3.22 多诱变性 - 高级
章节大纲
-
Human height—just two phenotypes?
::人类身高——只有两种人型?Of course not. Human height exhibits a large range of phenotypes . Normal phenotypes range from under 5 feet tall to over 7 feet tall. How does such a wide range occur? Well, not just from one gene .
::当然没有。 人身高显示出大量的苯型。 正常的苯型从5英尺以下高到7英尺以上不等。 如何发生如此之大的情况? 不仅来自一个基因,而且来自一个基因。Polygenic Traits
::多诱变轨数Polygenic traits are due to the actions of more than one gene and often, their interaction with the environment. These usually result in a measurable range in phenotype, such as height, eye color or skin color. These are known as multifactoral or quantitative characteristics. Polygenic inheritance results in an additive effect of the genes on a single phenotype.
::多基因特性是由于一个以上基因的动作,而且往往由于它们与环境的相互作用,通常导致在高、眼色或皮肤颜色等苯型中可以测量的范围,这些特征被称为多因或数量特征,多因继承导致基因在单一苯型中的添加效应。Human skin color is primarily due to the presence of the pigment melanin in the skin. Melanin is not a , but it is the product of a biosynthetic pathway. Skin color is a polygenic trait and obviously demonstrates quantitative characteristics. A number of genes factor into determining a person's natural skin color, so modifying only one of those genes changes the color only slightly. It is currently thought that at least three separately inherited genes contribute to skin pigmentation. Let’s call these three genes A, B, and C. A, B, and C are incompletely dominant to a, b, and c, with A, B, and C each contributing a “unit of darkness” to the phenotype. Therefore an AABBCC individual is very dark, darker than an AaBbCc individual, and much darker than a aabbcc individual. A person may have as many as 6 “dark units” to as few as no “dark units,” and any combination in between. This will result in a phenotypic spectrum of color gradation. When graphed, a phenotypic spectrum usually results in a bell-shaped curve, with extreme phenotypes on both ends and more common phenotypes in the center of the curve.
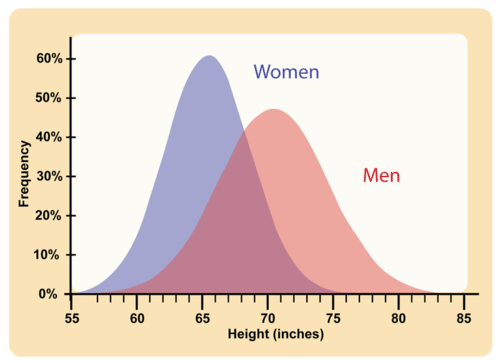
::人类皮肤的肤色主要归因于皮肤中色素的色素杂质。 美兰素不是生物合成途径的产物, 但它是生物合成途径的产物。 皮肤颜色是一种多元性特征, 并明显显示数量特性。 在确定一个人的自然肤色中, 有一些基因因素决定了一个人的自然肤色, 所以只改变其中的一个基因, 因而只略微改变颜色。 目前人们认为, 至少三个单独继承的基因有助于皮肤色素。 让我们将这三个基因A、 B 和 C. A、 B 和 C 称为不完全的主要基因A、 b 和 c, 与 A、 B 和 C 相配。 每一个基因颜色颜色颜色都是一个“ 黑暗的单位 ” 。 因此, AABCC 个人非常黑暗, 比 AABC 个人更黑暗, 比 aabc 个人更黑暗。 目前人们认为, 一个人可能有多达6个“ 暗单位” , 与不“ 暗单位 ” 和 C. C. B 和 C 之间的任何组合。 这将导致一个彩色谱谱谱系的频谱, 通常为平的平面, 的平面的平面, 。Another example of a human polygenic trait is adult height. If human height followed simple Mendelian genetics , than people would either be tall or short, with both phenotypes probably falling into a very narrow range. But like skin color, humans height fall into essentially a phenotypic spectrum. Within the human , every conceivable height between less than 5 feet and over 7 feet probably exists. This range can not be controlled by just one gene with two . In fact, several genes, each with more than one allele, contribute to human height, resulting in many possible adult heights. For example, one adult’s height might be 1.655 m (5.430 feet), and another adult’s height might be 1.656 m (5.433 feet) tall. Adult height ranges from less than 5 feet to more than 6 feet, but the majority of people fall near the middle of the range, as shown in Figure .
