12.6气候带和生物群系
章节大纲
-
Lesson
::经验教训How are altitude and latitude similar?
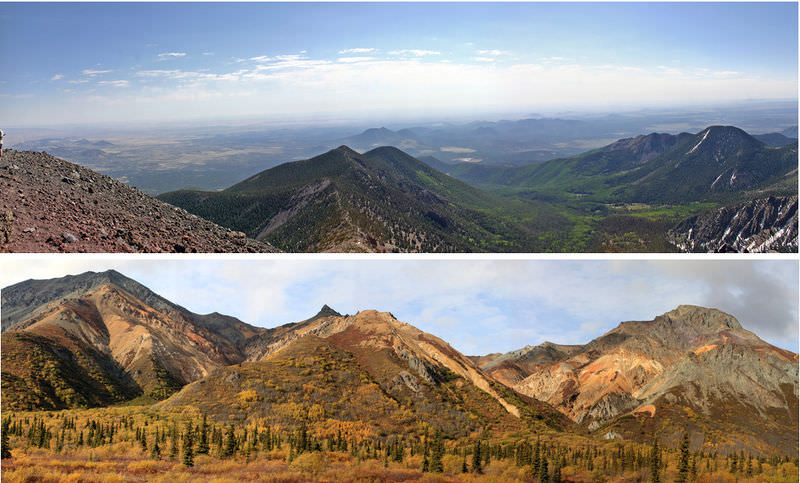
::高度和纬度如何相似?The top of Mt. Humphreys (top), the highest point in Arizona, is 12,637 feet (3,852 m). Only a few plants can live in this harsh environment. The life zone is tundra . Tundra is also seen in high latitudes, like Denali National Park in Alaska (bottom). Denali is at 63° north.
::亚利桑那州最高点汉弗莱山(顶部)的顶部是12 637英尺(3 852米),只有少数植物可以生活在这种恶劣环境中,生命区是苔原,在高纬度地区也可以看到通德拉,如阿拉斯加的Denali国家公园(底部),德纳利位于北纬63度。Major Climate Types
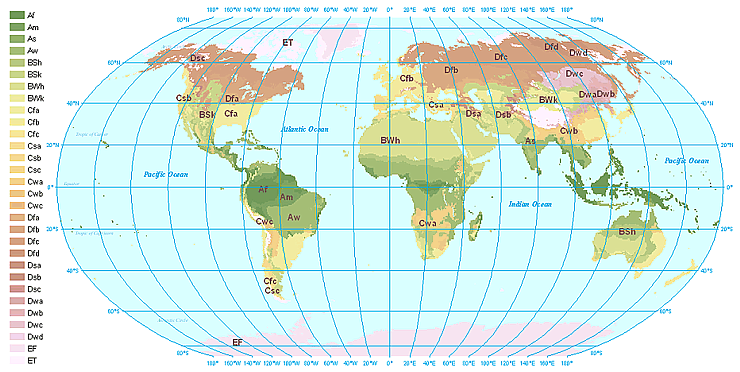
::主要气候类型Major climate types are based on and . plays an important role in determining the climate of a region. However, many other factors play a role in climate. Oceans and mountain ranges influence climate in the same ways worldwide ( Figure ). You can see where the climate types are on the , and then read about them below.
::主要气候类型基于一个区域的气候,在确定一个区域的气候方面发挥着重要作用。然而,许多其他因素在气候方面起着作用。海洋和山脉以同样的方式影响着世界范围的气候(图 )。你可以看到气候类型在哪些地方,然后阅读下文。The Koppen-Geiger climate classification divides climates into five major categories, denoted with a capital letter, and further subcategories based on temperature and precipitation, marked with lowercase letters. The major categories are: A-Tropical Climates; B- Dry Climates; C-Moist Subtropical Mid-Latitude Climates; D- Moist Continental Mid-Latitudes Climates; E- Polar Climates. What type of climate do you have where you live? Temperature and precipitation determine what types of plants can grow in an area. Animals and other living things depend on plants. So each climate is associated with certain types of living things. A major type of climate and its living things make up a biome . As you read about the major climate types below, find them on the map above ( Figure ).
