16.40 哺乳动物结构和功能 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
Does this mammal breathe like all other mammals?
::这哺乳动物的呼吸像其他哺乳动物一样吗?Essentially, yes it does. A whale is a mammal, so it has a pair of lungs , not gills like . As shown here, whales take oxygen out of the air, not out of the .
::鲸鱼是哺乳动物,所以它有肺部,而不是像刺一样的刺。正如这里所示,鲸鱼从空气中取出氧气,而不是从空气中取出氧气。Structure and Function in Mammals
::哺乳动物的结构和功能Feeding and Digestion in Mammals
::哺乳动物的喂养和消化In order to maintain a stable, warm body temperature, mammals need a great deal of energy . Therefore, they require a nutritious and plentiful diet. The earliest mammals probably ate , which are high in and high- calorie fats and are also very plentiful. Insect eaters are carnivores , or that eat other animals. As mammals underwent further evolution, some adapted to different types of diets. Some mammals became herbivores , or plant eaters. Among herbivores, some mammals eat mainly fruits , and some eat mainly grasses. Other mammals are omnivores , eating both animals and plants.
::为了保持稳定、温暖的身体温度,哺乳动物需要大量的能量。 因此,哺乳动物需要营养和充足的饮食。 最早的哺乳动物可能吃饱,它们高脂肪和高热量脂肪,而且非常丰富。 昆虫食用者是食肉动物,或食用其他动物。 随着哺乳动物进一步演进,有些哺乳动物适应了不同种类的饮食。 有些哺乳动物变成了食草动物或植物食植物动物。 在食草动物中,有些哺乳动物主要吃水果,有些主要吃草。 其他哺乳动物是食食食动物和植物。These various diets require differences in the . Carnivorous mammals have a relatively simple digestive system because their food consists mainly of proteins and fats that are easily and quickly digested. Herbivorous mammals tend to have a more complex digestive system. This is because complex , such as cellulose , which are found in plants, are difficult to digest. Herbivores may have more than one stomach in which food is stored while it is slowly digested.
::食肉动物哺乳动物的消化系统相对简单,因为其食物主要由容易和迅速消化的蛋白质和脂肪组成;食草动物的消化系统比较复杂,因为植物中发现的纤维素等复杂,难以消化;食草动物可能有一个以上的胃储存食物,而食物则慢慢消化。Which type of diet a mammal has depends, in part, on the animal’s size. Smaller mammals, such as mice and chipmunks, have a greater problem with heat loss than larger mammals such as bears and elk. To compensate, they generally must have a very high metabolic rate to generate enough heat. Maintaining a very high metabolic rate requires an easily-obtained, easily-digested, high-energy food source such as insects. Most small mammals could not survive on a plant diet because it takes too long to gather and digest plant food. A plant diet would not provide them with energy quickly enough to maintain their high metabolic rate.
::哺乳动物的哪一类饮食在某种程度上取决于动物的大小。 小哺乳动物,如小鼠和花栗鼠,在热量损失方面比熊和等大哺乳动物的问题更大。 为了补偿,它们一般必须具有极高的代谢率才能产生足够的热量。 保持非常高的代谢率需要一种容易获得、易于开发、高能的食物来源,如昆虫。 多数小型哺乳动物无法靠植物饮食生存,因为收集和消化植物食物的时间太长。 植物饮食不能迅速为它们提供维持高代谢率所需的能量。Type of Diet Foods Eaten Examples of Mammals with this Type of Diet herbivorous diet: plants leaves, grasses, shoots, , , tubers, seeds , nuts, fruits, bark , conifer needles , flowers rabbit, mouse, sea cow, horse, goat, elephant, zebra, giraffe, deer, elk, hippopotamus, kangaroo, monkey
::兔子、老鼠、海牛、马、山羊、大象、斑马、长颈鹿、鹿、鹿、驼鹿、河马、袋鼠、猴子carnivorous diet: animals other mammals, , , , fish, , worms, insects aardvark, anteater, whale, hyena, dog, jackal, dolphin, wolf, weasel, seal, walrus, cat, otter, mole
::aardvark, anteater, 鲸鱼, 土狼, 狗, jackal, 海豚, 狼, 黄鼠, 海豹, 海象, 海象, 猫, 水母, 摩尔omnivorous diet: plants and animals any of the foods eaten in herbivorous and carnivorous diets bear, badger, mongoose, fox, raccoon, human, rat, chimpanzee, pig
::熊、坏人、蒙古、狐狸、浣熊、人类、老鼠、黑猩猩、猪The different types of teeth of mammals allow them to break down food by biting and chewing prior to swallowing. Mammals also have a hard, bony palate that forms the roof of the mouth. This may help them chew food, as well as allow them to breathe and swallow at the same time. By chewing food, mammals can more rapidly digest it and release its energy. Thus, different types of teeth and a bony palate may help mammals maintain by making the energy in food more quickly available.
