19.2 免疫系统介绍
章节大纲
-
Worm Attack!
::虫子攻击!Does this organism look like a space alien? A scary creature from a nightmare? In fact, it’s a 1-cm long worm in the genus Schistosoma. It may invade and take up residence in the , causing a very serious illness known as schistosomiasis. The worm gains access to the human body while it is in a microscopic life stage. It enters through a hair follicle when the skin comes into contact with contaminated . The worm then grows and matures inside the human organism, causing disease.
::这个生物是否看起来像一个太空外星生物? 恶梦中的恐怖生物? 事实上,它是一个长1厘米长的长虫子,它可能入侵并占据其中,导致一种非常严重的疾病,即血吸虫病。当它处于微小的生命阶段时,虫子可以进入人体。当皮肤接触被污染的皮肤时,它会通过发泡进入。然后,虫子在人体中生长成熟,导致疾病。Host vs. Pathogen
::主机主对病原体The Schistosoma worm has a parasitic relationship with humans. In this type of relationship, one organism, called the parasite , lives on or in another organism, called the host . The parasite always benefits from the relationship, and the host is always harmed. The human host of the Schistosoma worm is clearly harmed by the parasite when it invades the host’s tissues . The urinary tract or intestines may be infected, and signs and symptoms may include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody stool, or in the urine . Those who have been infected for a long time may experience liver damage, kidney failure , infertility, or bladder . In children, Schistosoma infection may cause poor growth and difficulty learning .
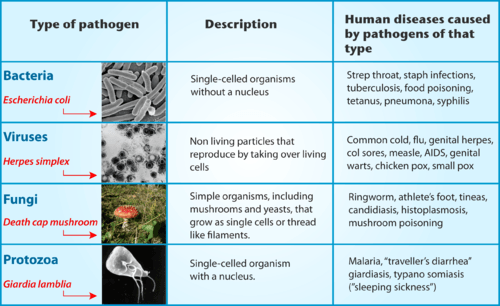
::脑瘤虫与人类有寄生虫关系。 在这种关系中,一种生物,叫做寄生虫,在另一生物中生活或生活,在宿主名下。寄生虫总是从关系中受益,宿主总是受到伤害。 寄生虫的人体宿主在侵入宿主组织时显然受到寄生虫的伤害。 尿道或肠可能受到感染,征兆和症状可能包括腹部疼痛、腹泻、血腥的凳子或尿液。 长期感染的人可能遭受肝脏损伤、肾衰竭、不育或膀胱伤害。 在儿童中,脑瘤感染可能导致生长不良和学习困难。Like the Schistosoma worm, many other organisms can make us sick if they manage to enter our body. Any such agent that can cause disease is called a . Most pathogens are microorganisms, although some — such as the Schistosoma worm — are much larger. In addition to worms, common types of pathogens of human hosts include , , , and single-celled organisms called . You can see examples of each of these types of pathogens in the table . Fortunately for us, our immune system is able to keep most potential pathogens out of the body, or to quickly destroy them if they do manage to get in. When you read this chapter, you’ll learn how your immune system usually keeps you safe from harm — including from scary creatures like the Schistosoma worm!
::与Schistosoma蠕虫一样,许多其他生物体如果设法进入我们的身体,就会让我们生病。任何可能导致疾病的病原体都被称为“......”。大多数病原体是微生物,尽管有些病原体——例如Schistosoma蠕虫——规模更大。除了蠕虫之外,人类宿主的常见病原体类型包括、 、 和单细胞生物。你可以在桌子上看到每一种病原体的例子。幸运的是,我们的免疫系统能够将大多数潜在的病原体排除在身体之外,或者在它们成功进入的情况下迅速消灭它们。当你阅读本章时,你会知道免疫系统通常如何能保证你免受伤害 — — 包括象Schistosoma蠕虫那样的可怕生物!Common types of pathogens that cause human disease, with an example shown for each.
::造成人类疾病的常见病原体类型,每个病原体都有一个例子。What is the Immune System?
