16.42 胎盘哺乳动物 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
Is this kangaroo a placental mammal?
::袋鼠是胎盘哺乳动物吗?You know that female kangaroos have a pouch for the final of their babies. So no, kangaroos are not placental mammals. What is a placental mammal?
::你知道雌性袋鼠有袋袋来做最后的婴儿。所以不,袋鼠不是胎盘哺乳动物。什么是胎盘哺乳动物?Placental Mammals
::胎盘哺乳动物Therian Mammals
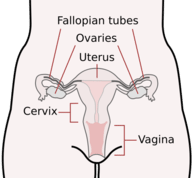
::Therian 哺乳动物Like other female vertebrates , all female mammals have ovaries . These are the organs that produce eggs ( Figure ). Therian mammals also have two additional female reproductive structures that are not found in other vertebrates. They are the uterus and vagina .
::与其他雌脊椎动物一样,所有雌性哺乳动物都有卵巢,这些是产卵的器官(图 ) 。 雌性哺乳动物还有另外两种女性生殖结构,在其他脊椎动物中找不到,它们是子宫和阴道。-
The
uterus
(plural, uteri) is a pouch-like, muscular organ. The
embryo
or
fetus
develops inside the uterus. Muscular contractions of the uterus push the offspring out during birth.
::子宫(多胞胎、子宫)是一种象邮袋一样的肌肉器官,胚胎或胎儿在子宫内发育,子宫的肌肉收缩将子孙在分娩期间推出。 -
The vagina is a tubular passageway through which the embryo or fetus leaves the mother’s body during birth. The vagina is also where the male deposits
during
mating
.
::阴道是胚胎或胎儿在分娩期间离开母亲身体的管状通道,阴道也是男方在交配期间沉积的地方。
The Female Reproductive System of a Therian Mammal (Human). Therian mammals are viviparous, giving birth to an embryo or infant rather than laying eggs. The female reproductive system of all therian mammals is similar to that of humans. Therian mammals are divided into two groups: placental mammals and mammals. Each group has a somewhat different reproductive strategy.
::遗传哺乳动物分为两组:胎盘哺乳动物和哺乳动物,各组的生殖战略略有不同。Placental Mammals
::胎盘哺乳动物Placental mammals are viviparous mammals in which a placenta develops during to sustain the fetus while it develops inside the uterus. The placenta is a spongy structure that nourishes and supports the developing fetus. All modern placental mammals belong to the infraclass Eutheria. There are more than 4,000 of placental mammals in existence today. They are found on every continent and throughout the oceans. The infraclass also includes extinct mammals that resembled modern placental mammals.
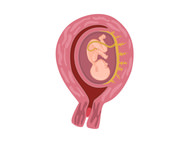
::胎盘是一种充满活力的哺乳动物,胎盘在胎儿在子宫内发育期间发育,以维持胎儿的生长。胎盘是一种养活胎儿的海绵结构。所有现代胎盘哺乳动物都属于次等动物。今天,有4 000多个胎盘哺乳动物存在。它们存在于每个大陆和整个海洋中。次等动物还包括类似于现代胎盘哺乳动物的灭绝哺乳动物。The Placenta of a Placental Mammal (Human). The placenta allows the exchange of gases, nutrients, and other substances between the fetus and the mother. The Placenta
::胎盘As shown in Figure , consists of membranes from both the mother and the embryo. The embryonic portion develops from the same sperm and egg that united to form the embryo. The fetal passes through umbilical arteries to fetal placental structures called villi . The arteries branch repeatedly before they enter the villi. Between the maternal and fetal membranes of the placenta are spaces, called intervillous spaces, that fill with blood from the mother.
::如图所示,胚胎由母胎和胚胎的膜组成,胚胎部分由同一精子和卵子形成,形成胚胎,胎儿通过宫颈动脉传入胎儿胎盘结构,称为Villi。动脉分支在进入宫内前反复出现。胎盘的母子和胎子膜之间是空隙,称为交织空间,充满母亲的血液。Unlike other vertebrates, including reptiles and birds, placental mammals develop membranes that form a placenta during pregnancy. The placenta consists of both embryonic and maternal membranes. It protects and nourishes the developing embryo or fetus. The mother’s blood enters the intervillous spaces through numerous arteries. Because blood in the arteries is under pressure, it is forced deep into the intervillous spaces, where it bathes the villi. This allows fetal blood and maternal blood to exchange substances without actually coming into contact. The placenta receives nutrients , oxygen, antibodies , and from the mother’s blood and passes out wastes from the fetus’ blood. It forms a barrier, called the placental barrier, that filters out some substances that could harm the fetus. For example, white blood cells and other immune system components in the mother’s blood cannot pass through the placental barrier to the fetus. Thus, the placenta ensures that the mother’s immune system does not attack the embryo as a “foreign invader.”
