12.23 复制真菌 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
How do reproduce? Sexually or asexually?
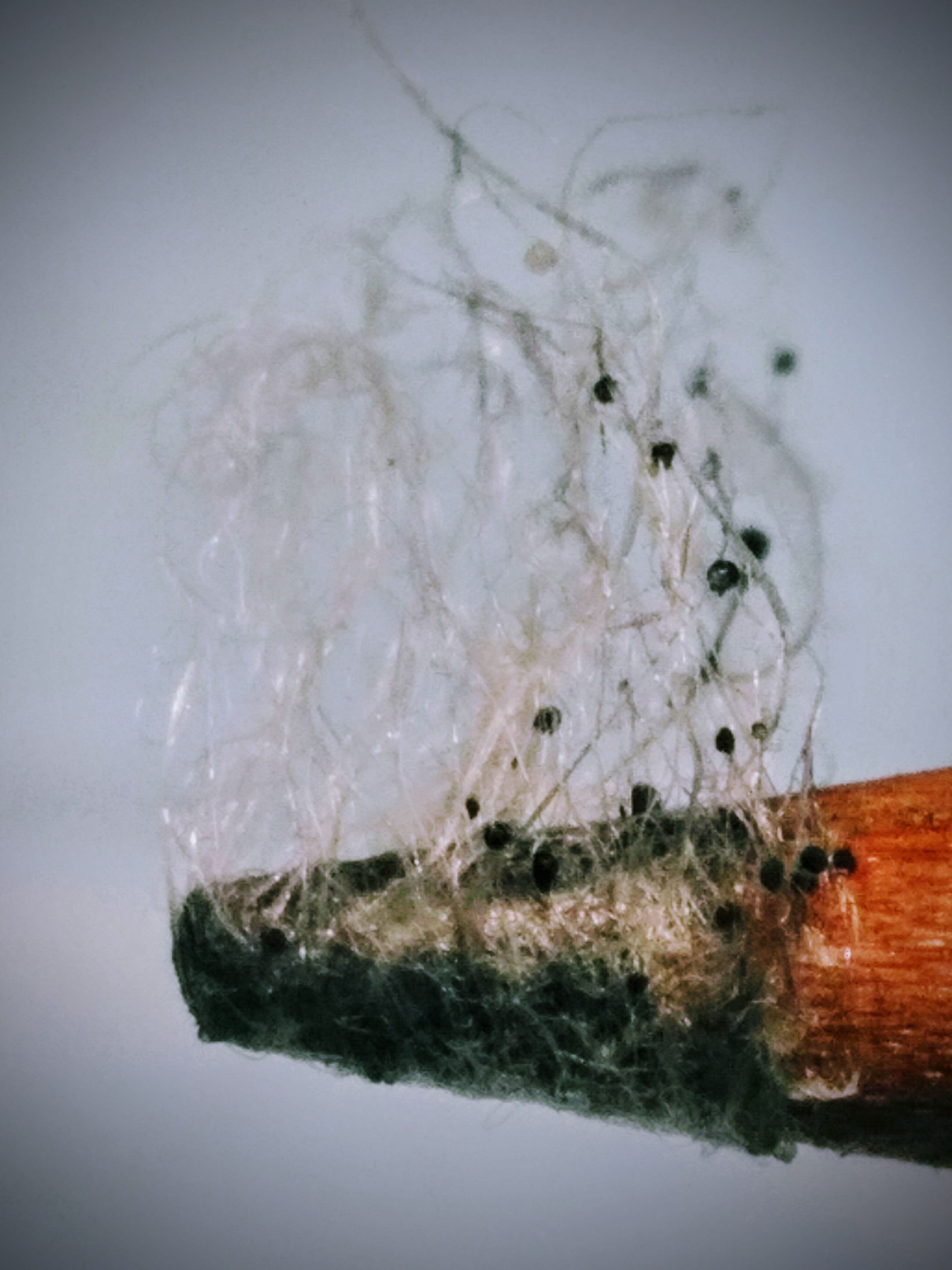
::如何繁殖?性还是性?How about both? That would suggest that fungi can produce both diploid and haploid , which they can. Shown above are fungi mycelia and haploid spores. Spores allow fungi to reproduce during unfavorable conditions.
::这说明真菌可以同时生产薄荷和薄荷。上面显示的是真菌的迷宫和薄荷。 Spories允许真菌在不利的条件下繁殖。Reproduction of Fungi
::复制真菌Most fungi are able to reproduce both sexually and asexually. Most fungi are haploid for the majority of their lifecycle. This is unlike other eukaryotes ; for example, humans spend the majority of their lives as diploid organisms .
::大部分真菌都能在性与性之间繁殖。 大多数真菌在其整个生命周期的大部分时间里都是杂乱无章的。 这与其他古代人不同;例如,人类的大部分生命都是作为稀释生物度过的。Asexual Reproduction
::性生殖Fungi reproduce asexually by producing genetically identical spores or by breaking off pieces of mycelia. A spore is a reproductive cell made by fungi and other organisms. Spores can grow into an individual without being fertilized. is common in many fungal , and it allows for more rapid spreading of the fungus than does.
