3.18 与性有关的悲剧 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
What number can you see?
::你看到多少号码了?Red-green colorblindness is a common inherited trait in humans. About 1 in 10 men have some form of color blindness, however, very few women are color blind. Why?
::红绿色盲是人类常见的遗传特征。 大约十分之一的男性有某种颜色失明,然而,很少有女性是颜色失明。 为什么?Sex-Linked Genes
::性链接的基因Sex-linked genes are located on either the X or Y chromosome , though it more commonly refers to genes located on the X- . For that reason, the genetics of sex-linked (or X-linked ) diseases, disorders due to in genes on the X-chromosome, results in a phenotype usually only seen in males. Can you explain why?
::性相关基因位于X或Y染色体上,尽管它更经常地指X-的基因。 因此,性相关(或X-相关)疾病的遗传学、因X-染色体上的基因造成的疾病,导致一种苯型,通常只见于男性。你能解释原因吗?In humans, the Y chromosome spans 58 million bases and contains about 78 to 86 genes, which code for only 23 distinct , making the Y chromosome one of the smallest chromosomes. The X chromosome , on the other hand, spans more than 153 million bases and represents about 5% of the total in women's , 2.5% in men's cells. The X chromosome contains about 2,000 genes, however few, if any, have anything to do with sex determination. The Y chromosome is the sex-determining chromosome in humans and most other mammals . In mammals, it contains the gene SRY (sex-determining region Y), which encodes the testes-determining factor and triggers testis , thus determining sex. It is the presence or absence of the Y chromosome that determines sex.
::在人类中,Y染色体横跨5 800万个基数,包含大约78至86个基因,这些基因只有23个不同的代号,使Y染色体成为最小的染色体之一。另一方面,X染色体覆盖1.53亿个基数,占女性总数的5%,男性细胞占2.5%。X染色体包含大约2 000个基因,尽管与性别确定有关,但数量很少。Y染色体是人类和大多数哺乳动物的性别确定染色体。在哺乳动物中,它包含SRY基因(性确定区域Y),它包含测试确定因素和触发测试的基因,从而确定性别。是Y染色体的存在与否决定了性别。X-Inactivation
::X 激活Early in embryonic development in females, one of the two X chromosomes is randomly inactivated in nearly all somatic cells. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by packaging into transcriptionally inactive heterochromatin. This process, called X-inactivation , ensures that females, like males, have only one functional copy of the X chromosome in each cell. X-inactivation creates a Barr body, named after their discover, Murray Barr. The Barr body chromosome is generally considered to be inactive, however there are a small number of genes that remain active and are expressed. Inactivating one X chromosome prevents any detrimental effects of having twice as many X-linked genes as males. X-inactivation is a dosage compensation process.
::在雌性胚胎早期发育中,两种X染色体中的一种在几乎所有的体细胞中随机失去活性。不活跃的X染色体通过包装成转录不活跃的异色素而消散。这一过程称为X不活跃,确保雌性与雄性一样,每个细胞中只有一个X染色体的功能复制件。X不活跃产生一个巴尔氏体,以其发现命名,Murray Barr。巴尔氏体染色体一般被认为是不活跃的,但有少数基因仍然活跃并表现。不活跃的一个X染色体防止产生比雄性多一倍的X联系基因的任何有害影响。X不活跃是一种剂量补偿过程。XIST and TSIX
::十一ST和三IXplays an important role in X inactivation. Specifically, two noncoding, complementary RNAs, XIST and TSIX, initiate and control the inactivation process. XIST, or X-inactive specific transcript, was discovered due to its specific expression from inactive female X chromosomes. XIST has four unique properties:
::具体地说,两个非编码、补充RNA、XIST和TISIX,启动和控制不激活过程。-
The XIST gene produces a 17 kilo base (kb) RNA molecule; the RNA is not translated into a protein.
::XIST基因产生17公斤基(kb)RNA分子;RNA没有转化为蛋白质。 -
The XIST gene is only expressed in cells containing at least two X chromosomes; it is not normally expressed in XY cells. Cells with more than two X chromosomes have higher levels of XIST RNA, resulting in the inactivation of the additional X chromosomes. The result is that only one X chromosome per cell can remain active.
::XIST基因仅以含有至少两个X染色体的细胞表示;通常不以XY细胞表示;两个以上X染色体的细胞具有XIST RNA的较高水平,导致其他X染色体的无活性,结果是每个细胞只能保持一个X染色体。 -
XIST RNA remains in the
where it binds to the chromosome from which it is produced.
