2.6 核酸 - 高级
章节大纲
-
You may have heard that "it's in your DNA." What does that mean?
::你可能听说过"在你的DNA里" 这是什么意思?Nucleic acids. Essentially the "instructions" or "blueprints" of life. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or , is the unique blueprints to make the that give you your traits. Half of these blueprints come from your mother, and half from your father. And they come in different combinations every time. In fact, every couple - every man and woman that has every lived - together has over 64,000,000,000,000 combinations of their , which is where the DNA is found. Therefore, every person that has ever lived - except for identical twins - has his or her own unique set of blueprints - or instructions - or DNA.
::核糖核酸。 生命中的“ 指示” 或“ 蓝印 ” 。 脱氧核糖核酸, 或者 , 是制造你特质的独特蓝图。 这些蓝图有一半来自你的母亲, 一半来自你的父亲。 它们每次都有不同的组合。 事实上, 每对夫妇—— 每一个生活在一起的男女—— 都有超过64,000,000万个组合, DNA就是在那里找到的。 因此, 每一个曾经生活过的人—— 除了相同的双胞胎之外—— 都有自己独特的蓝图—— 或指示—— 或DNA。Nucleic Acids
::核酸Nucleic acids are that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. They are made of smaller units called nucleotides . Nucleic acids are named for the of the , where some of them are found. Nucleic acids are found not only in all living cells but also in . Types of nucleic acids include deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) .
::核酸是指含有碳、氢、氧、氮和磷的核酸,由称为核糖核酸的较小单位制成。核酸在发现部分核酸的地方被命名为核酸。核酸不仅存在于所有活细胞中,也存在于核酸中。核酸的类型包括脱氧核糖核酸(DNA)和核糖核酸(RNA)。Structure of Nucleic Acids
::核酸结构A nucleic acid consists of one chain (in RNA) or two chains (in DNA) of nucleotides held together by chemical bonds . Each individual nucleotide unit consists of three parts:
::核酸包括一个链条(在RNA)或两个链条(在DNA中)的核糖酸,这些链条由化学链条合在一起。-
a base (containing nitrogen)
::a 基数(含氮) -
a sugar (ribose in
, deoxyribose in DNA)
::a 糖(在DNA中脱氧核糖核酸) -
a phosphate group (containing phosphorus)
::a 磷酸盐类(含磷)
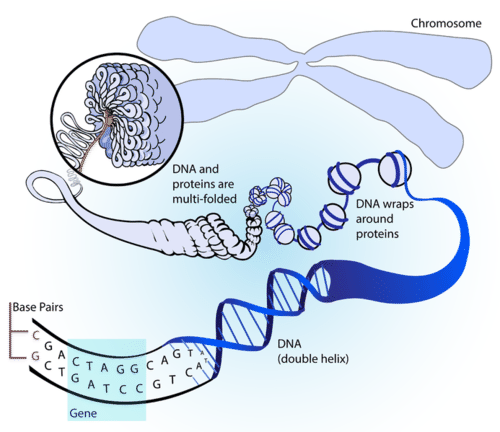
The sugar of one nucleotide binds to the phosphate group of the next nucleotide. Alternating sugars and phosphate groups form the backbone of a nucleotide chain, as shown in Figure . The bases, which are bound to the sugars, protrude from the backbone of the chain. In DNA, pairs of bases-one from each of two nucleotides-form the middle section of the molecule.
::如图所示,一个核核糖化物的糖与下一个核酸化物的磷酸盐组结合,交替糖和磷酸盐组构成核酸化物链的脊柱,如图所示。这些基底与糖结合,从链的脊柱中涌出。在DNA中,两个核酸化物-分子的中间部分,每两个核酸化物-形态的基底一对。Part of a Nucleic Acid (DNA). This small section of a nucleic acid shows how phosphate groups and sugars alternate to form the backbone of a nucleotide chain. The bases that jut out to the side from the backbone are adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. Hydrogen bonds between complementary bases, such as between adenine and thymine, hold the two chains of nucleotides together.
::核酸(DNA)的一部分。 核酸的这一小部分表明磷酸组和糖是如何交替形成核酸链的脊柱的。 从脊柱到侧面的基底是、胸腺、细胞素和guanine。 补充基底之间的氢联系,如和腺,将核酸的两个链连接在一起。RNA consists of a single chain of nucleotides, and DNA consists of two chains of nucleotides. Bonds form between the bases on the two chains of DNA and hold the chains together ( Figure ). There are four different types of bases in a nucleic acid molecule: cytosine (C), adenine (A), guanine (G), and either thymine (T) (in DNA) or uracil (U) (in RNA). Each type of base bonds with just one other type of base. Cytosine and guanine always bond together, and adenine and thymine (or uracil) always bond with one another. The pairs of bases that bond together are called complementary bases .
