18.34 人口结构转型 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
Do continuously grow?
::是否持续增长?Not necessarily. The growth of a population depends on a number of issues. Obviously, the average age of the individuals of that population is important. But other factors, such as the local economy, also play a role.
::人口的增长不一定取决于若干问题,显然,人口的平均年龄很重要,但其他因素,如地方经济也起着作用。Demographic Transition
::人口人口结构过渡Major changes in human began during the 18 th century, but they affected different regions at different times. We will first consider Europe, and later compare Europe to other regions of the world. In 18 th century Europe, seed planters, improved ploughs, threshing machines, crop rotation, and selective breeding of led to major growth in food supplies, so death rates due to starvation declined. With increasing understanding of the causes of disease, people improved supplies, sewers, and personal hygiene – and lowered death rates even more. The Industrial Revolution of the 19 th century developed new sources of energy , such as coal and electricity. These further increased the efficiency of new agricultural machines and promoted the of new forms of transportation, mainly railroads, which improved distribution of food. Death rates fell – particularly for those 5 to 10 years of age, allowing many more children to survive to reproduce. The pattern of human survivorship shifted toward a Type III curve.
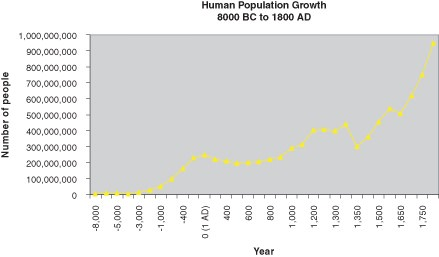
::人类的重大变化始于18世纪,但在不同的时间,它们影响着不同的地区。 我们将首先考虑欧洲,然后将欧洲与世界其它地区进行比较。 在18世纪,欧洲、种子种植者、改良的犁、采摘机、作物轮作和选择性育种导致了食品供应的大幅增长,因此饥饿导致的死亡率下降。 随着对疾病原因的日益了解,人们的供给、下水道和个人卫生状况的改善 — — 以及死亡率的下降。 19世纪的工业革命开发了新的能源来源,比如煤炭和电力。 这些都进一步提高了新农业机器的效率,促进了新型交通,主要是铁路,改善了食品分配。 死亡率下降 — — 特别是5至10岁儿童的死亡率,使得更多的儿童得以存活下来。 人类的存活模式转向了三型曲线。Although death rates fell, birth rates remained at earlier levels. The gap between birth and death rates increased, and population growth began to accelerate (remember that r = b – d ). Although this change did not happen uniformly throughout the world, it was soon reflected in world population levels: it took 200,000 years for the human population to grow to 1 billion, but only 123 years to grow to 2 billion!
::尽管死亡率有所下降,但出生率仍保持在较早的水平上。 出生率和死亡率之间的差距加大,人口增长开始加速(记住,r = b - d ) 。 尽管这一变化并非在全世界一致发生,但它很快反映在世界人口水平上:人口增长到10亿要花20万年时间,而增长到20亿却只有123年时间!Demographic transition theory holds that human populations pass through four stages of growth ( Figure ).
::人口结构转型理论认为,人类人口经历了四个增长阶段(图)。Demographic transition theory proposes that human populations pass through four or five predictable stages of population growth. The 1st and 4th stages are relatively stable, in the first stage because b and d are both high, and in the last because b and d are both low. The key to the theory (disputed by some) is this: once death rates fall due to industrialization and technology, birth rates will follow (the Transition, Stages 2 and 3). Because the theory is based on observations of developed countries, some people dispute its universality. -
Early human history, with its slow, uneven growth maintained by high rates of birth and death, illustrates Stage 1 (
Figure
, but compare to section “1” of
Figure
).
::早期人类历史缓慢、增长不均,由高出生率和高死亡率维持,说明了第一阶段(图......,但与图1“1”节比较)。
-
Stage 2, just discussed for Europe, involves a significant drop in death rate
not matched by an increase in birth rate
, resulting in an increasingly rapid rise in population –
exponential growth
.
::刚刚为欧洲讨论的第二阶段涉及死亡率的大幅下降,与出生率的上升不相称,导致人口快速增长 — — 快速增长。 -
In Stage 3, according to the theory, changes in technology and
society
lead to a decline in birth rate:
::在第三阶段,根据理论,技术和社会的变化导致出生率下降:
-
The decline in child mortality and improvement in
leads rural families to realize they no longer need to have as many children.
::儿童死亡率的下降和农村家庭的改善使农村家庭认识到,他们不再需要像现在这样多的儿童。 -
Agricultural improvements shift more people to urban areas and reduce the need for children.
::农业改良将更多的人转移到城市地区,减少对儿童的需要。 -
Compulsory education removes children from the work force but adds to the cost of raising them.
::义务教育将儿童从劳动力队伍中剔除,但增加了抚养儿童的费用。 -
Increasing education and employment of women reduces their time for and interest in having children.
::增加妇女的教育和就业减少了她们生育子女的时间和兴趣。 -
Birth control methods expand.
::节育方法扩大。 -
Later marriage and delayed childbearing further lower birth rate.
::晚婚和推迟生育进一步降低出生率。
Eventually, according to demographic transition theory, falling birth rates approach already-diminished death rates, and population growth begins to level off.
::最终,根据人口结构转型理论,出生率的下降接近已经下降的死亡率,人口增长开始稳定下来。-
In Stage 4, birth rates equal death rates,
r
= zero, and populations become stable.
::在第四阶段,出生率等于死亡率,r=零,人口稳定。
This somewhat idealistic theory suggests that societies pass through predictable changes which lead to resembling the logistic or S curve. As we have seen, world population growth does not (yet?) show Stages 3 or 4. However, individual countries appear to be at different stages along the continuum; some have reached Stage 4 and a few even require the addition of a 5th stage.
::这一有点理想主义的理论表明,社会经历了可预见的变化,从而导致后勤或S曲线的相似性。 正如我们所见,世界人口的增长没有显示第3或第4阶段。 然而,个别国家似乎处于整个过程的不同阶段;有些国家已经进入第4阶段,有几个国家甚至需要增加第5阶段。Summary
::摘要-
The demographic transition model suggests that human populations pass through four stages of population growth:
::人口结构转型模式表明,人类人口经历了人口增长的四个阶段:
- Stage 1: Growth is slow and uneven, because high death rate offsets high birth rate.
- Stage 2: Development and sanitation reduce death rates, so populations grow exponentially.
- Stage 3: With industrialization, urbanization and contraception, births fall, and growth begins to decline.
- Stage 4: Eventually, birth rate equals death rate, growth rate is zero, and the population stabilizes.
-
Because this model uses late 18
th
and 19
th
century European data, it correlates closely with demographic transitions throughout developed nations into the 20
th
century, but may not fit undeveloped countries.
::由于这一模式使用18世纪末和19世纪欧洲的数据,它与整个发达国家向20世纪的人口结构转型密切相关,但可能不适合不发达国家。
Review
::回顾-
Summarize the 4 stages of the demographic transition model in terms of
b
,
d
, and
r
.
::按b、d和r概述人口结构转型模式的4个阶段。 -
Explain issues associated with the original, four-stage demographic transition model of human population growth.
::解释与人类人口增长的最初四阶段人口过渡模式有关的问题。 -
What would be the characteristics of stage 5?
::第五阶段的特点是什么?
-
Early human history, with its slow, uneven growth maintained by high rates of birth and death, illustrates Stage 1 (
Figure
, but compare to section “1” of
Figure
).