::哺乳动物的不同牙齿允许它们通过吞咽前的咬和嚼断食物。哺乳动物还有一张硬的、坚硬的嘴唇,可以形成嘴顶,这样可以帮助他们咀嚼食物,同时让它们呼吸和吞咽。通过咀嚼食物,哺乳动物可以更快地消化食物,释放能量。因此,不同的牙齿和坚硬的嘴唇可以帮助哺乳动物保持活力,使食物中的能量能够更快地供应。Mammalian Teeth (Human). With their different types of teeth, mammals can eat a wide range of foods. Lungs and Heart
::肺和心肺Maintaining a high metabolic rate requires a steady and plentiful supply of oxygen for . Cellular respiration is the process in which energy is released from fuel molecules, such as glucose , in the presence of oxygen (see the Cellular Respiration concepts). Mammalian traits of the lungs and heart help ensure that have enough oxygen for the high cellular respiration demands of endothermy.
::保持高代谢率需要稳定而充足的氧气供给。 细胞呼吸是在氧气(见细胞呼吸概念)下从诸如葡萄糖等燃料分子中释放能量的过程。 肺部和心脏的哺乳性特征有助于确保有足够的氧气满足终端体细胞呼吸的高需求。Lungs and Ventilation
::肺和通风Although other vertebrates also have lungs, the lungs of mammals are unique because they have alveoli . Alveoli are tiny sac-like structures that are surrounded by a network of capillaries ( Figure ). Alveoli greatly increase the surface area for gas exchange. For example, human lungs contain about 300 million alveoli, giving the lungs a total internal surface area of 70 to 90 square meters. The network of capillaries around the alveoli is crucial for gas exchange. Oxygen from the air inside the alveoli diffuses across the thin capillary membranes into the bloodstream. Carbon dioxide from the bloodstream diffuses across the capillary membranes into the alveoli.
::虽然其他脊椎动物也有肺,但哺乳动物的肺是独特的,因为它们有alveoli。Alveoli是被一个毛细刺网(Figure)包围的微小的与血管相似的结构。Alveoli大大增加了气体交换的表面积。例如,人类肺中含有大约3亿阿耳维奥利,使肺的内表总面积达到70至90平方米。藻类周围的毛细刺网对于气体交换至关重要。在气流中,从空气中流出的气球渗入薄薄的毛细膜膜中的氧气。从血液中流出的二氧化碳穿过毛细膜,渗入气流。Alveoli in mammalian lungs provide a far larger surface area for gas exchange. They are surrounded by capillaries that have very thin walls across which gases can diffuse. Oxygen-poor blood enters the lungs through the pulmonary artery and picks up oxygen from the alveoli. Oxygen-rich blood leaves the lungs through the pulmonary vein, which carries the blood to the heart to be pumped to the rest of the body. Alveoli of Mammalian Lungs. Clusters of alveoli resemble tiny bunches of grapes. They are surrounded by many blood vessels for gas exchange. Moving air into and out of the lungs is called ventilation or . In mammals, ventilation is controlled by alternating contractions and relaxations of a large muscle called the diaphragm . The diaphragm extends across the bottom of the ribcage and separates the chest and abdominal cavities. Contraction of the diaphragm increases the volume of the chest, which decreases pressure on the lungs. The decreased pressure allows air to flow into the lungs. Relaxation of the diaphragm decreases the volume of the chest, which increases pressure on the lungs. The increased pressure forces air out of the lungs. In other vertebrates, ventilation is controlled by different and is generally less efficient. For example, in some reptiles, ventilation is controlled by muscles that are also used for running. As a result, these reptiles cannot breathe and run at the same time.
