13.5土壤特性
章节大纲
-
Lesson
::经验教训How does soil resemble weathered rock?
::土壤如何像被风吹过的岩石?The same processes that create soil . A large part of soil is weathered rock! If weathering processes didn't exist on earth we would have no soil. Earth wouldn't be a very good place to live. There would be very limited plant life and not much way to grow crops.
::产生土壤的同样过程。 大部分土壤是被风化的岩石! 如果地球上没有气候过程, 我们就不会有土壤了。 地球将不是一个很好的居住地点。 植物生命将非常有限, 种植作物的方式也很有限 。The Importance of Soil
::土壤的重要性You learned in the previous concept that weathering produces sediment . Weathering also produces soil.
::你从前一个概念中了解到,天气变暖会产生沉积。天气变暖也会产生土壤。People could not live on earth without soil! Your life and the lives of many land organisms depend on soil. Soil is only a very thin layer over solid rock. Yet, it is the place where reactions between solid rock, liquid water and air take place. Soil anchors plant roots and provides them with water and nutrients . We get wood, paper, cotton, medicines, and even pure water from soil. So soil is a very important resource. Our precious soil needs to be carefully managed and cared for. If we don’t take care of the soil we have, we may not be able to use it in the future.
::人不能在没有土壤的情况下在地球上生活!你的生命和许多陆地生物的生命都依赖于土壤。土壤只是一块非常薄的土壤,它只是固体岩石的一层。然而,土壤是固体岩石、液体水和空气之间发生反应的地方。土壤锚根植根并为他们提供水和养分。我们从土壤中获取木材、纸张、棉花、药品,甚至纯水。因此土壤是一个非常重要的资源。因此,土壤是一个非常重要的资源。我们宝贵的土壤需要谨慎地管理和照顾。如果我们不照顾土壤,我们今后可能无法使用土壤。Characteristics of Soil
::土壤特征Soil is a complex mixture of different materials.
::土壤是不同材料的复杂混合物。- Some of them are inorganic . Inorganic materials are made from non-living substances like pebbles and sand.
::其中一些是无机的,无机材料是用诸如石块和沙子等非生物物质制成的。
- Soil also contains bits of organic materials from plants and animals.
::土壤中还含有植物和动物的有机材料。
In general, about half of the soil is made of pieces of rock and . The other half is organic materials.
::一般说来,大约一半的土壤是由岩石和半块石头组成的,另一半是有机材料。In some soils, the organic portion is entirely missing. This is true of desert sand. At the other extreme, a soil may be completely organic. Peat, found in a bog or swamp , is totally organic soil. Organic materials are necessary for a soil to be fertile. The organic portion provides the nutrients needed for strong plant growth.
::在某些土壤中,有机部分完全缺失。沙漠沙子就是如此。在另一个极端,土壤可能是完全有机的。在沼泽或沼泽中发现的肉类是完全有机的土壤。有机材料是土壤肥沃的必要条件。有机部分提供了植物强劲生长所需的养分。Soil Texture
::土壤质质The inorganic portion of soil is made of many different size particles. These different size particles are present in different proportions. The sizes and proportions of particles determines some of the properties of the soil.
::土壤中的无机部分是由许多不同大小的颗粒组成的,这些不同大小的颗粒以不同的比例存在,颗粒的大小和比例决定着土壤的某些特性。- Water can flow easily through a permeable soil. Spaces between the inorganic particles are large and well connected. Sandy or silty soils are permeable, water-draining .
::无机颗粒之间的空间很大,而且连接良好。 桑迪或淤泥土壤是渗透性、排水性土壤。
- Soils with lots of very small spaces are water-holding soils. When clay is present in a soil, the soil holds together more tightly. Clay-rich soil can hold more water.
::土壤中有许多很小的空间,这些土壤是水的土壤。 当泥土存在于土壤中时,土壤会更紧密地凝聚在一起。 富含克莱的土壤可以容纳更多的水。
- When a soil contains a mixture of grain sizes, the soil is called a loam ( Figure ).
