18.47 酸雨 -- -- 高级
章节大纲
-
Can some rain be harmful?
::下雨会有害吗?What if that rain is full of pollutants, such as nitric and sulfuric acid? Acid rain is a serious environmental problem. Acid rain is particularly damaging to lakes, streams, and forests and the plants and that live in these .
::酸雨是一个严重的环境问题。酸雨对湖泊、溪流、森林、植物和生活在这些植物中的植物尤其有害。Acid Rain
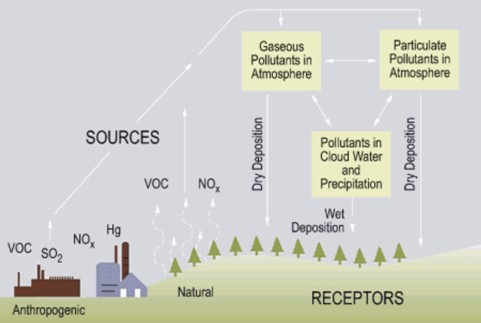
::酸酸雨雨Do you remember the pH scale? Its range is 0-14, and 7 is neutral – the pH of pure . You’ve probably measured the pH of various liquids such as vinegar and lemon juice, but do you know how important even very small changes in pH are for life? Your body maintains the pH of your between 7.35 and 7.45, and death results if blood pH falls below 6.8 or rises above 8.0. All life relies on relatively narrow ranges of pH, because structure and function is extremely sensitive to changes in concentrations of hydrogen ions . An important pollution problem which affects the pH of Earth’s environments is acid rain ( Figure ).
::记得pH尺度吗 ? 它的范围是 0-14, 7 是中性的, 纯的pH 。 你可能测量过各种液体(如醋和柠檬汁)的pH值, 但你知道PH的微小变化对生命的重要性吗? 你的身体维持着7.35到7.45之间的pH值,如果血液pH值降到6.8以下或高于8.0以上,则死亡结果。所有生命都依赖于相对狭窄的pH值,因为结构和功能对氢离子浓度的变化极为敏感。影响地球环境中pH值的一个重要污染问题就是酸雨(Figure ) 。Rain, snow, fog, dew, and even dry particles which have an unusually low pH are commonly considered together as acid rain, although more accurate terms would be acid precipitation or acid deposition. You will remember that a pH below 7 is acidic, and the range between 7 and 14 is basic. Natural precipitation has a slightly acidic pH, usually about 5, mostly because CO 2 , which forms 0.04% of the atmosphere , reacts with water to form carbonic acid:
::降雨、积雪、雾、露珠甚至干燥颗粒,其pH值异常低,通常被视为酸雨,但更精确的术语是酸性降水或酸沉降。你会记得,7岁以下pH值为酸性,7至14之间的范围是基本值。 自然降水的酸性pH值通常约为5, 通常约为5, 主要是因为二氧化碳占大气的0.04%,与水反应形成碳酸:CO 2 + H 2 O ⇌ H 2 CO 3 ⇌ HCO 3 - + H + carbon dioxide water carbonic Acid bicarbonate hydrogen ion This natural chemical reaction is actually quite similar to the formation of acid rain, except that levels of the gases which replace carbon dioxide are not normally significant in the atmosphere. The most common acid-forming pollutant gases are oxides of nitrogen and sulfur released by the burning of fossil fuels . Because burning may result in several different oxides, the gases are often referred to as “NO x and SO x .” This may sound rather affectionate, but it’s more accurate to think of it as obNOXious! Whereas the carbonic acid formed by carbon dioxide is a relatively weak acid, the nitric and sulfuric acids formed by NO x and SO x are strong acids, which ionize much more readily and therefore cause more damage. The reactions given below slightly simplify the chemistry (in part because NO x and SO x are complex mixtures of gases), but should help you see the acidic results of an atmospheric mixture of water and these gases.
