7.11 心理诊断 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
How do you make a cell with half the DNA?
::你如何用半个DNA做细胞?Meiosis. This process allows to have half the number of , so two of these cells can come back together to form a new organism with the complete number of chromosomes. It not only helps produce gametes , it also ensures .
::Meisisid 。 这个过程允许有一半的 数, 所以其中两个细胞可以重新组合 来形成一个新的有机体, 染色体的完整数量。 它不仅有助于生成调子, 而且还能确保 。Meiosis
::诊断joins haploid gametes into a diploid zygote . How do gametes end up with half the amount, a haploid amount, of ? The mechanism that produces haploid cells is meiosis. Meiosis is a type of that halves the number of chromosomes. Meiosis is specific to gamete producing cells in the gonads . Meiosis begins with a diploid cell and ends with four haploid cells. These cells eventually differentiate into mature or egg cells. During meiosis the pairs of homologous chromosomes separate and segregate randomly to produce gametes with one chromosome from each pair. Only germ cells like spermatocytes and oocytes, can undergo meiosis.
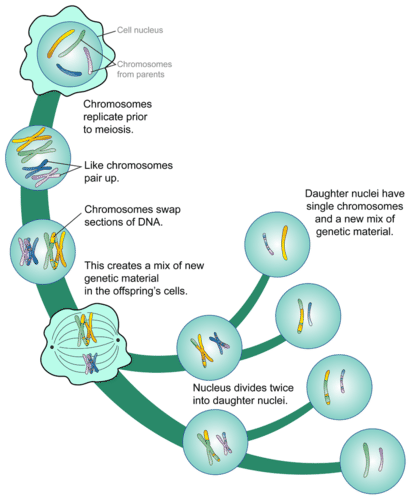
::将折叠式游戏将折叠式游戏编织成一个 diploid zygote 。 交叠式游戏的结局是如何用一半的量, 折叠式游戏的数量? 产生折叠式细胞的机制是 meiscois 。 Meisis 是一种将染色体数量减半的机制 。 Meisisis 是指在gonads 中生成折叠式细胞的游戏特有。 Meisic 开始于 diploid 细胞, 结束于 4 个折叠式细胞 。 这些细胞最终会分化为成熟或蛋细胞 。 在 meiscisation 期间, 将一对同性染色体分开并随机隔离, 产生一种染色体。 只有像精子细胞和卵细胞这样的细菌细胞, 才能经历混杂症。Overview of Meiosis. During meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate and go to different daughter cells. This diagram shows just the nuclei of the cells. Notice the exchange of genetic material that occurs prior to the first cell division. Prior to meiosis, the cell's DNA is replicated, generating chromosomes with two sister chromatids. Meiosis involves two nuclear and cell divisions without an interphase in between, so the DNA is not replicated prior to the second round of divisions. Each division, named meiosis I and meiosis II, has four stages: prophase , metaphase , anaphase , and telophase , followed by cytokinesis . These stages are similar to those of , but there are distinct and important differences.
::在美化之前,细胞的DNA被复制,产生配有两个姐妹染色体的染色体。美化涉及两个核分裂和细胞分裂,两者间没有间断,因此DNA在第二轮分裂之前没有复制。每个分裂,分别名为美化一和美化二,分为四个阶段:前阶段、元阶段、止阶段和调相,然后是细胞相位。这些阶段与...相似,但有明显和重要的差异。A human cell prior to meiosis will have 46 chromosomes, 22 pairs of homologous autosomes , and 1 pair of sex chromosomes . At the end of meiosis, each haploid cell will have 22 autosomes (not pairs) and 1 sex chromosome, either an X chromosome or a Y chromosome . You inherit one chromosome of each pair from your mother and the other one from your father.
::美化前的人类细胞将拥有46种染色体、22对同质异体和1对性染色体。在美化结束时,每只杂交细胞将拥有22种异体(非对)和1种性染色体,要么是X染色体,要么是Y染色体。你从你母亲那里继承每对染色体,另一个是你父亲的染色体。The Eight Phases
::八阶段Meiosis I begins after DNA replicates during interphase of the . In both meiosis I and meiosis II , cells go through the same four phases as mitosis - prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. However, there are important differences between meiosis I and mitosis. The eight stages of meiosis are summarized below. The stages will be described for a human cell, starting with 46 chromosomes.