::在哺乳动物中,通风是通过称为隔膜的大肌肉的交替收缩和放松来控制的。隔膜穿透肋骨底部,隔开胸腔和腹腔。隔膜的收缩会增加胸部的体积,从而降低肺部的压力。隔膜的减压允许空气进入肺部。隔膜的放松会减少胸部的体积,从而增加肺部的压力。增加肺部的压力。在其他脊椎动物中,通风受到不同的控制,而且一般效率较低。例如,在有些爬行动管中,通风由同样用于运行的肌肉控制。因此,这些爬行动管无法同时呼吸和运行。Heart and Circulation of Blood
::血液的心脏和血液流通Mammals have a heart with four chambers, or compartments, separated by valves. The human heart, shown in Figure , is an example of a mammalian heart. Each time the heart muscles contract, is pumped into arteries leaving the heart. The valves keep the blood flowing in just one direction. The only other vertebrates with a four-chambered heart are birds, which are also endothermic. The four chambers allow the heart to pump blood in two different directions. The right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen. The left side of the heart pumps blood containing oxygen to the rest of the body. Because of the dual pumping action of the heart, all of the blood going to is rich in oxygen. See the and Respiratory Systems concepts for additional information.
::哺乳动物的心脏有四个室室或舱室,用阀门隔开。图中显示的人类心脏是哺乳动物心脏的一个例子。每次心脏肌肉收缩时,都会抽进动脉,离开心脏。阀门只将血液流向一个方向。唯一一个有四组心脏的脊椎动物是鸟类,它们也是有内温的。四个室允许心脏在两个不同方向抽血。心脏的右侧将血液抽到肺部,以取取氧。心脏的左侧抽出含有身体其余部分氧的血液。由于心脏的双泵动作,所有血液都富含氧气。请参见“呼吸系统”概念以获取更多信息。This human heart, like the heart of other mammals, has four chambers: the right and left atria (singular, atrium) and the right and left ventricles. The superior vena cava is a large vein that brings oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium. The right atrium pumps blood to the right ventricle. From the right ventricle, blood is pumped through the pulmonary artery to the lungs, where it drops off carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen. The pulmonary vein returns oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium, which pumps it to the left ventricle. From the left ventricle, blood is pumped to the trunk and head through the large artery called the aorta. The left ventricle of the heart pumps oxygen-rich blood to the body. It is larger and stronger than the other chambers, and it pumps blood under high pressure into the aorta , which carries blood to the body. The aorta divides into progressively smaller and smaller arteries, all the way down to tiny capillaries. The high pressure of blood leaving the heart in the aorta is necessary to ensure adequate pressure to force blood through the capillaries. The high pressure enables blood—and oxygen—to reach all the cells of the body. Endotherms, with their higher oxygen requirements, have that is up to three times higher than the blood pressure of ectotherms . The right side of the heart pumps blood under relatively low pressure to the lungs. The lower pressure is necessary to prevent fluid from being forced across capillary membranes into the alveoli of the lungs. The dual pumping action of the four-chambered heart allows the two systems of circulation to operate under different pressures.
