒,食物都会从嘴里流到肚子里。这是因为食物的管子——食道——通过被称为“阴道”的肌肉收缩来移动食物。食道是构成上胃肠道的若干器官之一。Organs of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
::上胃肠道器官器官Besides the esophagus, organs of the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract include the mouth, pharynx , and stomach. These hollow organs are all connected to form a tube through which food passes during digestion . The only role in digestion played by the pharynx and esophagus is to move food through the GI tract. The mouth and stomach, in contrast, are organs where digestion — or the breakdown of food — also occurs. In both of these organs, food is broken into smaller pieces (mechanical digestion), as well as broken down chemically (chemical digestion). It should be noted that the first part of the (duodenum) is considered in some contexts to be part of the upper GI tract, but that practice is not followed here.
::除了食道外,上胃肠道的器官包括口腔、阴道和胃,这些空心器官都与形成一个在消化过程中通过的食物输送管相连,在消化过程中,Pharynx和食道的唯一作用是将食物通过食道,而口和胃则是也发生消化或食物分解的器官,在这两种器官中,食物被分解成小块(机械消化),化学分解(化学消化),应该指出,在某些情况下,(duodenum)的第一部分被认为是上胃的一部分,但这里没有遵循这种做法。Mouth
::嘴唇The mouth is the first organ of the GI tract. Most of the oral cavity is lined with mucous membrane . This tissue produces mucus , which helps moisten, soften, and lubricate food. Underlying the mucous membrane is a thin layer of smooth muscle to which the mucous membrane is only loosely connected. This gives the mucous membrane considerable ability to stretch as you eat food. The roof of the mouth, called the palate, separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity . The front part is hard, consisting of mucous membrane covering a plate of . The back part of the palate is softer and more pliable, consisting of mucous membrane over muscle and connective tissue . The hard surface of the front of the palate allows for pressure needed in chewing and mixing food. The soft, pliable surface of the back of the palate can move to accommodate the passage of food while swallowing. at either side of the soft palate contract to create the swallowing action.
::嘴部是 GI 草皮的第一个器官。 口腔腔大部分与粘结膜相连接。 组织产生粘结, 有助于湿润、 软软和润滑食品。 粘结膜下面是一个薄质的光滑肌肉层, 粘结膜只有松软的连接。 这让粘结膜在吃食物时有相当大的伸展能力。 口腔的顶部, 称为粘结, 将口腔和鼻腔分开。 前部是硬的, 由粘结膜组成, 覆盖一个盘子。 粘结膜的后部部分是软软的, 更柔软, 由粘结在肌肉和连接组织上的粘结膜组成。 粘结面的硬表面允许咀嚼和混合食物所需的压力。 粘结后部的柔软、 柔软的表面可以在吞食时移动食物的通道。 在软粘结面的两侧, 创造吞咽动作。Several specific structures in the mouth are specialized for digestion. These include salivary glands , tongue, and teeth.
::口腔中若干特殊结构专门用于消化,包括唾液腺、舌头和牙齿。Salivary Glands
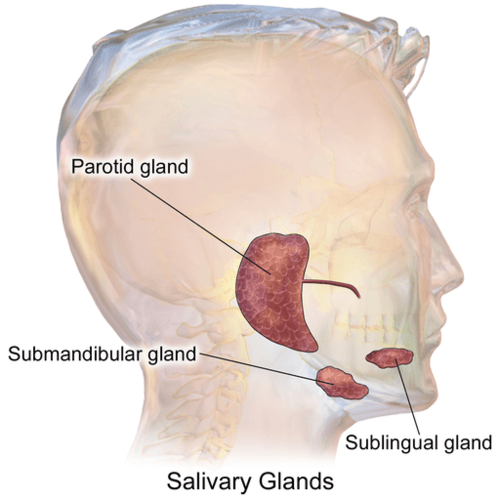
::盐盐地The mouth contains three pairs of major salivary glands , which are shown in the figure . These three pairs are all exocrine glands that secrete saliva into the mouth through ducts.
::口腔含有三对主要的口腔腺,图中显示了这些口腔腺。这三对口腔都是通过管子将唾液渗入口腔的外科腺。-
The largest of the three major pairs of salivary glands are the
parotid glands
, which are located on either side of the mouth in front of the ears.
