2.10 水与生命-高级
章节大纲
-
Is condensation just in clouds?
::凝结在云中吗?Condensation occurs in your constantly. It occurs in the form of a chemical reaction . These condensation reactions involve the formation of a molecule from two other molecules. Water forms when two molecules, such as amino acids or monosaccharides , are joined together. The amino acids join together to form peptides (or polypeptides or proteins) and the monosaccharides join together to form disaccharides or polysaccharides .
::凝聚会持续发生在您体内。 它会以化学反应的形式发生。 这些凝聚反应会从另外两个分子中形成分子。 当两个分子, 如氨基酸或单亚焦酸等, 结合在一起时, 水的形式。 氨基酸会结合成peptides( 或聚苯醚或蛋白) , 单亚酸会合在一起形成不相干或聚沙酸 。Water and Life
::水与生命Humans are composed of about 60-70 percent water (not counting water in body fat). This water is crucial for the normal functioning of the body. Water’s ability to dissolve most biologically significant compounds—from inorganic salts to large organic molecules—makes it a vital solvent inside organisms and cells.
::人类由大约60%-70%的水组成(不包括体脂肪中的水 ) 。 这种水对于身体的正常运转至关重要。 水溶解最重要的生物化合物的能力 — — 从无机盐到大型有机分子 — — 使水成为生物和细胞中重要的溶剂。Water is an essential part of most metabolic processes within organisms. Metabolism is the sum total of all body reactions, including those that build up molecules ( anabolic reactions ) and those that break down molecules ( catabolic reactions ). In anabolic reactions, water is generally removed from small molecules in order to make larger molecules. In catabolic reactions, water is used to break bonds in larger molecules in order to make smaller molecules.
::水是生物中大多数代谢过程的一个基本部分。代谢性是指所有身体反应的总和,包括分子积聚的总和,包括分子积聚的总和(血管反应 ) 和分子分裂的总和(代谢性反应 ) 。 在代谢性反应中,水一般从小分子中去除,以产生更大的分子。在代谢性反应中,水被用来断裂较大分子的联结,以制造较小的分子。Water is central to two related, fundamental metabolic reactions in organisms: and . All organisms depend directly or indirectly on these two reactions. In photosynthesis, cells use the energy in sunlight to change water and carbon dioxide into glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ) and oxygen (O 2 ). This is an anabolic reaction , represented by the chemical equation :
::在光合作用中,细胞利用阳光中的能量将水和二氧化碳转化为甘蔗(C6H12O6)和氧(O2)。6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + energy → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 .
::6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 能源 C6H12O6 + 6 O2。In cellular respiration, cells break down glucose in the presence of oxygen and release energy, water, and carbon dioxide. This is a catabolic reaction, represented by the chemical equation:
::在细胞呼吸中,细胞在氧气和释放能量、水和二氧化碳的情况下分解葡萄糖。这是一种代谢反应,以化学方程式为代表:C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 → 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + energy
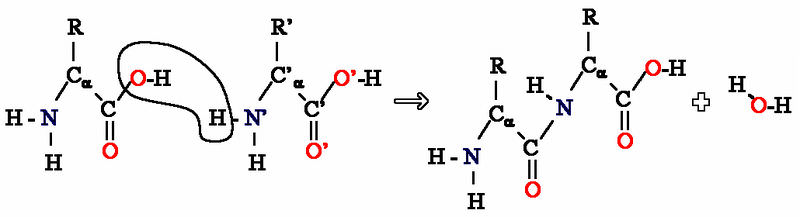
::C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 O2 + 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 能源Two other types of reactions that occur in organisms and involve water are dehydration and hydration reactions. A dehydration reaction occurs when molecules combine to form a single, larger molecule and also a molecule of water. (If some other small molecule is formed instead of water, the reaction is called by the more general term, condensation reaction .) It is a type of anabolic reaction. An example of a dehydration reaction is the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids in a polypeptide chain. When two amino acids bond together, a molecule of water is lost. This is shown in the Figure .
::在有机体中发生并涉及水的另外两类反应是脱水和水化反应。当分子组合成一个单一的、更大的分子和水的分子时,就会发生脱水反应。 (如果形成一些其他小分子而不是水,反应就叫作更一般的词,凝结反应。 )这是一种代谢反应。脱水反应的一个例子是在聚苯二酸链中氨基酸之间形成酸联系。当两个氨基酸结合在一起时,水的分子就会消失。图中显示了这一点。In this dehydration reaction, two amino acids form a peptide bond. A water molecule also forms. A hydration reaction is the opposite of a dehydration reaction. A hydration reaction adds water to an organic molecule and breaks the large molecule into smaller molecules. Hydration reactions occur in an acidic water solution. An example of hydration reaction is the breaking of peptide bonds in polypeptides. A hydroxide ion (OH - ) and a hydrogen ion (H + ) (both from a water molecule) bond to the carbon atoms that form the peptide bond. This breaks the peptide bond and results in two amino acids.
::水分反应与脱水反应正好相反。水分反应使水添加到有机分子中,并将大分子分解成较小的分子。水分反应发生在酸水溶液中。水分反应的一个例子是聚苯醚中的结断。氢氧化离子(OH)和氢离子(H+)(两者都是水分子)与形成peptide联结的碳原子的联结。这打破了水分联结,导致两种氨基酸。Water is essential for all of these important chemical reactions in organisms. As a result, virtually all life processes depend on water. Clearly, without water, life as we know it could not exist.
::水是生物中所有这些重要化学反应的关键。 因此,几乎所有生命过程都依赖于水。 显然,没有水,我们知道生命不可能存在。Summary
::摘要-
Water is essential for most life processes, including photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and other important chemical reactions that occur in organisms.
::水对大多数生命过程至关重要,包括光合作用、细胞呼吸和生物体中发生的其他重要化学反应。
Review
::回顾-
What percent of humans are composed of water?
::水是人类的多少比例? -
Summarize how metabolism in organisms depends on water.
::总结生物体中的新陈代谢如何依赖水。 -
What is a condensation reaction?
::什么是凝聚反应? -
Distinguish between anabolic and catabolic reactions.
::区分新陈代谢反应和新陈代谢反应。 -
Distinguish between hydration and dehydration reactions.
::水分和脱水反应之间的区别。
-
Water is essential for most life processes, including photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and other important chemical reactions that occur in organisms.