5.6 酶和生物化学反应 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
What is a biological catalyst?
::什么是生物催化剂?This super fast train can obviously reach great speeds. And there's a lot of technology that helps this train go fast. Speaking of helping things go fast brings us to enzymes. Life could not exist without enzymes. Essentially, enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up .
::这辆超快列车显然可以达到高速。而且有很多技术可以帮助这辆列车快速行进。说到帮助事情快速行进,我们就会发现酶。没有酶,生命就不可能存在。基本上,酶是加速发展的生物催化剂。Enzymes and Biochemical Reactions
::酶和生化反应Most chemical reactions within organisms would be impossible under the normal conditions within . For example, the body temperature of most organisms is too low for reactions to occur quickly enough to carry out life processes. Reactants may also be present in such low concentrations that it is unlikely they will meet and collide. Therefore, the rate of most biochemical reactions must be increased by a catalyst. A catalyst is a chemical that speeds up chemical reactions. In organisms, catalysts are called enzymes .
::例如,大多数生物体的体温太低,无法迅速发生反应,以致无法进行生命过程;再活性剂也可能存在于极低的浓度中,因此它们不可能满足并碰撞;因此,大多数生化反应的速度必须由催化剂来提高。催化剂是一种加速化学反应的化学物质。在生物体中,催化剂被称为酶。Like other catalysts, enzymes are not reactants in the reactions they control. They help the reactants interact but are not used up in the reactions. Instead, they may be used over and over again. Unlike other catalysts, enzymes are usually highly specific for a particular chemical reaction. They generally catalyze only one or a few types of reactions.
::与其他催化剂一样,酶在它们控制的反应中不是反应反应器,它们帮助反应器相互作用,但没有在反应中加以利用。相反,它们可能被反复使用。与其他催化剂不同,酶通常对特定化学反应非常特殊,它们通常只催化一种或几种反应。Enzymes are extremely efficient in speeding up biochemical reactions. They can catalyze up to several million reactions per second. As a result, the difference in rates of biochemical reactions with and without enzymes may be enormous. A typical biochemical reaction might take hours or even days to occur under normal cellular conditions without an , but less than a second with the enzyme.
::酶在加速生化反应方面极为有效,它们可以催化到每秒几百万次反应。 因此,生化反应率与无酶的差别可能很大。 典型的生化反应可能需要数小时甚至数天才能在正常的细胞条件下发生,没有细胞反应,但只有不到一秒钟的酶反应。How Enzymes Work
::酶如何工作How do enzymes speed up biochemical reactions so dramatically? Like all catalysts, enzymes work by lowering the activation energy of chemical reactions. This is illustrated in Figure . The biochemical reaction shown in the figure requires about three times as much activation energy without the enzyme as it does with the enzyme.
::酶是如何如此快速地加速生化反应的?像所有催化剂一样,酶通过降低化学反应的活性能量而发挥作用。图中说明了这一点。图中显示的生化反应需要大约三倍的活化能量,而没有酶则需要三倍的活化能量。The reaction represented by this graph is a combustion reaction involving the reactants glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ) and oxygen (O 2 ). The products of the reaction are carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and water (H 2 O). Energy is also released during the reaction. The enzyme speeds up the reaction by lowering the activation energy needed for the reaction to start. Compare the activation energy with and without the enzyme.
::本图所代表的反应是一种燃烧反应,涉及反应剂甘蔗(C6H12O6)和氧(O2),反应的产物是二氧化碳(CO2)和水(H2O),反应期间还释放了能量。酶通过降低反应启动所需的活性能量来加速反应。将活性能量与和没有酶的活性能量相比较。Enzymes generally lower activation energy by reducing the energy needed for reactants to come together and react. For example:
::通过减少反应剂聚集并作出反应所需的能量,酶一般会降低活性能。-
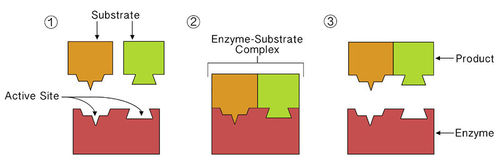
Enzymes bring reactants together so they don't have to expend energy moving about until they collide at random. Enzymes bind both reactant molecules (called
substrates
), tightly and specifically, at a site on the enzyme molecule called the
active site
(
Figure
). This forms an enzyme-substrate complex.
::酶将反应器聚集在一起,这样它们就不必在随机碰撞之前花费能量。酶将两种反应分子(所谓的子质)紧密和具体地结合在酶分子上的一个叫做活点(图 ) 的网址上。这构成了酶基复合体。 -
By binding reactants at the active site, enzymes also position reactants correctly, so they do not have to overcome intermolecular forces that would otherwise push them apart. This allows the molecules to interact with less energy.