::什么是免疫系统?The immune system is a host defense system. It comprises many biological structures — ranging from individual white blood cells to entire organs — as well as many complex biological processes. The function of the immune system is to protect the host from pathogens and other causes of disease, such as tumor . To function properly, the immune system must be able to detect a wide variety of pathogens. It also must be able to distinguish the cells of pathogens from the host’s own cells, and also to distinguish cancerous or damaged host cells from healthy cells. In humans and most other vertebrates , the immune system consists of layered defenses that have increasing specificity for particular pathogens or tumor cells. The layered defenses of the human immune system are usually classified into two subsystems, called the and the adaptive immune system.
::免疫系统是一种宿主防御系统,它包括许多生物结构——从单个白细胞到整个器官——以及许多复杂的生物过程。免疫系统的作用是保护宿主免受病原体和其他疾病原因(如肿瘤)的伤害。为了正常运转,免疫系统必须能够检测出各种各样的病原体。它还必须能够区分病原体细胞和宿主自己的细胞,并区分癌症或受损宿主细胞和健康细胞。在人类和大多数其他脊椎动物中,免疫系统由多层防御组成,对特定病原体或肿瘤细胞具有越来越大的特殊性。人类免疫系统的多层防御通常分为两个子系统,称为“适应性免疫系统”和“适应性免疫系统 ” 。Innate Immune System
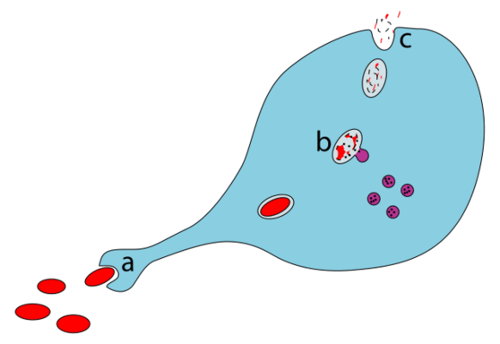
::原免疫系统The innate immune system provides very quick, but non-specific responses to pathogens. It responds the same way regardless of the type of pathogen that is attacking the host. It includes barriers — such as the skin and mucous membranes — that normally keep pathogens out of the body. It also includes general responses to pathogens that manage to breach these barriers, including chemicals and cells that attack the pathogens inside the human host. Certain leukocytes (white blood cells), for example, engulf and destroy pathogens they encounter in the process called phagocytosis , which is illustrated . Exposure to pathogens leads to an immediate maximal response from the innate immune system.
::内生免疫系统对病原体的反应非常迅速,但并不具体,无论攻击宿主的病原体类型如何,它都以同样的方式作出反应,其中包括通常不让病原体进入人体的障碍——例如皮肤和粘膜,还包括设法打破这些障碍的病原体的一般反应,包括攻击宿主内病原体的化学品和细胞,例如某些白血球(白血球),吞没和摧毁他们在称为发细胞病的过程中遇到的病原体,如说明的。A leukocyte called a macrophage phagocytizes bacteria in the series of steps shown here: (a) engulfing a (red) bacterium, (b) digesting the bacterium with (purple) enzymes, and (c) eliminating remaining waste particles.
::这里所展示的一系列步骤中,一个叫做“大型细胞孔”的白鲸在细菌中进行了分解a) 吞没一种(红)细菌,(b) 用(纯)酶消化细菌,(c) 消除残留的废物微粒。
Adaptive Immune System
::适应性免疫免疫系统The adaptive immune system is activated if pathogens successfully enter the body and manage to evade the general defenses of the innate immune system. An adaptive response is specific to the particular type of pathogen that has invaded the body, or to cancerous cells. It takes longer to launch a specific attack, but once it is underway, its specificity makes it very effective. An adaptive response also usually leads to . This is a state of resistance to a specific pathogen, due to the adaptive immune system's ability to “remember” the pathogen and immediately mount a strong attack tailored to that particular pathogen if it invades again in the future.
