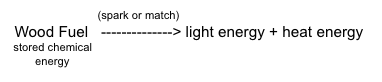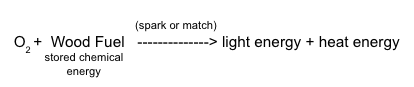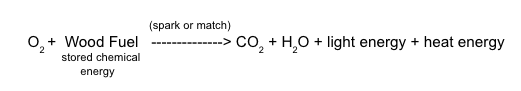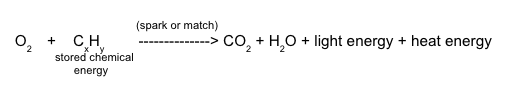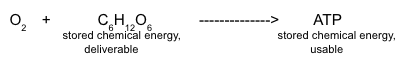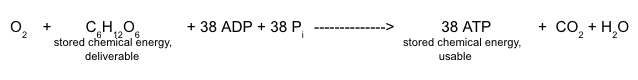6.10 细胞呼吸概览 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
Why eat?
::为什么吃?Because we're hungry. Not necessarily. Biologically speaking, we eat to get energy . The food we eat is broken down, the glucose extracted, and that energy is converted into ATP . In other words, energy is released from the food we eat so that energy can be used by our body. This happens most efficiently in the presence of oxygen.
::因为我们饿了,不一定。从生物学角度讲,我们吃东西是为了获得能量。我们吃的食物被分解,葡萄糖被提取,能量被转化成ATP。换句话说,我们吃的食物释放能量,这样我们的身体就可以使用能量。在氧气的存在下,这最为有效。In the Presence of Oxygen
::以氧气的存在,We breathe in oxygen, the oxygen enters our lungs where gas exchange occurs, and then the oxygen travels in our bloodstream to be delivered to each and every one of our . Why?
::我们在氧气中呼吸, 氧气进入我们的肺部, 当气体交换发生, 然后氧气在我们的血液中流动, 送到我们的每一个。为什么?So cellular respiration can occur efficiently.
::这样细胞呼吸就能高效地进行。You know that during cellular respiration, energy is converted from glucose, in the presence of oxygen, into numerous ATP molecules. Glucose contains lots of energy, but that energy must be converted into a form usable by cells. Glucose comes from the food you eat. But why is the presence of oxygen important?
::你知道,在细胞呼吸期间,能量从甘蔗中,在氧气的存在下,转换成无数ATP分子。甘蔗含有大量能量,但能量必须转换成细胞可以使用的形态。甘蔗来自你所吃的食物。但为什么氧气的存在很重要?One way to think about the role of oxygen in your body - and a good starting point for understanding the whole process of cellular respiration - is to recall (or imagine) the last time you sat by a campfire and noticed that it was "dying." Often people will blow on a campfire to keep it from "dying out." How does blowing help? What happens in a campfire?
::思考氧气在你身体中作用的一个方法 — — 以及理解整个细胞呼吸过程的一个良好起点 — — 是回忆(或想象)你最后一次坐在营火边,发现这是“死亡 ” 。人们常常会吹在营火上,以免“死亡 ” 。 吹气如何帮助?在营火里会发生什么?You know that a fire produces light and heat energy. However, it cannot create energy (remember that energy cannot be created or destroyed). Fire merely transforms the energy stored in its fuel – chemical energy – into light and heat. Another way to describe this energy transformation is to say that burning releases the energy stored in the fuel. As energy is transformed, so are the compounds that make up the fuel. In other words, burning is an energy-releasing chemical reaction , as is cellular respiration. Burning begins with a wood fuel (or other fuel source), whereas cellular respiration begins with glucose.
