15.1 电电和电 电 电 电 电 电 电 电 电 电 电 电 电
章节大纲
-
Lightning is the discharge of static electricity that has built up on clouds. Every year, the earth experiences an average of 25 million lightning strikes. Lightning bolts travel at speeds up to 60,000 miles per second, and can reach temperatures of 50,000°F, which is five times the of the surface of the sun. The contained in a single lightning strike could light a 100 Watt light bulb 24 hours per day for 90 days.
::闪电是云层形成的静电排放。 地球每年平均遭受2500万次闪电打击。 闪电螺栓以每秒60,000英里的速度运行,每秒可以达到50,000摄氏度,温度是太阳表面的五倍。 一次闪电打击中所含的电量可以连续90天每天24小时点亮100瓦特灯泡。Forces on Charged Objects
::对被充装物体的武力Electric charges exist within the atom. At the turn of the 20th century, J. J. Thomson and Ernest Rutherford determined that atoms contain very light- negatively charged particles called electrons and more massive, positively charged particles called protons . The protons are lodged in the nucleus of the atoms, along with the neutrally charged particles called neutrons , while the electrons surround the nucleus. When the number of electrons in the electron cloud and the number of protons in the nucleus are equal, the object is said to be neutral .
::原子内存在电荷。在20世纪初,J.J.汤姆森和欧内斯特·卢瑟福(Ernest Rutherford)确定原子含有非常轻度-负电荷粒子,叫做电子,以及更大规模、正电荷粒子,叫做质子。质子与中性电荷粒子一起嵌入原子核心,而核心周围是电子。当电子云中的电子数量和核心中的质子数量相等时,该物体据说是中性的。Changes to the nucleus of an atom require tremendous amounts of energy, so protons are not easily gained or lost by atoms. Electrons, on the other hand, are held fairly loosely and can often be removed quite easily. When an object loses some electrons, the remaining object is now positively charged because it has an excess of protons. The electrons may either remain free or may attach to another object. In that case, the extra electrons cause that object to become negatively charged. Atoms that have lost electrons and become positively charged are called positive ions , and atoms that have gained electrons and become negatively charged are called negative ions .
::原子核的改变需要巨大的能量,因此质子不会轻易地被原子获取或丢失。 另一方面,电子被控制得相当松散,而且往往很容易被移除。当一个物体失去一些电子时,剩下的物体现在被正电,因为它有超量质子。电子要么保持自由,要么可以附加到另一个物体上。在这种情况下,额外的电子导致该物体受到负电荷。失去电子的原子和正面电荷的原子被称为正离子,而获得电子和负电荷的原子则被称为负电离子。Electrons can be removed from some objects using , simply by rubbing one substance against another substance. There are many examples of objects becoming charged by friction, including a rubber comb through hair, and a balloon on a sweater. In both these instances, the electrons move from the second object to the first, causing the first object to become negatively charged and the second one positively charged. Friction between the tires on a moving car and the road cause the tires to become charged, and wind causes friction between clouds and air which causes clouds to become charged and can result in tremendous bolts of lightning.
::电可以从使用的某些物体上移走,只需擦擦一种物质来对付另一种物质即可。 有许多例子显示物体因摩擦而充电, 包括用橡胶梳子透透透头发和毛衣上的气球。 在这两种情况中,电子从第二个物体移到第一个物体,造成第一个物体负电,第二个物体正电。 轮胎在移动的汽车上和公路上的摩擦导致轮胎充电,风在云和空气之间造成摩擦,导致云层充电,并可能造成巨大的闪电栓。A common method of producing charge in the lab is to rub cat or rabbit fur against stiff rubber, producing a negative charge on the rubber rod. If you hold a rubber rod on one end and rub only the tip of the other end with a fur, you will find that only the tip becomes charged. The electrons you add to the tip of the rod remain where you put them instead of moving around on the rod. Rubber is an insulator . Insulators are substances that do not allow electrons to move through them. Glass, dry wood, most plastics, cloth, and dry air are common insulators. Materials that allow electrons to flow freely are called conductors. Metals have at least one electron that can move around freely, and all metals are conductors.