::RNA由单一的核糖核酸链组成,DNA由两条核酸链组成。在DNA两链的基底之间形成债券,并将链子绑在一起(图 )。核酸分子有四种不同类型的基底:细胞素(C),腺素(A),腺素(G),以及胸腺(T)(DNA)或核酸(U)(RNA)。每种基底关系只有另一种基底。Cytosine和guanine总是联系在一起,腺素和甲胺(或尿素)总是相互结合。连接在一起的基底被称为互补基底。The binding of complementary bases allows DNA molecules to take their well-known shape, called a double helix . Figure shows how two chains of nucleotides form a DNA double helix. A simplified double helix is illustrated in Figure . It shows more clearly how the two chains are intertwined. The double helix shape forms naturally and is very strong. Being intertwined, the two chains are difficult to break apart. This is important given the fundamental role of DNA in all living organisms .
::互补基点的结合使得DNA分子能够呈现出其众所周知的形状,称为双螺旋。图中显示了两个核糖核酸链是如何形成DNA双螺旋的。一个简化的双螺旋在图中展示了。它更清楚地显示了两个链的交织。双螺旋形状的自然形态非常强大。两个链因相互交织而难以分解。鉴于DNA在所有生物中的基本作用,这一点很重要。DNA Molecule. Hydrogen bonds between complementary bases help form the double helix of a DNA molecule. The letters A, T, G, and C stand for the bases adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. The sequence of these four bases in DNA is a code that carries instructions for making proteins. Shown is a representation of how the double helix folds into a chromosome. In this double-stranded nucleic acid, complementary bases (A and T, C and G) form hydrogen bonds that hold the two nucleotide chains together in the shape of a double helix. Notice that A always bonds with T and C always bonds with G. The hydrogen bonds help maintain the double helix shape of the molecule.
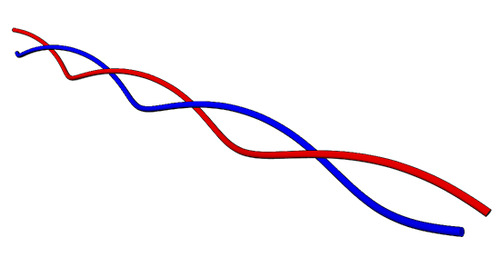
::DNA 分子 分子 。 互补基点之间的氢系有助于形成DNA分子的双螺旋。 字母 A、 T、 G 和 C 代表子宫、 胸腺、 guanine 和 cytosine 。 DNA 中这四个基点的序列是含有蛋白质制作指令的代码。 显示代表了双螺旋如何折成染色体。 在这个双弦核酸中, 互补基点( A 和 T 、 C 和 G) 形成氢结, 以双螺旋形状将两个核核酸链连接在一起。 注意 A 总是与 T 和 C 总是与 G 挂钩 。 氢 键有助于保持分子的双螺旋形状 。Simple Model of DNA. In this simple model of DNA, each line represents a nucleotide chain. The double helix shape forms when the two chains wrap around the same axis.
::简单的DNA模型。在这个简单的DNA模型中,每条线代表一个核酸链。当两条链环绕同一轴时,双螺旋形状会形成。Role of Nucleic Acids
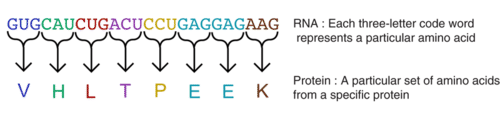
::核酸的作用The order of bases in nucleic acids is highly significant. The bases are like the letters of a four-letter alphabet. These "letters" can be combined to form "words." Groups of three bases form words of the . Each code word, called a codon , stands for a different amino acid . A series of many codons spells out the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide or protein ( Figure ). In short, nucleic acids contain the information needed for cells to make proteins. This information is passed from a body cell to its daughter cells when the cell divides. It is also passed from parents to their offspring when organisms reproduce.
::核酸基数的顺序非常重要 。 这些基数就像四字母字母字母的字母。 这些“ 字母” 可以合并成“ 字 ” 。 三个基数组组成 。 每个代码词, 称为codon , 代表不同的氨基酸 。 许多codon 串列了氨基酸的序列, 在聚苯酯或蛋白质中( Figure ) 。 简而言之, 核酸包含细胞制造蛋白所需的信息 。 当细胞分裂时, 这些信息会从身体细胞传到后代细胞中。 当生物繁殖时, 也会从父母传到后代 。How RNA codes for Proteins
::RNA 蛋白质编码如何The letters G, U, C, and A stand for the bases in RNA, specifically mRNA or messenger RNA. Each group of three bases makes up a codon, and each codon represents one amino acid (represented here by a single letter, such as V (valine), H (histidine), or L (leucine)). A string of codons specifies the sequence of amino acids in a protein.