::三对主要口腔腺中最大的一对是干燥的腺,它们位于耳朵前的嘴两侧。 -
The next largest pair is the
submandibular glands
, located beneath the lower jaw.
::下一个最大的一对是位于下下下下巴下方的亚管状腺。 -
The third pair is the
sublingual glands
, located underneath the tongue.
::第三对是亚语言的腺,位于舌头之下。
Salivary glands in the mouth include the three major pairs of glands shown here.
::口腔中的盐状腺包括这里显示的三对主要腺。In addition to these three pairs of major salivary glands, there are also hundreds of minor salivary glands in the oral mucosa lining the mouth and on the tongue. Along with the major glands, most of the minor glands secrete the digestive amylase , which begins the chemical digestion of starch and glycogen (polysaccharides). However, the minor salivary glands on the tongue secrete the fat-digesting enzyme lipase, which in the mouth is called lingual lipase (to distinguish it from pancreatic lipase secreted by the pancreas).
::除了这三对主要的唾液性腺外,口腔和舌头的口腔粘膜中还有数百个小的唾液性腺,与主要腺一起,大多数小腺分泌了消化性氨基酶,开始对淀粉和甘油(polysacharides)进行化学消化,但舌头上的小唾液性腺将脂肪消化的酶脂酶秘密起来,口腔中称之为语言性脂酶(以区别于胰腺中隐含的胰腺脂)。Saliva secreted by the salivary glands mainly helps digestion, but it also plays other roles. It helps maintain dental health by cleaning the teeth, and it contains antibodies that help protect against infection. By keeping the mouth lubricated, saliva also allows the mouth movements needed for speech.
::以唾液腺为秘而不宣的唾液主要有助于消化,但它也起到其他作用。 它通过打扫牙齿帮助保持牙科健康,并含有抗体来帮助防止感染。 通过保持口腔润滑,唾液也允许了口腔的交流。Tongue
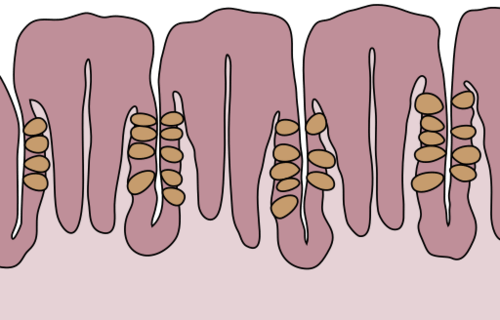
::舌语The tongue is a fleshy, muscular organ that is attached to the floor of the mouth by a band of ligaments that gives it great mobility. This is necessary so the tongue can manipulate food for chewing and swallowing. Movements of the tongue are also necessary for speaking. The upper surface of the tongue is covered with tiny projections called papillae, which contain taste buds. The latter are collections of chemoreceptor (shown in brown in the figure ). These sensory cells sense chemicals in food and send the information to the brain via cranial nerves , thus enabling the sense of taste.
::舌头是一种肉质、肌肉器官,由一团长袍附在嘴底上,使舌头具有很大的运动力。这很有必要,使舌头能够操纵食物,用于咀嚼和吞咽。舌头的移动也是说话所必需的。舌头的上方有小的投影,叫做papillae, 上面有味蕾。后者是切摩感官的集合(在图中以棕色形式出现 ) 。这些感官细胞在食物中感知化学物质,通过胸腔神经将信息传递给大脑,从而能够产生品味感。The purple structures shown in this drawing of the tongue surface are papillae, which contain taste buds. Chemoreceptor cells (brown) detect chemicals that allow our sense of taste.
::这幅舌头表面图示中的紫色结构是含有味蕾的papillae。 Chemoremeptionor细胞(棕色)检测了使我们有品味感的化学物质。There are five basic tastes detected by the chemoreceptor cells in taste buds: saltiness, sourness, bitterness, sweetness, and umami (often described as a meaty taste). Contrary to popular belief, taste buds for the five basic tastes are not located on different parts of the tongue. Why does taste matter? The taste of food helps to stimulate the secretion of saliva from the salivary glands. It also helps us to eat foods that are good for us, instead of rotten or toxic foods. The detection of saltiness, for example, enables the control of salt intake and salt balance in the body. The detection of sourness may help us avoid spoiled foods, which often taste sour due to by . The detection of bitterness warns of poisons, because many plants defend themselves with toxins that taste bitter. The detection of sweetness guides us to foods that supply quick energy . The detection of umami may signal protein-rich foods.
