14.2溪流沉积
章节大纲
-
Lesson
::经验教训Why is there a pile of rocks in that stream?
::为什么那溪流里有一堆石头?A river meanders causing erosion on one side of its bank. On the other side, sediments are deposited . In this photo of a meander , where is there erosion and where is there deposition?
::在河岸另一侧,沉积层被沉积。在这张照片中,一个米德人的照片中,哪里有侵蚀,哪里有沉积层?Sediment Transport
::沉积物运输The size of particles determines how they are carried by flowing water ; this is illustrated below ( Figure ).
::粒子的大小决定着它们如何由流水承载;下文对此作了说明(图)。How Flowing Water Moves Particles. How particles are moved by flowing water depends on their size.
::流水如何移动粒子。 流水如何移动粒子取决于其大小。Sediments are carried as:
::沉积物以下列方式携带:- Dissolved load : Dissolved ions are carried in the water. These ions usually travel all the way to the ocean.
::溶解的负载:溶解的离子在水中携带。这些离子通常通向海洋。
- Suspended load : Sediments carried as solids as the stream flows are suspended load. The size of particles that can be carried is determined by the stream’s velocity ( Figure ).
::悬浮负载: 沉积物随流流为悬浮负载,以固体形式携带。 能够携带的粒子大小取决于流速( 图 ) 。
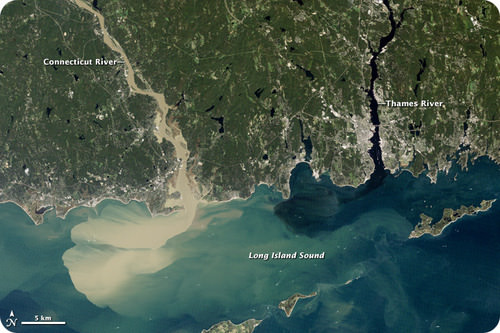
The Connecticut River is brown from the sediment it carries. The river drops the sediment offshore into Long Island Sound.
::康涅狄格河从它携带的沉积物中呈现出棕色,将沉积从岸外沉降到长岛湾。- Bed load : Some particles are too large to be carried as suspended load. These sediments are bumped and pushed along the stream bed as bed load. Bed load sediments do not move continuously. This intermittent movement is called saltation . Streams with high velocities that flow down steep slopes cut down into the stream bed. The sediments that travel as bed load do a lot of the downcutting.
::床位负荷:有些粒子太大,无法作为悬浮负荷携带。这些沉积物被挤压,作为床载物沿着河床推动。 床载沉积物不会连续移动。 这种间歇性运动被称为盐化。 高速度流下斜坡的溪流被切入河床。 作为床载物的沉积物会做许多下沉作业。
Deposition by Streams and Rivers
::溪流和河流沉积When a stream or river slows down, it starts dropping its sediments. Larger sediments are dropped in steep areas, but smaller sediments can still be carried. Smaller sediments are dropped as the slope becomes less steep.
::当溪流或河流放慢速度时,它开始沉积沉积,较大的沉积在陡峭地区沉积,但较小的沉积仍然可以携带,随着斜坡变低,较小的沉积会下降。Alluvial Fans
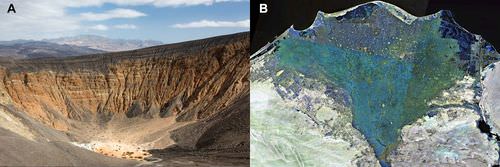
::冲积粉扇In arid regions, a mountain stream may flow onto flatter land. The stream comes to a stop rapidly. The deposits form an alluvial fan ( Figure ).
::在干旱地区,山河可能流到平坦的土地上,水流迅速停止。 矿床形成冲积层(图 ) 。(A) Alluvial fans in Death Valley, California (B) Nile River Delta in Egypt
:A) 埃及加利福尼亚州(B)尼罗河三角洲死亡谷的冲积粉丝
Deltas
::三角三角洲Deposition also occurs when a stream or river empties into a large body of still water. In this case, a delta forms. A delta is shaped like a triangle. It spreads out into the body of water. An example is pictured below ( Figure ).
