20.2 生殖系统介绍
章节大纲
-
It’s All about Sex
::这一切都与性有关A tiny from dad breaks through the surface of a huge egg from mom. Voilà! In nine months, a new son or daughter will be born. Like most other , human beings reproduce sexually. In human , males produce sperm and females produce eggs, and a new offspring forms when a sperm unites with an egg. How do sperm and eggs form? And how do they arrive together at the right place and time so they can unite to form a new offspring? These are functions of the reproductive system.
::父亲的一小块小块从妈妈的巨蛋的表面穿透了。 沃拉! 9个月后, 新的儿子或女儿就会出生了。 和大多数其他人一样, 人类在性方面繁殖。 在人类中, 男性生产精子和雌性产卵, 当精子与蛋结合时, 新的后代会形成。 精子和蛋是如何形成的? 他们是如何聚集在合适的地点和时间, 以便联合起来形成新的后代的? 这些是生殖系统的功能。What Is the Reproductive System?
::什么是生殖系统?The reproductive system is the human organ system responsible for the production and of gametes (sperm or eggs) and, in females, the carrying of a fetus . Both male and female reproductive systems have organs called gonads that produce gametes. A gamete is a haploid that combines with another haploid gamete during fertilization, forming a single diploid cell called a zygote . Besides producing gametes, the gonads also produce sex hormones . Sex hormones are endocrine that control of sex organs before birth, sexual maturation at , and once sexual maturation has occurred . Other reproductive system organs have various functions, such as maturing gametes, delivering gametes to the site of fertilization, and providing an environment for the development and growth of an offspring.
::生殖系统是人类器官系统,负责生产及生胎(精液或卵)和雌性携带。男性和女性生殖系统都拥有产卵的器官。一个果子系是一种杂交机,在授精期间与另一个手稿游戏结合,形成一个叫作zygote的单体滴细胞。除产生果子外,牙系还产生性激素。性激素是内分泌,在生育前控制性器官,在性成熟时和发生性成熟后控制。其他生殖系统器官有多种功能,如发芽游戏,在授精期间将游戏送至授地,并为后代的发育和成长提供环境。Sex Differences in the Reproductive System
::生殖系统中的性别差异The reproductive system is the only human organ system that is significantly different between males and females. Embryonic structures that will develop into the reproductive system start out the same in males and females, but by birth, the reproductive systems have differentiated. How does this happen?
::生殖系统是男女之间唯一明显不同的人体器官系统。 进入生殖系统的胚胎结构在男女生殖系统开始时都是一样的,但从出生开始,生殖系统就有所区别。 这如何发生呢?Sex Differentiation
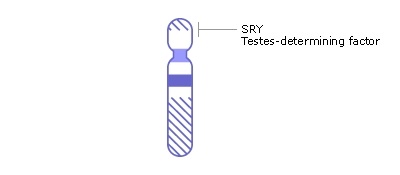
::性别差异Starting around the seventh week after conception in genetically male (XY) embryos , a gene called SRY on the Y chromosome (shown in the figure ) initiates the production of multiple . These proteins cause undifferentiated gonadal tissue to develop into male gonads (testes). The male gonads then secrete hormones — including the male sex hormone testosterone — that trigger other changes in the developing offspring (now called a fetus), causing it to develop a complete . Without a Y chromosome, an embryo will develop female gonads (ovaries) that will produce the female sex hormone estrogen . Estrogen, in turn, will lead to the formation of the other organs of a normal .
::从遗传男性胚胎(XY)受孕后大约七个星期开始,一种叫做Y染色体(图中显示的)SRY的基因开始生产多种基因。这些蛋白质导致不加区分的谷形组织发展成雄性腺组织(睾丸),而雄性甲状腺组织(包括男性性激素睾丸酮)则隐匿荷尔蒙——包括男性性激素睾丸酮——引发发育中的后代(现称胎儿)的其他变化,导致其完全发育。没有Y染色体,胚胎会形成雌性腺(卵巢),产生雌性激素雌性激素。而雌性激素则会导致其他正常器官的形成。The SRY gene on the short arm of the Y chromosome causes the undifferentiated gonads of an embryo to develop into testes. Otherwise, the gonads develop into ovaries.