::温度和降水量决定了某地区哪些种类的植物可以生长。动物和其他生物依赖植物。 因此,每种气候都与某些种类的生物相关。 一种主要类型的气候及其生物构成生物群落。 正如您所读到的以下主要气候类型, 请在以上地图( 图 ) 上找到它们。Altitude and Latitude
::高度和纬度Altitude mimics latitude in climate zones. Climates and biomes typical of higher latitudes may be found at high altitudes.
::高纬度在气候区模仿纬度,高纬度典型的气候和生物群落在高海拔地区可见。In the late 1800s, the American naturalist C. Hart Merriam noticed that the plant life changed with altitude in the same way it changes with latitude. If you travelled up a mountain in the southwestern United States, as Merriam did, you could see all of these life zones ( Figure ). In other parts of the world, the plant species are different, but the general pattern is similar.
::1800年代末期,美国自然主义者C. Hart Merriam注意到植物寿命随高度变化,与纬度变化相同。如果你像Merriam那样在美国西南部的一座山上旅行,你可以看到所有这些生命区(图 ) 。 在世界其他地区,植物物种不同,但一般模式相似。(1) Lower Sonoran, sea level to 4,000 feet: cactus, desert scrub. (2) Upper Sonoran, 4,000 to 7,000: pinyon-juniper. (3) Transition, 7,000 to 8,000 feet: Ponderosa Pine, some scrub; the snow-capped peak is Mt. Humphreys. (4) Lower Boreal, 8,000 to 11,000: Douglas fir, spruce; Douglas fir and Ponderosa pine are found together in some forests. (5) Upper Boreal, above 11,000 alpine tundra; see Mt. Humphreys above. Microclimates
::微气候Climate conditions in a small area may be different from those of the surroundings. The climate of the small area is called a microclimate . The microclimate of a valley may be cool relative to its surroundings since cold air sinks. The ground surface may be hotter or colder than the air a few feet above it. This is because and soil gain and lose heat readily. Different sides of a mountain will have different microclimates. In the Northern Hemisphere , a south-facing slope receives more solar energy than a north-facing slope. Each side supports different amounts and types of vegetation.
::小地区的气候条件可能与周围气候条件不同。小地区的气候称为微气候。自冷空气汇以来,山谷的微气候与其周围环境相比可能凉爽。地面可能比上面几英尺的空气更热或更冷。这是因为土壤随时会增加和失去热量。山的不同侧面将具有不同的微气候。在北半球,南面的斜坡得到的太阳能比北面的斜坡要多。每一面都支持不同数量和种类的植被。Further Reading
::继续阅读Summary
::摘要- Altitude and latitude produce similar climate zones and life zones.
::高度和纬度产生类似的气候区和生命区。
- A biome is a climate zone and the plants and animals that live in it.
::生物群落是一个气候区 生活在其中的植物和动物
- A microclimate has different climate conditions from the surrounding regions.
::微气候的气候条件与周围区域不同。
Review
::回顾- What factors determine a climate type?
::何种因素决定气候类型?
- How does a biome relate to a climate zone?
::生物群落与气候区的关系如何?
- Why would a region have its own microclimate, different from the surrounding climate?
::为什么一个区域有不同于周围气候的自身微气候?
- How are altitude and latitude similar for producing life zones?
::生产生命区的高度和纬度如何相似?
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resource below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。- What determines the characteristics of the Moab desert?
::何以决定莫阿布沙漠的特征?
- Where are deserts often found?
::哪里经常发现沙漠?
- Why are the poles cold?
::为什么柱子都冷了?
- How can the ocean heat the land?
::海洋如何能使陆地升温?
- How does the mean temperature at Reykjavik, Iceland compare with a similar latitude in Alaska?
::冰岛雷克雅未克的平均气温 与阿拉斯加相似的纬度相比如何?
- What brings the warm temperatures to Iceland?
::冰岛的暖温是什么?
- How do greenhouse gases affect climate?
::温室气体如何影响气候?
- What are the principal factors in determining climate?
::确定气候的主要因素是什么?
- Altitude and latitude produce similar climate zones and life zones.