17.5 肠胃肠道下肠道
章节大纲
-
What Is It?
::这是什么?This photomicrograph shows some of the of what has been called “the last human organ to be discovered.” This “organ” weighs about 200 grams (0.44 lb.) and consists of a hundred trillion cells, yet scientists are only now beginning to learn everything it does and how it varies among individuals. What is it? It’s the mass of that live in our lower gastrointestinal tract .
::这张摄影图展示了所谓的“最后发现的人类器官 ” 。 这个“器官”有大约200克(0.44磅 ) , 由100万亿个细胞组成,然而科学家们现在才刚刚开始学习它所做的一切,以及它如何在个人之间有所不同。它是什么?生活在我们下胃肠道中的那些人的数量是多少?Organs of the Lower Gastrointestinal Tract
::肠道下肠道下肠道的器官Most of the bacteria that normally live in the lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract live in the . They have important and mutually beneficial relationships with the human organism . We provide them with a great place to live, and they provide us with many benefits, some of which you can read about below. Besides the large intestine and its complement of helpful bacteria, the lower GI tract also includes the . The latter is arguably the most important organ of the . It is where most chemical digestion and virtually all absorption of nutrients take place.
::通常生活在下胃肠道(GI)的多数细菌都生活在这个地方。它们与人类有机体有着重要和互利的关系。我们为他们提供了一个伟大的居住地点,它们为我们提供了许多好处,下面可以读到其中的一些好处。除了大肠道及其辅助的有用细菌之外,下胃肠道也包括了这些。可以说,后者是最重要的器官。这就是大多数化学消化和几乎所有营养物吸收的地方。Small Intestine
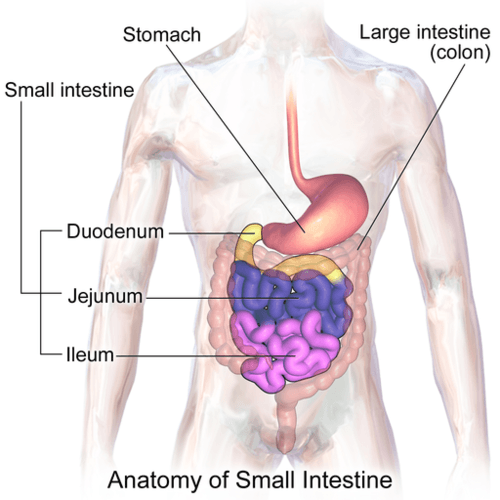
::小不小The small intestine (also called the small bowel or gut) is the part of the GI tract between the stomach and large intestine. Its average length in adults is 4.6 m (15 ft) in females and 6.9 m (22 ft, 8 in.) in males. It is approximately 2.5 to 3.0 cm (1.0 to 1.2 in.) in diameter. It is called “small” because it is much smaller in diameter than the large intestine. The internal surface area of the small intestine totals an average of about 30 m 2 (323 ft 2 ). Structurally and functionally, the small intestine can be divided into three parts, called the duodenum , jejunum , and ileum , as shown in the figure and described below.
::小肠道(也称为小肠胃或肠道)是胃与大肠之间GI道的一部分,其成人平均长度为雌性4.6米(15英尺)和雄性6.9米(22英尺,8英寸),直径约为2.5至3.0厘米(1.0至1.2英寸),其直径小于大肠道,其直径小于大肠道,小肠的内表面积平均约为30平方米(323英尺)。The three parts of the small intestine are color coded in this diagram, with yellow for the duodenum, blue for the jejunum, and pink for the ileum.
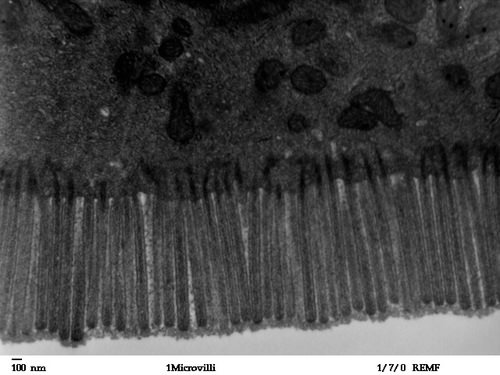
::小肠的三部分是在本图中的颜色编码, 黄色为二元,蓝色为JJJJNUNUM,粉红色为iLIUM。The mucosa lining the small intestine is very wrinkled and covered with the finger-like projections called villi . In fact, each square inch of mucosa contains around 20 thousand villi. The individual cells on the surface of the villi also have many finger-like projections — the microvilli shown in the figure . There are thought to be well over 100 billion microvilli per square inch of intestinal mucosa! All of these wrinkles, villi, and microvilli greatly increase the surface area for chyme to come into contact with digestive , which coat the microvilli, as well as forming a tremendous surface area for the absorption of nutrients. Inside each of the villi is a network of tiny and lymph vessels that receive the absorbed nutrients and carry them away in the blood or lymph circulation. The wrinkles and projections in the intestinal mucosa also slow down the passage of chyme so there is more time for digestion and absorption to take place.