::你也知道火能能产生光和热能。然而,火能不能创造能源(记住能源无法创造或摧毁 ) 。 火能只是将燃料中储存的能源 — — 化学能源 — — 转化为光和热。 另一种描述能源变化的方式是说燃烧释放燃料中储存的能源。 随着能源的转变,构成燃料的化合物也是如此。 换句话说,燃烧是一种能释放化学反应,就像细胞呼吸一样。 燃烧始于木柴燃料(或其他燃料源 ) , 而细胞呼吸则始于葡萄糖。We could write our understanding of this energy-releasing chemical reaction up to this point as:
::我们可以写下我们对这种能耗释放化学反应的理解,Now return to what happens when you blow on a fire. The fire was "dying out," so you blew on it to get it going again. Was it movement or something in the air that promoted the chemical reaction? If you have ever "smothered" a fire, you know that a fire needs something in the air to keep burning. That something turns out to be oxygen. Oxygen gas is a reactant in the burning process. Now we can add the oxygen reactant to our equation:
::现在回到你吹着火时发生的事情。 火正在“ 熄灭 ” , 于是你吹灭它, 让它重新燃起。 它是否在空气中运动, 或是什么促使化学反应的? 如果你曾经“ 窒息” 着火, 你知道火需要空气中的东西才能继续燃烧。 这实际上是氧气。 氧气是燃烧过程中的一种反应剂。 现在我们可以在等式中添加氧反应剂:To complete this equation, we need to know what happens to the atoms of oxygen and to the atoms of the wood fuel during this process. If you use a test tube to collect the gas rising from a piece of burning wood, you will notice condensation - droplets appearing on the sides of the tube. But what is this condensation? Is there another collected gas as well?
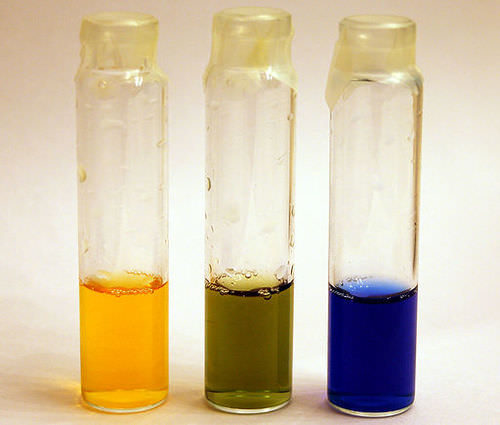
::要完成这个方程, 我们需要知道在这一过程期间氧原子和木柴燃料原子会发生什么。 如果您使用一个测试管收集燃烧木头产生的气体, 您将会注意到凝结- 管边上出现的滴子。 但是, 这个凝结是什么? 还有另一个收集的气体吗 ?To identify the products , two can be performed. When you add bromothymol blue (BTB) to a second tube of collected gases, the blue solution will change to green or yellow ( Figure ), indicating the presence of carbon dioxide. In addition, makes cobalt chloride paper change from blue to pink, so testing the condensation collected in a second test tube will allow this verification. These experiments will demonstrate that carbon dioxide and water are products of burning wood fuel
::为了识别产品,可以执行两个产品。当您在第二管收集的气体中添加溴二苯醚蓝色(BTB)时,蓝色溶液将变为绿色或黄色(图),表明二氧化碳的存在。此外,将氯化钴纸从蓝色变成粉色,因此测试在第二个试验管中收集的凝结将允许进行这一核查。这些实验将证明二氧化碳和水是燃烧木柴燃料的产品。Bromothymol blue (BTB) changes from blue to green to yellow as carbon dioxide is added. Thus, it is a good indicator of this product of burning or cellular respiration. The oxygen atoms have been incorporated into carbon dioxide and water, and these products can be added to our equation.
::氧原子已经融入二氧化碳和水中, 这些产品可以加入我们的方程。The oxygen atoms have been incorporated into carbon dioxide and water, but what are the sources of the carbon and hydrogen atoms? These atoms make up the wood fuel – and nearly all fuels we burn, from coal to propane to candle wax to gasoline. Obviously, the carbon and hydrogen atoms did not come from the oxygen gas, so they must come from the other reactant, the fuel source.
::氧原子已经融入二氧化碳和水中,但碳和氢原子的来源是什么? 这些原子构成木柴燃料 — — 以及几乎所有我们燃烧的燃料 — — 从煤炭到丙烷、蜡烛到汽油。 显然,碳和氢原子并非来自氧气,因此它们必须来自其他反应器 — — 燃料源。Overall, burning is the combining of oxygen with hydrogen and carbon atoms in a fuel (combustion or oxidation) to release the stored chemical energy as heat and light. Products of combustion are carbon dioxide (oxidized carbon) and water (oxidized hydrogen). The equation can now be modified.
