8.18 变异的意义 - 高级
章节大纲
-
Is this rat hairless?
::这只老鼠是无毛的吗?Yes. Why? The result of a , a change in the sequence. The effects of mutations can vary widely, from being beneficial, to having no effect, to having lethal consequences, and every possibility in between.
::突变的效果可能大不相同,从有益、无效果,到产生致命后果,以及各种可能性。Significance of Mutation
::变异的意义Are all mutations bad? No. Obviously large chromosomal changes are going to have a significant effect. But what about single base changes? Many single base mutations most likely have no effect, unless they change the reading frame . The effects of any one mutations can vary from having no effect to having lethal consequences.
::突变是否都不好? 不。显然,大型染色体变化将产生重大影响。但是单一基数变化怎么办?许多单一基数变异最有可能没有效果,除非它们改变读数框架。 任何一种变异的影响都可能从无效果到致命后果不等。Imagine the coding sequence (broken up into codons) TAC CCC GGG. This is a fairly generic coding sequence, and probably occurs many times in the . It transcribes into the following mRNA: AUG GGG CCC, which would translate into start-glycine-proline. As glycine is encoded by four codons (GGG, GGA, GGC, GGU), any change in the third position of that codon will have no effect. The same is true for the codon for proline. If a mutation does not change the amino acid sequence in a , the mutation will have no effect. In fact, the overwhelming majority of mutations have no significant effect, since mechanisms are able to mend most of the changes before they become permanent. Furthermore, many organisms have mechanisms for eliminating otherwise permanently mutated somatic .
::想象一下编码序列( 破解成codons) TAC CCC GGG 。 这是一个相当普通的编码序列, 可能在 . 中发生很多次 。 它转换成以下 mRNA : AUG GG CCC , 它会转换成开始的甘甘甘碱 。 由于甘蔗是由四个codons( GGG、 GGA、 GGC、 GGGU ) 编码的, 该codon 第三个位置的任何变化都不会产生任何效果 。 对 proline 来说, codon 也是如此 。 如果突变不会改变氨基酸序列, 突变不会产生任何效果。 事实上, 绝大多数突变机制在它们永久化之前就能够弥补大部分变化。 此外, 许多生物有机制来消除否则永久变异的土壤 。But what about changes in the other nucleotides in the sequence? They could have potentially dramatic effects. The effects depend on the outcome of the mutation. Obviously any change to the start codon will interrupt the start of . Turning the simple glycine into the nonpolar (and relatively large) tryptophan (UGG codon) could have dramatic effects on the function of the protein. And any change to a stop codon will extend translation until the next in-frame stop codon.
::但其他核核素在序列中的改变呢?它们可能具有潜在的巨大效果。 其影响取决于突变的结果。 显然, 任何对开始的 Codon 的改变都会中断开始。 将简单的甘油变成非极( 和相对较大的) Treptophan ( UGG Codon) 会对蛋白质的功能产生巨大影响。 任何对停止的codon 的改变都会将翻译延到下一个框架停止的codon 。Once again, a mutation is the change in the DNA or sequence. In , mutations can be subdivided into germline mutations and somatic mutations . Germline mutations occur in the DNA of sex cells, or gametes , and are therefore potentially very serious. These mutations can be passed to the next generation. If the zygote contains the mutation, every cell in the resulting organism will have that mutation. If the mutation results in a disease phenotype , the what is called a hereditary disease. Somatic mutations , which occur in somatic, or body, cells, cannot be passed to the next generation (offspring). Mutations present in a somatic cell of an organism will be present (by DNA replication and mitosis) in all descendants of that cell. If the mutation is present in a gene that is not used in that cell type, the mutation may have no effect. On the other hand, the mutation may lead to a serious medical condition such as .
::同样,突变是DNA或序列的变化。在突变中,突变可以细分为子系突变和体变变。 变异发生在性细胞或调子的DNA中, 因此可能非常严重。 这些突变可以传给下一代。 如果突变包含突变, 由此产生的生物体中的每个细胞都会发生突变。 如果突变导致一种疾病, 则称为遗传疾病。 体变或身体的突变不能传给下一代( 脱胎)。 生物体细胞的细胞中出现变异( 通过DNA复制和分裂) 。 如果突变存在于细胞型中, 突变可能没有效果。 另一方面, 突变可能导致严重的医学状况, 比如 。Mutations and Evolution
::变异和演变A gene pool is the complete set of unique in a or . Mutations create variation in the gene pool. Populations with a large gene pool are said to be genetically diverse and very robust. They are able to survive intense times of against certain phenotypes. During these times of selection, individuals with less favorable phenotypes resulting from deleterious alleles (due to mutations) may be selected against and removed from the population. Concurrently, the more favorable mutations that cause beneficial or advantageous phenotypes tend to accumulate in that population, resulting, over time, in evolution. In fact, without any change in the gene pool, without any new alleles added due to new mutations, evolution could not occur. Genetic change is the driving force of evolution. In fact, evolution can be genetically defined as the change allele frequencies over time.