::Meisisis I 是在DNA复制后开始的。在Meisis I 和 meisisis II 中,细胞经历与分裂症相同的四个阶段 -- -- 前期、后期、前期、后期、后期、后期、后期、后期等。但是,在美化一和后期之间有重大差异。兹将以下8个阶段的情况归纳如下。将描述人类细胞的阶段,从46个染色体开始。Phases of Meiosis. This flowchart of meiosis shows meiosis I in greater detail than meiosis II. Meiosis I—but not meiosis II—differs somewhat from mitosis. Compare meiosis I in this flowchart with the earlier figure featuring mitosis. How does meiosis I differ from mitosis? Meiosis I
::诊断一Meiosis I is referred to as a reductional division; it separates homologous chromosomes, producing two haploid cells. The starting diploid cell has 46 chromosomes (23 pairs of homologous chromosomes), each containing two sister chromatids attached at the centromere . After cytokinesis at the end of meiosis I, two haploid cells result. These cells contain 23 chromosomes, although each still contains two sister chromatids. Meiosis I separates the homologous pairs of chromosomes; one from each pair ends up in each resulting cell.
::甲状腺素I被称作一种减少分解法;它将同质染色体分离,产生两个杂交细胞;开始的低质细胞有46种染色体(共性染色体23对),每组含有两个姐妹染色体,附在中色素中;在美化I末端的细胞血色素后,有两个杂交细胞结果。这些细胞含有23种染色体,但每个细胞仍含有两个姐妹染色体。Meiscolid I将染色体的同质配对分离出来;每组的血色体各取一对。Prophase I
::第一阶段Prophase I is the longest phase of meiosis. It is very similar to prophase of mitosis, but with one very significant difference. In Prophase I, the nuclear envelope breaks down, the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and the centrioles begin to migrate to opposite poles of the cell, with the spindle fibers growing between them. During this time, the homologous chromosomes form pairs. These homologous chromosomes line up gene-for- gene down their entire length tetrads , allowing crossing-over to occur. This process is also called homologous recombination , and is an important step in creating genetic variation.
::预期期I是长期的梅氏病阶段。 它非常相似于肾上腺素的预期, 但有一个非常显著的差异。 在预期I中, 核包破裂, 染色体凝结为染色体, 中子开始迁移到细胞的对角, 脊椎纤维在生长。 在这段时间里, 同质染色体成对。 这些同质的染色体将基因异基因排列在它们整个四胞胎的长度上, 允许跨行。 这个过程也被称为同质重组, 并且是创造基因变异的重要一步 。Prophase I can be further divided into 5 distinct stages: Leptotene, Zygotene, Pachytene, Diplotene and Diakinesis.
::第一阶段可进一步分为5个不同阶段:莱普托坦、泽哥泰内、帕奇泰内、迪普洛滕和迪亚基内西。-
Leptotene
::列苯
The first stage of prophase I is the leptotene stage. During this stage, chromatin condenses into visible (under the microscope) chromosomes within the . Each chromosome contains two sister chromatids, and each chromosome has a homologue present in the nucleus. During this stage, the synaptonemal complex begins to assemble.
::预期I的第一阶段是异苯乙烯阶段。在这一阶段,染色素浓缩为可见的(显微镜下的)染色体。每个染色体含有两个姐妹染色体,每个染色体在核中有一个同族体。在这一阶段,苯丙胺综合体开始组装。-
Zygotene
::Zygotene 地区
The zygotene stage occurs as the chromosomes pair with their homologue forming homologous chromosome pairs, a process called synapsis . Homologous chromosomes are equal in size and genetic content, so the genes from the two chromosomes line up along the length of the chromosome. Therefore, the pairing is highly specific and exact. The paired chromosomes are called bivalent or tetrad chromosomes, as they are formed by a complex with four chromatids.
::zygotene阶段发生于染色体与同族染色体形成同族染色体的配对过程,称为同族染色体配对过程。同族染色体在大小和遗传内容上是相等的,因此两个染色体的基因与染色体的长度相依。因此配对非常具体和精确。配对染色体称为双价或四色体,因为它们是由四个染色体组成的综合体组成。-
Pachytene
::丙烯
The pachytene stage is the stage when chromosomal crossover (crossing-over) occurs. This is the process where non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes exchange segments over regions of homology. At the sites of genetic exchange, chiasmata form. This exchange of DNA results in genetic recombination , the formation of new combinations of . This process is much more common in autosomes than in sex chromosomes.