::乳房受体细胞在味蕾中检测到五种基本口味:咸、酸、苦、甜和番茄(通常被称为肉类味)。与流行的信仰相反,五种基本口味的味蕾并非位于舌头的不同部分。为什么味道有问题?食物的口味有助于刺激口腔唾液的分泌,也帮助我们食用对我们有益的食物,而不是腐烂或有毒的食物。例如,盐碱的检测可以控制体内的盐摄入和盐平衡。酸味的检测可以帮助我们避免被宠食的食物,这些食物往往因舌头而酸。苦味的检测警告毒药,因为许多植物用苦味的毒素保护自己。甜味的检测可以引导我们找到能提供快速能量的食品。亚米的检测可以发出富含蛋白质食物的信号。Teeth
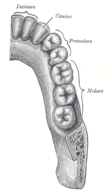
::牙齿The teeth are complex structures made of a bone-like material called dentin and covered with enamel, which is the hardest tissue in the body. Adults normally have a total of 32 teeth, with 16 in each jaw. The right and left sides of each jaw are mirror images in terms of the numbers and types of teeth they contain. Teeth have different shapes to suit them for different aspects of mastication (chewing). The different types of teeth are illustrated in the figure .
::牙齿是一种复杂的结构,由一种叫丹汀的骨类材料制成,上面盖着凝胶,这是身体中最难的组织;成年人通常共有32颗牙齿,每下巴有16颗;每下巴的右侧和左侧都是反映牙齿数量和类型的镜像;牙齿有不同的形状,适合不同方面的修剪(切牙)。图中显示了不同类型的牙齿。-
Incisors
are the sharp, blade-like teeth at the front of the mouth. They are used for cutting or biting off pieces of food. In adults, there are normally four incisors in each jaw, or eight in total.
::口前的牙尖尖尖尖尖尖尖尖,用于切割或咬断食物。在成年人中,每下巴通常有4个牙尖,或总共8个牙牙尖。 -
Canines
are the pointed teeth on either side of the incisors. They are used for tearing foods that are tough or stringy. Adults normally have two canines in each jaw, or four altogether.
::犬牙是切口器两侧的尖牙,用于撕裂坚硬或铁丝的食品。 成人通常每下巴有两只犬牙,或者总共四只。 -
Premolars
and
molars
are cuboid teeth with cusps and grooves that are located on the sides and toward the back of the jaws. Premolars are closer to the front of the mouth. Molars are larger and have more cusps than premolars, but both are used for crushing and grinding food. Adults normally have two premolars and three molars on each side of each jaw, for a total of eight premolars and twelve molars.
::Premolars和molars是幼齿,有两侧和下巴背面的幼齿和小和小;Premolars更靠近嘴前方;Molars大,比前摩尔人多,但两者都用于粉碎和研磨食物;成人通常每下巴两面各有两颗前摩尔和三颗摩尔,总共八个前摩尔人和十二个摩尔人。
In adults, both sides of each jaw normally have the same numbers of the four types of teeth shown here.
::在成人中,每下巴的两侧通常与这里显示的四种牙齿相同。Pharynx
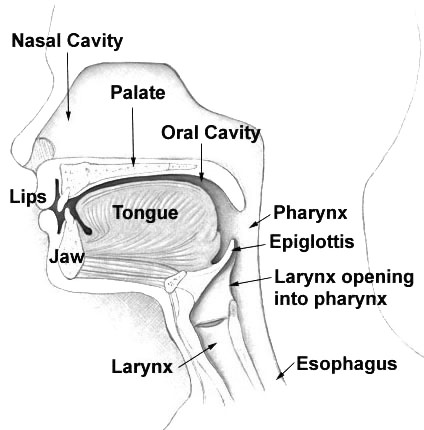
::Pharynx 双环The tube-like pharynx (see figure ) plays a dual role as an organ of both respiration and digestion. As part of the , it conducts air between the nasal cavity and larynx . As part of the , it allows swallowed food to pass from the oral cavity to the esophagus. Anything swallowed has priority over inhaled air when passing through the pharynx. During swallowing, the backward motion of the tongue causes a flap of elastic cartilage — called the epiglottis — to close over the opening to the larynx. This prevents food or drink from entering the larynx.
