13.7 单分违反
章节大纲
-
Though it looks like a double slit interference pattern, the pattern on the screen are actually the results of light diffracting through a single slit with the ensuing interference.
::屏幕上的图案其实是光线通过 与随后的干扰的单条截断 产生分解的结果。Single Slit Interference
::单分干涉度Interference patterns are produced not only by double slits but also by single slits, otherwise known as single slit interference . In the case of a single slit, the particles of medium at both corners of the slit act as point sources, producing circular waves from both edges. These circular waves move across to the back wall and interfere in the same way that interference patterns were produced by double slits.
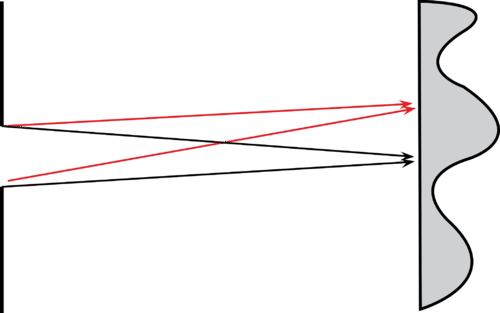
::干扰模式不仅由双断层产生,而且由单断层产生,也称为单一断层干扰,如果是单断层,两端的介质微粒作为点源,从两边产生循环波。 这些循环波波向后墙移动,干扰方式与干扰模式由双断层产生相同。In the sketch at below, the black lines intersect at the center of the pattern on the back wall. This center point is equidistanct from both edges of the slit. Therefore, the waves striking at this position will be in phase; that is, the waves will produce constructive interference . Also shown in the sketch, just above the central bright spot where the red lines intersect, is a position where destructive interference occurs. One of these red lines is one-half longer than the other, causing the two waves to hit the wall out of phase and undergo destructive interference. A dark bank appears at this position.
::在下面的草图中,黑线在后面墙的图案中心交叉。 这个中心点与断裂的两边缘相近。 因此, 撞击这个位置的波将处于阶段, 也就是说, 波将产生建设性的干扰。 在草图中, 就在红线交叉的中央亮点上方, 显示一个发生破坏性干扰的位置 。 其中一条红线比另一条长半年, 导致两道波将墙撞出阶段, 并受到破坏性干扰 。 黑银行出现在这个位置上 。Just as in double slit interference, a pair of similar triangles can be constructed in the interference pattern. The pertinent values from these triangles are the width of the slit, w , the wavelength, λ, the from the central bright spot to the first dark band, x , and the distance from the center of the slit to back wall, L . The relationship of these four values is
::和双斜线干扰一样,在干扰模式中也可以构造一对相似的三角形。这些三角形的相关值是斜线宽度、 w、波长、 、 从中央亮点到第一个暗带的宽度、 x 和从斜线中间到墙背的距离, L。 这四个值之间的关系是:@$\begin{align*}\frac{\lambda}{w}=\frac{x}{L} \ or \ \lambda=\frac{wx}{L}\end{align*}@$ .
::@ $\ begin{ leign} frac_ llambda} wfrac{x{L} 或\\\ lambda} frac{wx} {L} end{ leign} $。Example
::示例示例示例示例Monochromatic light of wavelength 605 nm falls on a slit of width 0.095 mm. The slit is located 85 cm from a screen. How far is the center of the central bright band to the first dark band?
::波长605纳米波长的单色光线落在宽度0.095毫米的切片上。 切片位于屏幕85厘米处。 中亮带的中心离第一个暗带有多远?@$\begin{align*}x=\frac{\lambda L}{w}=\frac{(6.05 \times 10^{-7} \ m)(0.85 \ m)}{(9.5 \times 10^{-5} \ m)}=0.0054 \ m\end{align*}@$
::@ $\ begin{ align} x\\\ frac\ llambda Lw\ frac{ (6. 05\ times 10\\ 7}\ m (0. 85\ m)\\ (9. 5\ times 10\ 5}\ m)\ 0.0054\ m\ end{ align} @Launch the PLIX Interactive below to observe light passing through a single slit and try to use the resulting interference pattern to determine the light’s wavelength:
::在下面启动PLIX交互式活动,观察光线穿过一个片断,并试图利用由此产生的干扰模式确定光线的波长:Summary
::摘要-
Interference patterns can also be produced by single slits.
::干涉模式也可以由单一的片断产生。 -
In the case of a single slit, the particles of medium at both corners of the slit act as point sources, and produce circular waves from both edges.