::心脏的左心室将含氧丰富的血液泵入身体。心脏的左心室比其他室室更大、更强大,在高压下将血液泵入动脉,将血液输送到有血的动脉中。动脉分解成逐渐小小的动脉,一直到细小的血管中。将心脏留在动脉中的高血压是必要的,以确保有足够的压力迫使血液通过毛细血管进入血液中。高压使血液和氧能进入身体的所有细胞。由于对氧气的要求较高,结果的热量比外生血压高三倍。心脏泵的右侧血液在相对较低的压力下向肺部输送相对低的血液。必须降低压力,以防止液体被压过毛膜压入肺的血管中。四层心脏的双泵动作使得两个循环系统在不同压力下运作。The mammalian heart must beat relatively quickly for cells to have enough oxygen to maintain endothermy. The heart rate is the number of times the heart muscles contract per minute. In humans, the average heart rate is about 70 beats per minute. Smaller mammals, because of their higher metabolic rates, have higher heart rates than larger mammals. For example, a chipmunk’s heart beats about 700 times per minute, whereas an elephant’s heart beats only about 25 times per minute.
::哺乳动物的心脏必须相对快速地跳动,以便细胞有足够的氧气维持外科。 心率是每分钟心脏肌肉萎缩的倍数。 在人类中,平均心率约为每分钟70下。 较小型的哺乳动物由于其代谢率较高,心率高于较大的哺乳动物。 比如,花栗鼠的心脏每分钟大约700次,而大象的心脏每分钟只跳25次。Nervous System, Intelligence, and Social Living
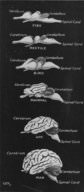
::神经系统、情报和社会生活Like all vertebrates, mammals have a that is divided into a (CNS) and a (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord , and the PNS consists of nerves that travel from the spinal cord to all parts of the body. The mammalian brain is the largest (relative to body size) and most complex of all vertebrate brains. The front part of the brain, called the cerebrum , is especially large in mammals. It is the part of the brain that controls most sensory perception, memory, and voluntary movement . Figure shows the relative size of the brain and cerebrum in mammals and other vertebrates.
::与所有脊椎动物一样,哺乳动物有一个分为一个(CNS)和一个(PNS)的哺乳动物。 CNS由大脑和脊髓组成,而PNS由神经组成,从脊髓穿行到身体的各个部分。哺乳动物大脑是所有脊椎动物大脑中最大的(与身体大小相对的)和最复杂的。大脑的前部部分叫做脑部,在哺乳动物中特别大。它是控制大多数感官感知、记忆和自愿运动的大脑的一部分。图显示了哺乳动物和其他脊椎动物中大脑和脑部的相对大小。Compared with other vertebrates, mammals have large brains. The area of the brain called the cerebrum is especially large in mammals. Of all mammals, humans have the largest brain relative to their body size. Humans also have the most highly developed cerebrum. All mammalian brains have a unique layer of nerve cells called the neocortex . The neocortex makes up the top layer of the cerebrum. It consists of grey matter, which surrounds the deeper white matter of the cerebrum. The neocortex plays an important role in many complex brain functions including memory and perception. In humans, it is involved in conscious thought and language, among other mental abilities. In small mammals, such as rats, the neocortex is relatively smooth. In many large mammals, the neocortex has deep grooves and wrinkles ( Figure ). These folds greatly increase the surface area of the neocortex. The larger the surface area, the greater the mental abilities of the neocortex.
::所有哺乳动物大脑都有一个独特的神经细胞层,称为新皮层。新皮层构成大脑的顶层。它由灰物质组成,环绕大脑深白物质。新皮层在许多复杂的大脑功能中起着重要作用,包括记忆和感知。在人类中,它涉及自觉思维和语言,以及其他精神能力。在小哺乳动物中,例如大鼠,新皮层相对光滑。在许多大型哺乳动物中,新皮层有深厚的和皱纹(Figure)。这些折叠极大地增加了新皮层的表层面积。表层面积越大,新皮层的智力能力就越大。In many species of mammals, the neocortex has grooves and wrinkles. Compare the neocortex of the human brain with the neocortex of the cat brain. The many folds in the human neocortex greatly increase its surface area and ability to function. Intelligence and Learning
::情报和学习Not surprisingly, given their large complex brains, mammals are also very intelligent animals. In this context, intelligence is defined as the ability to learn. Being able to learn allows mammals to be more flexible in their behavior than most other animals. Young mammals spend a relatively long period of time dependent on their mother for nourishment, which makes it possible for them to learn during this time. Learning permits the transfer of knowledge between generations. By learning from the experiences of the previous generation, individual mammals can make adaptive behavioral responses when environments change. Such behavioral responses to environmental changes are far quicker than genetic responses (that is, biological evolution), which generally take many generations. The ability of young mammals to learn from their elders is the main reason for the evolutionary advantage of the large mammalian brain. It is also the main reason for the evolutionary success of mammals.