::呼吸和消化器官(见图)具有双重作用,作为呼吸和消化的器官,作为其中一部分,它进行鼻腔和喉之间的空气。作为其中的一部分,它允许吞咽的食物从口腔传到食道。吞咽的任何东西在通过阴道时优先于吸入的空气。吞咽时,舌头的后向运动造成松动的软软软软的软体——称为缩头骨——在喉咙开口处关闭,从而阻止食物或饮料进入喉咙。The tongue moves backward during swallowing to cause the epiglottis to cover the opening to the larynx. As a result, food passes from the pharynx to the esophagus — and not into the larynx.
::吞咽时,舌头向后退,使蛋白质覆盖喉的开口。 结果,食物从Pharynx传到食道 — — 而不是进入喉咙。Esophagus
::Esophagus( 以硫磷)The esophagus (shown in the figure ) is a muscular tube through which food is pushed from the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus passes through an opening in the diaphragm (the large muscle that separates the abdomen from the thorax) before reaching the stomach. In adults, the esophagus averages about 25 cm (10 in.) in length, depending on a person’s height. The inner lining of the esophagus consists of mucous membrane, which provides a smooth, slippery surface for the passage of food. The cells of this membrane are constantly being replaced as they are worn away from the frequent passage of food over them.
::食道(如图所示)是一个肌肉管,将食物从Pharynx推向胃部。食道通过隔膜的开口(将腹部和胸部分开的大肌肉)才能到达胃部。在成人,食道平均长度约为25厘米(10英寸),视一个人的身高而定。食道的内衬由粘膜组成,为食物的通过提供了光滑滑的表面。这种膜的细胞不断被替换,因为它们被磨断,无法通过食物的频繁通道。The esophagus moves food by peristalsis from the pharynx to the stomach.
::食道将食物从阴道长到胃。When food is not being swallowed, the esophagus is closed at both ends by upper and lower esophageal sphincters. Sphincters are rings of muscle that can contract to close off openings between structures. The upper esophageal sphincter is triggered to relax and open by the act of swallowing, allowing a bolus of food to enter the esophagus from the pharynx. Then, the esophageal sphincter closes again to prevent food from moving back into the pharynx from the esophagus.
::当食物不吞咽时,上下食道螺旋钉将食道关闭两端,上下两端的食道螺旋藻关闭。 Sphincters是肌肉圈,可以连结关闭结构之间的开口。上食道螺旋杆通过吞咽行为被触发放松和打开,允许一团食物从pharynx进入食道。然后,食道螺旋丝再次关闭,以防止食物从食道返回pharynx。Once in the esophagus, the food bolus travels down to the stomach, pushed along by the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of muscles (peristalsis). The lower esophageal sphincter is located at the junction between the esophagus and the stomach. This sphincter opens when the bolus reaches it, allowing the food to enter the stomach. The sphincter normally remains closed at other times to prevent the contents of the stomach from entering the esophagus. Failure of this sphincter to remain completely closed can lead to heartburn . If it happens chronically, it can lead to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), in which the mucous membrane of the esophagus may become damaged by the highly acidic contents of the stomach.
::一旦进入食道,食物肉囊就会下到胃部,并被肌肉(阴性)的节奏收缩和放松所推动。低食道螺旋杆位于食道和胃之间的十字路口。这个螺旋杆在肉身到达食道时打开,允许食物进入胃部。在另一些时候,螺旋杆通常保持封闭,以防止胃内的东西进入食道。这个螺旋杆不能完全封闭,可能导致心脏灼伤。如果长期发生,它可能导致胃部复发性胃炎,其中食道的粘膜可能因胃内的酸性含量高而受损。Stomach
::胃The stomach is a J-shaped organ (shown ) that is joined to the esophagus at its upper end, and to the first part of the small intestine (duodenum) at its lower end. When the stomach is empty of food, it normally has a volume of about 75 mL, but it can expand to hold up to about a liter of food. Waves of muscle contractions (peristalsis) passing through the muscular walls of the stomach cause the food inside to be mixed and churned. The wall of the stomach has an extra layer of muscle tissue not found in other organs of the GI tract that helps it squeeze and mix the food. These movements of the stomach wall contribute greatly to mechanical digestion by breaking the food into much smaller pieces. The churning also helps mix the food with stomach secretions that aid in its chemical digestion.
