11.18 新型和新发疾病 -- -- 先进
章节大纲
-
Are antibiotics a good thing?
::抗生素是好事吗?Yes and no. It is true that the proper use of antibiotics is necessary and extremely beneficial. But the misuse or overuse of these drugs results in antibiotic-resistant , which can be very dangerous. MRSA is methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, a bacterium responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans.
::的确,正确使用抗生素是必要和极为有益的。 但滥用或过度使用抗生素会导致抗生素抗药性非常危险的抗药性。 MRSA是抗甲状腺素的抗甲状腺素(Staphylococcccus aureus ) , 这是一种细菌,导致人类几起难以治疗的感染。Emerging and Reemerging Diseases
::新型和新发疾病In most cases, microorganisms live in harmony with their hosts. Because the microbes and their hosts have evolved together, the hosts gradually become resistant to the microorganisms. When a microbe jumps from a long-time host to a human being, it may stop being a harmless symbiont and become pathogenic to the new host.
::多数情况下,微生物与其主机体和谐相处。 由于微生物及其主机体共同演变,因此主机体逐渐对微生物产生抗药性。 当微生物从长期主机体跳跃到人类时,它可能不再是一个无害的共生体,而成为新主机体的病原体。Several human activities have led to the emergence and spread of new diseases. When any of these situations occur, a that had been confined to a remote habitat appears in a new region or a microbe that had infected only animals may begin to cause disease in humans. These human activities include the following:
::一些人类活动导致新疾病的出现和蔓延,当出现上述任何一种情况时,一个局限于偏远生境的地区出现在一个新地区,或只感染动物的微生物可能开始对人类造成疾病。-
Moving into wildlife habitats. The construction of new homes and housing developments in rural areas brings people into contact with both animals that they would not normally encounter and the microbes that they carry.
::进入野生生物栖息地:在农村地区建造新的家园和住房发展,使人们与通常不会遇到的动物和携带的微生物接触。 -
Changes in
. The introduction of new crops attracts both new crop pests and the microbes that they carry to farming communities, exposing people to unfamiliar diseases.
::引进新作物既吸引新的作物害虫,也吸引它们携带到农业社区的微生物,使人们暴露在不熟悉的疾病中。 -
The destruction of habitats. As countries make use of their
natural resources
, such as forests, they clear areas for settlement or commercial use, and people encounter
and other animals harboring previously unknown microorganisms.
::破坏生境:各国利用森林等自然资源,清出定居区或商业用途区,清理遇到的人和存放以前未知微生物的其他动物。 -
Modern transport. Ships and other cargo carriers often harbor unintended "passengers" that can spread diseases to faraway destinations. With international jet airplane travel, people infected with a disease can carry it to distant lands or home to their families, even before their first symptoms appear.
::现代运输。 船舶和其他货运公司往往窝藏着可能把疾病传播到远方目的地的意外“旅客 ” 。 随着国际喷气式飞机的飞行,感染疾病的人可以将疾病带到遥远的土地或家人家中,甚至在他们最初出现症状之前。 -
Misuse of antibiotics. The intense use of antibiotics in agricultural
food
production (chicken, pigs, and cattle) has been associated with the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria, including
Salmonella, Campylobacter, Escherichia coli,
and
Enterococcus
, all of which can cause disease in humans. Self-medication with left-over antibiotics and the over-prescription of antibiotics by doctors has contributed to antibiotic resistant bacteria that are reemerging as health threats in the 21
st
century. Methicillin resistant
Staphlococcus aureus
(
MRSA
) and multi-drug resistant
tuberculosis
(MDR TB) (discussed below) are now important public health issues in many countries.
