7.14 性生活周期 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
Young to old: a life cycle?
::年轻到老:生命周期?Not in the biological sense. Life cycles refer to the amount of present at a specific stage or time in the life of an organism . Is there a haploid or diploid amount of DNA? That is the key question.
::不是生物意义上的。 生命周期是指在生物体生命的特定阶段或时间中存在的数量。 是否有DNA的随机或稀释量? 这是关键问题 。Sexual Life Cycles
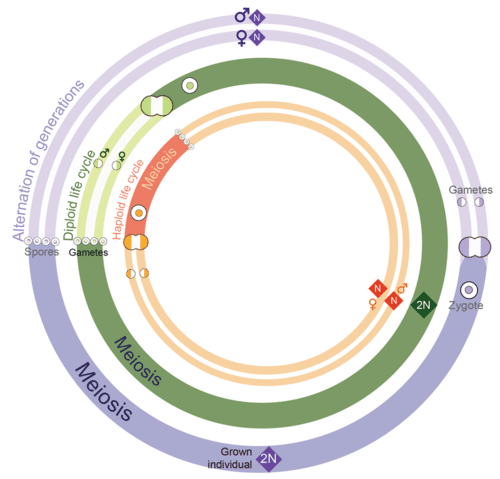
::性生活周期Eukaryotes have three different versions of the sexual life cycle : a haploid life cycle , a diploid life cycle , and a life cycle known as the alternation of generations ( Figure ). A life cycle is the span in the life of an organism from one generation to the next. All that reproduce sexually follow a basic pattern, alternating between haploid and diploid numbers. The sexual life cycle depends on when occurs and the type of that undergoes meiosis.
::Eukaryotes有三个不同版本的性生命周期:短暂的生命周期、短暂的生命周期和被称为世代交替的生命周期(图 ) 。 生命周期是指生物体从一代到下一代的生命周期。 所有性繁殖都遵循一种基本模式,在随机数字和低位数字之间交替。 性生命周期取决于发生时间和经历大病的类型。Sexual Life Cycles. Haploid Life Cycles
::人 类 类 类 类 人 寿命周期The haploid life cycle is the simplest life cycle. Organisms with this life cycle, such as many and some and , spend the majority of their life cycle as a haploid cell. In fact, the zygote is the only diploid cell. The zygote immediately undergoes meiosis, producing four haploid cells, which grow into haploid . These organisms produce gametes by . The gametes fuse through a process called syngamy to produce diploid zygotes which undergo meiosis, continuing the life cycle.
::机极生命周期是最简单的生命周期。 生物,如许多生物和某些生物, 将生命周期的大部分时间都作为机极细胞使用。 事实上, zygote 是唯一的机极细胞。 zygote 即刻就经过了 meiosis , 生成了四个机极细胞, 这些机极细胞生长成机极。 这些有机体通过 。 游戏板通过一个叫做 合成法的过程产生机极的zygots , 以产生机极细胞, 以进行机极, 延续寿命周期 。Diploid Life Cycles
::代数寿命周期Organisms that have a diploid life cycle spend the majority of their lives as diploid adults. All diploid adults inherit half of their DNA from each parent. When they are ready to reproduce, diploid reproductive cells undergo meiosis and produce haploid gametes. These gametes then fuse through and produce a diploid zygote, which immediately enters G 1 of the . Next, the zygote's DNA is replicated. Finally, the processes of mitosis and cytokinesis produce two genetically identical diploid cells. Through repeated rounds of growth and division, this organism becomes a diploid adult and the cycle continues. This is the life cycle of humans.
::具有极低寿命周期的生物体在一生中大部分时间都作为极低寿命的成年人。所有低低寿命的成年人都从父母中继承一半的DNA。当他们准备繁殖时,低脂生殖细胞会经历美化并产生杂交游戏。这些基因组会通过并产生一种极低寿命的zygote,然后立即进入G1。接下来,zygote的DNA会被复制。最后,细胞硬化和细胞基质会产生两个基因相同的低脂细胞。通过反复的生长和分化,这种生物体会变成低温成人,周期会继续。这就是人类的生命周期。Alternation of Generations
::代代相传Plants, algae, and some protists have a life cycle that alternates between diploid and haploid phases, known as alternation of generations . In plants, the life cycle alternates between the diploid sporophyte and haploid gametophyte . Spore forming cells in the diploid sporophyte undergo meiosis to produce spores , a haploid reproductive cell. Spores can develop into an adult without fusing with another cell. The spores give rise to a multicellular haploid gametophyte, which produce gametes by mitosis. The gametes fuse, producing a diploid zygote, which grow into the diploid sporophyte.
::植物、藻类和某些原生生物的生命周期是交替的, 代代相传, 代代相传。 在植物中, 代代相传, 代代相传。 在植物中, 代代相传, 代代相传, 代代相传。 代代相传的植物中, 代代代相传的植物、 代代代相传的植物、 代代代代相传的植物、 代代代代相传的植物、 代代代代代相传的植物、 代代代代代代相传的植物、 代代代代代代代相传的植物、 代代代代代代相传的植物、 代代代代代代代代相传的植物、 代代代代代代代代相传的植物、 代代代代代代代相传的植物、 代代代代代代代代代相传的植物、 代代代代代代代相传的植物、 代代代代代代代代代代相传的植物、 代代代代代代代代相传的植物、 代的植物、 代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代的植物、 代代代代代代代的植物、 代代代代代代代代代代代代的植物、 代的植物、 代代代的植物、 代的植物、 代代的植物、 、 代的植物、 代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代的植物、 、 代的植物、 代代的植物、 代代代代代代代代的植物、 、 、 代 代 代的植物、 代代代 代代代代代 、 代的植物、 代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代代Summary
::摘要-
A life cycle is the sequence of stages an organisms goes through from one generation to the next.
::生命周期是生物一代一代又一代经历的阶段的顺序。 -
Organisms that reproduce sexually can have different types of life cycles, such as haploid or diploid life cycles.
::性繁殖的生物可以有不同种类的生命周期,如杂交或低潮的生命周期。
Summary of all three life cycles. Review
::回顾-
What is meant by a "life cycle?"
::什么是“生命周期”的含义? -
Describe the main differences between a haploid and diploid life cycle.
::描述一个周期周期与周期周期之间的主要差异。 -
Define syngamy.
::定义共性。 -
What is alternation of generations?
::什么是世代的交替?
-
A life cycle is the sequence of stages an organisms goes through from one generation to the next.