::如果病原体成功进入人体,并设法逃避遗传免疫系统的一般防御,适应性免疫系统就会启动。适应性反应是针对侵入身体或癌症细胞的特定病原体的。发动特定攻击需要更长的时间,但一旦发动攻击,其特性就会使其非常有效。适应性反应通常也会导致.这是对特定病原体的抗体状态,因为适应性免疫系统有能力“记住”病原体,并立即针对该病原体发动强烈攻击,如果它今后再次入侵的话。Self vs. Non-Self
::自我与非自治领土Both innate and adaptive immune responses depend on the immune system's ability to distinguish between self and non-self molecules. Self molecules are those components of an organism’s body that can be distinguished from foreign substances by the immune system. Virtually all have surface that are part of a complex called major histocompatibility complex (MHC) . These proteins are one way the immune system recognizes body cells as self. Non-self proteins , in contrast, are recognized as foreign, because they are different from self proteins.
::自然和适应性免疫反应都取决于免疫系统区分自体分子和非自体分子的能力。自分子是有机体身体的成分,可以与免疫系统外体物质区分。 几乎所有生物体的表面都属于称为主要基因兼容综合体(MHC)的综合体的一部分。 这些蛋白质是免疫系统承认身体细胞为自体的一种方式。 相比之下,非自体蛋白被认为是外来的,因为它们与自蛋白有不同。Antigens and Antibodies
::抗原和抗体Many non-self molecules comprise a class of compounds called antigens . Antigens , which are usually proteins, bind to specific receptors on immune system cells and elicit an adaptive immune response . Some adaptive immune system cells (B cells) respond to foreign antigens by producing antibodies . An antibody is a molecule that precisely matches and binds to a specific antigen. This may target the antigen (and the pathogen displaying it) for destruction by other immune cells.
::许多非自体分子由一类称为抗原的化合物组成。抗原通常是蛋白质,与免疫系统细胞的特定受体结合,并产生适应性免疫反应。一些适应性免疫系统细胞(B细胞)通过产生抗体对外来抗原作出反应。抗体是一种分子,它与特定抗原完全匹配和结合。它可能针对抗原(及其显示的病原体),由其他免疫细胞进行破坏。Antigens on the surface of pathogens are how the adaptive immune system recognizes specific pathogens. Antigen specificity allows for the generation of responses tailored to the specific pathogen. It is also how the adaptive immune system ”remembers” the same pathogen in the future.
::病原体表面的抗原是适应性免疫系统如何承认特定病原体,抗原特性允许产生适合特定病原体的反应,适应性免疫系统如何在未来“结合”同样的病原体。Immune Surveillance
::免疫监测Another important role of the immune system is to identify and eliminate tumor cells. This is called immune surveillance. The transformed cells of tumors express antigens that are not found on normal body cells. The main response of the immune system to tumor cells is to destroy them. This is carried out primarily by aptly-named killer T cells of the adaptive immune system.
::免疫系统的另一个重要作用是识别和消除肿瘤细胞。这称为免疫监测。在正常身体细胞中无法找到的肿瘤变形细胞表示抗原。免疫系统对肿瘤细胞的主要反应是摧毁肿瘤细胞。这主要是由适应性免疫系统的恰当命名的致命T细胞进行。Lymphatic System
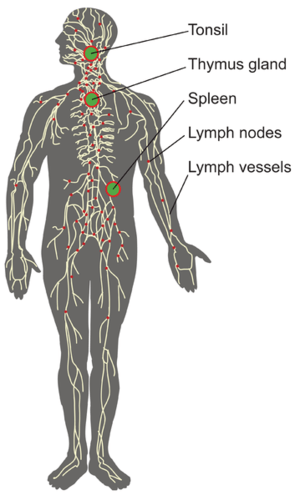
::淋巴系统The is a human organ system that is a vital part of the adaptive immune system. It is also part of the and plays a major role in the (see the concept Lymphatic System). The major structures of the lymphatic system are shown in the figure .