::菌类通过生产基因相同的螺旋状菌或打破神秘片进行性繁殖。 菌类是一种由真菌和其他有机体制造的生殖细胞。 菌类可以在不施肥的情况下成长为个体。 在许多真菌中很常见,它使得真菌的传播速度比以往更快。There is great variety of asexual reproductive structures. These structures can be used to identify certain fungi. Some fungi produce spores within a protective sac called a sporangium , while others produce spores that are not surrounded by a protective sac. In some cases, sporogenesis , or the creation of spores, occurs by . Other fungi produce spores by mitosis and .
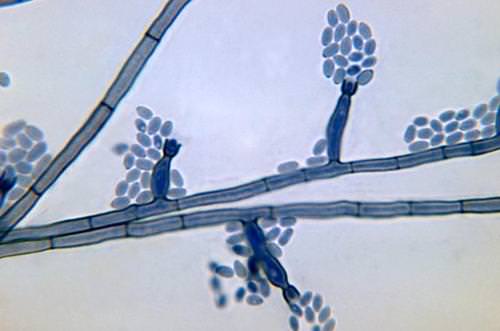
::有各种各样的性生殖结构,这些结构可以用来识别某些真菌。有些真菌在一种称为“”的保护性囊中产生螺旋,而另一些则产生没有被保护性囊包围的螺旋。 在某些情况下,由 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .Sporogenesis begins with the growth of special reproductive hyphae called sporangiophores . At the end of a sporangiophore is a structure called a sporangium (plural, sporangia ), shown in Figure . Spores are produced by the mitotic division of haploid spore mother cells within the sporangium.
::松动起源始于被称为螺旋藻的特殊的生殖性氢旋藻的生长,在无脊椎动物的末端,即图中所示的被称作状(多元体、双螺旋体)的结构。 螺旋体是由状细胞中状母细胞的线性分层生成的。A sporangium with spores. A mature sporangium of a Mucor fungus. Mucor is a genus of about 40 species of molds commonly found in soil and on plant surfaces, as well as in rotten vegetable matter. Conidia (singular, conidium ) are the asexual, non-motile spores of certain genera of fungi. They too are made by mitosis. Conidia are not enclosed in a protective sac like sporangiospores are. Conidia are haploid cells that are genetically identical to the haploid parent. They develop into a new organism when conditions are favorable for growth, such as when a food source is readily available or when humidity levels are right. Fungi of the genus Penicillium , which are used to make the antibiotic penicillin and to flavor certain cheeses, produce conidia, as shown in Figure .
::共产性细胞(共产性、共产性)是某些真菌基因的无性、非流动的颗粒体,它们也是由线虫病制成的。共产性细胞没有被附在保护性囊囊中,如无脊椎动物。共产性细胞在基因上与无脊椎动物的父母完全相同。当条件有利于生长时,它们会发展成为一种新的有机体,例如当食物来源随时可得或湿度正常时。五硝基的芬基,用于制造抗生素青霉素,并供应某些奶酪,产生共产性,如图所示。Conidia on the conidophores of a Phialophora verrucosa fungus. The trunk-like structure holding the conidia is the conidiophore. Spores may be dispersed by , wind, or other organisms. Some fungi even have “cannons” that “shoot” the spores far from the parent organism. This helps to ensure that the offspring will not have to compete with the parent for space or other resources. You are probably familiar with puffballs, like the one in Figure . They release a cloud of spores when knocked or stepped on. Wherever the spores happen to land, they do not germinate until conditions are favorable for growth. Then they develop into new hyphae .
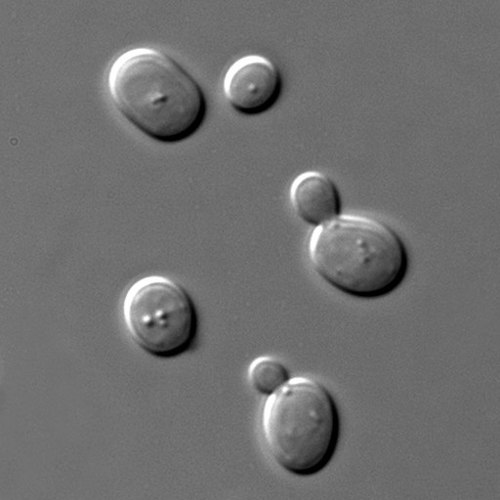
::一些真菌甚至拥有“射出”离母体更远的螺旋菌。这有助于确保后代不必与母体竞争空间或其他资源。您可能熟悉浮球,如图中的浮球。它们敲打或踩上时释放出一团星云。只要这些螺旋在陆地上发生,它们就不会发芽,直到生长的条件有利。然后它们会发展成新的螺旋。Puffballs release spores when disturbed. Yeasts do not produce spores, instead they reproduce asexually by budding . Budding is the asexual formation of a new organism by “pinching off” from the parent organism, as shown in Figure . The offspring yeast cell is always genetically identical to the parent cell .
