2.9 解决办法 - 先进
章节大纲
-
Acids and bases. Why are these important in biology?
::酸和碱,为什么这些在生物学中重要?It comes back to a number of biological and biochemical processes. For example, some work best at specific pH levels of acids. Other need a relatively neutral environment to function properly. Take your stomach , a very acidic environment. The enzyme pepsin that works best in that acidic environment could not work in your mouth. What would your food taste like if your mouth was also a very acidic environment? Other biochemical reactions need a relatively neutral environment to function properly.
::它可以追溯到一些生物和生化过程。例如,有些在特定的pH值酸水平上最有效。另一些需要相对中性的环境才能正常运转。 取下你的胃, 一个非常酸化的环境。 在酸性环境中最有效的酶在你的嘴里是行不通的。 您的食物会尝到什么味道呢? 其它的生化反应需要相对中性的环境才能正常运转。Solutions
::解决方案解决方案is one of the most common ingredients in solutions. A solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances. In a solution, one substance is dissolved in another substance, forming a mixture that has the same proportion of substances throughout. The dissolved substance in a solution is called the solute . The substance in which it is dissolved is called the solvent . An example of a solution in which water is the solvent is salt water. In this solution, a solid—sodium chloride—is the solute. In addition to a solid dissolved in a liquid, solutions can also form with solutes and solvents in other . Examples are given in Table .
::一种溶液是由两种或两种以上物质组成的同质混合物; 一种溶液,一种物质溶解于另一种物质中,形成一种混合物,其整个物质的比例相同; 溶液中的溶解物质称为溶液; 溶解物质称为溶剂; 溶解物质称为溶剂; 溶剂为溶液的溶液的一个例子是盐水; 在溶液中,固氯化钠为溶液; 除了溶解于液体中的固态外,溶液也可以与溶液和溶剂形成。Solutions and Three States of Matter Gas Liquid Solid Gas Oxygen and other gases in nitrogen (air) Liquid Carbon dioxide in water (carbonated water) Ethanol (an alcohol) in water Sodium chloride in water (salt water) Solid Hydrogen gas in metals Mercury in silver and other metals (dental fillings) Iron in carbon (steel) The ability of a solute to dissolve in a particular solvent is called solubility . Many chemical substances are soluble in water. In fact, so many substances are soluble in water that water is called the universal solvent. Water is a strongly polar solvent, and polar solvents are better at dissolving polar solutes. Many and other important biochemicals are polar, so they dissolve well in water. On the other hand, strongly polar solvents like water cannot dissolve strongly nonpolar solutes like oil. Did you ever try to mix oil and water? Even after being well shaken, the two substances quickly separate into distinct layers.
::溶液溶解于某一溶剂中的溶解剂的能力被称为溶解性。 许多化学物质在水中可以溶解。 事实上,许多物质在水中可以溶解,因此水被称为普遍溶解剂。 水是一种强烈的极地溶解剂,极地溶剂在溶解极地溶解溶液方面效果更好。 许多重要的生化化学品是极地的,因此在水中溶解。 另一方面,像水这样的极地溶解剂不能溶解极非极地溶液,例如油。 你有没有尝试过混合石油和水? 即使在摇晃之后,这两种物质很快被分解为不同的层。Acids and Bases
::酸和碱基Water is the solvent in solutions called acids and bases. To understand acids and bases, it is important to know more about pure water, in which nothing is dissolved. In pure water (such as distilled water), a tiny fraction of water molecules naturally breaks down, or dissociates, to form ions . An ion is an electrically charged atom or molecule. The dissociation of pure water into ions is represented by the chemical equation :
::水是溶液中的溶剂,溶液称为酸和碱。为了了解酸和碱,重要的是要更多地了解纯水,其中没有任何溶解物。在纯水(如蒸馏水)中,一小部分的水分子自然分解或分离成离子。离子是电载原子或分子。纯水分解成离子,化学方程式代表了化学方程式:2 H 2 O → H 3 O + + OH - .
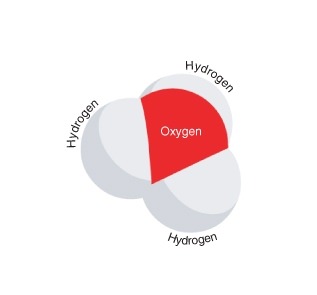
::2 H2O H3O+ + OH-。The products of this reaction are a hydronium ion (H 3 O + ) and a hydroxide ion (OH - ). The hydroxide ion is negatively charged. It forms when a water molecule donates, or gives up, a positively charged hydrogen ion. The hydronium ion, modeled in Figure , is positively charged. It forms when a water molecule accepts a positively charged hydrogen ion (H + ).
::这种反应的产物是氢离子(H3O+)和氢氧化离子(OH-),氢氧化离子为负电荷。当水分子捐赠或放弃正电离子时,氢氧化离子形成。以图3为模型的氢离子为正电荷。当水分子接受正电离子(H+)时,氢离子形成正电荷。A hydronium ion has the chemical formula H 3 O + . The plus sign ( + ) indicates that the ion is positively charged. How does this molecule differ from a water molecule?