::总体而言,燃烧是指将氧与燃料(燃烧或氧化)中的氢和碳原子结合起来,释放储存的化学能源作为热和光,燃烧产品是二氧化碳(氧化碳)和水(氧化氢)。Cellular Respiration
::细胞呼吸Recall that rate and oxygen intake relates to energy use. Burning consumes oxygen as it releases stored chemical energy, transforming it into light and heat. Cellular respiration is actually a slow burn. Your cells absorb the oxygen carried by your from your lungs, and use the oxygen to release stored chemical energy so that you can use it. Remember that ATP is often referred to as the energy currency of the cell, so the stored chemical energy must be converted into the usable form, ATP.
::提醒大家注意, 速度和氧摄入量与能源使用有关。 燃烧消耗氧, 因为它释放了储存的化学能量, 将它转化为光和热。 细胞呼吸实际上是一种缓慢的燃烧。 您的细胞吸收了您肺部携带的氧气, 并使用氧气释放存储的化学能量, 以便您使用。 记住, ATP通常被称为电池的能量货币, 因此存储的化学能量必须转换成可用的形式 , ATP 。Stages of Cellular Respiration
::细胞呼吸阶段Cellular respiration involves many chemical reactions. As you saw earlier, the reactions can be summed up in this equation:
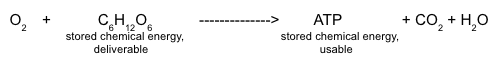
::细胞呼吸涉及许多化学反应。正如你先前所见,反应可以在此方程式中进行总结:C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 → 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + Chemical Energy (in ATP)
::C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6O2 + 6CO2 + 6H2O+ 化学能源(在ATP中)This reaction shows that all of the atoms in the glucose and oxygen gas reactants are accounted for in the carbon dioxide and water products. The reactions of cellular respiration can be grouped into three stages: , the (also called the citric acid cycle), and . Exactly how the energy held within glucose is converted into ATP will be the topic of subsequent concepts. So how does this reaction relate to the burning of wood fuel reaction introduced above?
::这种反应表明,所有葡萄糖和氧气反应器中的原子都计入二氧化碳和水产品中。细胞呼吸反应可以分为三个阶段:......(也称为柠檬酸循环)和.在葡萄糖中的能量是如何转化成ATP的,将是随后概念的主题。因此,这种反应与上述木柴燃料反应的燃烧有何关系?Obviously, releasing energy within cells does not produce light or intense heat. Cells run on chemical energy – specifically, the small amount temporarily stored in ATP molecules. Cellular respiration transfers chemical energy from a fuel molecule – glucose – to many usable molecules of ATP. Like oxygen, glucose is delivered by your blood to your cells. If ATP were delivered to cells, more than 60,221,417,930,000,000,000,000,000 of these large molecules (which contain relatively small amounts of energy) would clog your capillaries each day. Using to pump them across would actually use a great deal of energy. A single molecule of glucose actually contains a larger amount of chemical energy, in a much smaller package. Therefore, glucose is much more convenient for bloodstream delivery, but too "powerful" to work within the cell.
::显然,细胞中的释放能量不会产生光或高热。 细胞在化学能量上运行 — — 特别是少量临时储存在ATP分子中的能量。 细胞呼吸将化学能量从燃料分子 — — 葡萄糖 — — 转移到许多可用的ATP分子。 和氧一样,葡萄糖通过血液输送到细胞。 如果将ATP输送到细胞中,超过60,221,417,937,930,000,000,000,000,000,000个大型分子(其中含有相对少量的能量 ) , 每天会堵塞你的心血管。 使用抽动它们实际上会使用大量的能量。 一种单体细胞分子实际上含有较大数量的化学能量,在更小的组合中。 因此,葡萄糖对血液输送来说更为方便,但“力量”太大,无法在细胞中工作。The process of cellular respiration uses oxygen to help transfer the chemical energy from glucose to ATP, which can be used to do work in the cell. This chemical equation expresses what we have worked out:
::细胞呼吸过程使用氧气帮助将化学能量从甘蔗糖转移到ATP,ATP可用于在细胞中工作。As with burning, we must trace what happens to atoms during cellular respiration. Keep in mind the products of wood fuel burning discussed above. You can readily see that when the carbon atoms in glucose are combined with oxygen, they again form carbon dioxide. When the hydrogen atoms in glucose are oxidized, they form water, as in a burning reaction. You can detect these products of cellular respiration in your breath on a cold day (as water condensation) and in the lab (BTB turns yellow when you blow into it through a straw).