::这种自然化学反应实际上与酸雨的形成非常相似,但取代二氧化碳的气体水平通常在大气中并不显著。 最常见的酸化污染物气体是化石燃料燃烧释放的氮和硫氧化物。 由于燃烧可能导致几种不同的氧化物,因此气体通常被称为“氧化物和氧化物 ” 。 这听起来听起来相当贴切,但更准确地认为二氧化碳形成的碳酸是一种相对弱的酸,而由NOx和SOx形成的氮和硫酸则是强酸,它们更容易离子化,从而造成更多的破坏。 下面的反应略微简化了化学成分(部分因为NOx和SOx是气体的复杂混合物 ) , 但应该有助于你们看到大气中水和这些气体混合物的酸性结果。NO 2 + OH - → HNO 3 ⇌ NO 3 - + H + nitrogen dioxide hydroxide ion (from water)
::氢氧化离子(来自水)nitric Acid nitrate hydrogen ion SO 3 + H 2 O → H 2 SO 4 ⇌SO 4 -2 + 2H + sulfur trioxide water sulfuric acid sulfate hydrogen ions Nitrogen and sulfur oxides have always been produced in nature by volcanoes and wildfires and by biological processes in wetlands , oceans, and even on land. However, these natural levels are either limited in time or amount; they account for the slightly acidic pH of “normal” rain. Levels of these gases have risen dramatically since the Industrial Revolution began; scientists have reported pH levels lower than 2.4 in precipitation in industrialized areas. Generation of electricity by burning coal, industry, and automobile exhaust are the primary sources of NO x an SO x . Coal is the primary source of sulfur oxides, and automobile exhaust is a major source of nitrogen oxides.
::火山和野火以及湿地、海洋甚至陆地的生物过程通常自然产生氮和硫氧化物,但是,这些自然水平在时间或数量上是有限的;这些自然水平是“正常”雨中酸性pH值微弱的;这些气体水平自工业革命开始以来急剧上升;科学家报告说工业化地区降水量的pH值低于2.4;燃烧煤炭、工业和汽车排气产生的电是氧化氮和硫氧化物的主要来源。煤是硫氧化物的主要来源,汽车排气是氮氧化物的主要来源。Acid rain formation begins when nitrogen and sulfur oxides (here NO x and SO 2 ) and volatile organic compounds (VOC) from burning fossil fuels escape into the atmosphere. When these gases or particulates combine with water – either in the atmosphere or after reaching the ground – they become acid deposition. The term acid rain commonly refers to all forms of acid deposition.
::酸雨的形成始于燃烧化石燃料的氮和硫氧化物(这里为NOx和SO2)以及挥发性有机化合物(VOC)从燃烧化石燃料中逃入大气。 当这些气体或微粒与水 — — 无论是在大气中还是在到达地面 — — 相结合时,它们就变成了酸沉积。 酸雨一词通常指各种形式的酸沉积。Because most life requires relatively narrow pH ranges near neutral, the effects of acid rain can be devastating. In soils, lowered pH levels can kill microorganisms directly, altering decomposition rates, nutrient cycles, and soil fertility. A secondary effect of increased acidity is the leaching of nutrients, minerals , and toxic metals such as aluminum and lead from soils and bedrock. Depletion of nutrients and mobilization of toxins weakens trees and other plants, especially at higher altitudes where higher precipitation and acid fog damage leaves and needles , as well ( Figure ).
::由于大多数生命需要相对狭窄的pH范围,接近中性,酸雨的影响可能是毁灭性的。在土壤中,降低pH水平可以直接杀死微生物,改变分解率、营养循环和土壤肥力。酸性增加的次要影响是营养物、矿物和有毒金属(如铝和铝及土壤和基岩中的铅)的沥滤。养分的消耗和毒素的动员会削弱树木和其他植物,特别是在降水量和酸雾破坏叶和针叶的较高高度,以及(图 ) 。A mountain forest in the Czech Republic shows effects attributed to acid rain. At higher altitudes, effects on soils combine with direct effects on foliage of increased precipitation and fog.