::母亲的血液通过许多动脉进入交错空间。 由于动脉中的血液处于压力之下,血液被迫深入到交错空间中,并在那里洗澡。 这使得胎儿血液和产妇血液可以在不实际接触的情况下交换物质。胎盘接收营养、氧气、抗体和母亲的血液,从胎儿血液中排出废物。 它形成屏障,称为胎盘屏障,过滤了某些可能伤害胎儿的物质。 比如,白血细胞和母亲血液中的其他免疫系统组成部分不能通过胎盘屏障进入胎儿。 因此,胎盘可以确保母亲的免疫系统不会像“外来入侵者”那样攻击胚胎。Why is the placenta so important that its presence is used to subdivide the therian mammals? By nourishing the fetus, while protecting it from the mother’s immune system, the placenta allows an extended gestation period. Gestation is the carrying of an embryo or fetus inside a female viviparous . The gestation period refers to how long the fetus is carried inside the mother. Generally, the larger a placental mammal is, the longer its gestation period. For example, domestic cats have a gestation period of about two months, humans about nine months, and elephants almost two years.
::胎盘为什么如此重要,以至于它的存在被用来分解雌性哺乳动物? 通过养活胎儿,同时保护胎儿不受母体免疫系统的影响,胎盘允许延长妊娠期。 胎盘是在雌性活性中携带胚胎或胎儿。 妊娠期是指胎儿在母体内携带的时间。 一般而言,胎盘越大,哺乳动物的妊娠期越长。 比如,家猫的妊娠期大约两个月,人类大约九个月,大象几乎两年。Pros and Cons of Placental Reproduction
::原产地和原产地的有利和有利A longer gestation period means that offspring can become relatively large and well developed before they leave the mother’s body. For example, in some species of placental mammals, especially herbivores , the young are very mature at birth. Newborn horses, after an 11-month gestation period, can walk and even run within a few hours of birth. Being so mature greatly improves the offspring’s chances of survival. This is especially important in mammalian herbivores because most are prey animals that must be able to outrun predators to survive.
::更长时间的妊娠期意味着后代在离开母亲的身体之前可以变得相对较大和发育良好。 比如,在某些胎盘哺乳动物物种中,特别是食草动物,年轻人出生时非常成熟。 在11个月的妊娠期之后,新生的马可以步行甚至行走几小时。 如此成熟可以极大地改善后代的生存机会。 这在哺乳动物的食草动物中特别重要,因为大部分是猎物,它们必须能够战胜掠食动物生存。On the other hand, supporting a fetus during a long period of gestation can be very draining on the mother. Placental mothers put a big investment into their young. For example, the average human female needs an extra 200 kilocalories of energy per day during the last three months of gestation when the fetus is growing rapidly in size. Most nutrients, including and vitamins , are also needed in significantly greater amounts to ensure the health of both the mother and fetus. As the fetus grows larger, the mother becomes heavier and less mobile. Even if food is scarce, she cannot abandon the infant growing inside her uterus. Giving birth to a large infant can also be very risky for a mother. As many as 1 in 16 human females die during pregnancy or childbirth in areas where good medical care and adequate food are lacking.
::另一方面,在长期怀孕期间养育胎儿可能给母亲带来很大压力; 胎儿母亲对年轻母亲投入大量资金; 例如,当胎儿的体积迅速增长时,在妊娠的最后三个月里,女性平均每天需要200千卡热量的能量; 大部分营养物质,包括维生素,也大得多,以确保母亲和胎儿的健康; 随着胎儿长大,母亲变得更重和流动性更小; 即使食物稀少,她也不能放弃在子宫内生长的婴儿; 生育一个大的婴儿对母亲来说也非常危险; 16名女性中有1人在怀孕或分娩期间在缺乏良好医疗和充足食物的地区死亡。Summary
::摘要-
Therian mammals have two additional female reproductive structures that are not found in other vertebrates: the uterus and the vagina.
::在其他脊椎动物中没有发现另外两种雌性哺乳动物的生殖结构:子宫和阴道。 -
Placental mammals are viviparous mammals in which a placenta develops during pregnancy to sustain the fetus while it develops inside the uterus.
::胎盘哺乳动物是活性哺乳动物,胎盘在怀孕期间发育,在子宫内发育,以维持胎儿。 -
The placenta consists of membranes from both the mother and the embryo.
::胎盘由母亲和胚胎的膜组成。 -
By nourishing the fetus, while protecting it from the mother’s immune system, the placenta allows an extended gestation period.
::胎盘在保护胎儿不受母亲免疫系统影响的同时,通过喂养胎儿,胎盘允许延长妊娠期。 -
A longer gestation period means that offspring can become relatively large and well developed before they leave the mother’s body.
::较长的妊娠期意味着后代在离开母亲的身体之前可以变得相对较大和发育良好。
Review
::回顾-
What reproductive organs are unique to therian mammals?
::哪些生殖器官是神哺乳动物特有的? -
What is a common feature in all animals belonging to the infraclass Eutheria that are alive today?
::属于今天存活下来的次等安乐死的所有动物的共同特征是什么? -
How does the placenta allow nutrients to pass from the mother to the offspring?
::胎盘如何让养分从母亲传到后代? -
What is the role of the placental barrier?
::胎盘屏障的作用是什么? -
What are the pros and cons of having a long gestation period?
::长孕期的利弊何在?
-
The
uterus
(plural, uteri) is a pouch-like, muscular organ. The
embryo
or
fetus
develops inside the uterus. Muscular contractions of the uterus push the offspring out during birth.