::如图所示,酵母细胞的后代酵母细胞在基因上总是与母细胞完全相同。Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells in Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) microscopy showing budding. The buds will eventually separate from the parent cell. Sexual Reproduction
::性生殖Sexual reproduction via meiosis exists in all fungal phyla, except for the class Deuteromycota. Fungal sexual reproduction differs in many ways from sexual reproduction in or plants. Many differences also exist between fungal groups, and differences such as morphology, types of sexual structures, and types of spores have been used to classify fungi.
::性生殖在许多方面与植物中的性生殖不同,真菌群体之间也存在许多差异,并使用形态学、性结构类型和螺旋类等差异来分类真菌。For example, the spore-containing structures asci and basidia can be used in the identification of Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes respectively (see the Fungi: Basidiomycota (Advanced) and Fungi: (Advanced) concepts). Many fungal species have complex systems that allow mating only between individuals of opposite mating type (see below), while others can mate and sexually reproduce with any other individual, including themselves.
::例如,含有孔状结构(asi和basidiomistes)可分别用于识别Ascomycetes和Basidiomistes(见Fungi:Basidiomycota(Advanced)和FungiAdvanced)概念),许多真菌物种拥有复杂的系统,只能允许异型交配者之间交配(见下文),而其他物种则可以与包括自己在内的任何其他个人交配和性繁殖。
Fungal gametes usually look alike, and they are often referred to as "+" and "-" instead of "male" and "female.” In the case of yeasts, the mating types are called "a" and "α" (alpha). Other fungi phyla can have thousands of different mating types. Mating can only take place between different mating types. Each mating type can signal its presence to other individuals. This is done using chemical signals such as pheromones , steroids, or carotenoids. The two haploid mycelia eventually grow toward each other and fuse. After the fusion of the mycelia, some fungi go through a heterokaryotic stage in which cells contain two genetically distinct haploid that do not fuse right away. It may take hours, days, or even centuries before the parental nuclei fuse in the short-lived diploid phase.
::共生游戏通常看起来相似,它们通常被称为“+”和“-”而不是“男性”和“女性 ” 。 就酵母而言,交配类型被称为“a”和“α”。其他真菌螺旋可以有数千种不同的交配类型。配方只能在不同的交配类型之间发生。每种交配类型都可以向其他人发出其存在信号。这是使用诸如聚苯酮、类固醇或焦素等化学信号完成的。两种顺势的神秘体最终会向对方生长并产生引信。在迷宫的融合之后,有些真菌会穿过一个血色化阶段,在这个阶段,细胞中含有两种基因上不同的机类,但不会立即结合。这可能需要数小时、数天甚至数世纪的时间,才能在短寿命的极低阶段中将父母的核引信连接起来。The results of sexual reproduction are spores, called zygospores, that are genetically different from the parents. After they are released, the zygospores will germinate to form a haploid hyphae, and the lifecycle continues. The ability of some fungi to reproduce both sexually and asexually is a form of adaption to changes in the environment. This ability gives fungi an adaptive advantage and allows them to spread quickly into new areas.
::性生殖的结果是叫作zygospores的螺旋菌,它们与父母的基因不同。在它们被释放后,zygospores会发芽形成一个发炎的脑膜炎,生命周期会继续下去。一些真菌的性繁殖和性繁殖能力是适应环境变化的一种形式。这种能力赋予真菌一种适应性优势,使他们能够迅速扩散到新的地区。Summary
::摘要-
Fungi reproduce asexually by producing genetically identical spores either by mitosis or by breaking off pieces of mycelia.
::菌菌通过产生遗传上相同的螺旋状菌 来进行性繁殖, 或者是通过分裂或者通过分裂 神秘的碎片。 -
In sexual reproduction, fungal gametes fuse to produce zygospores.
::在性生殖方面,真菌游戏引信可产生zygospores。 -
Sporogenesis begins with the growth of special reproductive hyphae called sporangiophores. At the end of a sporangiophore is a structure called a sporangia, which is where spores are produced.
::发酵始于被称为螺旋状叶眼的生殖性子眼的生长。 在螺旋状磷的末端,一种叫做螺旋状磷的结构,就是产生螺旋状物的发源地。 -
Spores may be dispersed by water, wind, or other organisms.
::水、风或其他生物可能散布垃圾。
Review
::回顾-
Describe fungal asexual reproduction.
::描述真菌性生殖。 -
Do fungi produce male and female gametes? Explain your answer.
::真菌是否产生男性和女性的调子?解释一下你的答案。 -
What do conidia and sporangia have in common?
::共犯和恋童癖有什么共同点?
-
Fungi reproduce asexually by producing genetically identical spores either by mitosis or by breaking off pieces of mycelia.