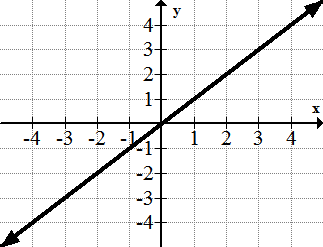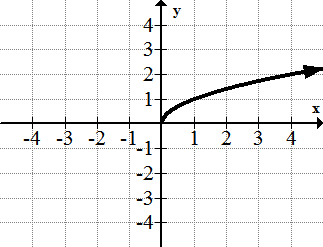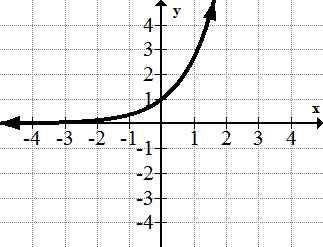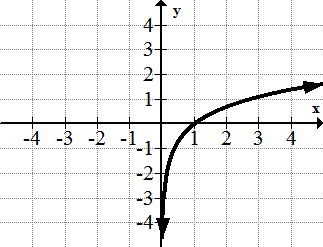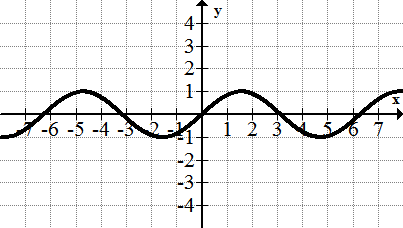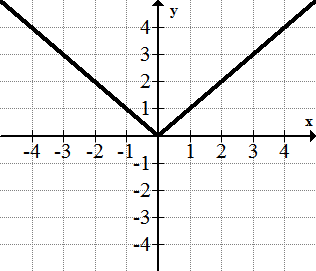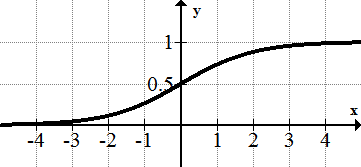2.7 功能家庭
章节大纲
-
Introduction
::导言Functions are used in mathematics to illustrate patterns. For example, when a ball is thrown into the air, it rises and then comes back to earth. Its height at any time can be determined by the mathematical function The rule defined by this function provides a way to calculate the height of the ball (in feet) at any time (in seconds) after the ball is thrown.
::函数用于数学以说明模式。例如,当球被投入空气时,它会上升,然后返回到地球。它的高度随时可以由数学函数 h(t)\\\ at2+bt+c来决定。此函数定义的规则提供了一种计算球在投入球后的任何时候(以秒计)的高度的方法。
Suppose the height function of a thrown ball is given by . The table of heights for some particular values of time is seen below. Notice that the heights repeat, due to the ball traveling up and then falling back to the ground.
::假设抛出球的高度函数由 h(t) 16t2+80t+6 给出, 某些特定时间 t 的高度( h(t) ) 表格在下面可以看到。 请注意, 高度重复, 原因是球向上移动, 然后返回地面 。
::球作为时间函数的高度
::时速06210247056In our example, the height is calculated as a function of time, because the height of the ball depends on the amount of time that has passed since it was released. This function is a member of a family of functions called quadratic functions .
::以我们为例,高度是按时间函数计算的,因为球的高度取决于球释放后所经过的时间。这个函数是一个称为二次函数的函数大家庭的成员。Basic Families of Functions
::功能基本家庭Mathematicians classify algebraic functions into several families, which have special characteristics. Analytical techniques use these characteristics to describe and explain situations in our world. Below are the graphs of the parent functions for some typical families of functions. The given characteristics of each of these parent functions are helpful to consider when thinking about transformations :
::数学家将代数函数分类为几个家庭,这些家庭具有特殊的特点。分析技术利用这些特点来描述和解释我们世界的情况。下面是某些典型功能家庭父子函数的图表。这些父子函数的每个特点有助于在考虑转变时加以考虑:The Identity Function:
::身份函数: f(x)=xThe identity function is a simple function, and yet all straight lines can be derived from it. It is called the identity function because each output value is the same as the value that was used for the input. In this sense, the identity function preserves the identity of an input.