::当溪流或河流渗入大片静水时,也会出现沉积。在这种情况下,形成三角洲。三角洲的形状像三角形。它会扩散到水体中。下面有一个例子(图 ) 。Deposition by Flood Waters
::洪水沉积A flood occurs when a river overflows it banks. This might happen because of heavy rains.
::洪水在河水溢出时发生,可能是因为暴雨而发生。Floodplains
::洪泛As the water spreads out over the land, it slows down and drops its sediment. If a river floods often, the floodplain develops a thick layer of rich soil because of all the deposits. That’s why floodplains are usually good places for growing plants. For example, the Nile River in Egypt provides both water and thick sediments for raising crops in the middle of a sandy desert .
::随着水在陆地上蔓延,水会放慢速度,沉积会下降。 如果河水泛滥频繁,洪水平原会因所有矿床而形成厚厚的土壤层。 这就是为什么洪水平原通常都是种植植物的好地方。 比如,埃及尼罗河既能提供水,又能提供厚厚的沉积物,在沙沙沙漠中种植作物。Natural Levees
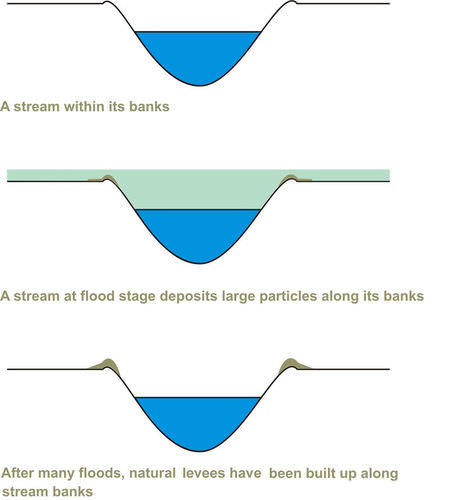
::自然自然收入A river often forms natural levees along its banks. A levee ( Figure ) is a raised strip of sediments deposited close to the water’s edge. Levees occur because floodwaters deposit their biggest sediments first when they overflow the river’s banks.
::河水往往沿河岸形成天然流层。 河堤(图 ) 是沉积在水边附近的高沉积层。 增水的原因是洪水在河岸溢出时首先沉积最大的沉积层。This diagram shows how a river builds natural levees along its banks.
::这个图显示了河水如何沿河岸建造天然堤坝。Summary
::摘要- Streams carry dissolved ions and sediments. The sizes of the sediments a stream can carry, its competence, depend on the stream's velocity.
::流体含有溶解离子和沉积物,流体的大小及其能力取决于流体的速度。
- Particles that are too large to be suspended move along the stream bed by saltation.
::长得无法悬浮的粒子通过盐化沿着河床移动。
- Rivers deposit sediments on levees, floodplains, and in deltas and alluvial fans.
::河流将沉积物沉积在堤坝、洪泛板、三角洲和冲积扇上。
Review
::回顾- If the amount of water in a stream in flood starts to go down, what will happen to sediments the stream is carrying? What will be deposited and where?
::如果洪水中溪流的水量开始下降,河水所承载的沉积物会发生什么情况?将沉积哪些情况,在哪里?
- What happens when a river floods? How are natural levees created?
::当河水洪水发生时会怎样?
- How do alluvial fans form?
::冲积层粉丝如何形成?
Explore More
::探索更多Use this resource (watch up to 8:00) to answer the questions that follow.
::使用此资源( 8: 00前监视)回答接下来的问题 。- What type of structure is the Lighthouse? What is that?
::灯塔是什么类型的结构?
- What is the rock that eroded away? Why was it removed?
::那 侵蚀 的 岩石 、 是 甚 麼 ? 为什么 被 拆去 呢
- What did the canyon start out as? What happened to make the canyon?
::峡谷的起源是什么?
- What rock type is most of the rock in this canyon? Why is that important?
::这峡谷中最坚固的岩石是什么类型的?
- What is the river doing now?
::河现在在干嘛?
- What is the major agent of erosion in the canyon? What is second?
::峡谷的主要侵蚀因素是什么?第二是什么呢?
- Dissolved load : Dissolved ions are carried in the water. These ions usually travel all the way to the ocean.