::这是一种人体器官系统,是适应性免疫系统的重要组成部分,也是这一系统的一部分,并在其中发挥着主要作用(见淋巴系统概念),淋巴系统的主要结构见图。The lymphatic system includes the organs and vessels illustrated here.
::淋巴系统包括此处说明的器官和船只。The lymphatic system consists of several lymphatic organs and a body-wide network of lymphatic vessels that transport the fluid called lymph . Lymph is essentially blood plasma that has leaked from capillaries into tissue spaces. It includes many leukocytes, especially lymphocytes , which are the major cells of the lymphatic system. Like other leukocytes, lymphocytes defend the body. There are several different types of lymphocytes that fight pathogens or cancer cells as part of the adaptive immune system.
::淋巴系统由若干淋巴器官组成,由运输称为淋巴体的液体的淋巴血管组成的一个全体网络组成。淋巴基本上属于血浆,从毛细血管渗入组织空间,包括许多白血球,特别是淋巴细胞,它们是淋巴系统的主要细胞。与其他白血球一样,淋巴细胞保护身体。有几种不同的淋巴细胞,作为适应性免疫系统的一部分,对抗病原体或癌症细胞。Major lymphatic organs include the thymus and bone marrow . Their function is to form and/or mature lymphocytes. Other lymphatic organs include the spleen , tonsils, and lymph nodes , which are small clumps of lymphoid tissue clustered along lymphatic vessels. These other lymphatic organs harbor mature lymphocytes and filter lymph. They are sites where pathogens collect, and adaptive immune responses generally begin.
::主要淋巴器官包括胸腺和骨髓,其功能是形成和(或)成熟的淋巴细胞,其他淋巴器官包括脾脏、扁桃腺和淋巴结,它们是淋巴血管聚集的淋巴组织小块。其他淋巴器官含有成熟的淋巴细胞和过滤性淋巴。它们是病原体采集和适应性免疫反应的场所。Neuroimmune System vs. Peripheral Immune System
::神经免疫系统与周边免疫系统The brain and spinal cord are normally protected from pathogens in the blood by the selectively permeable blood-brain and blood-spinal cord barriers. These barriers are part of the neuroimmune system. The neuroimmune system has traditionally been considered distinct from the rest of the immune system, which is called the peripheral immune system — although that view may be changing. Unlike the peripheral system, in which leukocytes are the main cells, the main cells of the neuroimmune system are thought to be cells called glial cells . These cells can recognize and respond to pathogens, debris, and other potential dangers. Types of glial cells involved in neuroimmune responses include microglial cells and astrocytes.
::大脑和脊髓通常不受血液中的病原体的保护,有选择地渗透血液脑部和血液-脊髓屏障,这些屏障是神经免疫系统的一部分,神经免疫系统传统上被认为有别于免疫系统的其他部分,后者被称为外围免疫系统,尽管这种观点可能正在改变,与外围系统不同的是,在外围系统中,白血球是主要细胞,神经免疫系统的主要细胞被认为是称为滑翔细胞的细胞,这些细胞能够识别和应对病原体、碎片和其他潜在危险,神经免疫反应中涉及的滑翔细胞类型包括微球细胞和小细胞。-
Microglial cells
are among the most prominent types of glial cells in the brain. One of their main functions is to phagocytize cellular debris that remains when
die. Microglial cells also “prune” obsolete
between neurons.
::微球细胞是大脑中最突出的微球细胞类型之一,其主要功能之一是将死亡时留下的细胞残块划成碎片。 微球细胞在神经元之间也“颗粒”过时了。 -
Astrocytes
are glial cells that have a different immune function. They allow certain immune cells from the peripheral immune system to cross the blood-brain barrier into the brain to target both pathogens and damaged
nervous tissue
.
::天体细胞是具有不同免疫功能的滑翔细胞,它们允许边缘免疫系统的某些免疫细胞通过血脑屏障进入大脑,以针对病原体和受损的神经组织。
Feature: Human Biology in the News
::特著:《新闻》中的人类生物学“They’ll have to rewrite the textbooks!”
