4.23 植物电池 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
How are plant cells different from animal cells?
::植物细胞与动物细胞有何不同?Plant and cells are quite similar in many aspects. For example, they are both eukaryotic cells , both contain in a , and both make in . However, plant cells also differ in some crucial ways from animal cells.
::植物和细胞在许多方面都非常相似。例如,它们既是产卵细胞,两者都包含在(a)中,也是在(b)中。然而,植物细胞在某些关键方面也与动物细胞不同。Plant Cells
::工厂电池Unique Structures, and Three Basic Types
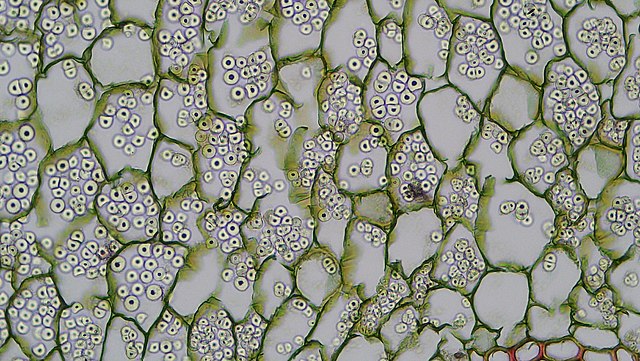
::独特结构和三种基本类型Because plants live by making food from sunlight, air (or the CO 2 in the air), and , the structure of plant cells ( Figure ) differs from that of other eukaryotic cells:
::由于植物靠日光、空气(或空气中的CO2)制造食物来生存, 植物细胞的结构(图)不同于其他水晶细胞的结构:Plant cells have all the same structures as animal cells, plus some additional structures. Can you identify the unique plant structures in the diagram? Major differences between a plant cell and animal cell are the large central vacuole , a cell wall , and :
::植物细胞和动物细胞之间的主要差异是大型中央真空、细胞墙和:-
A large
central vacuole
may occupy from 30 to 90% of a plant cell's volume. Surrounded by its own
semipermeable
membrane, the
vacuole
holds water,
ions
such as K
+
or Cl
-
,
, pigments, and even toxins. A primary role of the vacuole is to maintain
osmotic pressure
against the cell wall, giving the cell shape and helping to support the plant. The vacuole also pushes the chloroplasts outward toward the
, increasing their exposure to light. Toxins which might interfere with cellular
metabolism
may be removed to the vacuole, and in some cases the toxins can help protect the plant from
predators
. Excess cytoplasmic protons pumped into the vacuole can regulate enzyme activity, at the same time serving a waste disposal function. Pigments stored in the the vacuoles of
fruits
and
flowers
provide coloration.
::大型中央真空素可能占植物细胞体积的30%至90%。 真空素被其自身的半可渗透膜、 真空素拥有水、 K+ 或 Cl- 、 色素等离子、 甚至毒素所包围。 真空素的主要作用是保持细胞壁的表面压力, 使细胞形状形成并帮助支持植物。 真空素还将叶素推向外向外推, 增加其接触光线。 可能影响细胞代谢的毒素可能会移到真空, 在某些情况下, 毒素可以帮助保护植物免受掠食者的影响。 被抽进真空素中的超多细胞质子可以调节酶活动, 同时起到废物处理功能。 储存在水果和花的真空中的猪可以提供颜色。 -
A
cell wall
outside the cell membrane shapes, supports, and protects the cell. Composed of
cellulose
, other
polysaccharides
, and glycoproteins, the cell wall also acts as a filter, preventing large, potentially damaging molecules from reaching the cell membrane. Semi-rigid, the cell wall not only shapes the cell and supports the plant, but also limits
so that excess water cannot cause the cell to burst. An outer, gelatinous layer, the
middle lamella,
both joins and separates adjacent plant cells.
::细胞膜外的细胞墙形状、 支撑并保护细胞。 细胞墙由纤维素、 其他聚沙化合物和甘蓝蛋白组成, 也起到过滤器的作用, 防止大型、 潜在损坏的分子进入细胞膜。 半硬体, 细胞墙不仅形状细胞, 支撑植物, 并且限制过量的水不会导致细胞破裂。 外层、 凝胶层、 中层 瘸子, 两者都连接并隔离了相邻的植物细胞 。 -
After growth has stopped, many plant cells add a
secondary cell wall
, a thicker, more rigid layer of cellulose fibers, between the primary cell wall and the cell membrane. Additional molecules such as
lignin
and
suberin
may waterproof and strengthen secondary cell walls to make wood and cork, respectively. Pits in the secondary wall allow cells to
communicate
via the relatively free flow of small molecules and ions through
plasmodesmata
. Plasmodesmata connect adjacent cells' cytoplasms.