::小肠内衬的粘膜非常皱,并被称为Villi的指状图所覆盖。事实上,每平方英寸的混凝土含有大约2万瓦利。葡萄树表面的单细胞也有许多指状的图象——图中显示的微玻璃。人们认为每平方英寸肠内有1 000亿微瓦利!所有这些皱纹、维利和微微瓦都大大增加了与消化剂接触的表面面积,这种消化剂覆盖了微微瓦,并且形成了吸收营养素的巨大表面区域。每个葡萄树内都有一个微小的淋巴容器网络,接收了吸收的营养素,并将它们带到血液或淋巴循环中。肠内结结的皱纹和预测也减缓了微微微微孔的通过速度,因此有更多的时间进行消化和吸收。The fringe-like structures in this photomicrograph are microvilli lining the inside of the small intestine.
::照片摄影仪中的边缘结构 是微小肠内衬的微小病毒。Duodenum
::DuodenumThe duodenum is the first part of the small intestine, directly connected to the stomach. It is also the shortest part of the small intestine, averaging only about 25 cm (10 in.) in length in adults. Its main function is chemical digestion, and it is where most of the chemical digestion in the entire GI tract takes place.
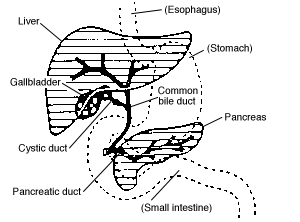
::是小肠肠的第一部分,与胃直接相连,也是小肠中最短的部分,成人平均只有大约25厘米(10英寸)长,其主要功能是化学消化,是整个GI道大部分化学消化的地方。The duodenum receives partially digested, semi-liquid chyme from the stomach. It receives digestive enzymes and alkaline bicarbonate from the pancreas through the pancreatic duct, and it receives bile from the liver via the gallbladder through the common bile duct (see figure ). In addition, the lining of the duodenum secretes digestive enzymes and contains glands — called Brunner’s glands — that secrete mucous and bicarbonate. The bicarbonate from the pancreas and Brunner’s glands — along with bile from the liver — neutralize the highly acidic chyme after it enters the duodenum from the stomach. This is necessary because the digestive enzymes in the duodenum require a nearly neutral environment in order to work. The three major classes of compounds that undergo chemical digestion in the duodenum are , , and .
::从胃部得到部分消化、半液态的曲子,从胰腺到胰腺管,从肝脏获得消化酶和碱性双碳酸盐,通过胆囊通过共同的胆汁管(见图)从肝脏中获得肉汁。此外,二环分泌的消化酶的衬里,含有被称为布伦纳腺的腺体,即分泌粘液和双碳酸液的腺体。来自胰腺和布伦纳腺的双碳酸盐与肝脏的粘液一起,在从胃部进入二丘后,将高酸性中和。这是必要的,因为二环的消化酶需要一个几乎中性的环境来工作。在二环中进行化学消化的三大化合物是,还有。This figure shows the liver, gallbladder and pancreas, along with the ducts that carry their secretions to the duodenum (labeled small intestine).
::下图显示了肝脏、胆囊和胰腺,以及将分泌到二元肠(标有小肠)的管道。Digestion of Carbohydrates in the Duodenum
::Duodenum的碳水合物消化Complex carbohydrates (such as starches) are broken down by the digestive enzyme amylase from the pancreas to short-chain molecules consisting of just a few saccharides (that is, simple sugars). Disaccharides , including sucrose and lactose, are broken down to simple sugars by duodenal enzymes. Sucrase breaks down sucrose, and lactase (if present) breaks down lactose. Some carbohydrates are not digested in the duodenum, and they ultimately pass undigested to the large intestine, where they may be digested by intestinal bacteria.
