1.12 坐标几何
章节大纲
-
Introduction
::导言Much of algebraic representation occurs within the coordinate (or Cartesian) plane. This lesson will review how to represent points, lines, and parallel and perpendicular lines graphically.
::许多代数表示式出现在坐标(或笛卡尔)平面内,该课程将用图形方式审查如何代表点、线条、平行线和垂直线。The Coordinate Plane
::协调计划The coordinate plane can be thought of as two number lines that meet at right angles. The horizontal line is called the -axis and the vertical line is called the -axis. Together the lines are called the axes , and the point at which they cross is called the origin . The axes split the coordinate plane into four quadrants , which are numbered sequentially (I, II, III, IV) moving counterclockwise from the upper right.
::坐标平面可被视为在右角度相交的两条数字线。 水平线称为 X 轴, 垂直线称为 Y 轴。 横线加起来称为轴, 其交叉点则称为原点。 轴将坐标平面分割成四个四方位, 从右上方按顺序编号( 一、 二、 三、 四) , 从右上方逆时针移动 。
Identify Coordinates of Points
::确定各点的坐标When given a point on a coordinate plane, you can easily determine its coordinates . The coordinates of a point are two numbers , and written together they are called an ordered pair . The numbers describe how far along the -axis and -axis the point is. The ordered pair is written in " data-term="Parentheses" role="term" tabindex="0"> parentheses , with the -coordinate (also called the abscissa ) 1st and the -coordinate ( also known as the ordinate ) 2nd.
::当在坐标平面上给定一个点时,您可以很容易地确定其坐标。一个点的坐标是两个数字,它们一起写成,被称为一个有顺序的对。数字说明在x轴和y轴之间的距离。定的对以括号写,有x坐标(也称为 abscissa) 1 和 y坐标(也称为坐标) 2 。
:1,7) 定购对,X值为1,Y值为7(0,0,5) 定购对,X值为0,Y值为5(2.5,4) 定购对,X值为-2.5,Y值为4(107.2,-0.005) 定购对,x值为-107.2,Y值为-0.005)
Identifying coordinates is just like reading points on a number line, except that the points do not actually lie on the number line!
::识别坐标与数字行的读点相同,但数字线上的点实际上并不在数字线上!Plot Points in a Coordinate Plane
::坐标平面中的绘图点Plotting points is simple, once you understand how to read coordinates and the scale on a graph. As a note on scale, in the next two examples pay close attention to the labels on the axes.
::绘图点很简单, 一旦您了解如何在图表中读取坐标和比例尺。 作为比例说明, 在接下来的两个示例中, 密切关注轴上的标签 。Watch this video for help with the examples below:
::观看这段影片,Slope
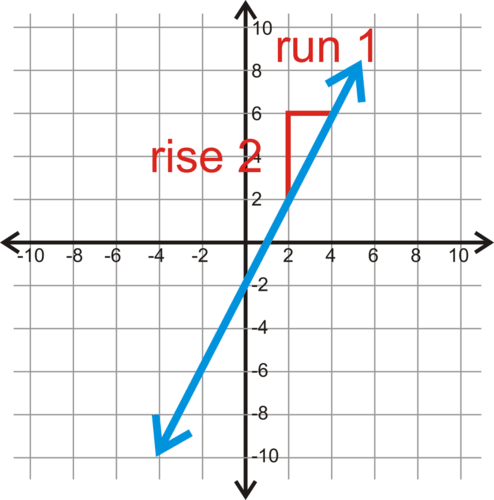
::斜斜度The following video provides an overview on the concept of the of a line. It defines slope, gives the formula , and works through examples:
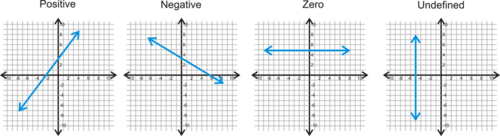
::以下视频概述了一条线的概念。它界定斜坡,给出公式,并通过实例发挥作用:Slope is the change in vertical direction over the change in horizontal direction. It is defined as the .