::XIST RNA仍与生产该物质时的染色体相连。 -
XIST RNA recruits additional silencing proteins to bind to the inactive X chromosome.
::XIST RNA 招聘了额外的静态蛋白质,与非活性X染色体结合。
TSIX, on the other hand, does the opposite of XIST. Notice that TSIX is XIST backwards. TSIX is XIST's antisense partner. The TSIX gene is transcribed in the opposite direction of the XIST gene, and it is transcribed across the entire XIST gene. TSIX is a 40 kb noncoding RNA transcribed from the X chromosome that does not produce the XIST RNA.
::另一方面,TSIX则与XIST相反。请注意,TSIX是 XIST 向后。TSIX是 XIST 的抗感伙伴。TSIX 基因被转录为XIST 基因的相反方向,并被转录为整个XIST 基因。TSIX 是来自X染色体的40 kb 非编码 RNA 转录,不会产生 XIST RNA 。There is an inverse relationship between TSIX and XIST expression. The X chromosome that expresses XIST does not transcribe TSIX as XIST expression leads to inactivation of that same X chromosome. On the other X chromosome, TSIX is expressed and XIST is not. This suggests that TSIX is required to block XIST expression on the active X chromosome, keeping that chromosome from being inactivated.
::TIX 表达式和 XIST 表达式之间存在反向关系。 X 表达 XIST 的 X 染色体不会将 TSIX 转换为 XIS 表达式, 因为 XIST 表达式导致相同的 X 染色体停止活动。 在其他 X 染色体中, TSIX 表达式被表达, 而 XIST 则不是 。 这意味着TIS 需要阻止 XST 表达式在活性 X 染色体上, 保持该染色体不被激活 。Sex-Linked Traits
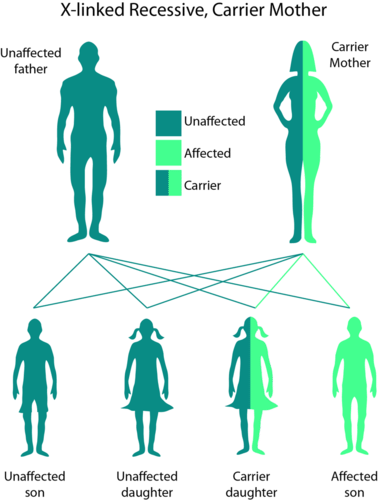
::与性有关的悲剧Inheritance of Sex Chromosomes. Mothers pass only X chromosomes to their children. Fathers always pass their X chromosome to their daughters and their Y chromosome to their sons. Can you explain why fathers always determine the sex of the offspring? Traits controlled by genes located on the sex chromosomes (X and Y) are called sex-linked traits ( Figure ). Remember, females have two X chromosomes and males have a X and a Y chromosome. Therefore, any recessive allele on the X chromosome of a male will not be masked by a dominant allele . X-linked traits include the hemophilia and color blindness. Hemophilia is the name of a family of hereditary genetic illnesses that impair the body's ability to control coagulation. Color Blindness, or color deficiency, in humans is the inability to perceive differences between some or all colors that other people can distinguish.
::由性染色体(X和Y)上的基因控制的外壳被称为与性有关的特性(Figure)。记住,雌性有2个X染色体,雄性有1个X和Y染色体。因此,男性的X染色体上的任何消退性异系不会被占支配地位的异族所遮盖。与X有关的特性包括血友病和色盲。血友病是影响身体控制凝固能力的遗传遗传遗传性疾病家族的名称。在人类中,色盲或色弱是无法察觉到他人可以辨别的某种或所有颜色之间的差异。X-linked recessive inheritance. As boys have only one X-chromosome, if they inherit the mutant allele from their mother, they will possess the phenotype that results from that allele. As shown in this example for color blindness, mothers pass the recessive allele for the trait to their sons, who pass it to their daughters. Hemophilia
::血友病Hemophilia is a group of diseases in which does not clot normally. Factors in the blood are involved in clotting. When you bleed, your body begins a coagulation cascade of reactions, involving special proteins known as coagulation factors to stop that bleeding. When one or more of these clotting factors are missing, there is a higher chance of having difficulties stopping the bleeding. Hemophiliacs lacking the normal Factor VIII are said to have Hemophilia A (or Factor VIII deficiency), the most common form. Hemophilia is a genetic disease, passed down through the family. It is linked to the X chromosome, so it mostly affects males. F8 is the gene for the Factor VIII protein. Mutations in the F8 gene lead to the production of an abnormal version of coagulation factor VIII, or reduce the amount of the protein. The altered or missing protein cannot participate effectively in the blood clotting process.