::复杂的碳水化合物(如淀粉)被消化酶氨基酶从胰腺分解为短链分子,由几颗沙焦(即简单的糖)组成,包括苏克罗斯和乳糖在内的分解为二极体酶的简单糖。苏克雷斯分解了苏克罗斯,乳酶(如果存在的话)分解了乳糖。有些碳水化合物没有在二核氨中消化,它们最终通过未消化的肠道进入大肠道,可能通过肠道细菌消化。Digestion of Proteins in the Duodenum
::Duodenum 蛋白质的消化In the duodenum, the pancreatic enzymes trypsin and chymotrypsin cleave proteins into peptides. Then, these smaller molecules are broken down into amino acids . Their digestion is catalyzed by pancreatic enzymes called peptidases.
::在二聚二聚苯乙烯中,胰腺酶突变素和旋膜酶素将蛋白质切成颗粒。然后,这些小分子被分解成氨基酸。它们的消化因被称为peptidas的胰腺酶而催化。Digestion of Lipids in the Duodenum
::Duodenum的利皮消化Pancreatic lipase breaks down triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol. Lipase works with the help of bile secreted by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile salts attach to triglycerides to help them emulsify, or form smaller particles (called micelles) that can disperse through the watery contents of the duodenum. This increases access to the molecules by pancreatic lipase.
::脂脂脂酶将三甘酸分解为脂肪酸和甘油醇。Lipase在肝脏密闭并储存在胆囊中的粘液下工作。Bile盐附于三甘酸盐以帮助他们乳化,或形成小粒子(称为小鼠类),通过二苯基的含水量弥散。这增加了通过胰腺脂酶接触分子的机会。Jejunum
::积君The jejunum is the middle part of the small intestine, connecting the duodenum and the ileum. The jejunum is about 2.5 m (8.2 ft) long. Its main function is absorption of the products of digestion, including sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids. Absorption occurs by simple ( and fatty acids), facilitated diffusion (the simple sugar fructose), or (amino acids, small peptides, water-soluble vitamins , and most glucose). All nutrients are absorbed into the blood, except for fatty acids and fat-soluble vitamins, which are absorbed into the lymph. Although most nutrients are absorbed in the jejunum, there are a few exceptions:
::jewunum是小肠的中间部分,连接了二元和二元。Jejunum长约2.5米(8.2英尺),其主要功能是吸收消化产物,包括糖、氨基酸和脂肪酸。吸附通过简单(和脂肪酸)、促进扩散(简单甘油)、或(氨酸、小、可溶水的维生素和大部分葡萄糖)发生。除了脂肪酸和脂肪溶性维生素之外,所有营养素都吸收在血液中,而脂肪酸和脂肪溶性维生素则被吸收在淋巴中。尽管大部分营养素被吸收在Jejunum,但也有少数例外:-
Iron is absorbed in the duodenum.
::铁被吸收在二元共聚物中。 -
Vitamin B12
and bile salts are absorbed in the ileum.
::维他命B12和易碎盐被吸收到ileum中。 -
Water and lipids are absorbed throughout the small intestine, including the duodenum and ileum in addition to the jejunum.
::在整个小肠道中吸收了水和脂质,包括二元和二元以及双元。
Ileum
::伊莱姆The ileum is the third and final part of the small intestine, directly connected at its distal end to the large intestine. The ileum is about 3 m (9.8 ft) long. Some cells in the lining of the ileum secrete enzymes that catalyze the final stages of digestion of any undigested protein and carbohydrate molecules. However, the main function of the ileum is to absorb vitamin B12 and bile salts. It also absorbs any other remaining nutrients that were not absorbed in the jejunum. All substances in chyme that remain undigested or unabsorbed by the time they reach the distal end of the ileum pass into the large intestine.
::是小肠的第三个也是最后一个部分,在肠道的阴端与大肠口直接相连。 长约3米( 9. 8英尺) 。 密酶衬里的一些细胞催化任何未消化蛋白和碳水化合物分子最后消化阶段。 但是, 的主要功能是吸收维生素B12和碱盐。 它吸收了其他任何未在jjununum吸收的营养素。 所有在中的物质,在它们到达池塘口的阴端进入大肠口时,尚未消化或吸收的所有物质。Large Intestine
::大型不适The large intestine — also called the large bowel — is the last organ of the GI tract. In adults, it averages about 1.5 m (5 ft) in length. It is shorter than the small intestine, but at least twice as wide, averaging about 6.5 cm (2.5 in.) in diameter. Water is absorbed from chyme as it passes through the large intestine, turning the chyme into solid feces . Feces is stored in the large intestine until it leaves the body during defecation.