::在生长停止后,许多植物细胞在主细胞壁和细胞膜之间添加了第二细胞壁,一个更厚、更硬的细胞素纤维层,其他分子,如列宁和亚丁,可以防水,加强第二细胞壁,分别制造木材和软木。在第二细胞墙中,薄膜允许细胞通过小分子和离子相对自由的流动通过plasmodesmata进行交流。 Plasmodesmata 连接邻近细胞的细胞板块。 -
Plastids
(
Figure
), closely related DNA-containing
, include chloroplasts,
chromoplasts
, and a diverse group of
leucoplasts
. As you learned in earlier chapters,
chloroplasts
(“green bodies” –
Figure
) contain the green pigment
chlorophyll
, and carry out
.
Chromoplasts
(“color bodies”) make and store plant pigments. Various types of
leucoplasts
(“white bodies”) store
starch
or fat, detect gravity, and modify and store protein.
::胶片(Figure ) , 紧密相连的含DNA,包括叶板、染色体和一组不同的乳胶。 正如你在前几章中所了解的那样,叶板(“绿色体 ” — 图 ) 包含绿色色素叶素,并进行. 染色体(“彩色体 ” ) 制造和储存植物色素。 各种色片(“白色体 ” ) 储存淀粉或脂肪、检测重力、修改和储存蛋白质。
-
Chloroplasts carry out photosynthesis
::氯甲醚进行光合作用。 -
Leucoplasts store starch, as in these potato cells.
::像这些土豆细胞一样
Three basic types of cells build most plants.
::三种基本细胞构成大多数植物。1. Parenchymal cells ( Figure ) most closely resemble the generalized plant cell discussed above. They make up the bulk of plant tissue . Thin-walled (no secondary walls), roughly cube-shaped, and often loosely packed, they are the least specialized of the three basic plant cell types. Parenchymal cells retain the ability to divide to form other types of cells, much as cells do in our own bodies. Their primary functions are metabolism, including photosynthesis and , and storage.The flesh of fruits and vegetables such as potatoes are made of parenchymal cells.
::1. 近似上述一般植物细胞(图),它们构成植物组织的主要部分:薄膜(没有第二面墙),大约立方体形,而且往往包装松散,它们是三种基本植物细胞中最不专门的细胞;与我们身体中的细胞一样,帕伦希摩细胞保留了分裂形成其他种类细胞的能力;其主要功能是新陈代谢,包括光合作用和储存。Parenchymal cells store starch in this buttercup (Ranunculus) root cross-section. Parenchymal cells are typically unspecialized with thin walls. 2. If you have ever pulled the “strings” from a stalk of celery, you are familiar with collenchymal cells ( Figure ). These cells are elongated, with irregularly thickened primary walls, and they provide support, especially for growing shoots. Mechanical stress (such as wind) can cause the plant to further thicken the walls, adding to the support.
::2. 如果你曾经从切菜片中拉出 " 绳索 " ,你就会熟悉圆心细胞(图.),这些细胞长长,主壁不规则地厚,它们提供支持,特别是为种植火苗提供支持。机械压力(如风)可以使植物进一步厚厚墙,增加支撑。Collenchyma tissue. Typically, collenchyma has thicker cell walls than parenchyma 3. Rope made of hemp, jute, or flax consists largely of the third type of cell, sclerenchyma ( Figure ). Whereas collenchymal cells support growing tissues, sclerenchymal cells strengthen and support parts of the plant that have completed elongation . Thick secondary walls made of cellulose and lignin can make up as much as 90% of the cell's volume; think of sclerenchyma as the plant's skeleton . Two types of sclerenchymal cells include fibers and sclereids. Fibers - long and strong - have walls made of cellulose and sometimes lignin; we use fibrous plants to make ropes and textiles. Sclereids are relatively short, and often grouped into bundles. You may be familiar with them as the gritty texture of pears or nutshells and pits of cherries or plums.