::氢离子具有化学公式H3O+。加号(+)表示正电离。该分子与水分子有何不同?Acidity and pH
::酸性和pH值Acidity refers to the hydronium ion concentration of a solution. It is measured by pH . In pure water, the hydronium ion concentration is very low. Only about one in ten million water molecules naturally dissociates to form a hydronium ion in pure water. This gives water a pH of 7. The hydronium ions in pure water are also balanced by hydroxide ions, so pure water is neutral (neither an acid nor a base).
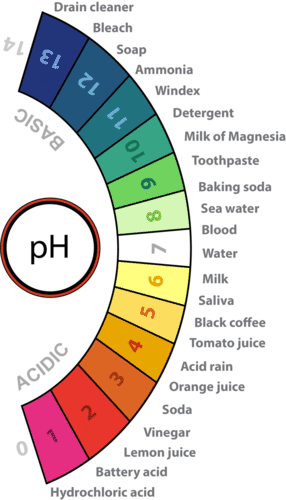
::酸度是指溶液的氢离子浓度。它用pH值测量。在纯水中,氢离子浓度非常低。在1,000万个水分子中,只有1个自然分解,形成纯水中的氢离子。这使水的pH值为7。纯水中的氢离子也由氢氧化离子平衡,因此纯水是中和的(既非酸也非碱)。Because pure water is neutral, any other solution with the same hydronium ion concentration and pH is also considered to be neutral. If a solution has a higher concentration of hydronium ions and lower pH than pure water, it is called an acid . If a solution has a lower concentration of hydronium ions and higher pH than pure water, it is called a base . Several acids and bases and their pH values are identified on the pH scale, which ranges from 0 to 14, in Figure .
::由于纯水是中性的,同一氢离子浓度和pH值的其他任何溶液也被认为是中性的。如果溶液的氢离子浓度高于纯水,而pH值低于纯水,则称为酸。如果溶液的氢离子浓度低于纯水,而pH值高于纯水,则称为基数。在pH尺度上确定了若干酸和基数及其pH值,在图1中,pH尺度介于0至14之间。Acidity and the pH Scale. Water has a pH of 7, so this is the point of neutrality on the pH scale. Acids have a pH less than 7, and bases have a pH greater than 7. Approximate pHs of examples are depicted.
::酸度和 pH 比例。 水的pH值为 7, 所以这是pH 比例的中点 。 酸的pH值小于 7 , 碱的pH值大于 7 。 描述了大约 pH值的示例。The pH scale is a negative logarithmic scale. Because the scale is negative, as the ion concentration increases, the pH value decreases. In other words, the more acidic the solution, the lower the pH value. Because the scale is logarithmic, each one-point change in pH reflects a ten-fold change in the hydronium ion concentration and acidity. For example, a solution with a pH of 6 is ten times as acidic as pure water with a pH of 7.
::pH 比例尺是一个负对数尺度。 因为比例尺是负的, 随着离子浓度的增加, pH 值会下降。 换句话说, 溶液酸度越高, pH 值越低。 由于比例尺是对数的, pH 的每个点变化都反映了氢离子浓度和酸度的十倍变化。 例如, pH 值为 6 的溶剂是纯水的十倍, pH 值是 7 的纯水的十倍。Acids
::酸酸An acid can be defined as a hydrogen ion donor. The hydrogen ions bond with water molecules, leading to a higher concentration of hydronium ions than in pure water. For example, when hydrochloric acid (HCl) dissolves in pure water, it donates hydrogen ions (H + ) to water molecules, forming hydronium ions (H 3 O + ) and chloride ions (Cl - ). This is represented by the chemical equation:
::氢离子结合与水分子,导致氢离子浓度高于纯水。例如,当盐酸(HCl)在纯水中溶解时,它将氢离子(H+)捐赠给水分子,形成氢离子(H3O+)和氯化离子(Cl-)。这表现为化学方程式:HCl + H 2 O → Cl - + H 3 O + .
::HCl + H2O Cl-+ H3O+ Cl-+ H3O+。Strong acids can be harmful to organisms and damaging to materials. Acids have a sour taste and may sting or burn the skin. Testing solutions with litmus paper is an easy way to identify acids. Acids turn blue litmus paper red.
::强酸可能对生物有害,对物质有害。酸有酸味,可能会刺伤皮肤或烧伤皮肤。用利木纸测试溶液很容易识别酸。酸会变成蓝石纸红色。Bases
::基底A base can be defined as a hydrogen ion acceptor. It accepts hydrogen ions from hydronium ions, leading to a lower concentration of hydronium ions than in pure water. For example, when the base ammonia (NH 3 ) dissolves in pure water, it accepts hydrogen ions (H + ) from hydronium ions (H 3 O + ) to form ammonium ions (NH 4 + ) and hydroxide ions (OH - ). This is represented by the chemical equation:
::碱可定义为氢离子接收器,接受氢离子氢离子氢离子,导致氢离子浓度低于纯水中浓度。例如,当基氨(NH3)在纯水中溶解时,它接受氢离子(H3O+)氢离子(HH)形成铵离子(NH4+)和氢氧化离子(OH-)。NH 3 + H 2 O → NH 4 + + OH - .