::胃部是一种J形器官,与上端的食道和下端的小肠(duodenum)的第一部分相连接,胃部一般有75毫升的体积,但可以膨胀到约一升的食物。胃部的肌肉收缩(阴性)波及胃部肌肉壁,导致腹部食物混杂和被染色。胃部的墙外有一层肌肉组织,没有在吉他河口的其他器官中找到,帮助它挤压和混合食物。胃壁的这些运动通过将食物破碎成小得多的碎片,对机械消化有很大作用。胃部的肌肉收缩也有助于将食物与胃分解混合,有助于其化学消化。The stomach is connected at the top to the esophagus and at the bottom to the duodenum of the small intestine. The pylorus, or pyloric sphincter, controls emptying of the stomach into the small intestine. The outer surface of the stomach is covered with fibrous connective tissue.
::胃部在顶部与食道相连,在底部与小肠的二元相连,小肠部(pylorus,或pyloric sphincter)控制胃部空入小肠部,腹部外表被纤维接合组织覆盖。Secretions of the stomach include gastric acid, which consists mainly of hydrochloric acid. This makes the stomach contents highly acidic, which is necessary so that the enzyme pepsin — also secreted by the stomach — can begin the digestion of . Mucus is secreted by the lining of stomach to provide a slimy protective coating against the otherwise damaging effects of gastric acid. The fat-digesting enzyme lipase is secreted in small amounts in the stomach, but very little fat digestion occurs there.
::胃的分泌物包括主要是盐酸的胃酸,这使胃内含的酸性很高,因此胃内含的酸性很高,这是必要的,使胃内也隐藏在胃内的酶能够开始消化。 胃内衬衬里将 Mucus隐藏起来,以提供黏液的保护性涂层,防止胃酸的有害影响。 脂肪稀释酶脂在胃内被小量地隐藏,但那里很少发生脂肪消化现象。By the time food has been in the stomach for about an hour, it has become the thick, semi-liquid chyme. When the small intestine is ready to receive chyme, a sphincter between the stomach and duodenum — called the pyloric sphincter — opens to allow the chyme to enter the small intestine for further digestion and absorption .
::当食物在胃里大约一个小时时,它就变成了厚厚的半液态环流,当小肠子准备接受环流时,胃与二二元之间就有一个螺旋,即所谓的pyloric 螺旋,可以让小肠子进入小肠,以便进一步消化和吸收。Feature: Reliable Sources
::特征:可靠来源The ongoing epidemic of obesity in the wealthier nations of the world, including the United States, has led to the of several different bariatric surgeries that modify the stomach to help obese patients reduce their food intake and lose weight. Go online to learn more about bariatric surgery. Find sources you judge to be reliable that answer the following questions:
::包括美国在内的世界较富裕国家目前流行的肥胖症导致若干不同的儿科手术,这些手术改变了胃部,帮助肥胖病人减少食物摄入量和减肥。 上网了解更多有关儿科手术的情况。 找到可靠来源回答下列问题:-
Who qualifies for bariatric surgery?
::谁有资格做儿科手术? -
Describe the bariatric surgeries commonly called stomach stapling, lap band, and gastric sleeve. How does each type of surgery modify the stomach? In terms of weight loss, how effective is each type?
::描述通常称为胃刺、大腿和胃袖的儿科手术。 每一种手术如何改变胃部? 在体重减肥方面,每种手术的效果如何? -
What are the major potential risks of bariatric surgery?
::儿科外科的主要潜在风险是什么? -
Besides weight loss, what other benefits have been shown to result from bariatric surgery?
::除了体重减重之外,还有哪些其他福利被证明来自儿科外科手术?
Summary
::摘要-
Organs of the upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract include the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, and stomach.