::斜坡是垂直方向相对于水平方向变化的变化。它被定义为上升。Slope of Line between Two Points
::两点间线的曲线The slope of the line passing through two points and is .Different Types of Slope :
::不同的斜坡类型 :Watch this video for help with the examples below:
::观看这段影片,Parallel Lines in the Coordinate Plane
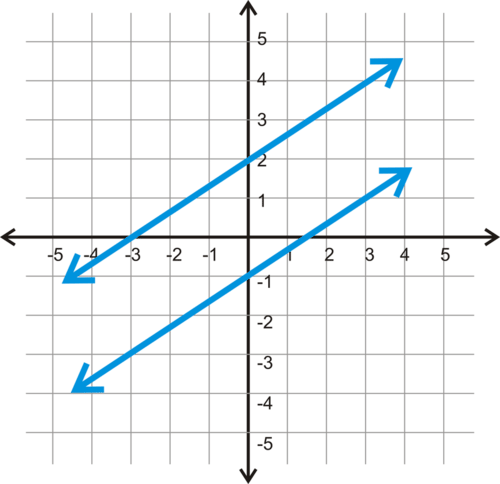
::坐标平面的平行线Parallel lines are two lines that never intersect. In the coordinate plane, that would look like this:
::平行线是两条从不交叉的线条。在坐标平面上,这看起来像:If we take a closer look at these two lines, we see that the slopes are both .
::如果我们仔细看一看这两条线,我们可以看到,斜坡是23。This can be generalized to any pair of parallel lines. Parallel lines always have the same slope and different intercepts .
::平行线总是有相同的斜坡和不同的y-inter概念。What if you were given two parallel lines in the coordinate plane? What could you say about their slopes?
::如果在座标飞机上给你两条平行线呢?Perpendicular Lines in the Coordinate Plane
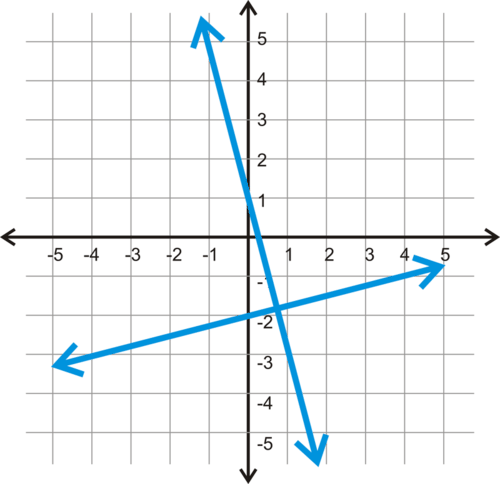
::坐标平面上的直直线Perpendicular lines are two lines that intersect at a or right angle. In the coordinate plane, that would look like this:
::垂直线是两条线,在90°C或右角交叉。在坐标平面上,这看起来像:If we take a closer look at these two lines, we see the slope of one is -4 and the other is .
::如果我们仔细看一看这两条线,我们看到一的斜坡是 -4,另一的斜坡是14。This can be generalized to any pair of perpendicular lines in the coordinate plane. The slopes of perpendicular lines are negative reciprocals of each other.
::这可以推广到坐标平面上任何一条垂直线,垂直线的斜坡是相互负对等的。This video explores the relationship between the slopes of perpendicular lines:
::这段影片探索垂直线斜坡之间的关系:Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1
Find the coordinates of the point labeled in the diagram above.
::在上面的图表中找到标有 P 点的坐标 。Solution:
::解决方案 :Imagine you are standing at the origin (the point where the -axis meets the -axis). In order to move to a position where is directly above you, you would move 3 units to the right. (We say this is in the positive direction.)
::想象一下您站在原点( X 轴与 Y 轴相交的点) 。 为了移动到 P 直接在你上方的位置, 您会移动到右边的 3 个单位 。 (我们说这是正 x 方向 。 )The -coordinate of is +3.
::P的x坐标为+3。Now, if you were standing at the 3 marker on the -axis, point would be 7 units above you. (Above the axis means it is in the positive direction.)
::现在,如果你站在X轴上方的3个标记处,P点在你上面7个单位。 (轴是正向y方向。 )The -coordinate of is +7.
::P的 Y 坐标是+ 7 。The coordinates of point are (3, 7).
::P点的坐标是(3,7)Example 2
::例2
Find the coordinates of the points labeled and in the diagram above .
::在上述图表中查找标有Q和R的点的坐标。Solution:
::解决方案 :In order to get to , we move 3 units to the right, in the positive direction, then 2 units down, in the negative direction. The -coordinate of is +3, and the -coordinate of is −2.
::为了到达Q,我们将3个单位向右移动,向正x方向移动,然后向下移动2个单位,向负y方向移动。Q的x坐标是+3,而Q的Y坐标是-2。The coordinates of are found in a similar way. The -coordinate is +5 (meaning 5 units in the positive direction), and the -coordinate is again −2.
::R 的坐标也以类似的方式找到。 x 坐标是+ 5 (表示正向 x 方向 5 个单位),Y 坐标是 -2 。The coordinates of are (3, −2). The coordinates of are (5, −2).
