4.33 手机通讯-高级
章节大纲
-
What does adrenaline do?
::肾上腺素会做什么?Adrenaline, or epinephrine, is a and a neurotransmitter . It increases heart rate, constricts , dilates air passages, and participates in the fight-or- flight response of the sympathetic . Adrenaline is produced in the adrenal medulla of the adrenal gland. So how does it affect processes all over the body?
::肾上腺素,或者肾上腺素,是神经分泌剂。它会增加心率、收缩、扩大空气通道,并参与同情者的战斗或飞行反应。肾上腺素在肾上腺的肾上腺肾上腺膜中生成。它会如何影响全身的流程?The Language of Cells
::单元格语言To survive and grow, need to be able to communicate with their neighboring cells and be able to detect changes in their environment. "Talking" with neighboring cells is even more important to a cell if it is part of a . Cell communication, or cell signaling, is the basis of , tissue repair, and . It is also necessary for normal tissue . The trillions of cells that make up your body need to be able to communicate with each other to allow your body to grow and to keep you alive and healthy. The same is true for any organism . Cell signaling is part of a complex system of that governs basic cellular activities and coordinates cell actions. Cell signaling is a major area of research in biology today. Defects in cell signaling are associated with diseases such as , autoimmunity, and .
::为了生存和成长,需要能够与周围的细胞进行交流,并且能够检测到环境的变化。如果细胞是...细胞通信或细胞信号的一部分,那么与周围的细胞进行交流对于细胞更为重要。细胞通信或细胞信号是正常组织的基础、组织修复和。构成身体的数万亿细胞需要能够相互交流,以便身体生长并保持你的生命和健康。对于任何生物体也是如此。细胞信号是管理基本细胞活动和协调细胞动作的复杂系统的一部分。细胞信号是当今生物学研究的一个主要领域。细胞信号的缺陷与疾病有关,如自发性和自发性。Recently scientists have discovered that many different cell types, from to plants, use similar types of communication pathways, or cell-signaling mechanisms. This suggests that cell-signaling mechanisms evolved long before the first multicellular organism did.
::最近科学家发现,从植物到植物,许多不同的细胞类型都使用类似类型的通信途径或细胞信号机制。 这意味着细胞信号机制远比第一种多细胞有机体早得多地演变。For cells to be able to signal to each other, a few things are needed:
::为使细胞能够相互信号,需要做一些事情:-
a signal,
::信号 -
a
cell receptor
, which is a
usually on the plasma membrane, but can be found inside the cell,
::细胞受体,通常在等离子膜上,但可以在细胞内找到, -
a response to the signal.
::对信号的反应。
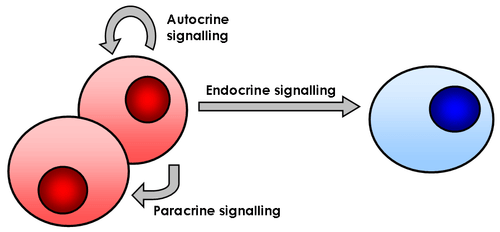
Cells that are communicating may be right next to each other or far apart. In juxtacrine signaling , also known as contact-dependent signaling, two adjacent cells must make physical contact in order to communicate. In autocrine signaling , the signaling cell and the target cell can be the same or a similar cell. Cell communication may also occur over short distances, which is known as paracrine signaling , or over large distances, which is known as endocrine signaling (see the Figure ).
::交流的单元格可能彼此相邻或相距甚远。在平行观测器信号中,又称依赖接触的信号,两个相邻的细胞必须进行物理接触才能进行交流。在自动化信号中,信号电池和目标细胞可以是相同的,也可以是类似的细胞。细胞通信也可能发生在很短的距离上,即所谓的paracrine信号,或者长的距离上,即内分泌信号(见图 )。Different types of cell signaling mechanisms The type of chemical signal a cell will send differs depending on the distance the message needs to go. For example, hormones , ions , and neurotransmitters are all types of signals that are sent depending on the distance the message needs to go. Endocrine signals are hormones, produced by endocrine organs . These signals travel through the bloodstream to reach all parts of the body.
::细胞发送的化学信号类型不同, 取决于信息需要去的距离。 例如, 荷尔蒙、 离子和神经传送器都是根据信息需要去的距离发出的信号。 内分泌信号是内分泌器官生成的荷尔蒙。 这些信号通过血液流传到身体的所有部位。The target cell then needs to be able to recognize the signal. Chemical signals are received by the target cell on receptor proteins . Most receptor proteins are found associated with the plasma membrane, but some are also found inside the cell. Receptor proteins are very specific for only one particular signal molecule, much like a lock that recognizes only one key. Therefore, a cell has lots of receptor proteins to recognize the large number of cell signal molecules. There are three stages to sending and receiving a cell "message": reception, transduction , and response.
::目标细胞随后需要能够识别信号。 目标细胞在受体蛋白上接收化学信号。 大多数受体蛋白都与血浆膜相关, 但也有一些在细胞内部发现。 受体蛋白只针对一个特定的信号分子非常具体, 类似于只识别一个钥匙的锁。 因此, 细胞有很多受体蛋白可以识别大量的细胞信号分子。 发送和接收细胞“ 信息” 有三个阶段: 接收、 转换和响应。-
Reception occurs when a ligand binds to its receptor.
::接收发生于被约束于其受体时。 -
Through transduction, the signal is then internalized. The ligand does not have to be internalized for this process to occur.
::通过转换,该信号随后内部化。 离子和离子不必内部化, 才能进行此过程 。 -
The response may initiate a cascade of reactions including the activation/deactivation of
and/or an alternation in
gene
.
::反应可能引发一系列反应,包括基因的激活/停止和/或变换。
Summary
::摘要-
Cell communication or cell signaling describes how cells share information.
::单元格通信或单元格信号说明单元格如何分享信息。 -
Cell communication usually begins when a molecule (a ligand) binds to its receptor.
::细胞通信通常在分子(ligand)与其受体捆绑时开始。 -
Cell communication can be over short or long distances.
::细胞通信可以短距离或长距离。
Review
::回顾-
Define cell communication.
::界定单元格通信。 -
Compare juxtacrine, paracrine, and endocrine signaling.
::比较杂交石蜡 石蜡 和内分泌信号 -
Describe the process of cell signaling.
::描述单元格信号的过程 。
-
a signal,