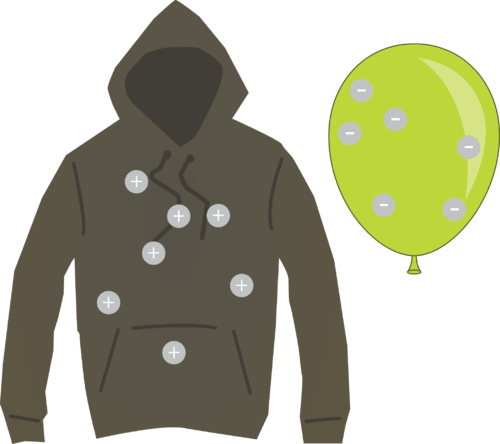
::实验室中一种常见的充电方法就是对硬橡胶涂抹猫毛或兔子毛毛,在橡胶棒上产生负电荷。如果你把橡胶棒放在一端,而只用毛皮把另一端的顶部涂上,你就会发现只有尖子才会受到电荷。在杆子顶部添加的电子仍然留在你放置它们的地方,而不是在杆子上移动。橡胶是一种绝缘器。绝缘器是不允许电子穿过它们的物质。玻璃、干木、大多数塑料、布料和干燥空气都是常见的绝缘器。允许电子自由流通的材料被称为导电器。金属至少有一种电子可以自由移动,所有金属都是导电器。Forces are exerted on charged objects by other charged objects. You've probably heard the saying "opposites attract," which is true in regards to charged particles. Opposite charges attract each other, while like charges repulse each other. This can be seen in the image below. When two negatively charged objects are brought near each other, a repulsive force is produced. When two positively charged objects are brought near each other, a similar repulsive force is produced. When a negatively charged object is brought near a positively charged object, an attractive force is produced. Neutral objects have no influence on each other.
::由其它有电物体对充电物体施加力量。 您可能听到过“ 反向吸引” 这个词, 这在充电粒子方面是有道理的。 反向吸引互相吸引, 而像电荷互相击退一样。 从下面的图像中可以看到这一点。 当两个负向充电物体相互靠近时, 产生一种令人厌恶的力量。 当两个有电物体相互靠近时, 产生类似的反向力量。 当负向充电物体接近有电物体时, 产生一种有吸引力的力量。 中性物体对彼此没有影响 。Use the PLIX Interactive below to try to predict the attractive and repulsive forces exerted on one charged object by another charged object:
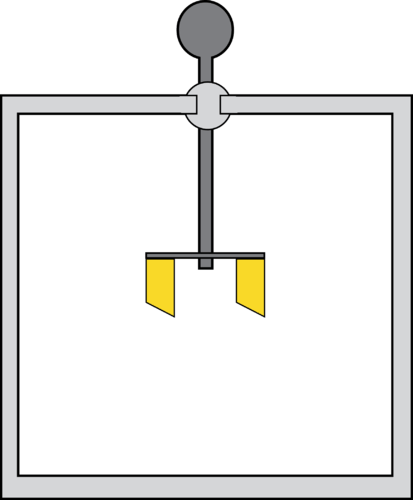
::使用下面的 PLIX 互动 来尝试预测另一个充电对象对一个充电对象施加的诱人和令人厌恶的力量:A laboratory instrument used to analyze and test for static charge is called an electroscope . Seen below, an electroscope consists of a metal knob connected by a metal stem to two very lightweight pieces of metal called leaves, shown in yellow. The leaves are enclosed in a box to eliminate stray air currents.
::用于分析和试验静态电荷的实验室仪器称为电子望远镜,下面显示,一个电子望远镜是由金属干叶连接到两块称为叶子的非常轻的金属块的金属把手组成的,用黄色显示,叶子被装在一个盒子里,以消除流散的空气流。When a negatively charged object is brought near the knob of a neutral electroscope, the negative charge repels the electrons in the knob, and those electrons move down the stem into the leaves. Excess electrons flow from the rod into the ball, and then downwards making both leaves negatively charged. Since both leaves are negatively charged, they repel each other. When the rod is removed, the electroscope will remain charged because of the extra electrons added to it.