::和燃烧一样, 我们必须追踪细胞呼吸期间原子发生的情况。 记住上文讨论过的木柴燃料燃烧产物。 您可以很容易看到, 当葡萄糖中的碳原子与氧相结合时, 它们会再次形成二氧化碳。 当葡萄糖中的氢原子被氧化时, 它们会形成水, 就像燃烧反应一样。 您可以在寒冷的一天( 水凝结) 和实验室中检测出呼吸中的细胞呼吸产物( 当通过吸管吹入时, BTB 变成黄色 ) 。This equation accounts for the energy transfer and the carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, but it does not show the "raw materials" or reactants that build ATP. Recall that the energy temporarily stored in ATP is released for use when the bond between the second and third phosphate is broken. The resulting ADP can be recycled within the cell by recombining it with inorganic phosphate (P i ).
::这个方程式可以计算能量转移和碳、氢和氧原子,但不能显示制造ATP的“原材料”或反应剂。提醒注意,在二、三磷酸盐的结合破裂时,暂时储存在ATP中的能量会释放出来使用。 由此产生的ADP可以通过与无机磷酸( Pi)重组在细胞内回收利用。Like recharging batteries, cells recycle ATP and ADP (and AMP) molecules by combining them with inorganic phosphate. When the high-energy bond between phosphate groups in ATP breaks, its chemical energy can do cellular work. The bonds between phosphate groups can be broken and reformed, recycling this cellular energy. The source of energy for re-attaching the phosphate and making ATP is the chemical energy in glucose. Materials cycle and recycle, but energy gets used up and must be replaced. That is the key to understanding cellular respiration: it is a "recharging of the batteries" - ATP molecules – which power cellular work. How many ATP can be made by harnessing the energy in a single glucose molecule? Although this number varies under certain conditions, most cells can capture enough energy from one molecule of glucose to build 38 molecules of ATP. Our equation now becomes:
::重新连接磷酸盐和制造ATP的能量来源是葡萄糖中的化学能量。 材料循环和再循环,但能量被耗尽,必须被替换。 这是理解细胞呼吸的关键:它是“电池的补给 ” — —ATP分子 — —是哪个细胞的动力工作。通过在单一葡萄糖分子中利用能量可以制造多少ATP?尽管这个数字在某些条件下有所不同,但大多数细胞可以从一个葡萄糖分子中捕捉足够的能量来制造ATP的38个分子。我们现在的公式是:Mitochondria
::密托昆德里亚NameThis equation for cellular respiration is not quite complete, however, because we can easily mix air and glucose sugar (even adding ADP and P i ) and nothing will happen. For the campfire, we indicated above the arrow that a necessary condition was a spark or match to start the reaction. A spark or match would damage or destroy living tissue . What necessary condition initiates the slow burn that is cellular respiration?
::然而,细胞呼吸的这个方程式并不完全,因为我们很容易混合空气和葡萄糖糖(甚至添加ADP和Pi),不会发生任何事情。对于营火,我们在箭头上表示,一个必要的条件是引发反应的火花或匹配。一个火花或匹配会破坏或摧毁活组织。什么必要条件会引发细胞呼吸的缓慢燃烧?Recall that are highly specific that "speed up" or catalyze chemical reactions in living cells. More than 20 different enzymes are necessary to carry out cellular respiration. Recall also that membranes within often sequence enzymes for efficiency. Just as membranes sequence enzymes for , membranes ( Figure ), sequence enzymes for cellular respiration - at least in eukaryotes .
::提醒人们注意“ 加速” 或催化活体细胞中的化学反应非常具体。 20多种不同的酶是实施细胞呼吸所必需的。 还要提醒人们注意经常序列酶中的膜, 以提高效率。 正如膜序列酶, 用于细胞呼吸的膜序列酶( Figure ) , 用于细胞呼吸的序列酶( eukaryotes ) —— 至少在 eukaryotes 中 。Mitochondria, shown here as the green ovals in this animal cell, are membranous organelles which sequence enzyme and electron carrier molecules to make cellular respiration highly efficient. Mitochondria have both an inner and outer membrane, with a matrix inside the inner membrane. The inner membrane has many internal folds, increasing the surface area for proteins and molecules involved in cellular respiration. Within each eukaryotic cell , the membranes of a few to a few thousand mitochondria sequence enzymes and electron carriers and compartmentalize ions so that cellular respiration proceeds efficiently.