::毫不奇怪,考虑到哺乳动物的庞大复杂大脑,哺乳动物也是非常聪明的动物。在这种情况下,智力被定义为学习的能力。能够学习哺乳动物的行为比大多数其他动物更灵活。年轻的哺乳动物需要相当长的时间依赖母亲的营养,这使他们在此期间能够学习。学习可以让知识在世代之间转移。通过学习上一代人的经验,个体哺乳动物可以在环境变化时作出适应性的行为反应。这种对环境变化的行为反应比基因反应(即生物进化)要快得多,遗传反应通常需要许多代人。年轻哺乳动物向长辈学习的能力是哺乳动物大大脑进化优势的主要原因。这也是哺乳动物进化成功的主要原因。Social Living
::社会生活Intelligence in animals is often associated with living in social groups, which is another characteristic of many mammals including humans. Social groups may form for reproductive and defensive purposes. Living in groups is an effective survival strategy. For example, many large herbivores, such as zebras, form social groups called herds . Adults in the herd surround and protect the young, who are most vulnerable to predators . Lions live in social groups called prides . Adult females in the pride hunt cooperatively, which is more efficient than hunting alone, and then share the food with the rest of the pride. Adult males patrol the pride’s territory and defend it from other predators.
::动物的智力往往与社会群体有关,这是包括人类在内的许多哺乳动物的另一个特征。社会群体可能出于生殖和防御目的形成。集体生活是一种有效的生存策略。例如,许多大型食草动物,如斑马,组成称为畜牧的社会群体。牧群中的成年人包围并保护最易受食肉动物伤害的年轻人。狮子生活在称为自豪感的社会群体中。成年女性在自豪感中合作打猎,这比单独打猎更有效,然后与其余的自豪者分享食物。成年男性在骄傲的领地巡逻,保护它不受其他掠食者的伤害。Generally, a hierarchy of dominance prevails within mammalian social groups. A dominance hierarchy is an arrangement of the individuals in a social group that determines how resources, such as food and mates, are distributed within the group. In some dominance hierarchies, a single individual controls all the other individuals in the social group. In other dominance hierarchies, each individual has a specific rank and is dominant to all those lower in the hierarchy and subordinate to all those higher in the hierarchy. The ranking is typically based on physical differences, such as differences in size, among individuals in the group. In many cases, dominance hierarchies are maintained by behaviors that show aggression without actually involving physical combat, which wastes energy and endangers survival. For example, chimpanzees may slap the ground, shake branches, and shriek loudly to display their dominance over other members of their social group.
::一般而言,哺乳动物社会群体中占主导地位的等级制度是哺乳动物社会群体中占主导地位的,支配性等级制度是社会群体中个人的一种安排,这种安排决定了食物和伴侣等资源是如何在群体中分配的。在某些占支配地位的等级制度中,单个个人控制着社会群体中所有其他个人。在其他占支配地位的等级制度中,每个个人都有特定的等级制度,对等级制度下层的所有人占主导地位,从属于等级制度上的所有较高者。这种等级制度通常基于物质差异,例如群体中个人之间的规模差异。在许多情况下,统治性等级制度是通过一些行为维持的,这些行为显示侵略,而没有实际的战斗,从而浪费了能量并危及生存。例如,黑猩猩可能敲打地面,摇晃树枝,大声呼喊,以展示其对本社会群体中其他成员的主导地位。Dominant males in many mammalian social groups tend to have priority in mating . Therefore, they are likely to father more offspring than less dominant males. As a result, the traits of dominant males are likely to increase in frequency through time due to (see the Evolution (Advanced) concepts). Because dominant males tend to be those that are largest and best able to fight, dominance often leads to the evolution of sexual dimorphism . Sexual dimorphism is a marked difference between males and females of the same in traits that are not directly related to . It is typical of social mammals. For example, males may be much larger than females of the same species, and they may have structures, such as antlers, that make them more threatening to other males. Compare the male and female moose shown in Figure . The male is bigger than the female and also has antlers.