::G、U、C和A字母表示RNA的基地,特别是 mRNA 或 送信 RNA 。 每组由三座基地组成一个codon, 每一个codon代表一种氨酸( 这里用一个字母表示, 如 V( valine )、 H( histedine ) 或 L( Leucine ) ) 。 一连串codon 指定了蛋白质中氨酸的序列 。DNA and RNA have different functions relating to the genetic code and proteins. Like a set of blueprints, DNA contains the genetic instructions for the correct sequence of amino acids in proteins. RNA uses the information in DNA to assemble the amino acids and make the proteins. More about the genetic code and the role of nucleic acids will be discussed in Concept Molecular Biology (Advanced) .
::RNA和DNARNA在遗传编码和蛋白质方面有不同功能,与一套蓝图一样,DNA含有蛋白质氨基酸正确序列的遗传指示。RNA利用DNA中的信息组装氨基酸和蛋白质。关于遗传编码和核酸作用的更多内容将在“分子生物学概念”(高级)中讨论。Adenosine Triphosphate
::亚丁磷酸三磷酸酯Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) , or Adenosine-5'-triphosphate, is another important nucleic acid. ATP is described as the " energy currency" of the cell or the "molecular unit of currency." One molecule of ATP contains three phosphate groups, and it is produced by ATP synthase from inorganic phosphate and adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or adenosine monophosphate (AMP). The structure of ATP consists of the purine base adenine, attached to the 1' carbon atom of the pentose sugar ribose. Three phosphate groups are attached at the 5' carbon atom of the pentose sugar. It is the removal of these phosphate groups that convert ATP to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and to AMP (adenosine monophosphate). ATP is produced during , and will be further discussed in the Cellular Respiration (Advanced) concepts.
::Adenosine Tri磷酸酯(ATP),或Adenosine-5'-tri磷酸,是另一个重要的核酸,ATP被称为细胞的“能量货币”或“货币分子单位”。ATP的一个分子含有三个磷酸组,由ATP合成酶从无机磷酸和二磷酸乙酯(ADP)或一磷酸乙烷(AMP)产生。ATP的结构由附于1糖碳原子的纯碱基亚丁组成。三种磷酸组附在五碳糖的碳原子上。这是将ATP转化为ADP(乙醇磷酸酯)和AMP(亚丁酸单磷酸)的磷酸酯组的清除。ATP的结构是在此期间产生的,并将在细胞呼吸(乙酸)概念中进一步讨论。ATP is used as a substrate in signal transduction pathways by kinases that phosphorylate proteins and , as well as by adenylate cyclase, which uses ATP to produce the second messenger molecule cyclic AMP (cAMP). The ratio between ATP and AMP determines the amount of available energy. This regulates the metabolic pathways that produce and consume ATP. Apart from its roles in energy metabolism and signaling, ATP is also incorporated into DNA and RNA by polymerases during both DNA replication and . When ATP is used in DNA synthesis, the ribose sugar is first converted to deoxyribose by ribonucleotide reductase.
::在信号传输路径中,磷酸甲酯蛋白和亚甲酸甲酯的动脉酶,以及使用亚甲酸甲酯生产第二信使分子循环AMP(CAMP)的亚甲酸酯环环环酶(ATP),ATP和AMP之间的比例决定了可用能量的量。ATP和AMP之间的比例对生产和消费亚甲酸乙酯的代谢途径进行调节。除其在能源代谢和信号方面的作用外,ATP还在DNA复制和DNA合成过程中被聚合酶纳入DNA和RNA。当DNA合成中使用亚甲酸甲酯时,糖首先通过肋核乳酸再溶酶转换为脱氧核糖。ATP. The ATP molecule clearly shows the three phosphate groups.
::ATP. ATP分子清楚地显示了三种磷酸盐组。Summary
::摘要-
Nucleic acids are organic compounds that consist of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus.
::核酸是由碳、氢、氧、氮和磷组成的有机化合物。 -
DNA, RNA and ATP are important nucleic acids.
::DNA、RNA和ATP是重要的核酸。 -
DNA and RNA are made up of repeating units called nucleotides. They contain genetic instructions for proteins, help synthesize proteins, and pass genetic instructions on to daughter cells and offspring.
::RNA和RNA由称为核糖核酸的重复单位组成,它们含有蛋白质的遗传说明,帮助合成蛋白质,并将遗传说明传给女儿细胞和后代。
Review
::回顾-
What is a nucleic acid?
::什么是核酸? -
Identify the three parts of a nucleotide.
::识别核糖核酸的三部分。 -
What is the structure of DNA?
::DNA的结构是什么? -
Bases in nucleic acids are represented by the letters A, G, C, and T (or U). How are the bases in nucleic acids like the letters of an alphabet?
::核酸基数由字母A、G、C和T(或U)表示。核酸基数如何像字母字母一样? -
Describe the role and structure of ATP.
::说明贸易援助方案的作用和结构。
-
a base (containing nitrogen)