::人类多致性特征的另一个例子是成人身高。 如果人类身高是简单的门德利基因,那么人身高可能比人身高高或短,两者的个性类型都可能都属于非常狭窄的范围。但是,像肤色一样,人类身高基本上会掉入一个小范围。在人类中,每个可以想象的身高在5英尺以下和7英尺以上之间,都可能存在。这一范围不可能仅由一个具有2个基因的基因来控制。事实上,数个基因,每个有1个以上的异种,都会导致人类身高,导致许多可能的成人身高。例如,一个成人身高可能为1.655米(5.430英尺),另一个成人身高可能高达1.656米(5.433英尺),成年身高可能从不到5英尺到6英尺以上不等,但多数人接近射程的中间,如图所示。Human Adult Height. Like many other polygenic traits, adult height has a bell-shaped distribution. Many disorders with genetic components are polygenic, including autism, certain cancers, and numerous others. Most phenotypic characteristics are the result of the interaction of multiple genes. The environment plays a significant role in many of these phenotypes. But what happens when multiple genes are either missing or duplicated?
::许多具有遗传成分的疾病是多基因的,包括自闭症、某些癌症和许多其他疾病。 多数胎儿特征是多种基因相互作用的结果。 环境在许多这些苯型中起着重要作用。 但是,当多重基因缺失或重复时会怎样呢?Changes in Chromosome Number
::染色体数变化So far we have focused on traits due to one gene or several genes. But what about many genes? 100s or 1000s of genes? What would happen if an entire were missing or duplicated? What if a human had only 45 chromosomes? Or 47? This real possibility is usually due to mistakes during ; the chromosomes do not fully separate from each other during or egg formation. Specifically, nondisjunction is the failure of replicated chromosomes to separate during anaphase II. If a zygote forms from a gamete lacking a chromosome, a viable embryo cannot be produced. Most human abnormal chromosome numbers result in the death of the developing embryo, often before a woman even realizes she is pregnant. Occasionally, a zygote with an extra chromosome can become a viable embryo and develop.
::到目前为止,我们一直关注一个基因或几个基因的特性。但是许多基因呢?100或1000个基因呢?如果整个基因丢失或复制,会发生什么情况?如果一个人类只有45个染色体呢?还是47?这种真实可能性通常是由于在出现错误时发生的;染色体在产卵或产卵过程中没有完全分离。具体地说,不相容是指复制染色体在二期期间没有分离。如果一个缺乏染色体的游戏中的zgote形式不能产生,那么一个可行的胚胎就无法产生。大多数异常的染色体数量导致发育中的胚胎死亡,往往在妇女发现怀孕之前。偶尔,带有额外染色体的zyote可以成为可行的胚胎并发育。Trisomy is a state where humans have an extra autosome . That is, they have three of a particular chromosome instead of two. For example, trisomy 18 results from an extra chromosome 18, resulting in 47 total chromosomes. To identify the chromosome number (including an abnormal number), a sample of is removed from an individual or developing fetus . Metaphase chromosomes are photographed and a karyotype is produced. A karyotype will display any abnormalities in chromosome number or large chromosomal rearrangements. Trisomy 8, 9, 12, 13, 16, 18, and 21 have been identified in humans. Trisomy 16 is the most common trisomy in humans, occurring in more than 1% of pregnancies. This condition, however, usually results in spontaneous miscarriage in the first trimester. The most common trisomy in viable births is Trisomy 21 .
::特里索米是人类具有超异性状态的状态。 也就是说, 他们有3种特定的染色体, 而不是2种。 例如, 3个染色体 18 由额外的染色体 18 产生, 共产生47个染色体。 要识别染色体数( 包括异常数), 将样本从个体或发育中的胎儿中取出。 代相色谱染色体被拍照, 并产生一种甲状腺型。 一种卡约型将显示染色体数或大型染色体重新组合中的任何异常。 3个色体8、 9、 12、 13、 16、 18 和 21 已经识别在人类中。 特里索米 16 是人类中最常见的三色体, 发生在超过1%的怀孕中。 然而, 这种状况通常导致第一个三联产期的自发性流产。 最常见的三联产期是 Trisomy 21。Trisomy 21: Down Syndrome
::三索米21:唐氏综合症One of the most common chromosome abnormalities is Down syndrome , due to nondisjunction of chromosome 21 resulting in an extra complete chromosome 21, or part of chromosome 21 ( Figure ). Down syndrome is the only autosomal trisomy where an affected individual may survive to . Individuals with Down syndrome often have some degree of mental retardation, some impairment of physical growth, and a specific facial appearance. With proper assistance, individuals with Down syndrome can become successful, contributing members of society . The incidence of Down syndrome increases with maternal age. The risk of having a child with Down syndrome is significantly higher among women age 35 and older.