::Y染色体短臂上的SRY基因导致胚胎无区别的鼻腺发展成睾丸,否则,鼻腺发展成卵巢。Homologous Structures
::同族结构Undifferentiated embryonic tissues develop into different structures in male and female fetuses. Structures that arise from the same tissues in males and females are called homologous structures . T he male testes and female ovaries , for example, are homologous structures that develop from the undifferentiated gonads of the embryo. Likewise, the male penis and female clitoris are homologous structures that develop from the same embryonic tissues.
::未婚胚胎组织在男女胎儿中发展成不同的结构,由男女相同的组织产生的结构被称为同质结构,例如,男睾丸和女卵巢是同质结构,它们从胚胎的无差别的血浆中发展而来,同样,男阴茎和女阴蒂也是同质结构,它们从相同的胚胎组织中发展而来。Sex Hormones and Maturation
::性激素和成熟期Male and female reproductive systems are different at birth, but they are immature and incapable of producing gametes or sex hormones. Maturation of the reproductive system occurs during puberty, when hormones from the hypothalamus and pituitary gland stimulate the testes or ovaries to start producing sex hormones again. The main sex hormones are testosterone in males and estrogen in females. Sex hormones, in turn, lead to the growth and maturation of the reproductive organs, rapid body growth, and the development of secondary sex characteristics. Secondary sex characteristics are traits that are different in mature males and females, but are not directly involved in reproduction. They include facial hair in males and breasts in females.
::男性和女性生殖系统在出生时是不同的,但是它们不成熟,无法产生调味剂或性激素;生殖系统的成熟发生在青春期,即低脑和垂垂体腺的激素刺激睾丸或卵巢重新开始产生性激素;主要的性激素是雄性睾酮和雌性雌性激素;性激素反过来又导致生殖器官的生长和成熟、身体的迅速生长和第二性特征的发展;第二性特征在成熟的男性和女性中是不同的特征,但并不直接涉及生殖,包括雄性和雌性胸部的面部毛发。Male Reproductive System
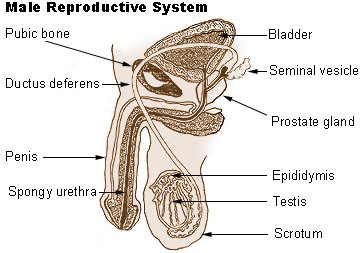
::男性生殖系统The main structures of the male reproductive system are external to the body and illustrated in the figure . The two testes (singular, testis) hang between the thighs in a sac of skin called the scrotum . The testes produce both sperm and testosterone. Resting atop each testis is a coiled structure called the epididymis (plural, epididymes). The function of the epididymes is to mature and store sperm. The penis is a tubular organ that contains the urethra and has the ability to stiffen during sexual arousal. Sperm passes out of the body through the urethra during a sexual climax (orgasm). This release of sperm is called ejaculation .
::男性生殖系统的主要结构是身体外部的,图中说明了男性生殖系统的主要结构。两个睾丸(双胞胎、睾丸)在大腿之间挂在称为阴囊的皮肤囊中,睾丸产生精子和睾丸酮。在每根睾丸上休息是一种循环结构,叫做肾上腺(花生、奶子)。 肾上腺的功能是成熟和储存精子。阴茎是一种管状器官,内含尿素,在性激素期间有能力僵硬。在性高潮(orgasm)期间,精子通过尿素从身体中流出。这种精子的释放被称为射精。Most of the major male reproductive organs are located outside of the body.
::大多数主要的男性生殖器官位于身体之外。In addition to these organs, the male reproductive system consists of several ducts and glands that are internal to the body. The ducts, which include the vas deferens (also called the ductus deferens), transport sperm from the epididymis to the urethra. The glands, which include the prostate gland and seminal vesicles , produce fluids that become part of semen . Semen is the fluid that carries sperm through the urethra and out of the body. It contains substances that control pH and provide sperm with nutrients for energy .