::大型肠胃——也称为大肠胃——是大肠道最后的器官,在成人中,平均长度约为1.5米(5英尺),比小肠胃短,但至少是直径的两倍,平均约为6.5厘米(2.5英寸),水在大肠道穿透时从刺状中吸收,将刺状变成坚固的粪便,粪便储存在大肠道中,直到排便时离开身体。Parts of the Large Intestine
::大不列颠人的一部分,Like the small intestine, the large intestine can be divided into several parts, as shown in the figure . The large intestine begins at the end of the small intestine, where a valve separates the small and large intestines and regulates the movement of chyme into the large intestine. Most of the large intestine is called the colon . The first part of the colon, where chyme enters from the small intestine, is called the cecum . From the cecum, the colon continues upward as the ascending colon, travels across the upper abdomen as the transverse colon, and then continues downward as the descending colon. It then becomes a V-shaped region called the sigmoid colon, which is attached to the rectum . The rectum st ores feces until elimination occurs. It transitions to the final part of the large intestine, called the anus, which has an opening to the outside of the body for feces to pass through.
::如图所示,大肠可以分为几个部分,如小肠。大肠从小肠的末端开始。大肠从小肠的末端开始,一个阀门将小肠和大肠分离开来,并调控小肠曲曲向大肠的移动。大肠大部分称为结肠。结肠的第一部分,即从小肠中插入的,称为小肠。结肠继续向上移动,作为上升的结肠,横跨上腹部,然后继续向下,作为递增的结肠。然后,它成为一个V形区域,即与直肠相连的小肠结口。直肠胃股股,直到消化为止,通向大肠的最后一个部分转变,称为肛门,通向身体外,通向大肠通过。The parts of the large intestine include the cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, and anus.
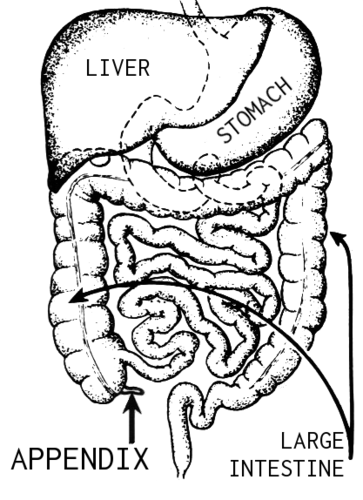
::大肠的部分包括蓄积、上升的结肠、横贯的结肠、降的结肠、小结、直肠和肛门。The diagram shows a projection from the cecum of the colon that is known as the appendix. The function of the appendix is uncertain, but it does not seem to be involved in digestion or absorption. It may play a role in , and in the fetus , it seems to have an endocrine function, releasing needed for . Some biologists speculate that the appendix may also store a sample of the colon’s normal bacteria. If so, it may be able to repopulate the colon with the bacteria if illness or antibiotic medications deplete these microorganisms. Appendicitis, or infection and inflammation of the appendix, is a fairly common medical problem, typically resolved by surgical removal of the appendix (appendectomy). People who have had their appendix surgically removed do not seem to suffer any ill effects, so the organ is considered dispensable. As such, it is often referred to as a vestigial organ, which is a previously useful organ that has been retained over evolutionary time as part of the anatomy, even though it no longer has a function in the body.
::图表显示了从结肠的积分中( 称为附录) 的投影。 附录的功能是不确定的, 但它似乎并未涉及消化或吸收。 它可能具有内分泌功能, 而在胎儿中, 它似乎具有内分泌功能, 需要释放出来。 一些生物学家推测, 附录还可能储存结肠正常细菌的样本。 如果是的话, 它也许能够将结肠与细菌重新混合, 如果疾病或抗生素药物消耗了这些微生物。 附录的感染和炎是相当常见的医学问题, 通常通过对附录进行外科切除( 外科切除) 来解决。 被外科切除的附录的人似乎没有受到任何不良的影响, 因此器官被认为是可以解开的。 因此, 它常常被称为前科器官, 在进化过程中被保留作为解剖体的一部分。The appendix is a projection of the cecum of the large intestine.
::附录是对大肠子的累积值的预测。Functions of the Large Intestine
::大型内托丁的函数The removal of water from chyme to form feces starts in the ascending colon and continues throughout much of the length of the organ. Salts (such as sodium) are also removed from food wastes in the large intestine before the wastes are eliminated from the body. This allows salts — as well as water — to be recycled in the body.