::血友病是一种通常不会凝血的疾病。血液中的因素与凝血有关。当你流血时,你的身体开始出现一种凝聚反应,其中含有特殊蛋白质,被称为凝凝因素,以阻止血流。如果缺少一个或多个凝凝血因素,则很难止血。缺乏正常系数八的血友病据说有血友病A(或因子八缺乏症),最常见的形式是血友病A(或因子八缺乏症),血友病是一种遗传疾病,通过家庭传下来。血友病与X染色体有关,因此主要影响男性。F8是系数八蛋白的基因。F8基因突变导致产生异常的血清系数八,或减少蛋白质的数量。改变或缺失的蛋白无法有效地参与血凝结过程。England's Queen Victoria was a carrier of this disease. The was passed to two of her daughters and one son. Since royal families in Europe commonly intermarried, the allele spread, and may have contributed to the downfall of the Russian monarchy.
::英国王后维多利亚曾是这种疾病的携带者。这个疾病被传给了两个女儿和一个儿子。由于欧洲的皇室家庭通常是异族通婚,因此,异族相传,并可能促成了俄罗斯君主制的垮台。Hemophilia B is another type of hemophilia, caused by a mutation in the F9 gene, resulting in an abnormal Factor IX protein. This protein is normally also involved in the coagulation cascade. Hemophilia B is also caused by an inherited X-linked recessive trait, with the defective gene located on the X chromosome.
::血友病B是另一类血友病,由F9基因突变导致,导致出现一种不正常的因数九蛋白质,这种蛋白质通常也包含在凝固级联中,血友病B也是由继承的与X有关的后继特征造成的,其缺陷基因位于X染色体上。Von Willebrand disease is the most common hereditary bleeding disorder. Von Willebrand disease is caused by a deficiency of von Willebrand factor, which helps blood platelets clump together and stick to the wall. This is necessary for normal blood clotting. The von Willebrand factor (VWF) gene is located on chromosome 12.
::Von Willebrand疾病是最常见的遗传性出血紊乱症。 Von Willebrand疾病是由von Willebrand的缺陷引起的,它有助于血小板凝结并粘在墙上。这是正常血凝结所必须的。 von Willebrand (VWF) 基因位于染色体12上。Color Blindness
::颜色盲度Genetic red-green color blindness affects men much more often than women, because the genes for the red and green color receptors are located on the X chromosome. Females are red-green color blind only if both of their X chromosomes carry the defective gene, whereas males are color blind if their single X chromosome carries the defective gene. As males have only one X-chromosome, the gene for red-green color blindness is transmitted from a color blind male to all his daughters, who are usually heterozygous carriers and, therefore, unaffected ( Figure ) . Subsequently, this carrier woman has a fifty percent chance of passing on an X chromosome with a defective gene to each of her male offspring. The sons of an affected male will not inherit the trait from him since they receive his Y chromosome and not his X chromosome. Should an affected male have children with a carrier or colorblind woman, their daughters may be colorblind by inheriting an X chromosome with the mutant gene from each parent.
::红绿色色盲对男性的影响比对女性的影响大得多,因为红色和绿色受体的基因位于X染色体上。只有当女性的X染色体同时含有有缺陷的基因时,女性才具有红绿色色盲,而男性的单一X染色体携带有缺陷的基因时,男性才具有色盲。由于男性只有一个X色色素,红绿色失盲的基因从一个色盲男性传给其所有女儿,这些女儿通常是异体携带者,因此不受影响(Figure )。随后,该女性携带者拥有50%的机会将带有缺陷基因的染色体传给其每个男性后代。一个受影响的男性的儿子不会继承他的特征,因为他们得到了他的Y色素,而不是他的X色色色素。如果受影响的男性有孩子,或者有色盲妇女,那么她们的女儿可能通过继承每个父母的变异基因而成为X色色色素。Inheritance of Sex Chromosomes. Female parents pass only X chromosomes to their offspring. Male parents always pass their X chromosome to their female offspring and their Y chromosome to their male offspring. Color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. Female parents pass the recessive allele for the trait to their male offspring, who pass it to their female offspring. Muscular Dystrophy
::肌肉萎缩Muscular dystrophy is a term encompassing a variety of muscle wasting diseases. The most common type, Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) , affects cardiac and , as well as some mental functions. DMD is caused by a defective gene for dystrophin, a protein prevalent in skeletal and cardiac . DMD is an X-linked recessive disorder occurring in 1 in 3,500 male newborns. Because DMD is X-linked, no females are affected. Most affected individuals die before their 20th birthday. Daughters of female carriers of the mutant allele have a 50% chance of also being carriers.