::Q座标为(3,-2),R座标为(5,-2)。Example 3
::例3Triangle is shown in the diagram below. Find the coordinates of the vertices , and .
::三角 ABC 显示在下图中。请查找 A、B 和 C 顶点的坐标 。
Solution:
::解决方案 :Point :
::A点:A(-2,5)
::x坐标坐标=-2
::y- 坐标% 5Point :
::B点:B(3,3,3)
::x 坐标% 3
::Y 坐标=-3Point :
::C点:C(4-4-1)
::x坐标坐标=-4
::Y- 坐标=-1Example 4
::例4Plot the following points on the coordinate plane:
::在坐标平面上绘制下列点:
::A(2,7)B(4,6)D(3,3)E(0,2)F(7,5)Solutions:
::解决办法:
Point is 2 units right, 7 units up. It is in Quadrant I.
::A点( 2, 7) 是 2 个单位右侧, 向上 7 个单位。 在 Quadrant I 中 。Point is 4 units left, 6 units up. It is in Quadrant II.
::B点( 4, 6) 是剩下4个单元, 向上 6个单元, 在 Quadrant II 中 。Point is 3 units left, 3 units down. It is in Quadrant III.
::D( 3 - 3) 点是左3个单位, 向下3个单位, 在 Quadrant III 中 。Point is 2 units up from the origin. It is right on the -axis, between Quadrants I and II.
::点E( 0. 2) 是从源起向上移动的 2 个单位。 它位于 y 轴上, 介于 夸德兰特 II 和 II 之间 。Point is 7 units right, 5 units down. It is in Quadrant IV.
::F(7,5)点是右7个单位,向下5个单位,在Quadrant IV。Example 5
::例5a) What is the slope of the line through (2, 2) and (4, 6)?
:a) 线的坡度是多少(2、2和4、6)?
Solution:
::解决方案 :Use the slope formula to determine the slope. Use (2, 2) as and (4, 6) as .
::使用斜坡公式确定斜坡。 使用 2( 2, 2) 作为 (x1, y1) , 4, 6) 作为 (x2, y2) 。
::my2-y1x2-x1=6-24-2=42=2Therefore , the slope of this line is 2. This slope is positive.
::因此,这条线的斜坡是2。 这个斜坡是正的。b) Find the slope between (-8, 3) and (2, -2).
:b) 在(8,3)和(2,2)之间找到斜坡。
Solution:
::解决方案 :
::m2 - 32 - (-8) 510 - 12This is a negative slope .
::这是一个负斜坡。c) Find the slope between (-5, -1) and (3, -1).
:c) 在(5-1)和(3-1)之间找到斜坡。
Solution:
::解决方案 :
::m1 - (- 1) 3 - (-5) = 08=0Therefore, the slope of this line is 0, which means it is a horizontal line. Horizontal lines always pass through the axis. Notice that the coordinate for both points is -1. In fact, the coordinate for any point on this line is -1. This means the horizontal line must cross .
::因此,这条线的斜坡是 0, 意思是它是一个水平线。 水平线总是通过 y - 轴线。 请注意, 两个点的 y - 坐标是 - 1 。 事实上, 该线上任何点的 y - 坐标是 - 1 。 这意味着水平线必须横过 y * 1 。d) Find the slope of the line through (3, 2) and (3, 6).
:d) 找到横穿线的斜坡(3,2)和(3,6)。
Solution:
::解决方案 :
::m=6 - 23 - 3=40=未定义Therefore, the slope of this line is undefined , which means it is a vertical line. Vertical lines always pass through the axis. Notice that the coordinate for both points is 3. In fact, the coordinate for any point on this line is 3. This means the vertical line must cross .
::因此,这条线的斜坡是未定义的, 这意味着它是一条垂直线。 垂直线总是通过 x- 轴线。 注意两个点的 x- 坐标是 3 。 事实上, 这条线上任何点的 x- 坐标是 3 。 这意味着垂直线必须跨 x= 3 。Example 6
::例6a) Find the slope of the line that is perpendicular to this line: .
:a) 找到与该线垂直的线的斜坡:y23x-5。
Solution:
::解决方案 :, take the reciprocal and change the sign, (⊥ is the notation for perpendicular) .
::má23, 拿对等的, 并更改符号, m32 (是垂直的标记) 。b) Find the slope of the line that is perpendicular to this line: .
:b) 查找与该线垂直的线的斜坡:y=x+2。
Solution:
::解决方案 :Because there is no number in front of , the slope is 1. The reciprocal of 1 is 1, so the only thing to do is make it negative, .
::因为x前面没有数字, 斜坡是 1 。 1 的对等值是 1, 所以唯一要做的就是让它负, m1 。Example 7
::例7Find the equation of the line that is perpendicular to and passes through (9, -5).