::将曲流水从曲流排入粪便的过程始于不断上升的结肠,并持续到器官大部分时间,盐(例如钠)在从身体中清除废物之前,还从大肠中的食品废物中去除,从而使盐类和水在身体中回收利用。The large intestine is also the site where huge numbers of beneficial bacteria ferment many unabsorbed materials in food waste. The bacterial breakdown of undigested polysaccharides produces nitrogen, carbon dioxide, methane, and other gases responsible for intestinal gas, or flatulence. These bacteria are particularly prevalent in the descending colon. Some of the bacteria also produce vitamins that are absorbed from the colon. The vitamins include vitamins B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B7 (biotin), B12, and K. Another role of bacteria in the colon is an immune function. The bacteria may stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies that are effective against similar, but pathogenic, bacteria, thereby preventing infections. Still other roles played by bacteria in the large intestine include breaking down toxins before they can poison the body, producing substances that help prevent colon , and inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria.
::大型肠道也是大量有益细菌发酵的场所,食品废物中许多未吸收材料都是如此。未开发的多沙岩化物的细菌分解产生氮、二氧化碳、甲烷和其他导致肠道气或扁平气的气体。这些细菌在下层结肠中特别普遍。有些细菌还产生从结肠中吸收的维生素。维生素包括维生素B1(硫胺)、B2(里波夫拉文)、B7(比奥丁)、B12和K。细菌在结肠中的另一个作用是免疫功能。细菌可以刺激免疫系统产生抗体,对类似但病原的细菌有效,从而防止感染。在大肠中细菌发挥的其他作用还包括在毒害人体之前先解毒毒素,产生有助于防止结肠的物质,抑制有害细菌的生长。Feature: My Human Body
::特质:我的人体Colorectal cancer, or cancer of the colon or rectum, is the fourth most common cancer in the United States. It is also the second most common cause of cancer deaths in this country. Widespread screening of patients for signs of colorectal cancer has significantly lowered the death rate in recent years. Because early-stage colorectal cancer is usually asymptomatic, routine screening is important for identifying cancer early, when chances of a cure are still high.
::直肠癌或直肠癌是美国第四大常见癌症,也是美国第二大常见癌症死亡原因。 近些年来,通过广泛筛查患者发现直肠癌症状,大幅降低了死亡率。 由于早期直肠癌通常是无症状的,因此常规筛查对于早期发现癌症非常重要,因为当治愈的可能性仍然很高时。Screening for colorectal cancer has also become easier and less invasive in recent years. One way to test for colorectal cancer is to examine a sample of stool and look for occult (hidden from the unaided eye) blood in the stool. This test is based on the assumption that in cancer are fragile and may be easily damaged by the passage of feces through the colon or rectum. The damaged vessels may bleed into the feces, but rarely bleed enough for blood to be visible in the stool. Stool for the occult blood test can be collected by the patient at home with a test kit provided by a doctor. If occult blood is detected in the stool, a different type of follow-up test is generally needed to determine whether cancer is the cause of the bleeding.
::直肠癌的检查近年来也变得更加容易,也减少了侵入性。直肠癌的检测方法之一是检查凳子样本和在凳子中寻找神秘(隐蔽于无辅助眼睛的隐蔽)血液。这一检测依据的假设是,癌症脆弱,很容易因肠道或直肠的粪便通过而受损。受损的容器可能流血到粪便中,但鲜少出血,以致无法在凳子中看到血液。病人可以在家里用医生提供的测试包收集神秘血液测试工具。如果在凳子中检测到隐蔽的血液,通常需要另一种后续检测,以确定癌症是否是出血的原因。A similarly simple and noninvasive but more definitive test for colorectal cancer looks for from cancer cells in the stool. Again, the patient can collect the stool sample at home using a simple test kit and mail the specimen to a lab, which does the analysis. If the test comes back positive, then a direct visual examination of the colon and rectum by colonoscopy is required.