::除这些器官外,雄性生殖系统由身体内部的若干管道和腺组成,包括血管延后线(也称为结构延后线),将精子从表面迁移到尿道;腺,包括前列腺和精液,产生流体,成为精液的一部分;精液是通过尿道和体外携带精子的液体,含有控制pH的物质,为能量提供精子营养素。Female Reproductive System
::妇女生殖系统The main structures of the female reproductive system are internal to the body and shown in the figure. They include the paired ovaries, which are small, ovoid structures that produce eggs and secrete estrogen. The two Fallopian tubes start near the ovaries and end at the uterus . Their function is to transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. If an egg is fertilized, it usually occurs while it is traveling through a Fallopian tube. The uterus is a pear-shaped muscular organ that functions to carry a fetus until birth. It can expand greatly to accommodate a growing fetus, and its muscular walls can contract forcefully during labor to push the baby out of the uterus and into the vagina . The vagina is a tubular tract connecting the uterus to the outside of the body. The vagina is where sperm are usually deposited during sexual intercourse and ejaculation. The vagina is also called the birth canal because a baby travels through the vagina to leave the body during birth.
::雌性生殖系统的主要结构是身体的内部结构,并在图中显示,包括产卵和雌激素的小型无脊椎动物。两个Fallopian管子从卵巢附近开始,端端端为子宫。它们的作用是将卵子从卵巢运到子宫。如果卵子受精,通常在通过Fallopian管子穿梭时发生。子宫是一种小耳形肌肉器官,在分娩前可以携带胎儿。它可以大大扩展以容纳一个不断成长的胎儿,而它的肌肉壁在分娩期间可以紧紧紧地收缩,将婴儿从子宫推出并插入阴道。阴道将子宫连接到身体外部。阴道一般在性交和射精液过程中放置。阴道也称为生胆,因为婴儿在分娩期间穿过阴道离开身体。The main organs of the female reproductive system lie within the abdominal cavity.
::女性生殖系统的主要器官在腹腔内。The external structures of the female reproductive system are referred to collectively as the vulva . They include the clitoris, which is homologous to the male penis. They also include two pairs of labia (singular, labium), which surround and protect the openings of the urethra and vagina.
::女性生殖系统的外部结构统称为阴道,包括阴蒂,与男性阴茎同质,还包括两对阴唇(阴唇、),围住并保护尿道和阴道的开口。Summary
::摘要-
The reproductive system is the human organ system responsible for the production and fertilization of gametes and, in females, the carrying of a fetus.
::生殖系统是人体器官系统,负责编织和授精以及雌性胎儿的生育和受精。 -
Both male and female reproductive systems have organs called gonads (testes in males, ovaries in females) that produce gametes (sperm or eggs) and sex hormones (such as testosterone in males and estrogen in females). Sex hormones are endocrine hormones that control the prenatal development of reproductive organs, sexual maturation at puberty, and reproduction after puberty.
::男性和女性生殖系统都有被称为“鼻腔”的器官(雄性测试,雌性卵巢测试),这些器官产生色调(阳极或蛋)和性激素(如雄性睾酮和雌性雌性激素),性荷尔蒙是内分泌激素,控制生殖器官的产前发育、青春期的性成熟和青春期后的生殖。 -
The reproductive system is the only organ system that is significantly different between males and females. A Y-chromosome gene called SRY is responsible for undifferentiated embryonic tissues developing into a male reproductive system. Without a Y chromosome, the undifferentiated embryonic tissues develop into a female reproductive system.
::生殖系统是男女之间唯一明显不同的器官系统,一种叫SRY的Y-染色体基因是无差别胚胎组织发展成男性生殖系统的责任,没有Y染色体,无差别胚胎组织发展成女性生殖系统。 -
Structures such as testes and ovaries that arise from the same undifferentiated embryonic tissues in males and females are called homologous structures.