::“他们必须改写教科书!”That sort of response to a scientific discovery is sure to attract media attention, and it did. It’s what Kevin Lee, a neuroscientist at the University of Virginia, said in 2016 when his colleagues told him they had discovered human anatomical structures that had never before been detected. The structures were tiny lymphatic vessels in the meningeal layers surrounding the brain.
::这种对科学发现的反应肯定会吸引媒体的关注,而且确实如此。 2016年,弗吉尼亚大学神经科学家李凯文(Kevin Lee)说,他的同事告诉他,他们发现了前所未有的人类解剖结构。 这些结构是脑下脑层的微小淋巴类血管。How these lymphatic vessels could have gone unnoticed when all human body systems have been studied so completely is amazing in its own right. The suggested implications of the discovery are equally amazing:
::当所有人体系统都经过如此彻底的研究时,这些淋巴类容器是如何被忽略的,这本身就令人惊叹。-
The presence of these lymphatic vessels means that the brain is directly connected to the peripheral immune system, presumably allowing a close association between the human brain and human pathogens. This suggests an entirely new avenue by which humans and their pathogens may have influenced each other’s evolution. The researchers speculate that our pathogens even may have influenced the evolution of our social behaviors.
::这些淋巴动物的存在意味着大脑与外围免疫系统直接相连,大概可以让人类大脑与人类病原体密切相连。 这意味着人类及其病原体可能通过一个全新的途径影响彼此的进化。 研究人员推测我们的病原体甚至可能已经影响我们社会行为的进化。 -
The researchers think there will also be many medical applications of their discovery. For example, the newly discovered lymphatic vessels may play a major role in neurological diseases that have an immune component, such as
multiple sclerosis
. The discovery might also affect how conditions such as autism spectrum disorders and schizophrenia are treated.
::研究人员认为他们发现的体能应用也会有很多。 比如,新发现的淋巴类血管在具有免疫成分的神经疾病(如多发性硬化症)中可能起到重要作用。 发现还可能影响自闭症谱谱系障碍和精神分裂症等疾病的治疗方式。
Summary
::摘要-
Any agent that can cause disease is called a pathogen. Most human pathogens are microorganisms, such as bacteria and viruses. The immune system is the
body
system that defends the human host from pathogens and cancerous cells.
::大多数人类病原体是微生物,如细菌和病毒,免疫系统是人体系统,保护人体免受病原体和癌症细胞的侵袭。 -
The innate immune system is a subset of the immune system that provides very quick, but non-specific responses to pathogens. It includes multiple types of barriers to pathogens, leukocytes that phagocytize pathogens, and several other general responses.
::内生免疫系统是免疫系统的一个子集,对病原体的反应非常迅速,但并不具体,其中包括对病原体的多种障碍、对病原体进行截肢的白血球和其他几种一般性反应。 -
The adaptive immune system is a subset of the immune system that provides specific responses tailored to particular pathogens. It takes longer to put into effect, but it may lead to immunity to the pathogens.
::适应性免疫系统是免疫系统的一个子集,提供针对特定病原体的具体反应,需要更长的时间才能实施,但可能导致病原体的豁免。 -
Both innate and adaptive immune responses depend on the immune system's ability to distinguish between self and non-self molecules. Most body cells have major histocompatibility complex (M
HC
) proteins that identify them as self. Pathogens and tumor cells have non-self antigens that the immune system recognizes as foreign.
::自然和适应性免疫反应都取决于免疫系统区分自体分子和非自体分子的能力。 大部分身体细胞有主要的生理兼容性综合蛋白质(MHC),这些蛋白质将其识别为自体。 病原体和肿瘤细胞有免疫系统承认为外来的非自体抗原。 -
Antigens are proteins that bind to specific receptors on immune system cells and elicit an adaptive immune response. Generally, they are non-self molecules on pathogens or infected cells. Some immune cells (B cells) respond to foreign antigens by producing antibodies that bind with antigens and target pathogens for destruction.