::类似简单、非侵入性、但更明确的直肠癌检测来自凳子上的癌症细胞。 患者也可以使用简单的测试工具收集家里的凳子样本,并将样本邮寄到实验室,实验室进行分析。 如果检测结果呈阳性,那么就需要通过结肠镜检查直接直视结肠和直肠检查。Colonoscopy is the gold standard for diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Using a tiny camera at the end of a long tube inserted up into the colon, a doctor can directly visualize the lining of the large intestine and spot any suspicious areas that may be cancerous. While a colonoscopy is invasive and requires the patient to prepare for the test for a couple of days by changing his or her diet and drinking special fluids, it reveals more than just cancer. A colonoscopy also reveals any growths called polyps in the colon. Colon polyps are not cancer but often develop into cancerous lesions, so if they are found during a colonoscopy, a surgical instrument inserted with the scope is usually used to remove them. Therefore, a colonoscopy can not only detect cancer at its early stages, but it can even help prevent cancer by enabling the removal of potentially pre-cancerous polyps.
::结肠镜是诊断结肠癌的金本位标准。 在结肠内插入长管的末端,医生可以直接直视大肠胃的内衬,并发现任何可疑的癌症区。 虽然结肠镜是侵入性的,需要病人通过改变饮食和饮用特殊液体来准备几天的检查,但它揭示的不仅仅是癌症。结肠镜还揭示出任何叫作结肠内聚苯的生长。 结肠片不是癌症,但往往会发展成癌症,因此如果在结肠镜中发现,通常会使用插入外科手术仪器来清除这些肿瘤。 因此,结肠镜不仅可以在早期检测癌症,而且它甚至能够帮助通过消除潜在的先发性聚虫来预防癌症。A test similar to a colonoscopy may be done in some patients. Called a flexible sigmoidoscopy, it allows a doctor to use a small camera to inspect the rectum and lower third of the colon, where the majority of cases of colorectal cancer occur. However, the rest of the colon cannot be examined with a sigmoidoscopy. Another alternative to a full-blown colonoscopy is a virtual colonoscopy, in which a CT scan of the rectum and colon is used to make detailed cross-sectional images of the organs. The images can then be studied by a specialist to detect cancers or polyps. For both of these colonoscopy alternatives, a follow-up colonoscopy is required if polyps or potentially cancerous lesions are detected.
::一些病人可以进行类似结肠镜检查的测试。 称为柔性西格米多镜检查, 医生可以使用小型相机检查直肠和下三分之一结肠, 大部分是结肠癌病例。 但是, 结肠的其余部分不能用西格米多镜检查。 全面结肠镜检查的另一种替代办法是虚拟结肠镜检查, 使用直肠和结肠的CT扫描来制作器官的详细截面图像。 然后, 这些图像可以由专家研究以检测癌症或聚虫。 对于这两种结肠镜检查替代品,如果检测到聚苯或潜在的癌症损伤, 还需要后续的结肠镜检查。Unless you have a family history of colorectal cancer or certain other risk factors, you probably do not need to start routine screening for the disease until middle age. Your doctor can tell you the most appropriate starting age for your particular case, given your risk factors and current cancer guidelines. You may be able to be screened with one of the less invasive methods until you are somewhat older. Again, check with your doctor for specific recommendations. All of the testing methods have pros and cons that should be taken into consideration by a given patient and medical provider.
::除非有直肠癌或某些其他风险因素的家庭史,否则在中年之前,你可能不需要开始常规的疾病检查。考虑到你的风险因素和当前的癌症指南,你的医生可以告诉你具体病例最合适的起始年龄。你可以使用一种侵犯性较小的方法进行检查,直到你年龄稍大一些。请再向医生查询一下具体的建议。所有检测方法都有利弊,应由特定病人和医疗提供者加以考虑。Summary
::摘要-
The lower GI tract includes the small intestine and large intestine. The small intestine is where most chemical digestion and virtually all absorption of nutrients occur. The large intestine contains huge numbers of beneficial bacteria and removes water and salts from food waste before it is eliminated.
::低肠道包括小肠道和大肠道,小肠道是化学消化和吸收营养物质最多的地方,大肠道含有大量有益的细菌,在消除之前从食物废物中除去水和盐类。 -
The small intestine consists of three parts: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. All three parts of the small intestine are lined with mucosa that is very wrinkled and covered with villi and microvilli, giving the small intestine a huge surface area for digestion and absorption.
::小肠由三部分组成:二元肠、六元肠和二元肠。小肠的所有三个部分都与粘膜粘合在一起,粘糊糊糊,上面盖着葡萄酒和微小树脂,使小肠有一个巨大的消化和吸收地表面积。 -
The duodenum secretes digestive enzymes, and also receives bile from the liver or gallbladder and digestive enzymes and bicarbonate from the pancreas. These digestive substances neutralize acidic chyme and allow for the chemical digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids in the duodenum.