::许多哺乳动物社会群体中占主导地位的男性往往在交配方面享有优先权,因此,他们生儿育女的可能性大于占支配地位的男性,因此,由于(见进化(高级)概念)的缘故,占支配地位的男性的特征可能随着时间而增加。由于占支配地位的男性往往是那些最大和最有能力抗争的男性,支配地位往往导致性畸形的演化。性畸形是同属同属特征的男性和女性之间的明显差异,这些特征与......没有直接关系。这是社会哺乳动物的典型特征。例如,男性可能比同一物种中的女性大得多,而且它们可能具有结构,例如蚂蚁,使男性受到更大的威胁。与图中显示的男女驼鹿相比,男性比女性大,而且还有蚂蚁。The male moose on the right is larger in overall body size than the female moose on the left. The male also has antlers, whereas the female does not. These differences are examples of sexual dimorphism. Summary
::摘要-
In order to maintain a stable, warm body temperature, mammals need a great deal of energy.
::为了保持稳定的温暖身体温度,哺乳动物需要大量能量。 -
Carnivorous mammals have a relatively simple digestive system. Herbivorous mammals tend to have a more complex digestive system.
::食肉哺乳动物有相对简单的消化系统,食肉哺乳动物有较复杂的消化系统。 -
Maintaining a high metabolic rate requires a steady and plentiful supply of oxygen for cellular respiration.
::保持高代谢率需要稳定和充足的供细胞呼吸用的氧气供应。 -
Although other vertebrates also have lungs, the lungs of mammals are unique because they have alveoli.
::虽然其他脊椎动物也有肺,但哺乳动物的肺是独一无二的,因为它们有阿尔维奥利。 -
The mammalian heart must beat relatively quickly for cells to have enough oxygen to maintain endothermy.
::哺乳动物的心脏必须较快跳动 让细胞有足够的氧气 来保持循环 -
All mammalian brains have a unique layer of nerve cells called the neocortex.
::所有哺乳动物大脑都有一个独特的神经细胞 叫做新皮层 -
Because dominant males tend to be those that are largest and best able to fight, dominance often leads to the evolution of sexual dimorphism.
::由于占支配地位的男性往往是那些最大和最有能力抗争的男性,支配地位往往导致性畸变的演变。
Review
::回顾-
If you had to compare a random carnivorous mammal with a random herbivorous mammal, which digestive system would probably be more complex?
::如果你不得不将随机食肉哺乳动物与随机食草哺乳动物相比较, 哪种消化系统可能更复杂? -
Why are there almost no small mammals that are pure herbivores?
::为什么几乎没有一个小哺乳动物 是纯草食动物? -
What is unique about mammalian lungs?
::哺乳动物肺有什么独特之处? -
How is ventilation controlled by mammals? How is this different from other animals?
::哺乳动物如何控制通风?这与其他动物有何不同? -
What are some advantages of having a dual-pumping, four-chambered heart?
::拥有一个双压、四位组合的心脏有什么好处呢? -
What is unique about the mammalian brain?
::哺乳动物大脑有什么独特之处? -
Why is there usually sexual dimorphism in social mammals?
::为什么社会哺乳动物中通常会有性畸形?
-
In order to maintain a stable, warm body temperature, mammals need a great deal of energy.