::抗原是蛋白质,与免疫系统细胞上的特定受体结合,并产生适应性免疫反应,一般是病原体或受感染细胞上的非自我分子,有些免疫细胞(B细胞)通过产生与抗原结合的抗体和将病原体作为销毁目标,对外来抗原作出反应。 -
Tumor surveillance is an important role of the immune system. Killer T cells of the adaptive immune system find and destroy tumor cells, which they can identify from their abnormal antigens.
::肿瘤监测是免疫系统的一个重要作用。 适应性免疫系统的杀手T细胞发现并摧毁肿瘤细胞,这些细胞可以从异常抗原中识别出来。 -
The lymphatic system is a human organ system vital
to
the adaptive immune system. It consists of several organs and a system of vessels that transport lymph. The main immune function of the lymphatic system is to produce, mature, and circulate lymphocytes, which are the main cells in the adaptive immune system.
::淋巴系统是人体器官系统,对适应性免疫系统至关重要,由若干器官和载运淋巴的船舶系统组成,淋巴系统的主要免疫功能是生产、成熟和循环淋巴细胞,这是适应性免疫系统的主要细胞。 -
The neuroimmune system that protects the central nervous system is thought to be distinct from the peripheral immune system that protects the rest of the human body. The blood-brain and blood-spinal cord barriers are one type of protection of the neuroimmune system. Glial cells also play role in this system, for example, by carrying out phagocytosis.
::保护中枢神经系统的神经免疫系统被认为有别于保护人体其余部分的外围免疫系统,血液脑部和血液脊髓屏障是神经免疫系统的一种保护形式,淋巴细胞在该系统中也起着作用,例如,通过进行脑细胞结扎。
Review
::回顾1. What is a pathogen?
::1. 什么是病原体?2. State the purpose of the immune system.
::2. 说明免疫系统的目的。3. Compare and contrast the innate and adaptive immune systems.
::3. 比较和比较原生和适应性免疫系统。4. Explain how the immune system distinguishes self molecules from non-self molecules.
::4. 解释免疫系统如何区分自分子和非自分子。5. What are antigens?
::5. 什么是抗原?6. Define tumor surveillance.
::6. 界定肿瘤监测。7. Briefly describe the lymphatic system and its role in immune function.
::7. 简要说明淋巴系统及其在免疫功能方面的作用。8. Identify the neuroimmune system.
::8. 确定神经免疫系统。9. Which of the following is NOT a function of the immune system?
::9. 以下哪一种不是免疫系统的功能?a. protecting the body against fungi
::a. 保护身体免受真菌感染b. protecting the body against bacteria
::b. 保护身体免受细菌的侵害c. protecting the body against cancerous cells
::c. 保护身体免受癌症细胞的伤害c. none of the above
::c. 以上无一情况10. What does it mean that the immune system is not just composed of organs?
::10. 免疫系统不仅仅是由器官组成的,这是什么意思?11. What are the general relationships between the terms lymphocytes, leukocytes, and white blood cells ?
::11. 淋巴细胞、白血球和白血细胞之间的一般关系是什么?12. True or False: Phagocytosis occurs in the innate immune system.
::12. 真实或假:古代免疫系统会发生细胞分裂。13. True or False: Major histocompatibility complex proteins are antibodies.
::13. 真实或假:主要的遗传兼容性综合蛋白质是抗体。14. True or False: Only the adaptive immune response requires the ability to distinguish between self and non-self.
::14. 真实或假:只有适应性免疫反应才要求有能力区分自我和非自我。15. Why is the immune system considered “layered?”
::15. 为什么免疫系统被认为是 " 层次的? "Explore More
::探索更多Check out this video to learn more about the immune system:
::以了解更多有关免疫系统的影片:Scientists predict that we may be facing an "antibiotic apocalypse ." L earn more here:
::科学家预测,我们可能会面临一个“抗生生物世界末日”。 -
Microglial cells
are among the most prominent types of glial cells in the brain. One of their main functions is to phagocytize cellular debris that remains when
die. Microglial cells also “prune” obsolete
between neurons.