::由同一种无差别的男女胚胎组织产生的睾丸和卵巢等结构被称为同质结构。 -
Male and female reproductive systems are different at birth, but at that point, they are immature and nonfunctioning. Maturation of the reproductive system occurs during puberty, when hormones from the hypothalamus and pituitary gland stimulate the gonads to
produce
sex hormones again. The sex hormones, in turn, cause the changes of puberty.
::男性和女性的生殖系统在出生时是不同的,但在出生时是不成熟和不起作用的,生殖系统的成熟是在青春期发生的,在青春期,低脑和垂体腺的荷尔蒙激素刺激性激素再次产生性激素,而性激素反过来又导致青春期的变化。 -
Male reproductive system organs include the testes, epididymis, penis, vas deferens, prostate gland, and seminal vesicles.
::男性生殖系统器官包括睾丸、肾上腺素、阴茎、软骨、前列腺和精液。 -
Female reproductive system organs include the ovaries, Fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, clitoris, and labia.
::女性生殖系统器官包括卵巢、输卵管、子宫、阴道、阴蒂和阴唇。
Review
::回顾1. What is the reproductive system?
::1. 什么是生殖系统?2. Define gonad.
::2. 界定gonad。3. What are sex hormones? What are their general functions?
::3. 什么是性激素?它们的一般功能是什么?4. Distinguish between male and female sex hormones.
::4. 区分男女性激素。5. How does differentiation of the reproductive system occur in males and females?
::5. 生殖系统的男女差别如何?6. I n the context of human male and female reproductive systems, w hat are homologous structures?
::6. 在人的生殖系统方面,什么是同族结构?7. When and how does the human reproductive system mature?
::7. 人类生殖系统何时成熟以及如何成熟?8. List organs of the male reproductive system.
::8. 男性生殖系统机构名单。9. List organs of the female reproductive system.
::9. 妇女生殖系统机构名单。10. Female gametes are called _________ and male gametes are called _________ .
::10. 女性调子称为,男性调子称为。11. True or False: The vagina is the homologous structure to the penis.
::11. 真实或假:阴道是阴茎的同质结构。12. True or False: In the absence of a Y chromosome in humans, ovaries will develop.
::12. 真实或假:在没有人类Y染色体的情况下,卵巢会发育。13. Which are secondary sex characteristics?
::13. 哪些是第二性别特征?a. Fallopian tubes
::a. 输卵管b. ovaries
::b. 卵巢c. breasts
::c. 乳房d. all of the above
::d. 以上所有情况14. Fertilization usually occurs in the _________________.
::14. 化肥化通常发生在________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________a. ovary
::a. 卵子体b. Fallopian tube
::b. 下游管管c. uterus
::c. 子宫d. vagina
::d. 阴道15. Explain the difference between the vulva and the vagina.
::15. 解释阴道和阴道之间的区别。Explore More
::探索更多People's sense of gender identity does not always match their anatomy. Some people do not identify as either male or female, and instead, they identify as non-binary, or genderqueer. Others may identify as a gender that i s the opposite of what is typically associated with their chromosomes or reproductive organs. These people are called transgender, and they may choose to transition to the opposite gende r, a process which may or may not involve physical modifications. Watch the video below to learn about the use of hormones in gender transitioning.
::人们的性别认同感并不总是与其生理特征相符,有些人并不确认男女为男性或女性,相反,他们确认为非二进制或性别抑制者,其他人则可能确认为与通常与其染色体或生殖器官相关的性别相反的性别,这些人被称为变性人,他们可能选择向相反的性别过渡,这一过程可能涉及身体上的改变,或者可能不涉及身体上的改变。Sex determination may be more complicated than originally thought. Check out this video to learn more:
::性别认定可能比原先想象的要复杂得多。 -
The reproductive system is the human organ system responsible for the production and fertilization of gametes and, in females, the carrying of a fetus.