::在单一切片的情况下,切片两角的介质微粒作为点源,从两边产生循环波。 -
The wavelength can be determined by this equation:
@$\begin{align*}\frac{\lambda}{w}=\frac{x}{L} \ or \ \lambda=\frac{wx}{L}\end{align*}@$
.
::此方程式可以决定波长 : @ $\ begin{ align}\ frac_ lambda} wfrac{ xL} \ 或\\ lambda} frac{ wx} {wx}L{ end{ leign} $ 。
Review
::回顾-
The same set up is used for two different single slit diffraction experiments. In one of the experiments, yellow light is used, and in the other experiment, green light is used. Green light has a shorter wavelength than yellow light. Which of the following statements is true?
-
The two experiments will have the same distance between the central bright band and the first dark band.
::这两个实验在中央亮度波段和第一个暗度波段的距离相同。 -
The green light experiment will have a greater distance between the central bright band and the first dark band.
::绿色光实验在中央明亮波段和第一个暗波段之间 将会有更大的距离。 -
The yellow light experiment will have a greater distance between the central bright band and the first dark band.
::黄光实验在中央亮度波段和第一个暗度波段之间距离更大。
::相同的设置用于两个不同的单切断裂实验。 在其中一个实验中, 使用黄色光, 在另一个实验中, 使用绿色光。 绿光的波长比黄色光短。 以下的哪个语句是真实的 。 两项实验在中亮带和第一个暗带之间有相同的距离。 绿色光实验在中亮带和第一个暗带之间有更大的距离。 黄色光实验在中亮带和第一个暗带之间有更大的距离。 黄色光实验将在中亮带和第一个暗带之间有更大的距离 。 -
The two experiments will have the same distance between the central bright band and the first dark band.
-
Why are the edges of shadows often fuzzy?
-
Interference occurs on the wall on which the shadow is falling.
::阴影掉落的墙上出现干扰。 -
Light diffracts around the edges of the object casting the shadow.
::抛出阴影的物体边缘周围有光亮的细微变化。 -
The edges of the object casting the shadow is fuzzy.
::抛出阴影的物体的边缘是模糊的。 -
Light naturally spreads out.
::光自然会散开
::为什么阴影的边缘往往模糊不清?阴影倒塌的墙上会发生干扰。抛出阴影的物体的边缘周围会出现亮光。投出阴影的物体的边缘是模糊的。光自然会散开。 -
Interference occurs on the wall on which the shadow is falling.
-
Monochromatic, coherent light passing through a double slit will produce exactly the same interference pattern as when it passes through a single slit.
-
True
::真实 -
False
::假假
::单色、连贯的光线穿过双片段,会产生与通过单一片段时完全相同的干扰模式。 -
True
-
If monochromatic light passes through a 0.050 mm slit and is projected onto a screen 0.70 m away with a distance of 8.00 mm between the central bright band and the first dark band, what is the wavelength of the light?
::如果单色光穿过0.050毫米的斜面,并投射到0.70米的屏幕上,中间亮带与第一个暗带之间距离为8.00毫米,那么光的波长是什么? -
A krypton ion laser with a wavelength of 524.5 nm illuminates a 0.0450 mm wide slit. If the screen is 1.10 m away, what is the distance between the central bright band and the first dark band?
::一个波长为524.5纳米的克里普顿离子激光照射0.0450毫米宽的切片。如果屏幕距离1.10米,中亮带与第一个暗带之间的距离是多少? -
Light from a He-Ne laser
@$\begin{align*}(\lambda = 632.8 \ nm)\end{align*}@$
falls on a slit of unknown width. In the pattern formed on a screen 1.15 m away, the first dark band is 7.50 mm from the center of the central bright band. How wide is the slit?
::来自 He-Ne 激光的光@$\ begin{ ALign}}(\ lambda = 632.8\ nm)\ end{ align}$$ 落在一个未知宽度的切片上。 在屏幕上1.15米外形成的图案中, 第一个暗带距中亮带中心7. 50毫米。 切片宽度多大 ?
Explore More
::探索更多Use this resource to answer the question that follows.
::使用此资源回答以下问题 。-
What are interference patterns caused by?
::是什么引起的干扰模式? -
What does the placement of light and dark bands or fringes depend on?
::光和暗带或边缘的布置取决于什么? -
How do the fringes change as you move away from the center?
::当你离开中心时,边缘是如何变化的? -
What happens when white light is used instead of monochromatic light?
::当使用白光而不是单色光时会怎样?
-
Interference patterns can also be produced by single slits.