11.27 液循环 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
What is the first step in viral ?
::病毒的第一步是什么?Infection of a host . To reproduce or replicate, a must use the , , and building blocks of a host cell.
::受宿主感染 。要复制或复制,必须使用宿主单元格的 、 和构件。Viral Lifecycles: Lytic Cycle
::活性活性生命周期: 液循环The lytic cycle is one of the two cycles of viral reproduction, the other being the . These cycles should not be seen as separate; they should rather be seen as two parts of viral reproduction. The lytic cycle is typically considered the main method of viral replication since it results in the destruction of the infected cell and the release of new viruses.
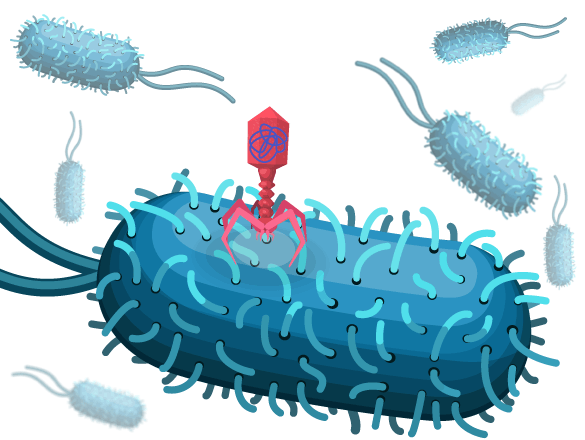
::液态循环是病毒复制的两个周期之一,另一个是病毒复制的循环。这些循环不应被视为是分开的,而应被视为病毒复制的两个部分。 液态循环通常被认为是病毒复制的主要方法,因为它导致被感染细胞的破坏和新病毒的释放。The lytic lifecycle of a phage is shown in Figure . The lytic cycle is a three-stage process.
::图中显示了一条象的淋巴寿命周期。 淋巴循环是一个三阶段过程。- 1. Penetration
- To infect a cell, a virus must first attach to or enter a cell and inject its genetic material into the cell. The host cell is now infected. If the infected cell is in a , the cell can be targeted for destruction by the immune system .
- 2. Biosynthesis
- The virus' remains separate from the hosts and forms a loop of DNA. The virus uses the host cell’s machinery to make large amounts of viral proteins. In the case of DNA viruses , the DNA is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules that are then translated into proteins.
- 3. Maturation and lysis
- After many copies of viral components are made, they are assembled into complete viruses. The virus then directs the production of an that breaks down the host's cell wall and allows fluid to enter. The cell eventually becomes filled with viruses (usually about 100 to 200) and bursts (lyses) - which gives the lytic cycle its name. The new viruses are then free to infect other cells.
Bacteriophages infecting bacteria go through the lytic (1, 2, 3) and lysogenic (i, ii, iii) cycles. The lytic and lysogenic cycles are explained in the text. Lytic Cycle Without Lysis
::无利西斯的中性循环Some viruses escape the host cell without bursting the . Instead, they bud off from it by taking a portion of the membrane with them, or they are released by vacuoles . This is still called lysis because, even though the host cell does not burst and die immediately, this process is otherwise characteristic of the lytic cycle. Lytic cycles without lysis include budding and exocytosis . Influenza viruses bud from their host cells, as shown in Figure , and Hepatitis B viruses are released from the host cell from vacuoles.
::有些病毒在未爆裂的情况下逃离宿主细胞。 相反,它们通过携带一部分膜而从宿主细胞中分离出来,或者通过真空释放出来。 这还是所谓的解析,因为即使宿主细胞没有爆裂和立即死亡,但这一过程也是淋巴循环的特征。无透析的流体循环包括胚胎和排出性硬化。如图所示,流感病毒从宿主细胞中萌芽出来,乙型肝炎病毒从宿主细胞中释放出来。Lytic Cycles without lysis. Left, Influenza A virus budding from a cell. Right, Hepatitis C viruses are released in vacuoles, a process called exocytosis. Viruses are able to infect certain cells because their capsid proteins are specific for receptors on the cell's surface. This specificity determines the host range of a virus. This process has evolved to favor those viruses that only infect cells in which they are capable of replication. The following describes the steps depicted in Figure :
::以下描述图中描述的步骤:-
A
virion
attaches to the host cell membrane by recognizing specific proteins on the cell's surface. The virus then enters the
cytoplasm
by
endocytosis
.
::通过识别细胞表面的特定蛋白质,一种病毒附着在宿主细胞膜上,然后通过内分泌进入细胞顶层。 -
The envelope wall of the virus breaks down and the genetic material of the virus moves into the the
of the host cell.
::病毒的封墙破裂,病毒的遗传物质进入宿主细胞。 -
In the nucleus, viral polymerases transcribe and replicate the viral RNAs. Newly made viral mRNAs move to cytoplasm where they are translated into viral proteins.
::在核心中,病毒聚合酶会转录并复制病毒RNA。新制造的病毒MRNA会转移到细胞图层,并转化成病毒蛋白。 -
Viral envelope
proteins are then moved to the cell membrane by the cell’s
.
::然后将活性信封蛋白转移到细胞膜的细胞膜上。 -
Other viral proteins that are made in the cytoplasm move to the nucleus where they bind with newly made viral genomes (
or DNA).
::以细胞托巴拉斯制成的其他病毒蛋白质转移到核心,与新制成的病毒基因组(或DNA)结合。 -
The newly formed
nucleocapsids
move into the cytoplasm and toward the cell membrane where viral envelope proteins may be inserted.
::新近形成的核子卡普西德体进入细胞托盘,进入细胞膜,可以插入病毒信封蛋白。 -
The newly made viruses are released from the infected cell.
::新制造的病毒是从受感染的细胞中释放出来的。
Viral shedding refers to the production of new viruses, with the newly made viruses leaving the cell to infect other host cells. Viral shedding is often carried out by lysis, in which the cell bursts and dies. Once replication has been completed and the host cell is exhausted of all resources, the viruses may leave the cell.
::活性切除是指新病毒的产生,新制造的病毒将细胞留给其他宿主细胞感染,活性切除通常通过透析进行,在透析中,细胞暴发和死亡,一旦复制完成,宿主细胞用尽所有资源,病毒就可能离开细胞。Watch the video below and focus on the lytic cycle:
::关注流体循环:Summary
::摘要-
In the lytic cycle, the viral genetic material remains separate from the host DNA. It codes for the production of viral proteins which assemble and burst out of the host cell, killing the host.
::在液态循环中,病毒遗传材料仍然与主机DNA分开,它为产生病毒蛋白进行编码,这些病毒蛋白会聚集并冲出主机细胞,杀死主机。
Review
::回顾-
What is the lytic cycle?
::流体循环是什么? -
What does the term “lytic cycle without lysis” mean?
::“无透析的周期”一词是什么意思?