::身份函数是一个简单的函数, 但所有直线都可以从中产生。 它被称为身份函数, 因为每个输出值与输入所使用的值相同。 从这个意义上讲, 身份函数保存输入的特性 。The Quadratic Function:
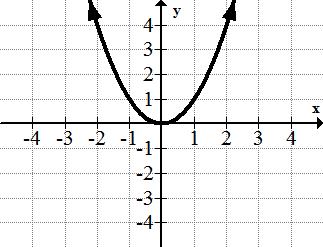
::二次曲线函数: f( x) =x2
The quadratic function's graph is called a parabola . symmetric in respect to the -axis and has a minimum -value. In general, quadratic functions are symmetric in respect to a vertical line. This parent function is symmetric in respect to the particular vertical line, the -axis. Also, quadratic functions have either a minimum or maximum value. The vertex of a quadratic function occurs at the minimum or maximum value. These ideas are also discussed in the following video:
::二次函数的图形称为 parabola。 这个特定的二次函数对于 y 轴是对称的, 并且具有最小的 y 值。 一般而言, 二次函数对于垂直线是对称的。 这个母函数对于特定的垂直线, y 轴是对称的。 另外, 二次函数具有最小值或最大值。 二次函数的顶部值是最小值或最大值。 以下视频也讨论这些想法:The Cubic Function:
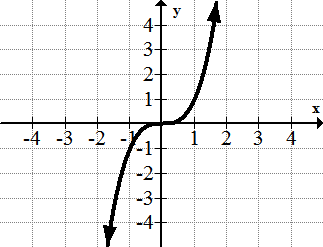
::Cubic 函数: f( x)=x3The cubic function exhibits a different kind of than the quadratic function. In this parent function, the point of symmetry occurs at (0, 0) and the point (1,1) has a mirror image in the origin as the point (-1,-1). This is true for every point on the graph. In general, cubic functions will have a point of symmetry where the two other parts of the graph are mirror images of each other.
::立方函数显示与二次函数不同种类的函数。在这个父函数中,对称点发生于 0, 0 和点(1, 1) 的对称点是源点的镜像图像( 1, 1) 。 对于图形中的每个点来说都是如此。 一般来说, 立方函数将有一个对称点, 即图形的另外两个部分是彼此的镜像图像 。The Square Root Function :
::平方根函数: f( x)=x=x12The square root function is half of a side-opening parabola. The parent function has a vertex at (0, 0) and is only defined for in the real number system. In general, a square root function with a vertex point at is only defined for in the real number system.
::平方根函数是侧开面抛物线的一半。父函数在( 0, 0) 时有一个顶点, 且只在实际数字系统中为 x%0 定义。 一般来说, 在( a, a) 时有顶点的平方根函数只为实际数字系统中的 xa 定义。The Reciprocal Function:
::互惠函数: f(x)=1x=x-1The graph of the reciprocal function is a hyperbola . This parent function is the basis for some rational functions . Notice the way the graph gets close to the -axis without touching it as the absolute value of gets larger and as gets smaller. This is called asymptotic behavior as approaches .
::对应函数的图形是一个双倍函数。 此父函数是某些理性函数的基础 。 注意当x的绝对值越来越大, x 的绝对值越来越小时, 该图形在不触动 X 轴的情况下接近 X 轴的方式 。 这被称为“ 无症状行为 ” ( xapproaches ) 。The Exponential Function :
::指数函数: f(x)=bx, b>0, b1The exponential function is used to model growth. In this graph, , so . Notice the way the graph gets close to the -axis without touching it, so the exponential function also exhibits asymptotic behavior as gets smaller. As gets larger, this function grows very quickly.
::指数函数用于模拟增长。 在这个图形中, b=3, 所以 f( x) =3x 。 注意图形如何在不触动 X 轴的情况下接近 X 轴, 因此指数函数也显示出 x 变小时的无症状行为。 随着 x 变大, 此函数增长很快 。The Logarithm Function:
::对数函数: f( x) =logbx, b>0, b1The logarithmic function is the inverse to the exponential function. In this graph, , so . Notice the way the graph gets close to the -axis without touching it, so the exponential function also exhibits asymptotic behavior as approaches 0 from the right.
::对数函数是指数函数的反向函数。在此图中, b=3, 所以 f( x) =log3 x。 注意图形在不触动 y 轴的情况下接近 y 轴的方式, 因此指数函数也显示出 x 从右向接近 0 时的无症状行为 。The Sine Function:
::Sine 函数 : f( x)=sinxThe sine function is one of six basic periodic functions. In this graph, the sine function is graphed using radian mode. P eriodic refers to the fact that the sine exhibits cycles that repeat at regular intervals. The maximum -value for this parent function is 1 and the minimum -value is -1.
::正弦函数是六个基本周期函数之一。在此图中,正弦函数是使用弧度模式绘制的。周期是指定期重复的正弦显示周期。此父函数的最大 y 值为 1, 最小 y 值为 - 1 。The Absolute Value Function:
::绝对值函数 : f(x)The absolute value function is similar to the quadratic function, except the lines are straight rather than curved and meet at a point . The vertex of the absolute value is this point. Similar to the quadratic, this parent function symmetric in respect to the -axis and has a minimum -value. In general, a bsolute value functions are symmetric in respect to a line and have either a minimum or maximum value.
::绝对值函数与二次函数相似, 但线条是直线而不是曲线, 在一个点会合。 绝对值的顶点是此点。 与二次函数相似, 此母函数对齐了 y 轴, 并具有最小 y 值。 一般来说, 绝对值函数对齐了一行, 并且具有最小值或最大值 。The Logistic Function :
::后勤职能:f(x)=11+b-xThe logistic function is a combination of the exponential function and the reciprocal function. In this graph, , so . This function models environmental populations, which cannot grow in an unrestricted fashion. At a certain point, a population will outgrow its food source and space, so its growth will diminish. The level of population that can be sustained by an environment is called the carrying capacity . The graph approaches the carrying capacity level as increases.