::在每一尤卡利细胞中, 几到几千毫微分数序列酶和电子载体的膜, 以及分离离子, 以便细胞呼吸的有效进行。Within each eukaryotic cell, the membranes of a few to a few thousand mitochondria sequence enzymes and electron carriers and compartmentalize ions so that cellular respiration proceeds efficiently.
::在每一尤卡利细胞中, 几到几千毫微分数序列酶和电子载体的膜, 以及分离离子, 以便细胞呼吸的有效进行。Including these necessary conditions and balancing numbers of atoms on both sides of the arrow, our final equation for the overall process of cellular respiration is:
::包括这些必要条件和平衡箭头两侧原子的数量,我们细胞呼吸总体过程的最后等式是:In words, cellular respiration uses oxygen gas to break apart the carbon- hydrogen bonds in glucose and release their energy to build 38 molecules of ATP. Most of this process occurs within the mitochondria of the cell. Carbon dioxide and water are waste products. This is similar to burning, in which oxygen breaks the carbon-hydrogen bonds in a fuel and releases their chemical energy as heat and light. Again, carbon dioxide and water are waste.
::换句话说,细胞呼吸利用氧气打破葡萄糖中的碳-氢联结,释放其能量以制造ATP的38个分子。这一过程大多发生在细胞的分子内,二氧化碳和水是废物产品。这与燃烧类似,在燃烧中,氧打破燃料中的碳-氢联结,释放其化学能量作为热和光。二氧化碳和水也是废物。Highly Valuable Symbionts
::高可贵的交苯Mitochondria, like chloroplasts, contain their own and and resemble certain . The Theory of Endosymbiosis holds that mitochondria, like chloroplasts, were once independently living . Larger prokaryotes engulfed (or enslaved) these smaller aerobic cells, forming eukaryotic cells. Many prokaryotes today can perform cellular respiration; perhaps they and mitochondria have common ancestors . Their expertise in generating ATP made mitochondria highly valued symbionts.
::Mitochondria像叶绿板一样,含有自己的和类似某些东西。“内地生物论”认为,像叶绿板一样的米托乔因德里亚曾经独立生活过。较大的蛋白质被吞没(或被奴役 ) , 这些较小的有氧细胞组成了eukary细胞。今天,许多prokaryotes可以进行细胞呼吸;也许他们和mitochondria有共同的祖先。他们在产生ATP(ATP)方面的专门知识是高价值的共生体。Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
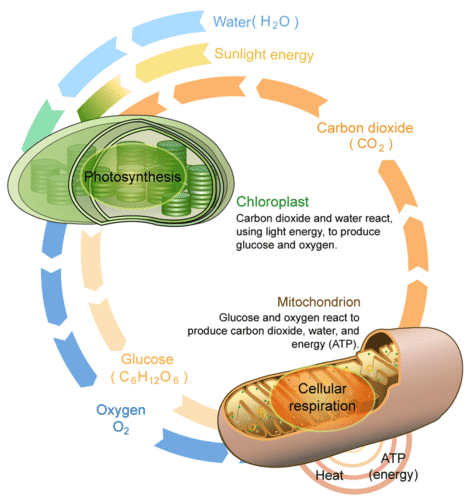
::细胞呼吸和相光合成Comparing this process to that of photosynthesis, the similarity between the two processes is striking. Both are processes within the cell that make chemical energy available for life. Photosynthesis transforms light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose, and cellular respiration releases the energy from glucose to build ATP, which does the work of life. Moreover, photosynthesis reactants CO 2 and H 2 O are products of cellular respiration. And the reactants of respiration , C 6 H 12 O 6, and O 2 , are the products of photosynthesis. This interdependence is the basis of the carbon-oxygen cycle ( Figure ), which connects to consumers and their environment. At first glance, the cycle merely seems to show mitochondria undoing what chloroplasts do; but the cycle's energy transformations power all the diversity, beauty, and mystery of life.