::上胃肠道的器官包括口腔、阴道、食道和胃部。 -
The mouth is the first organ of the GI tract. It has several structures that are specialized for digestion, including salivary glands, tongue, and teeth. Both mechanical digestion and chemical digestion of carbohydrates and fats begin in the mouth.
::口腔是GI道的第一个器官,它有几种专门用于消化的结构,包括唾液腺、舌头和牙齿,碳水化合物和脂肪的机械消化和化学消化始于口腔。 -
The pharynx and esophagus move food from the mouth to the stomach, but are not involved in the process of digestion or absorption. Food moves through the esophagus by peristalsis.
::Pharynx和esophagus将食物从嘴里移到胃里,但没有参与消化或吸收过程。 食物通过直肠通过食道。 -
Mechanical and chemical digestion continue in the stomach. Acid and digestive enzymes secreted by the stomach start the chemical digestion of proteins. The stomach turns masticated food into a semi-fluid mixture called chyme.
::胃部继续发生机械和化学消化过程。胃部隐藏的酸和消化酶开始蛋白质的化学消化。胃部将松动食品变成一种半流体混合物,叫做。
Review
::回顾1. List organs of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
::1. 列出上胃肠道的器官。2. Identify structures in the mouth that are specialized for digestion.
::2. 查明口腔中专门用于消化的结构。3. Describe digestion in the mouth.
::3. 描述口腔消化的情况。4. What general role do the pharynx and esophagus play in the digestion of food?
::4. pharynx和esophagus在食物消化方面发挥什么一般作用?5. How does food travel through the esophagus?
::5. 食物如何通过食道?6. Describe digestion in the stomach.
::6. 描述胃部消化的情况。7. In which of the following structures does chemical digestion occur?
::7. 化学消化在以下哪些结构中发生?a. mouth
::a. 口b. esophagus
::b. 食道c. stomach
::c. 胃d. A and C
::d. A和Ce. A, B, and C
::e. e. A、B和C8. In which of the following structures does mechanical digestion occur?
::8. 机械消化在以下哪些结构中发生?a. mouth
::a. 口b. pharynx
::b. 光环c. stomach
::c. 胃d. A and C
::d. A和Ce. A, B, and C
::e. e. A、B和C9. Describe the differences between how air and food normally move past the pharynx.
::9. 说明空气和食物通常如何经过法林克斯的差别。10. Name two structures in the mouth that contribute to mechanical digestion.
::10. 说明口腔中有助于机械消化的两个结构。11. What structure normally keeps stomach contents from backing up into the esophagus?
::11. 哪种结构通常使胃内含物从后退到食道?12. True or False: Peristalsis occurs in the esophagus, but not in the stomach.
::12. 真实或假:持久性出现在食道中,但不出现在胃中。13. True or False: Our sense of taste is based on the detection of chemicals by the tongue.
::13. 真实或假:我们的品味感是以舌头检测化学品为基础的。14. Thirty minutes after you eat a meal, where is most of your food located? Explain your answer.
::吃完一顿饭30分钟后,你的大部分食物在哪里?15. What are two roles of mucus in the upper GI tract?
::15. 上GI大草原的粘液发挥什么两种作用?Explore More
::探索更多In June of 2016, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration passed final approval on a new surgically implanted medical device that obese patients can use to pump out the contents of their stomach in order to lose weight. Although critics of the device refer to it as “assisted bulimia,” implanting the device is reversible and less invasive than traditional bariatric surgery. Clinical trials have also established its efficacy for significant weight loss. Watch this short video to see how the device works:
::2016年6月,美国食品和药品管理局最终批准了一种新的外科植入医疗设备,肥胖患者可以使用该设备抽出胃部,以减肥。 尽管该设备批评者称其为“辅助性贪食症 ” , 但植入该设备是可逆的,而且比传统大巴手术少侵入性。 临床试验也为大量体重损失确定了其有效性。 观看这个短片看该设备是如何工作的:Check out this video to learn about how taste and smell are perceived by the brain:
::以了解大脑对口味和嗅觉的看法: -
The largest of the three major pairs of salivary glands are the
parotid glands
, which are located on either side of the mouth in front of the ears.