::通过在活跃点的绑定反应器,酶还正确地定位反应器,因此它们不必克服会将他们分开的分子间联力量。这使得分子能够以较少的能量进行互动。 -
Enzymes may also allow reactions to occur by different pathways that have lower activation energy.
::酶还可能允许不同途径发生反应,而不同途径的活性能较低。
This enzyme molecule binds reactant molecules—called substrate—at its active site, forming an enzyme-substrate complex. This brings the reactants together and positions them correctly so the reaction can occur. After the reaction, the products are released from the enzyme's active site. This frees up the enzyme so it can catalyze additional reactions.
::这种酶分子将反应分子 — — 即所谓的基质 — — 结合到其活跃的站点,形成酶基质复合体,将反应分子聚集在一起,并正确定位它们,以便发生反应。反应后,产品从酶活跃的站点释放出来,释放酶,从而催化更多的反应。The activities of enzymes also depend on the temperature, ionic conditions, and the pH of the surroundings. Some enzymes work best at acidic pHs, while others work best in neutral environments.
::酶的活动也取决于周围的温度、电离条件和pH值。 有些酶在酸性pH值方面最有效,而另一些则在中性环境中最有效。-
Digestive enzymes secreted in the acidic environment (low pH) of the
stomach
help break down
into smaller molecules. The main digestive enzyme in the stomach is
pepsin
, which works best at a pH of about 1.5). These enzymes would not work optimally at other pHs.
Trypsin
is another enzyme in the
which break protein chains in the
food
into smaller parts. Trypsin works in the
, which is not an acidic environment. Trypsin's optimum pH is about 8.
::胃酸环境(低pH)中隐蔽的消化酶会帮助分解成小分子。胃中主要的消化酶是pepsin,在pH值约为1.5。这些酶在其他pH值上不会发挥最佳作用。 Tripsin是将食物中的蛋白链破碎成小部分的另一个酶。 Tripsin在不是酸环境的这个环境中起作用。 Tripsin的最佳pH值约为8。 Tripsin的最佳pH值约为8。 -
Biochemical reactions are optimal at physiological temperatures. For example, most biochemical reactions work best at the normal body temperature of 98.6˚F (37˚C). Many enzymes lose function at lower and higher temperatures. At higher temperatures, an enzyme's shape deteriorates, and only when the temperature comes back to normal does the enzyme regain its shape and normal activity.
::生物化学反应在生理温度下是最佳的。例如,大多数生物化学反应在正常体温98.6 °F (37 °C) 时效果最好。许多酶在低温和高温下失去功能。在高温下,酶的形状会恶化,只有在温度恢复正常时,酶才会恢复其形状和正常活动。
Importance of Enzymes
::酶的重要性Enzymes are involved in most of the chemical reactions that take place in organisms. About 4,000 such reactions are known to be catalyzed by enzymes, but the number may be even higher. In , an important function of enzymes is to help digest food. Digestive enzymes speed up reactions that break down large molecules of , proteins, and fats into smaller molecules the body can use. Without digestive enzymes, animals would not be able to break down food molecules quickly enough to provide the energy and nutrients they need to survive.
::酶涉及大多数在生物中发生的化学反应。已知约有4,000种反应被酶催化,但数量可能更高。在其中,酶的一个重要功能是帮助消化食物。消化酶加速反应,将大型分子、蛋白质和脂肪分解成体能使用的较小分子。没有消化酶,动物将无法快速地分解食物分子,以提供它们生存所需的能量和营养。Summary
::摘要-
Enzymes are needed to speed up chemical reactions in organisms. They work by lowering the activation energy of reactions.
::需要酶来加速生物体中的化学反应,通过降低反应的活性能量来发挥作用。 -
Enzymes position substrates into active sites.
::酶位置基质进入活动站点。 -
Various conditions affect enzyme function. Pepsin and trypsin are two digestive enzymes that work in contrasting environments.
::各种条件影响酶功能。Pepsin和trypsin是两种消化酶,在对比环境下起作用。
Review
::回顾-
In general, how do enzymes speed up chemical reactions?
::一般而言,酶如何加速化学反应? -
How do enzymes bring reactants together? How is it beneficial?
::酶如何将反应体凝聚在一起?它有什么好处? -
Explain why organisms need enzymes to survive.
::解释为什么生物需要酶生存。 -
What are the conditions necessary for enzymes to perform optimally?
::酶发挥最佳作用的必要条件是什么? -
What are pepsin and trypsin?
::什么是pepsin和trypsin? 和试探?
-
Enzymes bring reactants together so they don't have to expend energy moving about until they collide at random. Enzymes bind both reactant molecules (called
substrates
), tightly and specifically, at a site on the enzyme molecule called the
active site
(
Figure
). This forms an enzyme-substrate complex.