::这些消化物质能中和酸性旋律,并允许碳水化合物、蛋白质、脂类和核酸的化学消化。 -
The jejunum carries out most of the absorption of nutrients in the small intestine, including the absorption of simple sugars, amino acids, fatty acids, and many vitamins.
::Jejunum在小肠中吸收了大部分养分,包括吸收简单的糖、氨基酸、脂肪酸和许多维生素。 -
The ileum carries out any remaining digestion and absorption of nutrients, but its main function is to absorb vitamin B12 and bile salts.
::进行任何剩余的消化和吸收养分,但其主要功能是吸收维生素B12和Bile盐。 -
The large intestine consists of the colon (which, in turn, includes the cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, and sigmoid colon), rectum, and anus. The vestigial organ called the appendix is attached to the cecum of the colon.
::大肠由结肠(包括结肠、直肠、直肠、直肠、直肠、直肠、直肠、直肠)、直肠和肛门组成。 -
The main function of the large intestine is to remove water and salts from chyme for recycling within the body and eliminating the remaining solid feces from the body through the anus. The large intestine is also the site where trillions of bacteria help digest certain compounds, produce vitamins, stimulate the immune system, and break down toxins, among other important functions.
::大型肠道的主要功能是将水和盐从神经管中除去,以便在体内进行循环利用,并消除从身体到肛门的剩余固体粪便;大型肠道也是数万亿细菌帮助消化某些化合物、生产维生素、刺激免疫系统、分解毒素等重要功能的场所。
Review
::回顾1. Which organs are included in the lower GI tract?
::1. 哪些器官包括在下GI大道中?2. Name the parts of the small intestine.
::2. 说明小肠的部位。3. How is the mucosa of the small intestine specialized for digestion and absorption?
::3. 小型肠胃的粘膜如何专门用于消化和吸收?4. What digestive substances are secreted into the duodenum? What compounds in food do they help digest?
::4. 什么是消化物质被隐藏在二元体中?它们帮助消化的食品中有哪些化合物?5. What is the main function of the jejunum?
::5. 犹太人的主要职能是什么?6. What roles does the ileum play?
::6. 利昂起什么作用?7. Name the parts of the large intestine.
::7. 列出大肠部分的名称。8. Identify the main functions of the large intestine.
::8. 确定大肠的主要功能。9. How do beneficial bacteria in the large intestine help the human organism?
::9. 大肠中的有益细菌如何帮助人体?10. True or False: The first part of the large intestine is where most chemical digestion takes place.
::10. 真实或假:大型肠道的第一部分是大部分化学消化发生的地方。11. True or False: The small intestine is actually longer than the large intestine.
::11. 真实或假:小肠实际上比大肠长。12. When diarrhea occurs, feces leaves the body in a more liquid state than normal. What part of the digestive system do you think is involved in diarrhea? Explain your answer.
::12. 腹泻发生时,粪便会以比正常更液态的状态离开身体。你认为消化系统中哪些部分与腹泻有关?请解释你的答案。13. Arrange the following parts of the lower GI tract in order of how food passes through them, from earliest to latest. Note that not all parts are listed.
::13. 按照食物从最早到最晚是如何经过的顺序,排列下GI草道的以下部分,注意并非所有部分都列出。cecum; duodenum; sigmoid colon; jejunum; rectum; ileum
::cum; duodenum; sigmod 结肠; jjunuum; 直肠; ileum14. Which enzyme digests proteins?
::14. 哪种酶是蛋白质的消化酶?a. trypsin
::a. 试录器b. amylase
::b. 氨基酶c. lipase
::c. 脂脂d. lactase
::d. 乳腺15. What causes intestinal gas, or flatulence?
::15. 是什么导致肠道气体或通气?Explore More
::探索更多Did you know you have about 100 million neurons in your intestines? In this TED talk, food scientist Heribert Watzke talks about the "hidden brain" in our gut and the surprising things it makes us feel.
::你知道你的肠子里有大约一亿个神经元吗?在这个TED演讲中,食品科学家Heribert Watzke谈到我们内心的“隐蔽的大脑”以及它让我们感到惊奇的东西。Check out this video to learn what your poop may mean about your health:
::看看这段视频, 来了解你的便便对健康可能意味着什么: -
Iron is absorbed in the duodenum.