::基因库是整个基因库中独有的。 突变在基因库中造成变异。 拥有大量基因库的人群据说具有遗传多样性和很强的活力。 他们能够对某些苯型动物在紧张的时期生存下来。 在选择的这一时期, 由(因突变)的有害异象导致的不那么有利的苯型个体可能会被选中和从人群中移除。 同时, 导致有利或有利的人型的更有利的突变往往会在这个人群中积累, 随着时间的推移, 导致进化。 事实上, 基因库中的任何变化, 如果不能因新的变异而增加任何新的异象, 则不会发生进化。 基因变化是进化的动力。 事实上, 进化可以被基因定义为随时间而变化的异位频率。Mutations are the key to species evolving. Lets say an organism "mutates" due to a new allele for a gene that determines coat color. There are, theoretically, only three outcomes of that mutation:
::突变是物种进化的关键。 可以说, 一种生物“ 变异 ” , 是由于一种新的基因变异来决定外衣颜色。 从理论上讲, 突变的结果只有三种:-
The "new" coat color does not allow the organism to camouflage itself. The organism dies and the new allele dies with it.
::“ 新的” 外衣颜色不允许有机体伪装自己。 有机体会死,新的异性会死。 -
The mutation has no significant effect on organism. The organism lives as before, passing the allele to its offspring.
::突变对生物没有重大影响 生物和以前一样活下来 将异变传给后代 -
The mutation is beneficial to the organism. The organism can hunt and survive more efficiently than before. Individuals with this beneficial allele live longer and reproduce more; they are more "fit" to survive in their environment. This is the basis of Darwin's "survival of the fittest" philosophy. Soon more individuals within the population have the beneficial allele.
::突变有利于生物体。 生物体可以比以前更高效地捕捉和生存。 拥有这种有益的生物体的个人寿命更长,繁殖量更多; 他们更适合在环境中生存。 这是达尔文的“ 适者生存” 哲学的基础。 人口中很快有更多的人拥有有益的生物体。
Beneficial Mutations
::受益性变异Heart disease is the number one killer of Americans, and a significant health concern all over the world. Except for a small community in Italy.
::心脏病是美国人的头号杀手,也是全世界一个重大的健康问题。意大利的一个小社区除外。All humans have a gene for a protein called Apolipoprotein A1 (Apo-A1), which is part of the system that transports cholesterol through the bloodstream. Apo-A1 is an high density lipoprotein (HDL). HDLs are known as "good" cholesterol as they remove cholesterol from artery walls. A small community in Italy is known to have a mutant version of this protein, named Apolipoprotein A1-Milano (or Apo A1M). This protein is even more effective at removing cholesterol from cells and dissolving arterial plaques associated with heart disease. It also acts as an antioxidant, preventing arterial damage from inflammation that normally occurs in arteriosclerosis . People with the Apo-A1M gene have significantly lower levels of risk than the general population for heart disease.
::人类都有蛋白质基因Apolipoprotein A1(Apo-A1),这是通过血液输送胆固醇的系统的一部分,Apo-A1是一种高密度的脂质脂质(HDL),HDL被称为“好”胆固醇,因为从动脉壁上取出胆固醇。意大利的一个小社区已知有这种蛋白质的变异版本,名为Apolipopotein A1-Milano(或Apo A1M)。这种蛋白在将胆固醇从细胞中除去和溶解与心脏病有关的动脉片方面甚至更加有效。它也是一种抗氧化剂,防止动脉损伤,通常在动脉硬化中发生。患有Apo-A1M基因的人的心脏病风险水平远远低于一般人群。Antioxidants are important for the health of a cell. An antioxidant is a molecule that inhibits the oxidation of other molecules. Oxidation is a chemical reaction that transfers electrons or hydrogen from a substance to an oxidizing agent, producing free radicals in the process. These free radicals initiate a chain reaction in the cell that can cause cell damage, or can lead to cell death. Antioxidants prevent these chain reactions from even initiating.