::3. 由黄麻、黄麻或麻麻麻制成的第二层墙大部分由第三类细胞组成,即:细胞细胞(Figure),而细胞细胞则支持生长组织,而细胞细胞细胞则支持生长的细胞,而细胞细胞细胞细胞则加强和支持植物中完成延长的部分。由纤维素和螺旋素制成的厚的第二层墙壁可占细胞体积的90%;认为细胞细胞细胞是植物的骨骼;两种细胞的细胞包括纤维和细胞细胞。长而坚固的纤维壁由纤维素制成,有时是螺旋素制成;我们用纤维植物制作绳子和纺织品。石器的长度相对较短,而且往往被分组成捆包。你可能熟悉它们,因为它们是梨子、坚果和樱桃或羽子的坑状纹质。A cross-section of a flax stem reveals sclerenchymal cells which form fibers used to make rope and textiles such as linen. Sclerenchyma has the thickest cell walls of the three basic types of cells. As for all animals, your body is made of four types of tissue: epidermal (covering), muscle, nerve , and connective tissues . Plants, too, are built of tissues, but not surprisingly, their very different lifestyles derive from different kinds of tissues. Specialized cells derived from the three basic cell types discussed above combine to form three basic types of plant tissues: or covering tissue, or body tissue, and or conducting tissue. We will look at these “fabrics” that build plants in the concepts that follow: Plants: Dermal Tissue (Advanced), Plants: Ground Tissue (Advanced), and Plants: Vascular Tissue (Advanced).
::至于所有动物,你的身体由四类组织组成:上皮类(覆盖)、肌肉、神经和连接组织;植物也由组织组成,但毫不奇怪的是,它们非常不同的生活方式来自不同种类的组织;上文讨论的三种基本细胞类型的专门细胞组成三种基本植物组织:或覆盖组织或人体组织,或组织组织;我们将研究这些在以下概念下建造植物的“结构”:植物:皮肤组织(高级);植物:地面组织(高级);植物:血管组织(高级);植物:血管组织(高级)。Summary
::摘要-
Plant and animal cells share common features as eukaryotic cells with DNA in a nucleus and ribosome-mediated protein synthesis.
::植物和动物细胞的共同特征是,在核和血清介质蛋白合成中具有DNA的泌尿细胞。 -
Plant cells have unique structures, including a large central vacuole, a cell wall, and chloroplasts, setting them apart from animal cells.
::植物细胞有独特的结构,包括一个大型中央真空体、一个细胞墙和叶板,将它们与动物细胞分开。
::植物细胞有独特的结构,包括一个大型中央真空体、一个细胞墙和叶板,将它们与动物细胞分开。 -
The central vacuole, surrounded by a membrane, plays a vital role in maintaining osmotic pressure, supporting the cell, and storing various substances.
::中央真空体环绕着膜,在保持表面压力、支持细胞和储存各种物质方面发挥着至关重要的作用。
::中央真空体环绕着膜,在保持表面压力、支持细胞和储存各种物质方面发挥着至关重要的作用。 -
Plant cells exhibit three basic types—parenchymal, collenchymal, and sclerenchymal cells—each with distinct functions in metabolism, support, and strengthening.
::植物细胞有三种基本类型,即:甲型甲型、丙型、丙型、丙型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、乙型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、型、型、型、双型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型
::植物细胞有三种基本类型,即:甲型甲型、丙型、丙型、丙型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、乙型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、甲型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、双型、型、型、型、双型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型、型
Review
::回顾-
What are two common features shared by plant and animal cells?
::动植物细胞具有哪些共同特征? -
Name three unique structures found in plant cells that make them different from animal cells.
::列出植物细胞中发现的三个独特结构,这些结构使它们不同于动物细胞。
::列出植物细胞中发现的三个独特结构,这些结构使它们不同于动物细胞。 -
What is the primary role of the central vacuole in a plant cell?
::植物细胞中中央真空分子的主要作用是什么?
::植物细胞中中央真空分子的主要作用是什么? -
List the three basic types of plant cells and briefly describe one function for each type.
::列出三种基本类型的植物细胞,并简要说明每种类型的一种功能。
::列出三种基本类型的植物细胞,并简要说明每种类型的一种功能。
-
A large
central vacuole
may occupy from 30 to 90% of a plant cell's volume. Surrounded by its own
semipermeable
membrane, the
vacuole
holds water,
ions
such as K
+
or Cl
-
,
, pigments, and even toxins. A primary role of the vacuole is to maintain
osmotic pressure
against the cell wall, giving the cell shape and helping to support the plant. The vacuole also pushes the chloroplasts outward toward the
, increasing their exposure to light. Toxins which might interfere with cellular
metabolism
may be removed to the vacuole, and in some cases the toxins can help protect the plant from
predators
. Excess cytoplasmic protons pumped into the vacuole can regulate enzyme activity, at the same time serving a waste disposal function. Pigments stored in the the vacuoles of
fruits
and
flowers
provide coloration.