::当土壤含有谷物大小的混合物时,土壤称为岩浆(图)。
Two layers of soil are shown here. A sandy soil is at the bottom. A soil with more clay is at the top.
::这里显示两层土壤。 沙质土壤在底部, 粘土较多的土壤在顶部 。Classification
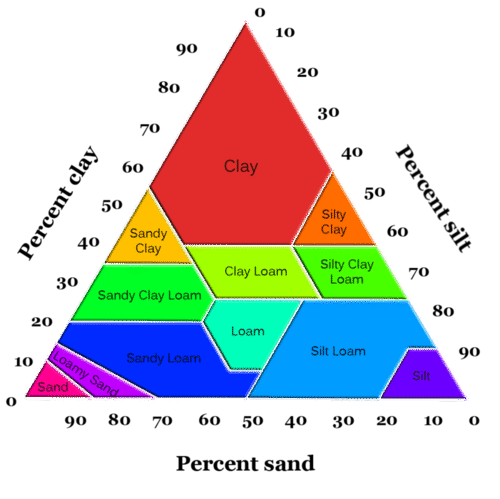
::分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类分类Soil scientists classify soil by measuring the percentage of sand, silt, and clay. They plot this information on a triangular diagram. Each size particle is at one corner ( Figure ). The soil type is then known from the on the diagram. At the top, a soil would be clay; at the left corner, it would be sand; at the right corner, it would be silt. Soils in the lower middle with less than 50% clay are loams.
::土壤科学家通过测量沙子、淤泥和粘土的百分比对土壤进行分类。 他们在三角图中绘制了这一信息。 每个大小的粒子都位于一个角落( 图表 ) 。 土壤类型从图上得知。 在顶部, 土壤将是泥土; 在左角, 土壤将是沙; 在右角, 泥土将是淤泥。 在下半部, 泥土不到50% 的土壤是泥土。Soil types by particle size.
::按粒子大小分列的土壤类型。Soil: The Ecosystem
::土壤:生态系统We can think about soil as a living resource. Soil is an ecosystem all by itself! In the spaces of soil are millions of living organisms. These include earthworms, ants, bacteria, and fungi. ( Figure ).
::我们可以将土壤视为一种生物资源。 土壤本身就是一个生态系统。 在土壤空间里,有数百万活生物体,其中包括蚯蚓、蚂蚁、细菌和真菌。 (图 )Earthworms and insects are important residents of soils.
::蚯蚓和昆虫是土壤的重要居民。Further Reading
::继续阅读Summary
::摘要- Soil reflects the interactions between the lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.
::土壤反映了地圈、大气、水圈和生物圈之间的相互作用。
- Permeable soils allow water to flow through.
::可渗透土壤允许水流过。
- The proportions of silt, clay, and sand allow scientists to classify soil type.
::淤泥、粘土和沙土的比例使科学家能够对土壤类型进行分类。
Review
::回顾- What are the inorganic materials that make up a soil?
::构成土壤的无机物质是什么?
- What are the organic materials that make up a soil?
::构成土壤的有机材料是什么?
- In what environment are there no organic materials in soils? What soils are nearly all organic?
::在什么环境中土壤中没有有机材料?什么土壤几乎都是有机的?
- How are living organisms important to soil?
::活生物体对土壤有何重要性?
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resource below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。- Why is soil important?
::为什么土壤很重要?
- How many different types of soils are there? What is the composition of average soil?
::土壤有多少种不同的类型?平均土壤的构成是什么?
- What is humus?
::什么是胡穆斯?
- What does the amount of humus determine?
::胡穆斯的数量决定了多少?
- How can texture affect plant growth?
::质地如何影响植物生长?
- What type of soil do farmers prefer?
::农民喜欢哪类土壤?
- How much soil being lost each year in the U.S.?
::美国每年损失多少土壤?
- Describe the different types of erosion.
::描述不同的侵蚀类型。
- Some of them are inorganic . Inorganic materials are made from non-living substances like pebbles and sand.