::捷克共和国的山林显示出酸雨的影响,在较高高度,对土壤的影响与降雨量和雾量增加对树叶的直接影响相结合。The flow of acid rain through watersheds increases acidity, nutrients, and toxins in ecosystems. and are sensitive to changes in pH, although different can tolerate different levels of acidity ( Figure ). disruption can compound even slight changes in pH; for example, acid-sensitive mayflies provide food for less-sensitive frogs . Additional nitrates in aquatic systems can lead to eutrophication and algal blooms , which are discussed in additional concepts.
::酸雨通过分水岭流动会增加生态系统中的酸性、养分和毒素,并且对pH值的变化十分敏感,尽管不同之处可以容忍不同程度的酸性(图)。破坏甚至会加剧pH值的微小变化;例如,对酸敏感的绵羊为不太敏感的青蛙提供食物。水生系统中的更多硝酸盐可导致富营养化和藻类开花,在另外的概念中讨论。Aquatic species show varying sensitivity to pH levels. Colored bars show survival ranges. Trout are more sensitive to increasing acidity than frogs, but mayflies, which frogs consume, are even more sensitive. Consequently, changes in a lake’s acidity may affect ecosystems more severely than simple species sensitivity charts would indicate.
::水生物种对pH水平的敏感度不同。 彩色条形条显示了生存范围。 青蛙比青蛙对酸度增加更为敏感,而青蛙消费的青蝇则更为敏感。 因此,湖泊酸度的变化可能对生态系统的影响可能比简单的物种敏感度图表所显示的更为严重。The sensitivity of lakes, streams, and soils to damage from acid rain depends on the nature of the soils and bedrocks. Watersheds containing limestone, which can buffer (partially neutralize) the acid, are less severely affected. In addition, northern regions with long winters suffer “acid shock” when spring thaws dump months of accumulated acid precipitation into streams and rivers. In the US, lakes and streams in the Appalachians, northern Minnesota and upper New York, and Western mountains have been more severely impacted by acid rain. According to the EPA, the pH of Little Echo Pond in New York state, 4.2, is one of the lowest in the U.S.
::湖泊、溪流和土壤对酸雨损害的敏感度取决于土壤和基岩的性质。 含有石灰岩的流域能够缓冲(部分中和)酸,其影响较小。 此外,冬季长的北部地区在春天将积积聚的酸性降水倒入溪流和河流时遭受“酸震荡 ” 。 在美国,阿帕拉契亚、明尼苏达北部和纽约上游以及西方山脉的湖泊和溪流受到酸雨的影响更为严重。 根据美国环保署(EPA),纽约州小回声池塘的pH(4.2)是美国最低的国家之一。Another class of victims of acid rain is entirely within the realm of human culture and history. Acid’s ability to corrode metal, paints, limestone, and marble has accelerated erosion of buildings, bridges, statues, monuments, tombstones, and automobiles ( Figure ).
::另一种酸雨的受害者完全属于人类文化和历史范畴。 酸化腐蚀金属、油漆、石灰岩和大理石的能力加速了建筑物、桥梁、雕像、纪念碑、墓碑和汽车的侵蚀(图 ) 。Acid rain accelerates erosion of statues, monuments, buildings, tombstones, bridges, and motor vehicles.
::酸雨加速了雕像、纪念碑、建筑物、墓碑、桥梁和机动车辆的侵蚀。Attempts to solve the problem of acid rain began with building taller smokestacks. These only sent the polluting gases higher into the atmosphere, relieving local problems temporarily, but sending the damage to areas far from their industrial sources. Today in the U.S. and other western nations, smokestacks increasingly use “scrubbers” which remove as much as 95% of SO x from exhausts; the resulting sulfates “scrubbed” from the smokestacks can sometimes be sold as gypsum (used in drywall, plaster, fertilizer and more), but may also be landfilled. Catalytic converters and other emission control technologies remove NO x from motor vehicle exhaust. However, and throughout the world is increasing pressures to use more fossil fuels and high-sulfur coal, often without these expensive technologies.