::当负电荷物体靠近中性电子望远镜的把手部时,负电荷反射器会将电荷反射到把手部中的电子,而那些电子则会向叶部下移。多余的电子从棒向球中流动,然后向下使两个叶子负电荷。由于两个叶子都有负电荷,它们会互相反射。当棒被移走时,电动镜会继续充电,因为增加了额外的电子。Conversely, if the rod is brought near the knob but doesn’t touch it, the electroscope will appear the same while the rod is near. That is, the negative charge in the rod repels the electrons in the ball, causing them to travel down to the leaves. The leaves will separate while the rod is nearby. No extra electrons were added to the electroscope, meaning that the electrons in the electroscope will redistribute when the negatively charged rod is taken away. The leaves return to neutral, and they stop repelling each other. If the rod touches the knob, the electroscope leaves are permanently charged but if the rod is brought near but does not touch the knob, the electroscope leaves are only temporarily charged.
::反之,如果棍子靠近棒子,但是不触动它,那么电动望远镜就会在棒子靠近的时候出现同样的效果。也就是说,棒子中的负电荷将球中的电子反射,导致它们下到叶子上。树叶在棒子附近时会分开。电动望远镜没有增加额外的电子,这意味着电动望远镜中的电子在负电击棒被拿走时会重新分配。叶子回到中性,它们停止相互反射。如果棍子触碰了Knob,电动望远镜叶就会永久充电,但如果棍子靠近但不触动Knob,电动眼镜叶只是暂时充电。If the leaves are permanently charged and the rod removed, the electroscope can then be used to determine the type of unknown charge on an object. If the electroscope has been permanently negatively charged, and a negatively charge object is brought near the knob, the leaves will separate even further, showing the new object has the same charge as the leaves. If a positively charged object is brought near a negatively charged electroscope, it will attract some of the excess electrons up the stem and out of the leaves, causing the leaves to come slightly together.
::如果叶子永久充电,棒子被移走,那么电子望远镜就可以用来确定一个物体的未知电荷类型。如果电动望远镜被永久负电荷,而负电荷对象接近顶部,叶子将进一步分离,显示新对象的电荷与叶子的电荷相同。如果正电动对象靠近负电动显影,它将吸引一些超电子到干叶上和叶子上,使叶子稍有结合。Similar to the results of a negatively charged rod, if a positively charged rod is brought near the knob of a neutral electroscope, it will attract some electrons up from the leaves onto the knob. That process causes both of the leaves to be positively charged (excess protons), and the leaves will diverge. If the positively charged rob is actually touched to the knob, the rob will remove some electrons and then when the rob is removed, the electroscope will remain positively charged. This is a permanent positive charge.
::与负电击棒的结果相似的是,如果正电击棒靠近中电子望远镜的把手,它将吸引一些电子从叶子上移到把手上,这一过程导致叶子上移积极电(超过质子),而叶子上移。如果正电击棒实际触动到把手上,抢劫将去除一些电子,当抢走时,电击手将保持正电击。这是一个永久正电击。Charging an object by touching it with another charged object is called charging by conduction . By bringing a charged object into contact with an uncharged object, some electrons will migrate to even out the charge on both objects. Charging by conduction gives the previously uncharged object a permanent charge. An uncharged object can also be charged using a method called charging by induction . This process allows a change in charge without actually touching the charged and uncharged objects to each other. Imagine a negatively charged rod held near the knob, but not touching. If we place a finger on the knob, some of the electrons will escape into our body, instead of down the stem and into the leaves. When both our finger and the negatively charged rod are removed, the previously uncharged electroscope now has a slight positive charge. It was charged by induction. Notice that charging by induction causes the newly charged object to have the opposite charge as the originally charged object, while charging by conduction gives them both the same charge.
::通过触碰另一受控物体而使物体与另一受控物体发生电荷,即称为电动。通过将受控物体与未充电物体发生接触,一些电子将迁移,以平衡对两物体的电荷。通过电动充电使先前未充电物体成为永久电荷。未充电物体也可以使用上传电荷的方法提出电荷。这一过程允许改变电荷,而不会实际触碰被控和未充电物体;想象在Knob附近持有的负电棒,但不会触碰。如果我们在Knob上指向负电击杆,一些电子将跳入我们的身体,而不是向干线和叶中。当我们手指和负电击杆被移走时,先前未充电动的电镜现在有轻微的正电荷。这是感应电荷。通过感应通知,通过感应使新受控物体的电荷与最初受电荷物体产生相反的电荷,同时通过操电荷给予它们相同的电荷。Further Reading
::继续阅读Summary
::摘要-
Electric charges exist with the atom.
