6.1 光合合成物 - 高级
章节大纲
-
When you're hungry, what do you do?
::当你饿了,你会做什么?Well, a plant cannot eat. So it has to make its own food . How does it do this? . And it all starts with sunlight.
::植物不能吃东西,所以它必须自己做食物。它是如何做到的?它从阳光开始。Photosynthesis
::光合作用All living things require an ongoing source of energy to do the work of life. You often see energy in action on a large scale: a whale breaches, apple blossoms swell and burst, a firefly glows, or an inky cap mushrooms overnight. However, energy works constantly to maintain life on a very small scale as well. Inside each of every organism , energy assembles chains of information and constructs cellular architecture. It moves tiny charged particles and giant molecules. Moreover, it builds and powers cell systems for awareness, response, and . All life’s work requires energy.
::所有生物都需要不断的能源来完成生命。 你经常看到大规模地在行动上的能量:鲸鱼破裂、苹果花膨胀和爆裂、萤火虫发光或一对晚上的圆顶蘑菇。 然而,能源也不断在维持非常小的规模的生命。 在每个生物体中,能源集合信息链和构建细胞结构。它移动微小的带电粒子和巨型分子。 此外,它为意识、反应和 — — 建立和增强细胞系统。 所有生命的工作都需要能量。Physics tells us that organized systems, such as living organisms, tend to disorder without a constant input of energy. You have direct, everyday experience with this law of nature: after a week of living in your room, you must spend energy in order to return it to its previous, ordered state. Tides and rain erode your sandcastles, so you must work to rebuild them. And your body, after a long hike or big game, must have more fuel to keep going. Living things show amazing complexity and intricate beauty, but if their source of energy fails, they suffer injury, illness, and eventually death.
::物理学告诉我们,有组织系统,如生物体,在没有不断投入能量的情况下,往往会扰乱秩序。你对自然法则有直接的日常经验:在你住在家里一周后,你必须花精力将它恢复到原来的状态。潮汐和雨水侵蚀你的沙砾,因此你必须努力重建它们。在远足或大游戏之后,你的身体必须有更多燃料才能继续发展下去。生活的东西表现出惊人的复杂性和复杂的美貌,但如果能量来源失效,他们就会受伤、生病并最终死亡。Physics also tells us that, although energy can be captured or transformed, it inevitably degrades, becoming heat, a less useful form of energy. This is why organisms require a constant input of energy; the work they must do uses up the energy they take in. Energy, unlike materials, cannot be recycled. The story of life is a story of – its capture, transformation, use for work, and loss as heat.
::物理学还告诉我们,尽管能源可以被捕捉或改变,但它不可避免地会退化,变成热力,成为较不有用的能源形式。 这就是为什么生物体需要不断投入能源;他们必须利用所吸收的能源。 能源与材料不同,不能被回收。 生命的故事是一个故事 — — 它的捕捉、转化、工作使用和作为热力的流失。Energy , the ability to do work, can take many forms: heat, nuclear, electrical, magnetic, light, and chemical energy. Life runs on chemical energy - the energy stored in covalent bonds between atoms in a molecule. Where do organisms get their chemical energy? That depends. Most organisms get their energy from the food they make, eat or absorb. Plants, for example, make their own "food" through the process of photosynthesis. When we eat a plant, such as lettuce or a tomato, we acquire energy. This energy is in the form of glucose , a simple sugar . Or the energy may be in the form of a starch , which we eat and then our body breaks down into glucose. This glucose then must be converted into usable chemical energy. Chemical energy in our cells is ATP . Glucose is converted into ATP during .
::能源、 工作能力可以采取多种形式: 热、 核、 电、 磁、 光、 化学能。 生命在化学能上运行, 能量储存在分子中的原子之间的共价联系中。 生物的化学能量在哪里得到? 这取决于生物的化学能量在哪里? 大多数生物的能量来自它们制造、 食用或吸收的食物。 例如, 植物通过光合作用的过程, 生产自己的“ 食物 ” 。 当我们吃一种植物, 如生菜或番茄, 我们获得能量。 这种能量以葡萄糖的形式, 一种简单的糖。 或者能量可能以恒星的形式存在, 我们吃, 然后我们的身体分解成葡萄糖。 这种葡萄糖随后必须转化成可用的化学能量。 我们细胞中的化学能量是 ATP。 甘蔗在使用期间被转化成ATP 。This diagram depicts photosynthesis. CO 2 and H 2 O enter the plant leaf cell, and in the presence of solar energy, these reactants are converted into the products O 2 and glucose.
::该图描绘了光合作用。 CO2和H2O进入植物叶细胞,在有太阳能的情况下,这些反应器转换成O2和葡萄糖产品。Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
::光合成和细胞呼吸What is the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration? Does photosynthesis have to occur prior to cellular respiration? No. Though it is true that the products of photosynthesis are the reactants of cellular respiration, the two can occur simultaneously in the . The of photosynthesis also obviously occur during daylight hours, while the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis and the reactions of cellular respiration can occur whenever reactants are available.
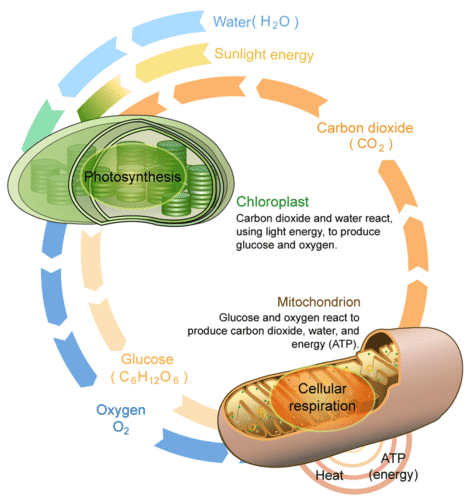
::光合作用与细胞呼吸之间的关系是什么?光合作用是否必须在细胞呼吸前发生?不。虽然光合作用的产品是细胞呼吸的反作用物,但两者可以同时发生。光合作用显然也在白天发生,而光合作用和细胞呼吸的轻度独立反应可以在有反应物时发生。This diagram compares and contrasts photosynthesis (in the chloroplast) and cellular respiration (in the mitochondria). It also shows how the two processes are related.
::该图比较并对比了光合作用(氯平板)和细胞呼吸(mitochondria),还显示了这两个过程之间的关系。Summary
::摘要-
All organisms require a constant input of energy to do the work of life; life runs on chemical energy.
::所有生物都需要不断投入能量来完成生命的工作;生命依靠化学能量进行。 -
Energy cannot be recycled; energy must be constantly captured by organisms in an ecosystem, transformed and passed to other organisms.
::能源不能回收利用;能源必须不断被生态系统中的有机体吸收、转化并传递给其他有机体。 -
Most energy is lost to the environment as heat.
::大部分能源随着热量而丧失于环境之中。
Review
::回顾-
Compare the behavior of energy to the behavior of matter in living systems.
::将能量的行为与物质在生命系统中的行为作比较。 -
Describe the forms of energy in living organisms.
::描述活生物体中的能量形式。 -
What happens to most of an ecosystem's energy?
::生态系统的大部分能量会怎么样? -
Do photosynthesis and cellular respiration occur dependent of each other? Does photosynthesis have to occur prior to cellular respiration?
::光合作用和细胞呼吸是否互相依赖?光合作用是否必须在细胞呼吸前发生?
-
All organisms require a constant input of energy to do the work of life; life runs on chemical energy.