::肌肉萎缩是一个术语,包括各种肌肉消瘦疾病,最常见的类型是:Duchenne肌肉萎缩症(DMD),它影响心脏和某些心理功能。DMD是由骨骼和心脏中流行的一种蛋白质,即痢疾的缺陷基因造成的。DMD是3 500名新生儿中1名男性患的与X有关的休眠障碍。由于DMD与X有关,没有女性受到影响。受影响者大多在20岁生日前死亡。变种异异体女性携带者的女儿也有50%的携带者。The dystrophin gene, abbreviated DMD, is the largest known human gene. It is over 2 million base pairs long. In skeletal and cardiac muscles, dystrophin is part of a group of proteins (a protein complex) that work together to strengthen muscle fibers and protect them from injury as muscles contract and relax. The dystrophin complex acts as an anchor, connecting each muscle cell's cytoskeleton with the lattice of proteins and other molecules outside the cell (extracellular matrix). The dystrophin complex may also play a role in cell signaling by interacting with proteins that send and receive chemical signals. Many different mutations that result in DMD have been identified in the DMD gene. These mutations typically prevent any functional dystrophin from being produced. Skeletal and cardiac muscle cells without enough functional dystrophin become damaged as the muscles contract and relax. The damaged muscle cells weaken and die over time, causing the muscle weakness and heart problems characteristic of muscular dystrophy. Other forms of muscular dystrophy exist and include Becker muscular dystrophy and myotonic dystrophy.
::减缩的DMD是已知最大的人类基因,有200多万对基底基因。在骨骼和心脏肌肉中,减缩性营养素是一组蛋白质(一个蛋白综合体)的一部分,它们合力加强肌肉纤维并保护它们免受肌肉萎缩和放松的伤害。减缩性营养素综合体作为锚,将每个肌肉细胞的细胞萎缩与细胞外其他分子的裂纹连接起来(伸缩式矩阵),减缩性营养素综合体也可能在细胞信号中发挥作用,通过与发出和接收化学信号的蛋白进行互动。DMD基因中发现了许多导致DMD的突变。这些突变通常防止产生任何功能性营养素。骨骼和心脏肌肉细胞没有足够功能性营养素就会随着肌肉萎缩和放松而受损。受损的肌肉细胞会变弱,会随着时间而死亡,造成肌肉虚弱和心脏问题,造成肌肉萎缩性肌肉萎缩和心脏问题特征。其他形态和肌肉萎缩性形式包括:Summary
::摘要-
Sex chromosomes specify an organism's genetic sex. Humans have two different sex chromosomes, one called X and the other Y.
::人类有两种不同的性染色体,一种叫X,另一种叫Y。 -
Sex-linked genes are located on either the X or Y chromosome, though it more commonly refers to genes located on the X-chromosome.
::与性别有关的基因位于X或Y染色体上,但更常见的是X-染色体上的基因。 -
Color blindness, hemophilia and muscular dystrophy are three x-linked phenotypes.
::色盲、血友病和肌肉萎缩是三种与X挂钩的苯型。
Review
::回顾-
Why is it more common for males to have X-linked disorders?
::为什么男性患X连带疾病更为常见? -
What is X-inactivation?
::什么是X - 停止活动? -
Describe XIST and TSIX and explain their relationship.
::描述XIST和TSIX 并解释它们之间的关系。 -
What is SRY?
::什么是SRY? (SRY: SRY: SRY: SRY: SRY: SRY: SRY: SRY: SRY: SRY: SRY: SRY)什么是SRY? -
Describe two X-linked phenotypes.
::描述两个X链接的苯型。
-
The XIST gene produces a 17 kilo base (kb) RNA molecule; the RNA is not translated into a protein.