::将这个过程与光合作用的过程相比,这两个过程的相似性是惊人的。这两个过程都是使化学能量可以用于生命的细胞内过程。光合作用将光能转化为储存在甘蔗糖中的化学能源,而细胞呼吸则释放出从葡萄糖中的能量,以建立适合生命的ATP。此外,光合作用反应剂CO2和H2O是细胞呼吸的产物。呼吸反应剂C6H12O6和O2是光合作用产物。这种相互依存性是碳氧循环(Figure)的基础,它与消费者及其环境相连。第一眼看,这个循环似乎只是显示Mitocondria来消除叶绿石的作品;但循环的能量转换了生命的多样性、美和神秘性。Photosynthesis in the chloroplast and cellular respiration in the mitochondrion shows the interdependence of producers and consumers, the flow of energy from sunlight to heat, and the cycling of carbon and oxygen between the living world and the environment. Summary
::摘要-
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that transfer energy from glucose (deliverable or fuel energy) to ATP (usable energy).
::细胞呼吸是一系列化学反应,将能量从葡萄糖(可交付或燃料能源)转移到可使用能源(可使用能源)。 -
Analyzing a campfire can clarify your understanding of cellular respiration. A campfire breaks chemical bonds in wood, releasing stored energy as light and heat; respiration breaks chemical bonds in glucose, releasing stored energy and transferring some to 38 ATP; some energy is lost as heat.
::分析营火可以澄清你对细胞呼吸的理解。 营火打破了木材中的化学键,释放了储存的光能和热能;呼吸打破了葡萄糖中的化学键,释放了储存的能量,转移了大约38个ATP;一些能量因热而丧失。 -
In eukaryotic cells, mitochondria organize enzymes and electron carriers and compartmentalize ions so that cellular respiration proceeds efficiently.
::在衣原体细胞中,mitochondria组织酶和电子载体,将离子分离,以便细胞呼吸有效进行。 -
Cellular respiration, in many ways the opposite of photosynthesis, shows the interdependence of producers and consumers. Combined, the two equations demonstrate how energy flows and the carbon and oxygen cycle between organisms and the environment.
::细胞呼吸在许多方面与光合作用相反,显示了生产者和消费者之间的相互依存关系。 两者加在一起,两个方程式显示了生物与环境之间的能源流动以及碳和氧循环。
Review
::回顾-
What source of energy do cells use to build ATP by cellular respiration?
::细胞通过细胞呼吸来制造ATP的能量来源是什么? -
Compare the purpose and energy content of glucose to the function and energy content of ATP; in other words, why do organisms need both kinds of energy-rich molecules?
::将葡萄糖的目的和能量含量与ATP的功能和能量含量作比较;换句话说,为什么生物需要两种能源丰富的分子? -
Compare the process of burning gasoline in your automobile's engine to the process of cellular respiration in terms of reactants, products, and necessary conditions.
::在反应器、产品和必要条件方面,将汽车发动机燃烧汽油的过程与细胞呼吸的过程进行比较。 -
Write out the chemical reaction which summarizes the overall process of cellular respiration, first in symbols as a chemical equation, and then in words in a complete sentence.
::写出化学反应,总结细胞呼吸的整个过程,首先用符号作为化学方程式,然后用文字作为句子。 -
In what eukaryote organelle does cellular respiration take place? Does this mean that prokaryotes cannot carry out the entire process of cellular respiration? Explain.
::细胞呼吸在哪个尤卡利奥特有机体中发生?这是否意味着prokaryoytes无法进行细胞呼吸的整个过程?解释一下。 -
Compare and contrast cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
::比较和对比细胞呼吸和光合作用
Recall that breathing rate and oxygen intake relates to energy use. Burning consumes oxygen as it releases stored chemical energy, transforming it into light and heat. Cellular respiration is a slow burn. Your cells absorb the oxygen carried by your blood from your lungs and use the oxygen to release stored chemical energy so that you can use it. Remember that ATP is often referred to as the energy currency of the cell, so the stored chemical energy must be converted into the usable form, ATP.
::回顾呼吸率和氧气摄入与能源使用有关。 燃烧消耗氧,因为它释放了储存的化学能源,将之转化为光和热。 细胞呼吸是一种缓慢的燃烧。 您的细胞吸收了您血液中携带的血液氧气, 并使用氧气释放了存储的化学能源, 以便您使用。 记住ATP通常被称为细胞的能量货币, 因此存储的化学能源必须转换成可用的形式 , ATP 。 -
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that transfer energy from glucose (deliverable or fuel energy) to ATP (usable energy).