::抗生素的滥用:在农业粮食生产中大量使用抗生素(芯片、猪和牛)与出现抗生素抗菌菌菌株有关,这些菌株包括Salmonella、Campylobacter、Escherichia coli和Enterococcacus,所有这些菌株都可能造成人类疾病。 医生用残留的抗生素进行自我治疗和过多地使用抗生素有助于21世纪再次成为健康威胁的抗生素抗菌。 抗体抗体抗体抗体菌菌株(MRSA)和抗多种药物抗结核病(MDR TB)(下文将讨论)是许多国家目前的重要公共卫生问题。
Lyme Disease : An Emerging Disease
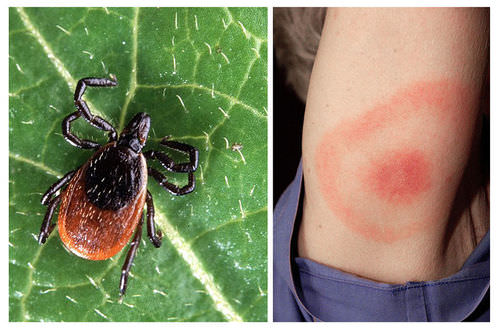
::Lyme疾病:一种新出现的疾病Lyme disease is an emerging infectious disease that is caused by the Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria. This bacterium normally lives in mice, squirrels, and other small animals. It is passed from these animals to humans through the bites of certain species of ticks. The infected tick is usually a black-legged or deer tick; the tick is the vector that transmits the disease ( Figure ). The vector is an organism that does not cause a disease itself, but which spreads the disease by carrying the pathogen from one host to another. The ticks do not get Lyme disease, they just pass the Borrelia bacteria into people when biting them.
::莱姆病是Borrelia burgdorferi细菌引起的一种新出现的传染病。 这种细菌通常生活在小鼠、松鼠和其他小动物体内。 它通过某些种类的滴子的咬痕从这些动物传染给人类。 被感染的滴子通常是黑腿或鹿的滴子; 滴子是传播疾病的媒介( 图表 ) 。 病媒是一种不引起疾病本身的有机体, 但它通过将病原体从宿主携带到另一个宿主而传播疾病。 滴子不会感染莱姆病, 它们只是在咬它们的时候将波里利亚细菌传给人。Symptoms of Lyme disease include fever, headache, fatigue, and a characteristic skin rash, shown below. If left untreated, infection can spread to , the heart, and the . Recently, the number of reported cases of Lyme disease has been increasing. The main reason for this is the increased contact between people and the remote areas where the animal hosts and ticks are found. Every year more people are moving into newly constructed areas to live or vacation, and they encounter organisms that they would not normally meet.
::莱姆病的症状包括发烧、头痛、疲劳和典型皮疹,如下文所示。如果不加治疗,感染会蔓延到心脏和皮肤。最近,报告的莱姆病病例数量一直在增加,主要原因是人们与动物宿主和虱子所在的偏远地区的接触增加。每年有更多的人进入新建地区生活或度假,他们遇到通常不会遇到的有机物。Deer ticks (left) are a common vector of Lyme disease. A bite from an infected tick causes a “bull’s-eye” rash to develop in about 70-80% of infected people. The rash is not an immune reaction, rather, it is a result of infection of the bite site by Borrelia bacteria. Lyme disease was identified when a cluster of cases were identified in three towns in southeastern Connecticut in 1975, including the towns Lyme and Old Lyme, giving the disease its name. Reemerging Diseases
::复发疾病Reemerging diseases are diseases that have reappeared after a large decline in their incidence levels. Such diseases are returning because the bacteria that cause them have become more pathogenic. The bacteria that cause these diseases may have become resistant to antibiotics or they may make stronger toxins. Clostridium difficile are Gram-positive, anaerobic , spore-forming bacilli that cause severe diarrhea. Strains of C. difficile have become resistant to antibiotics and produce stronger toxins, which makes C. difficile infections more difficult to treat.