::解决酸雨问题的尝试始于建造高高的烟囱,这些烟囱只能将污染气体送到大气中,暂时缓解当地问题,但将损害送到远离工业来源的地区。 如今,在美国和其他西方国家,烟囱越来越多地使用“灌木机 ” , 将95%的硫酸盐从废气中排出;由此而来的硫酸盐“灌木机”有时可以作为石膏出售(在干墙、石膏、化肥等地使用 ) , 也可能被填埋。 催化转换器和其他排放控制技术将NOx从机动车排气中清除出来。 然而,全世界也越来越需要使用更多的化石燃料和高硫酸煤,而这些技术往往没有这些昂贵的技术。Acidic Seas
::酸海Melting glaciers, rising temperatures, and droughts are all impacts of . But how does global warming actually affect the oceans? The ocean acts like a giant sponge, absorbing carbon dioxide emissions from the air. And as we add more and more carbon dioxide to air by burning fossil fuels, the ocean is absorbing it. On one level, it's done us a big favor. Scientists say that we would be experiencing much more extreme climate change were it not for the ocean's ability to remove the heat-trapping gas. However, these emissions are causing the oceans to become more acidic. Changing pH levels threaten entire food webs , from coral reefs to salmon.
::融化冰川、气温上升和干旱都是由 。但全球变暖如何影响海洋?海洋是如何像巨型海绵那样吸收空气中的二氧化碳排放的?当我们通过燃烧化石燃料在空气中增加二氧化碳时,海洋正在吸收这些二氧化碳。从某种程度上说,这对我们大有裨益。科学家们说,如果海洋不能够去除高温气体,我们将会经历更极端的气候变化。然而,这些排放正在使海洋变得更加酸化。改变pH水平会威胁整个食物网,从珊瑚礁到鲑鱼。Summary
::摘要-
Rain, snow, fog, dew, and even dry particles which have an unusually low pH are commonly considered together as Acid Rain.
::雨、雪、雾、露甚至干燥的颗粒,其pH值异常低,通常被一并视为酸雨。 -
Normal rain has a pH of about 5, due in part to formation of a weak (carbonic) acid from CO
2
.
::正常雨的pH值约为5,部分原因是二氧化碳形成一种弱(碳酸)酸。 -
Burning fossil fuels adds NO
x
and SO
x
gases to the atmosphere; these form strong acids (nitric and sulfuric) and change the pH of rain to as low as 2.4.
::燃烧的化石燃料将NOx和SOx气体添加到大气中;这些气体形成强酸(氮和硫),并将pH值的降雨量降低到2.4。 -
Acid rain leaches nutrients and toxins from soils, weakening forests and killing aquatic animals.
::酸性雨水沥滤液从土壤中产生营养物和毒素,削弱森林并杀死水生动物。 -
Limestone in bedrock or watersheds buffers the effects of acid rain for certain lakes.
::基岩或流域中的石灰岩缓冲酸雨对某些湖泊的影响。 -
The development of taller smokestacks only sent pollution elsewhere, but scrubbers in smokestacks and catalytic converters in motor vehicles help to reduce emissions.
::更高的烟囱的开发只会造成污染,但烟囱中的洗涤器和机动车辆中的催化转换器有助于减少排放。
Review
::回顾-
Define acid rain and trace the steps in its formation.
::确定酸雨的定义,追踪酸雨形成过程中的步骤。 -
Why is rain with a pH of 5 not considered acid rain?
::为何五分之五的pH值雨不视为酸雨? -
Analyze the effects of acid rain on soils, water resources, vegetation, animals, and humans.
::分析酸雨对土壤、水资源、植被、动物和人类的影响。
-
Rain, snow, fog, dew, and even dry particles which have an unusually low pH are commonly considered together as Acid Rain.