8.17 DNA DNA 修理 - 高级
章节大纲
-
How is DNA repaired?
::DNA是如何修复的?Not by nanobots. But luckily the does have mechanisms to repair mistakes in the . And these mechanisms involve .
::不是纳米机器人。但幸运的是,这些机器确实有修复错误的机制。这些机制涉及。DNA Repair
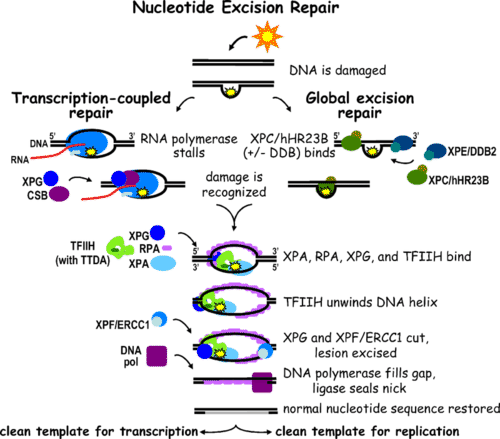
::DNA修复DNA repair refers to a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to DNA. Many have no effect on the organism because they are repaired before occurs. Cells have multiple repair mechanisms to fix mutations in DNA. One way DNA can be repaired, called nucleotide excision repair is illustrated in Figure . If a cell’s DNA is permanently damaged and cannot be repaired, the cell is likely to be prevented from dividing.
::DNA修复是指细胞识别和纠正对DNA的损害的过程汇编。许多人对有机体没有影响,因为它们在DNA发生之前就已经修复过。细胞有多种修复机制可以修复DNA中的突变。一种方法可以修复DNA,称为核酸解剖修复。如果细胞的DNA永久受损,无法修复,细胞就可能无法分离。When DNA is damaged by sunlight, the damage is recognized differently depending on whether the DNA is transcriptionally active (transcription-coupled repair) or not (global excision repair). After the initial recognition step, the damage is repaired in a similar manner with the final outcome being the restoration of the normal nucleotide sequence. One form of DNA repair corrects mistakes made during DNA replication or recombination . DNA mismatch repair is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion and mis-incorporation of bases that can arise during these processes. Mismatch repair is a highly conserved process from to eukaryotes . The Mut proteins are the major active components of this repair system. MutS, MutH and MutL are three proteins essential in detecting the mismatch and directing repair machinery to it. These three proteins recognize the mismatch and cause the DNA to loop out. MutH cuts the DNA strand near the closest methylated site to the mismatch, and a helices separates the DNA strands. The entire MutSHL complex then slides along the DNA in the direction of the mismatch, followed by an exonuclease that digests the single-stranded DNA. The single-stranded gap created by the exonuclease is then be repaired by DNA Polymerase III.
::DNA修复的一种形式是DNA复制或重组过程中的错误纠正。DNA脱节修复是一种识别和修复错误插入、删除和错误整合这些过程中可能出现的基础的系统。 错配修复是一种高度节制的过程, 是一个从eukaryotes到eukaryotes的高度节制的过程。 穆特蛋白是这一修复系统的主要活性组成部分。 Muts、 MutH和MutL是检测不匹配和引导修复机器对它至关重要的三种蛋白质。 这三种蛋白都承认不匹配, 并导致DNA循环出去。 Muth在离不匹配最近的甲基点附近切除DNA, 并且将DNA线隔开。 整个 MutSHL 综合体随后沿着DNA向不匹配方向滑动, 其次是消化单strandDNA的解脱氧素。 然后由脱氧核素生成的单strangs。 由脱氧核素产生的单strangs 由DNA聚合酶III进行修复。Nucleotide Excision Repair
::切切刀修复Nucleotide excision repair (NER) removes the vast majority of UV-induced DNA damage, mostly in the form of thymine dimers. Genetic diseases that result from mutations in the NER genes include Xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne's syndrome. NER recognize changes in the shape of the DNA double helix . Recognition of these changes leads to the removal of the damage, creating a single-strand gap in the DNA. This gap is subsequently filled in by DNA polymerase, which uses the undamaged strand as a template . In E. coli , this process is controlled by the UvrABC endonuclease enzyme complex, which consists of four Uvr proteins: UvrA, UvrB, UvrC, and DNA helicase II (or UvrD). In eukaryotes, this process is more complicated, controlled by nine major proteins.