::pachymatene 阶段是染色体交叉(交叉)发生时的阶段。 在这个过程中,同质染色体的非姐妹染色体的染色体在同族体区域之间交换部分。 在基因交换地点, Chiasmata 形式。 这种DNA交换导致基因重组, 形成新的组合。 这一过程在异体中比在性染色体中更为常见。-
Diplotene
::diplotene 双极
The diplotene stage is when the synaptonemal complex degrades and homologous chromosomes disassociate slightly from each other, though they are still bound at the chiasmata (the regions of recombination).
::双硝基苯甲醚阶段是注射激素复合体降解和同族染色体略有脱钩时,尽管它们仍然被绑在黑马塔(重组区)上。In human fetal oogenesis , all developing oocytes develop to this stage and the stop. This happens in all females prior to birth. This suspended state of the oocytes is referred to as the dictyotene stage and the eggs remains in this stage until released following .
::在人类胚胎的产卵中,所有发育中的卵细胞都发展到这个阶段和停止阶段。所有雌性细胞在出生前都会出现这种情况。这种卵细胞的悬停状态被称为二甲酸酯阶段,卵子一直处于这一阶段,直到随后释放为止。-
Diakinesis
::异性恋
During the diakinesis stage, chromosomes further condense. The chiasmata remain intact during this stage. The remainder of this stage is similar to prometaphase of mitosis: the nucleoli disappear, the nuclear membrane disintegrates, and the meiotic spindle begins to form.
::在二亚辛基底阶段,染色体会进一步凝结。 奇亚斯玛塔在这个阶段保持完好无损。 本阶段的剩余部分与分裂症的甲状腺相类似:核核素消失,核膜分解,以及中子脊椎开始形成。Metaphase I
::第一阶段In metaphase I, the 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes line up along the equator or the metaphase plate of the cell. During mitosis, 46 individual chromosomes line up during metaphase, however during meiosis I, the 23 homologous pairs of chromosomes line up. Chromosomes pairs are moved into position by the spindle fibers, which are now attached to the kinetochores at the centromeres. Some chromosomes inherited from the father are facing one side of the cell, and some are facing the other side. This is the basis of independent assortment of chromosomes as suggested by Gregor .
::在元阶段一,23对同族染色体沿着赤道或细胞元阶段板块排成一列。在分裂期间,46对个别染色体在元阶段排成一列,但在分裂期间,23对同族染色体排成一列。染色体配对由螺旋纤维移到一个位置,这些纤维现在与中子体的皮质植物相连。父亲继承的一些染色体在细胞的一边,有些则在另一边。这是Gregor建议的对染色体进行独立分类的基础。Anaphase I
::分析阶段一During anaphase I the spindle fibers shorten, and the homologous chromosome pairs are separated from each other. This occurs as the chiasmata are severed, pulling homologous chromosomes apart. One chromosome from each pair moves toward one pole, with the other moving toward the other pole, resulting in a cell with 23 chromosomes at one pole and the other 23 at the other pole. Each chromosome still contains a pair of sister chromatids; the sister chromatids remain attached at the centromere.
::在前段I期间,脊椎纤维缩短,同质染色体对对彼此分离。这表现在焦马塔被割开,将同质染色体分开。一对染色体从每对移到一根杆,另一对移到另一根杆,导致一个细胞在一根杆上有23个染色体,另一根杆有23个染色体。每个染色体仍含有一对姐妹染色体;姐妹染色体仍附在中间色谱上。Because human cells have 23 pairs of chromosomes, this independent assortment of chromosomes produces 2 23 , or 8,388,608 possible chromosome configurations. More on independent assortment of chromosomes will be presented in the concepts on Mendelian Genetics .
::由于人类细胞有23对染色体,这种独立的染色体组合产生223种染色体,或8,388,608种可能的染色体组合。 更多关于染色体独立分类的介绍将在“门德勒遗传学”的概念中出现。Telophase I
::电频一一Telophase I followed by cytokinesis ends the first division of meiosis. This reduction division results in two haploid cells, each with a unique combination of chromosomes, some from the father and the rest from the mother. At this time, each chromosome is comprised of a pair of sister chromatids, even though one has undergone recombination with its homologue.
::Teloprophine I 和 cytokinesis 之后的 cytokinesis 结束了第一道梅毒分解。 这个分解导致两个手动细胞,每个细胞有独特的染色体组合,有些来自父亲,其他来自母亲。 此时, 每一个染色体由一对姐妹染色体组成, 尽管一个细胞与其同族体进行了重组。During telophase I, the spindle fiber disassembles and the nucleus reforms. The genetic material briefly uncoils back into chromatin. This is quickly followed by cytokinesis. Cells may enter a period of rest known as interkinesis or interphase II, or immediately enter meiosis II. No DNA replication occurs between meiosis I and meiosis II.