::原子有电费 -
Atoms contain light-weight, loosely held, negatively charged particles called electrons and heavier, tightly-held, positvely charged particles called protons.
::原子含有轻量级、松散的负电荷粒子,称为电子,以及较重、较紧固控的、实实在在的有电粒子,称为质子。 -
When the number of electrons and the number of protons are equal, the object is neutral.
::当电子数和质子数相等时,该对象为中性。 -
The loss of electrons gives an ion a positive charge, while the gain of electrons gives it a negative charge.
::电子损失给电离子带来正电荷,而电子收益给电离子带来负电荷。 -
Materials that allow electrons to flow freely are called conductors, while those that do not are called insulators.
::允许电子自由流通的材料被称为导体,而不使用这种材料的材料则被称为绝缘器。 -
Opposite charges attract, and like charges repel.
::反向收费吸引, 和类似收费反射。 -
Charging an object by touching it with another charged object is called charging by conduction.
::将物体与另一物体触碰以充电,即称为操控充电。
Review
::回顾-
How does friction generate static electricity?
-
Friction heats the materials, thus causing electricity.
::摩擦使材料加热,从而造成电力供应。 -
Rubbing materials together displaces atoms, causing sparks to fly.
::挤压材料合在一起取代原子,引起火花飞翔。 -
Rubbing materials together can strip electrons off atoms, causing one material to become positive and the other to become negative.
::挤压材料合在一起可以将电子从原子上剥离,造成一种物质呈阳性,另一种物质呈负性。 -
Rubbing materials together causes neutrons and electrons to trade places.
::挤压材料合在一起导致中子和电子进入交换地点。 -
None of the above.
::上述情况无一例外。
::摩擦如何产生静电? 摩擦如何产生静电? 摩擦使材料加热,从而造成电力。 挤压材料合在一起取代原子,造成火花飞翔。 挤压材料合在一起可以将电子从原子上剥离,造成一种物质呈阳性,另一种物质则变成负性。 挤压材料合在一起导致中子和电子交易。 以上没有一种。 -
Friction heats the materials, thus causing electricity.
-
What electrical charge does an electron have?
-
A negative charge.
::负指控 -
A positive charge.
::一个正面的指控。 -
A neutral charge.
::中性炸药 -
May be any of the above.
::可能属于上述任何一种情况。 -
None of the above.
::上述情况无一例外。
::电子的电荷是多少? 负电荷是负电荷,正电荷是正电荷,中性电荷是中性电荷,可能是以上任何一种,以上任何一种都不是。 -
A negative charge.
-
What happens when opposite charges get close to each other?
-
They repel each other.
::他们互相击退 -
They attract each other.
::他们互相吸引 -
Nothing happens.
::什么都没有发生。 -
They attract surrounding objects.
::它们吸引周围的物体。 -
They repel surrounding objects.
::他们击退周围的物体。
::当相反的电荷接近对方时会怎样?它们互相击退,互相吸引,没有发生什么。它们吸引周围的物体,它们击退周围的物体。 -
They repel each other.
-
What is an electrical conductor?
-
A material that allows electrons to travel through it freely.
::一种允许电子自由穿梭的材料。 -
A material that doesn’t allow electrons to travel through it freely.
::一种不允许电子自由穿梭的材料。 -
A material that melts at low temperature.
::一种在低温下熔化的物质 -
A material that creates free electrons.
::一种能产生自由电子的材料 -
None of the above.
::上述情况无一例外。
::电导器是什么? 一种允许电子自由穿透的材料。 一种不允许电子自由穿透的材料。 一种在低温下熔化的材料。 一种可以产生自由电子的材料。 上述材料都不存在。 -
A material that allows electrons to travel through it freely.
-
Which of the following is a good insulator of electricity?
-
Copper
::铜铜 -
Iron
::铁铁铁 -
Rubber
::橡胶橡胶 -
Salt water
::盐水 -
None of these.
::没有一个这些。
::以下哪一种是良好的电绝缘器? -
Copper
Explore More
::探索更多Use this resource to answer the questions that follow.
::使用此资源回答下面的问题 。-
What will happen to Barbie's hair when
the lady
touches
the Van de Graaff Generator
?
::当这位女士触摸Van de Graaff发电机时 芭比的头发会怎么样? -
Why do you think this happens to
Barbie's
hair?
::为什么你认为这是发生在芭比的头发上?