::核脑切除修复(NER)消除了绝大多数由紫外线引起的DNA损害,主要以甲状腺素的形式。NER基因突变导致的遗传疾病包括Xeroderma 色素和Cockayne综合症。NER识别DNA双螺旋形状的变化。承认这些变化导致消除损害,在DNA中造成单干和空白。这一缺口随后由DNA聚合酶填充,该聚合酶使用未损坏的线作为模板。在E. coli,这一过程由UvrABC 内源酶综合体控制,该综合体由四种Uvr蛋白组成:UvrA、UvrB、UvrC和DNA肝脏II(或UvrD)。在eukaryotes,这一过程更加复杂,由九种主要蛋白质控制。Two forms of NER exist within the cell. Global genomic NER (or global excision repair) repairs damage in both transcribed and untranscribed DNA strands in active and inactive genes throughout the genome . This process utilizes damage sensing proteins that constantly scan the DNA for distortions in the helix. Repair proteins then verify and repair the damage. This process is ongoing as at any one time, most of the DNA is not undergoing . Transcription-coupled NER (TC-NER) is a faster process than global genomic NER. In TC-NER, RNA polymerase serves as the damage recognition signal when it stalls at a change in the shape of the DNA double helix. This allows repair to proceed much quicker then with global repair mechanisms.
::细胞内存在两种NER形式:全球基因组NER(或全球切除修补)修复过程,在整个基因组中,转录和未转录的DNA链在活跃和不活跃的基因中都有损坏感应蛋白质,不断扫描DNA,以扭曲螺旋。修复蛋白质,然后核实和修复损害。这一过程与任何时候一样,大多数DNA都没有在进行中。转录并合NER(TC-NER)比全球基因组N(TC-NER)要快得多。在TC-NER,RNA聚合酶在DNA双螺旋形状变形时起到损害识别信号作用。这样可以使修复过程比全球修理机制更快。Base Excision Repair
::基本切切切手术修理Base excision repair repairs small, non-helix distorting changes in the DNA, usually resulting from damage during the . The process begins with enzymes known as DNA glycosylases, which recognize and remove specific damaged or inappropriate bases, forming AP sites. AP sites are apurinic or apyrimidinic sites (or a basic sites), which are locations in DNA that have neither a purine nor a pyrimidine base. The gap is then recognized by an AP endonuclease, which nicks the sugar-phosphate backbone . DNA polymerase and DNA ligase then fill in and close the gap.
::这个过程始于一种称为DNA甘蔗球菌的酶,该酶识别并去除具体的受损或不适当的基地,形成AP站点;AP站点是净性或阳性动物场所(或基本站点),这些场所位于DNA中,既不是纯基,又没有火利米丁基;然后,这种差距被割裂甘蔗-磷酸盐脊椎的AP endonuclease所识别;DNA聚合酶和DNA螺旋酶随后填补并弥合了这一差距。Summary
::摘要-
DNA repair mechanisms correct mistakes caused naturally or by mutagens in the DNA sequence.
::DNA修复机制纠正自然错误或DNA序列中的诱变性造成的错误。 -
DNA repair mechanisms may excise the base or the whole nucleotide prior to repairing with the correct sequence.
::DNA修复机制在用正确的序列进行修复之前,可以对底部或整个核酸进行切除。 -
Numerous proteins are involved in this process.
::这一过程涉及许多蛋白质。
Review
::回顾-
What is DNA repair?
::什么是DNA修复? -
Describe the general nucleotide excision repair process.
::描述一般核酸切除术修复过程。 -
Describe the general base excision repair process.
::描述一般的基本切除修补过程。 -
Compare nucleotide excision repair to base excision repair.
::将核酸切除术修补与基本切除术修补相比。 -
What are Mut proteins? Describe their role in nucleotide excision repair.
::突变蛋白是什么? 描述它们在核糖核酸切除修复中的作用。
-
DNA repair mechanisms correct mistakes caused naturally or by mutagens in the DNA sequence.