::抗氧化剂对细胞健康很重要,抗氧化剂是一种抑制其他分子氧化的分子,氧化是一种化学反应,将电子或氢从一种物质转移至氧化剂,在此过程中产生自由基。这些自由基在细胞中引发链反应,可能造成细胞损伤,或可能导致细胞死亡。抗氧化剂防止这些链反应甚至产生。Beneficial mutations are also found in many that allow them to survive in the presence of antibiotic drugs . The mutations lead to antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria, producing strains that have adapted to their environment. By definition, that is evolution.
::许多人还发现,在抗生素药物的出现下,它们也能生存下来。 突变导致细菌的抗生素菌株,产生适合其环境的菌株。 顾名思义,这就是进化。Harmful Mutations
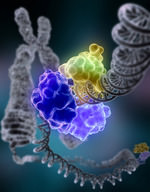
::有害变异Mutations can result in errors in protein sequence, creating partially or completely non-functional proteins. These can obviously result in harm to the cell and organism. To function correctly and maintain , each cell depends on thousands of proteins to all work together to perform the functions of the cell. When a mutation alters a protein that plays a critical role in the cell, the cell, tissue , organ , or organ system may not function properly, resulting in a medical condition. A condition caused by mutations in one or more genes is called a or genetic disease. However, only a small percentage of mutations cause genetic disorders; most have no impact on health. If a mutation does not change the protein sequence or structure, resulting in the same function, it will have no effect on the cell. Often, these mutations are repaired by the DNA repair system of the cell. Each cell has a number of pathways through which recognize and repair mistakes in DNA ( Figure ). Because DNA can be damaged or mutated in many ways, the process of DNA repair is an important way in which the cell protects itself to maintain proper function.
::突变可能导致蛋白质序列错误, 产生部分或全部不起作用的蛋白质。 这显然会导致对细胞和生物的伤害。 要正确运行和维护, 每个细胞要依靠数千个蛋白来一起工作来完成细胞的功能。 当突变改变一个在细胞中起关键作用的蛋白质时, 细胞、 组织、 器官或器官系统可能无法正常运转, 从而导致医疗状况。 一种或多种基因突变引起的状况被称为一种或一种或多种基因疾病。 但是, 只有一小部分突变会导致基因紊乱; 多数对健康没有影响。 如果突变不改变蛋白序列或结构, 导致同样的功能, 则对细胞没有影响。 这些突变通常由细胞的DNA修复系统进行修复。 每个细胞都有一系列路径, 可以识别和修复DNA中的错误( Figure ) 。 由于DNA在许多方面会被损坏或变形, DNA的修复过程是保护细胞保持正确功能的重要方式。DNA repair. Shown is a model of DNA ligase repairing chromosomal damage. DNA ligase is an enzyme that joins broken nucleotides together by catalyzing the formation of a bond between the phosphate group and deoxyribose sugar of adjacent nucleotides in the DNA backbone. Cystic fibrosis is an example of a genetic disorder. A mutation in a single gene causes the body to produce thick, sticky mucus that clogs the lungs and blocks ducts in digestive organs.
::细胞纤维化是遗传病的一个例子。 单一基因的突变导致身体产生厚粘粘的粘性粘性粘性粘性粘性粘性粘性粘性,将肺部和消化器官的管管堵塞。Cancer is a disease in which cells grow out of control and form abnormal masses of cells. It is generally caused by mutations in genes that regulate the . Because of the mutations, cells with damaged DNA are allowed to divide without limits. Cancer causing genes can be inherited.
::癌症是一种细胞无法控制地生长并形成细胞异常质量的疾病,一般是由调节细胞的基因突变引起的。由于突变,有受损DNA的细胞可以不受限制地分裂,造成基因的癌症可以继承。Summary
::摘要-
Mutations are essential for evolution to occur because they increase genetic variation and the potential for individuals to differ.
::变异对于演进至关重要,因为它们增加了遗传变异,并有可能使个人变异。 -
The majority of mutations are neutral in their effects on the organisms in which they occur.
::大多数突变对发生突变的生物体的影响是中性的。 -
Harmful mutations can result in errors in protein sequence, creating partially or completely non-functional proteins.
::有害的突变可能导致蛋白质序列错误,产生部分或全部不起作用的蛋白质。 -
Harmful mutations may cause genetic disorders or cancer.
::有害的突变可能导致基因紊乱或癌症。
Review
::回顾-
What is a germline mutation? A somatic mutation?
::什么是子宫突变? -
Explain why some mutations are harmful and some beneficial.
::解释为什么有些突变是有害的和有益的。 -
Define a genetic disease.
::定义一种遗传疾病。 -
Define cancer.
::给癌症下定义
-
The "new" coat color does not allow the organism to camouflage itself. The organism dies and the new allele dies with it.