::查找与 y13x+4 垂直的直线的方程,然后通过 (9,5) 。Solution:
::解决方案 :First, the slope is the opposite reciprocal of . So, .
::首先,斜坡是-13的对等。所以,m=3。The equation of a line can be written using slope-intercept form , .
::线条的方程式可以用 y=mx+b 的斜体界面写出。Plug in 9 for and -5 for to solve for the new intercept :
::x 和 - 5 y 的插件在 9 中, 用于 y - interfict (b) 的 y - interview (b) 解答 :
::- 5=3(9)+b-5=27+b-32=bTherefore, the equation of the perpendicular line is .
::因此,垂直直线的方程式是y=3x-32。Note that you can use the same process, but keep the slope identical if solving for the equation of the line that is parallel.
::请注意,您可以使用相同的进程,但如果解决平行线的方程式,则保持斜度相同。Example 8
::例8Graph and . Determine if they are perpendicular.
::图3 - 4y=8和4x+3y=15。确定它们是垂直的。Solution:
::解决方案 :First we have to change each equation into slope-intercept form. In other words, we need to solve each equation for :
::首先,我们必须将每个方程式改变为斜坡界面形式。 换句话说, 我们需要为 y 解析每个方程式 :
::3x-4y=84x+3y=15-4y3x+83y4x+15y=34x-2y43x+5Now that the lines are in slope-intercept form (also called intercept form), we can tell they are perpendicular because their slopes are opposite reciprocals.
::现在线以斜坡界面的形式(也称为 y - interphysict form)出现, 我们可以看出来它们是垂直的, 因为它们的斜坡是相反的对等的 。Example 9
::例9Find the slope of the interval between the two given points:
::查找两个给定点间距的斜坡 :a) (3, -4) and (3, 7)
:a) (3,4)和(3,7)
Solution:
::解决方案 :These two points create a vertical line, so the slope is undefined.
::这两个点形成一条垂直线,所以斜坡是未定义的。b) (6, 1) and (4, 2)
:b) (6,1)和(4,2)
Solution:
::解决方案 :The slope is .
::斜坡为(2-1)(4-6)12。c) (5, 7) and (11, 7)
:c) (5,7)和(11,7)
Solution:
::解决方案 :These two points create a horizontal line, so the slope is zero.
::这两个点形成水平线,所以斜坡为零。Review
::回顾-
Identify the coordinates of each point,
, on the graph below.

::在下图中标明每个点的坐标A-F。 -
Draw a line on the above graph connecting point
with the origin. Where does that line intersect the line connecting points
and
?
::绘制上图中连接点B和来源的线条。 该线条在哪里交叉连接点C和D的线条?
Identify which quadrant each point lies in:
::确定每个点的象限值 :- (4, 2)
- (-3, 5.5)
- (4, -4)
- (-3, -5)
Find the slope between the two given points:
::查找两个给定点之间的斜坡 :-
(-9, 5) and (-6, 2)
:9,5)和(6,2)
-
(-6, 0) and (-1, -10)
:-6,0)和(-1,-10)
-
(1, -2) and (3, 6)
:1,2)和(3,6)
-
(-4, 5) and (-4, -3)
:-4、5和4)和(-4、3)
-
(4, 1) and (7, 1)
:第4、第1、第4、第1和第7、第1段)
-
(13, 12) and (-23, 14)
:13、12)和(23、14)
-
(-4, 2) and (-16, 12)
:4-4,2)和(16,12)
Determine if each pair of lines are parallel, perpendicular, or neither. Then graph each pair on the same set of axes:
::确定每一条线是否平行, 垂直, 或两者都不是。 然后在同一组轴上绘制每对图 :-
and
::y=4x-2和y=4x+5 y=4x-2和y=4x+5 -
and
::yx+5和y=x+1 yx+5和y=x+1 -
and
::5x+2y4和5x+2y=8 -
and
::y2x+3和y=12x+3 -
and
::y3x+1和y=3x-1
Determine the equation of the line that is parallel to the given line, through the given point:
::通过给定点确定与给定线平行的线条的方程 :-
::y5x+1;(-2,3) -
::y=23x-2; (9,1) -
::x-4y=12; (- 16-2)
Determine the equation of the line that is perpendicular to the given line, through the given point:
::通过给定点确定与给定线垂直的线条的方程:-
::y=x-1; (- 6, 2) -
::y=3x+4; (9,-7) -
::5x-2yy=6; (5,5) -
::y=4; (-1) (-1)
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。 -
Identify the coordinates of each point,
, on the graph below.