::在电讯阶段一期间,脊椎纤维分解和核改革。遗传材料短暂地不凝固地返回到染色体中。紧随其后的是细胞基质。细胞可以进入一个休息期,即Interkinesis或间歇阶段二,或者立即进入 meisisis II。Miisisis I和Miisisis II之间没有DNA复制。Meiosis II
::诊断二Meiosis II includes a division of the chromosomes, similar to that of mitosis. This division separates the sister chromatids. After cytokinesis, four haploid cells result, each with 23 chromosomes. Now each chromosome contains the equivalent of material from one chromatid . Thus, when two of these cells join in fertilization, the resulting diploid zygote has just as much DNA as a cell after mitotic cell division.
::Meisisid II 包含一个与分裂相类似的染色体的分解。 这个分解将姊妹染色体分离。 在细胞基质后, 4个手动细胞结果, 每个细胞有23个染色体。 现在每个染色体含有一个染色体的等同材料。 因此, 当其中两个细胞加入受精时, 产生的diploid zygote 拥有的DNA和 线性细胞分解后的细胞一样多。Prophase II
::第二阶段In prophase II, once again the nucleolus disappears and the nucleus breaks down. The chromatin condenses into chromosomes. The spindle begins to reform as the centrioles move to opposite sides of the cell.
::在第二期,核核素再次消失,核核崩溃。染色体凝结为染色体。脊椎开始改革,因为核素向细胞两侧移动。Metaphase II
::第二阶段During metaphase II, the spindle fibers align the 23 chromosomes, each made out of two chromatids, along the equator of the cell. The new metaphase plate is rotated by 90 degrees when compared to meiosis I, perpendicular to the previous plate.
::在元阶段二,脊椎纤维对齐了23个染色体,每个染色体由两个染色体组成,沿着细胞赤道。新的元相板与前一个盘体垂直,与第1部部部位相比,旋转90度。Anaphase II
::第二阶段Anaphase II separates chromatids, similar to anaphase of mitosis. During anaphase II, sister chromatids are separated as the centromeres are cleaved. The chromatids move to opposite poles of the cell. As the chromatids separate, each is known as a chromosome. Anaphase II results in a cell with 23 chromosomes at each pole of the cell; each chromosome contains half as much genetic material as at the start of anaphase II.
::相位二分离染色体,类似于分裂相。在相位二期间,姐妹染色体随着中子切开而分离。相色谱体移动到细胞的对角。相色谱体分开时,每个相色谱体被称为染色体。相位二的结果是细胞各极有23个染色体;每色谱体含有一半的遗传物质,与相位二开始时相同。Telophase II
::第二阶段Telophase II and cytokinesis end meiosis. During this last phase of meiosis, the nucleus reforms and the spindle fibers break down. The chromosomes uncoil into chromatin. Each cell undergoes cytokinesis, producing four haploid cells, each with a unique combination of genes and chromosomes.
::Telotephone II 和 cytokinesis 终止了 meisis 。 在最后的 meisis 阶段, 核改造和脊椎纤维破裂。 染色体没有凝固到染色体中。 每个细胞都经过细胞细胞化, 产生四个手动细胞, 每个细胞都有独特的基因和染色体组合。Meiosis, divided into meiosis I and meiosis II, is a process in which a diploid cell divides itself into four haploid cells. Note that meiosis II immediately follows meiosis I; DNA replication does not occur after meiosis I. Notice how the chromosomes align in prophase I. The alignment of homologous chromosomes allows for crossing-over, a process that increases genetic variability, which will be discussed in more detail in another concept. Summary
::摘要-
Meiosis is a type of cell division that halves the number of chromosomes.
::Meisisis是一种细胞分裂, 将染色体数量减半。 -
There are eight stages of meiosis, divided into meiosis I and meiosis II. DNA is not replicated between meiosis I and meiosis II.
::有8个阶段的肾上腺素中毒,分为1级和2级。 DNA在1级和2级之间没有复制。
Review
::回顾-
Outline the phases of meiosis.
::剖析部位的轮廓 。 -
Compare and contrast meiosis I and meiosis II.
::对比和对比一和二 -
Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis.
::比较和对比 肾上腺素和肾上腺素。 -
Explain why sexual reproduction results in genetically unique offspring.
::解释为什么性生殖导致遗传上独特的后代。 -
Name and describe the processes shown in this diagram.
::名称并描述此图表中显示的程序 。
-
Leptotene