::复发性疾病是发病率大幅下降后又重新出现的疾病,这些疾病正在重新出现,因为导致这些疾病的细菌已变得更加致病性。导致这些疾病的细菌可能已经对抗生素产生抗药性,或可能形成更强的毒素。显微菌阳性、厌氧性、骨质成型、导致严重腹泻的巴西里菌。C. 显微菌的斯特拉因抗抗抗生素并产生更强的毒素,这使得C. 敏性感染更难治疗。Increased and sometimes improper use of antimicrobial drugs has led to the of resistant pathogens. Many diseases that were formerly treatable with drugs have begun to make a comeback. Hospital-acquired infections, such as methicillin resistant Staphlococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin resistant enterococci, along with community acquired multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR TB), are becoming more common.
::抗微生物药物的使用增加,有时不当使用,导致抗药性病原体的出现,许多以前可使用药物治疗的疾病开始重新出现,医院感染的病例,如抗甲状腺素(MRSA)和抗vancomycin抗肠道菌(Vancomycin 抗肠道菌),以及社区获得的耐多种药物结核病(MDR TB)越来越普遍。Antibiotic Resistance
::抗生素抗药性Bacterial infections are usually treated with antibiotics. There are many types of antibiotics; some antibiotics prevent bacteria from making peptidoglycan , while others prevent bacterial from making . Some antibiotics are specific for Gram-positive bacteria , and others are specific for Gram-negative bacteria . Broad-spectrum antibiotics are antibiotics that act against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Amoxicillin is a common broad spectrum antibiotic.
::细菌感染通常用抗生素进行治疗,有多种抗生素;有些抗生素防止细菌制造小儿麻痹剂,而另一些则防止细菌制造。有些抗生素是格菌阳性细菌特有的,有些是格菌阴性细菌特有的。广谱抗生素是抗格菌阳性和格菌阴性细菌的抗生素。阿莫西林是一种常见的广谱抗生素。Antibiotics are used both in treating human diseases and in certain types of farming, in order to promote animal growth. Some of these practices have contributed to the development of antibiotic resistance in bacterial .
::抗生素既用于治疗人类疾病,也用于某些类型的耕作,以促进动物生长,其中一些做法有助于细菌抗生素抗药性的发展。Antibiotic resistance is the ability of a microorganism to withstand the effects of an antibiotic. Antibiotic resistance evolves naturally by through . When a population of bacteria is exposed to an antibiotic, only the bacteria that are resistant to the effect of the drug survive. These surviving resistant bacteria will reproduce and become the most common in the “final” population, as seen in Figure .
::抗生素抗药性是微生物抵抗抗生素影响的能力,抗生素抗药性自然通过.当细菌种群接触抗生素时,只有抗生素抗菌性细菌才能存活下来。 这些存活的抗生素性细菌会繁殖并成为“最终”种群中最常见的,如图所示。Once such a gene is generated, bacteria can then pass the "resistance gene" by plasmid exchange to other bacteria. Antibiotic resistance genes are commonly found on bacterial plasmids. If a bacterium carries several resistance genes, it is called multiresistant or a superbug. These have the potential to be very dangerous.
::一旦产生了这种基因,细菌就可以通过向其他细菌交换颗粒状的基因来传递“抗生素基因 ” 。 抗生素抗药性基因通常存在于细菌粒子上。 如果细菌含有几种抗生素基因,那么它就被称为多抗性基因或超级虫。 它们具有非常危险的潜能。A representation of how antibiotic resistance evolves by natural selection. The “Before selection” section represents a population of bacteria before exposure to an antibiotic. The middle “After Selection” section shows the population directly after exposure. Only the most resistant cells survived the antibiotic. The final population is entirely made up of highly resistant bacteria that will not be killed by the antibiotic. Summary
::摘要-
Bacterial pathogens can cause both minor and devastating human diseases. Usually, these diseases can be treated with antibiotics.
::细菌病原体可造成轻微和毁灭性的人类疾病,这些疾病通常可以用抗生素治疗。 -
Antibiotic resistance has created potentially harmful superbugs.
::抗生素抗药性产生了潜在的有害超级虫。
-
Moving into wildlife habitats. The construction of new homes and housing developments in rural areas brings people into contact with both animals that they would not normally encounter and the microbes that they carry.