::NH3 + H2O + NH4+ + OH-。Like strong acids, strong bases can be harmful to organisms and damaging to materials. Bases have a bitter taste and feel slimy to the touch. They can also burn the skin. Bases, like acids, can be identified with litmus paper. Bases turn red litmus paper blue.
::像强酸一样,坚固的基底对生物有害,对物质有害。 基底的味道很苦,对触摸感到粘糊糊的味道。它们也可以烧皮肤。 基底,如酸,可以用利特姆纸来识别。 基底可以把红柱纸变成蓝色。Neutralization
::失效What do you think would happen if you mixed an acid and a base? If you think the acid and base would “cancel each other out,” you are right. When an acid and base react, they form a neutral solution of water and a salt (a molecule composed of a positive and negative ion). This type of reaction is called a neutralization reaction . For example, when the base sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) react, they form a neutral solution of water and the salt sodium chloride (NaCl). This reaction is represented by the chemical equation:
::如果将酸和碱混合在一起,你会认为会发生什么?如果你认为酸和碱会“相互分离 ” , 你说得对。当酸和碱反应时,它们会形成水和盐的中性溶液(由正和负离子组成的分子 ) 。这种反应被称为中性反应。例如,当碱氢氧化钠(NaOH)和盐酸(HCl)反应时,它们会形成水和氯化钠(NaCl)的中性溶液。这种反应表现为化学方程式:NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H 2 O.
::NaOH + HCl NaCl + H2O。In this reaction, hydroxide ions (OH - ) from the base combine with hydrogen ions (H + ) from the acid to form water. The other ions in the solution (Na + ) and (Cl - ) combine to form sodium chloride.
::在这一反应中,基底的氢氧化离子(OH-)与从酸到形成水的氢离子(H+)结合,溶液(Na+)和(Cl-)中的其他离子结合形成氯化钠。Acids and Bases in Organisms
::生物体中的酸和碱Enzymes are needed to speed up biochemical reactions. Most enzymes require a specific range of pH in order to do their job. For example, the enzyme pepsin , which helps break down in the human stomach, requires a very acidic environment in order to function. Strong acid is secreted into the stomach, allowing pepsin to work. Once the contents of the stomach enter the , where most digestion occurs, the acid must be neutralized. This is because enzymes that work in the small intestine need a basic environment. An organ near the small intestine, called the pancreas , secretes bicarbonate ions (HCO 3 - ) into the small intestine to neutralize the stomach acid.
::需要酶来加速生化反应。 大部分酶需要一定范围的pH, 才能完成它们的工作。 例如, 有助于人类胃破裂的酶epsin 需要一种非常酸化的环境才能起作用。 强酸被隐蔽在胃里, 允许 pepsin 工作。 一旦胃部进入, 大部分消化发生, 酸必须中和。 这是因为在小肠部工作的酶需要一个基本的环境。 一个小肠部位附近的器官, 叫做 Pancreas , 将双碳酸离子( HCO3 - ) 分解到小肠部, 以中和胃酸 。Bicarbonate ions play an important role in neutralizing acids throughout the body. Bicarbonate ions are especially important for protecting tissues of the from changes in pH. The central nervous system includes the brain , which is the body's control center. If pH deviates too far from normal, the central nervous system cannot function properly. This can have a drastic effect on the rest of the body.
::生物碳酸离子在使整个身体酸失效方面起着重要作用。 生物碳酸离子对于保护pH值变化的组织特别重要。 中枢神经系统包括大脑,这是人体的控制中心。 如果pH值偏离正常水平太远, 中枢神经系统无法正常运转。 这可能对身体的其余部分产生剧烈影响 。Summary
::摘要-
A solution is a homogeneous mixture in which a solute dissolves in a solvent. Water is a very common solvent, especially in organisms.
::溶液是一种同质混合物,溶液溶解在溶剂中溶解,水是一种非常常见的溶剂,特别是在生物体中。 -
The ion concentration of neutral, pure water gives water a pH of 7 and sets the standard for defining acids and bases. Acids have a pH lower than 7, and bases have a pH higher than 7.
::中性、纯净水的离子浓度使水的pH值为7,并规定了界定酸和碱的标准。酸的pH值低于7,碱的pH值高于7。
Review
::回顾-
What is pH?
::什么是PH? -
Define solution, and give an example of a solution.
::定义解决方案, 并给出一个解决方案的示例 。 -
What is the pH of a neutral solution? Why?
::中性解决方案的pH值是什么?为什么? -
What type of reaction is represented by this chemical equation: KOH + HCl → KCl + H
2
O? Defend your answer.
::此化学方程式代表何种反应: KOH + HCl KCl + H2O? 捍卫您的回答 。 -
What is pepsin and give an example of how the body neutralizes its environment?
::Pepsin是什么呢? 举个例子来说明身体是如何使环境中和的?
-
A solution is a homogeneous mixture in which a solute dissolves in a solvent. Water is a very common solvent, especially in organisms.