::最常见的染色体异常现象之一是唐氏综合症,因为21世纪染色体没有分离,导致21世纪染色体或21世纪染色体的一部分(Figure ) ; 唐氏综合症是受影响个人唯一能够存活下来的自发性生理三联症; 患有唐氏综合症的个人往往有一定程度的智力迟钝、身体发育障碍和特定的面部外貌; 在适当的帮助下,患有唐氏综合症的人可以取得成功,对社会作出贡献; 唐氏综合症的发病率随着孕妇年龄的增加而增加; 患有唐氏综合症的妇女患唐氏综合症的风险在35岁及35岁以上的妇女中要高得多。Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome) Karyotype. A karyotype is a picture of a cell's chromosomes. Note the extra chromosome 21. Child with Down syndrome, exhibiting characteristic facial appearance. Abnormal Numbers of Sex Chromosomes
::性染色体异常数量What about when a person has more than two Y chromosomes, or more than two X chromosomes? Or a female with only one X chromosome ? Sex-chromosome abnormalities may be caused by nondisjunction of one or more sex chromosomes . Many conditions are known in which there are an abnormal number of sex chromosomes. An X chromosome may be missing (XO), or there may be an extra one (XXX or XXY). There may also be an extra Y chromosome (XYY). Any combination of X and Y chromosomes, as long as there is a Y chromosome, will produce a male (up to XXXXY). These individuals can lead relatively normal lives, but they cannot have children. They may also have some degree of intellectual disability. These syndromes include Klinefelter syndrome , Turner syndrome and trisomy X.
::当一个人拥有两个以上Y染色体或两个以上X染色体时呢?还是只有一个X染色体的女性呢?性-染色体异常可能是由于一种或多种性染色体的不相交而导致的。已知有许多性染色体异常的情况。X染色体可能失踪(XO),或者可能另有一个(XXX或XXY)。还可能有另外的Y染色体(XYY)。只要存在一个Y染色体,任何X和Y染色体的组合都会产生一个男性(高达XXXXY)。这些人可以过相对正常的生活,但他们不能有孩子。他们也可能有一定的智力残疾。这些综合体包括Klinefelter综合症、Turner综合症和Trisomy X。Klinefelter syndrome is caused by the presence of one or more extra copies of the X chromosome in a male's cells. Extra genetic material from the X chromosome interferes with male sexual , preventing the testicles from functioning normally and reducing the levels of testosterone . Triple X syndrome (trisomy X) results from an extra copy of the X chromosome in each of a female's cells. Females with trisomy X have a lower IQ than their siblings. Turner syndrome results when each of a female's cells has one normal X chromosome and the other sex chromosome is missing or altered. The missing genetic material affects development and causes the characteristic features of the condition, including short stature and infertility.
::Klinefelter综合症是由男性细胞中存在一个或更多份的X染色体引起的。X染色体的外遗传物质干扰男性的性活动,阻止睾丸正常运转,降低睾丸素水平。三联X综合症(三联X)是女性细胞中每个细胞中多一份X染色体的结果。三联X女性的智商比其兄弟姐妹低。特纳综合症的结果是,女性细胞中的每个细胞都有一个正常的X染色体,而其他性别染色体则丢失或改变。缺失的遗传物质影响发育,并造成该病的特征,包括身材短小和不孕症。Genetic Disorder Genotype Phenotypic Effects Down syndrome extra copy (complete or partial) of chromosome 21 (see Figure ) developmental delays, distinctive facial appearance, and other abnormalities (see Figure ) Turner syndrome one X chromosome but no other sex chromosome (XO) female with short height and infertility (inability to reproduce) Triple X syndrome three X chromosomes (XXX) female with mild developmental delays and menstrual irregularities Klinefelter syndrome one Y chromosome and two or more X chromosomes (XXY, XXXY) male with problems in sexual development and reduced levels of the male testosterone Summary
::摘要-
Polygenic traits are due to the actions of more than one gene and often, their interaction with the environment.
::多基因特征是由于一个以上基因的动作,而且往往由于它们与环境的相互作用。 -
Trisomy is a state where humans have an extra autosome; they have three of a particular chromosome instead of two.
::特里索米是一种状态, 人类拥有一个超异性; 他们有三个特定的染色体, 而不是两个。 -
The most common trisomy in viable births is Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome).
::在可存活的分娩中最常见的三联产物是Trisomy 21(低发综合征)。
Review
::回顾-
Define polygenic traits.
::定义多元特性。 -
What is meant by trisomy?
::三角交配是什么意思? -
How can trisomy phenotypes be detected?
::如何检测到三索米苯型? -
What is the most common viable trisomy disorder?
::什么是最常见的 可行的三索氏紊乱症? -
List conditions involving an abnormal number of sex chromosomes.
::列出涉及异性染色体异常数量的条件清单。
-
Polygenic traits are due to the actions of more than one gene and often, their interaction with the environment.