::后勤功能是指数函数和对等函数的组合。 在本图中, b=e, so f(x)=11+e-x。 此函数模拟环境人口, 环境人口不能不受限制地增长。 在某一时刻, 人口将超越食物来源和空间, 从而缩小其增长。 可以通过环境维持的人口数量被称为承载能力。 该图将承载能力水平作为x增加值接近 。Play, Learn, and Explore Function Families:
::玩耍、学习和探索功能家庭:Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Compare and contrast the graphs of the two functions and .
::比较和对比两个函数 f( x) 的图形 f( x) =logbx 和 h( x) =x。Solution:
::解决方案 :Similarities: Both functions increase without bound as gets larger. Both functions are not defined for negative numbers.
::相似点: 两项功能均在增加, 但没有被约束, 因为 x 越大。 这两种功能没有被定义为负数 。Differences: The graph of the logarithmic function exhibits asymptotic behavior as approaches 0. Notice that the -values approach negative infinity as approaches 0. The square root function is defined at .
::差异: 对数函数图显示 x 接近 0 的无症状行为。 注意 Y 值接近负无限度, x 接近 0 。 平方根函数定义为 x= 0 。Example 2
::例2Describe the symmetry displayed by the parent functions discussed in this section .
::描述本节讨论的父函数所显示的对称 。Solution:
::解决方案 :The graphs of these functions are symmetric with respect to the -axis.
::这些函数的图形与 Y 轴对齐。
:xx) =x2,g(x) x
The graph of has a point of symmetry at (0, 0) .
::f(x) =x3 的图形对称点为 0, 0 。Example 3
::例3Which parent function families have a minimum -value ?
::哪个父系功能家庭有最小的 Y 值 ?Solution:
::解决方案 :The families with a minimum -value are:
::具有最低y价值的家庭是:
:xx) =x2,g(x) x,h(x) =x,k(x) =sinx
Example 4
::例4Which parent functions are defined for all values of ?
::为 x 的所有值定义了哪个父函数 ?Solution:
::解决方案 :
::y=x,y=x2,y=x3,y=3,y=x,y=abx,y=11+ab-x,y=sinxExample 5
::例5Below is the graph of the function , which models the height of a ball:
::下面是函数 h(t)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\可以模拟球的高度。
Determine the following:
::确定如下:a) the times that the height is 70 feet
::a) 高度为70英尺的乘以Solution:
::解决方案 :The two points on the graph that have a -value of 70 are (1,70) and (4,70). This means that the ball reaches a height of 70 feet at and 4 seconds.
::图表上Y值70的两点是(1、70和4、70),这意味着球在t=1和4秒时达到70英尺的高度。b) the maximum height and the time that the ball reaches the maximum height
::b) 球最大高度和球达到最大高度的时间Solution:
::解决方案 :The maximum height occurs at the vertex. The graph is symmetrical about the vertical line through the vertex . This means that the maximum height is reached at seconds. The height is 106 feet.
::最大高度出现在顶端。 图形通过顶部 x=2.5 的垂直线对齐。 这意味着最大高度在 t=2.5 秒时达到。 高度为 106 英尺。
::h(2.5)162.52+80(2.5)+6h(2.5)=106Summary
::摘要-
The basic families of functions are used as a starting point to study techniques used to analyze functions.
::功能的基本类别被用作研究用于分析功能的技术的起点。 -
Important features of a graph include maximum or minimum values, symmetry, and asymptotic and periodic behavior.
::图表的重要特征包括最大值或最低值、对称性、无症状和周期行为。 -
A graph is
symmetrical
about the
-axis
if, when
is
on the graph, then
is also on the graph.
::如果(x,y)在图形上,而(-x,y)在图形上,那么(-x,y)也在图形上,则图在Y - 轴上对称。 -
A graph is
symmetrical
about the origin
if, when
is on the graph, then
is also on the graph.
::如果(x,y)在图表上,而(-x,-y)在图表上,那么(-x,-y)在图表上,则图表对称来源。 -
Asymptotic behavior
occurs when a graph approaches a line or axis as
approaches a specific value.
::当一个图形接近一条线或轴,而 x 接近一个特定值时,就会发生无药可救的行为。 -
The
vertex
is the point on a parabola where either the minimum or maximum value occurs.
::顶点是出现最小值或最大值的抛物线上的点。
Review
::回顾For 1-10, sketch a graph of the function from memory:
::1- 10, 从内存绘制函数图示 :1.
::1.y=bx2.
::2.y=logbx3.
::3.y=sin(x)4.
::4. y=x25.
::5 y x6.
::6. y=1x7.
::7.y=11+b-x8.
::8.y=x 8y=x9.
::9. y=x310.
::10.y=x11. Which parent function is not defined at 0? Why?
::11. 在0时没有界定哪一种母函数?为什么?12. Name four basic functions that do not have a maximum y-value.
::12. 列出四个没有最大y值的基本功能。13. What are the differences between and ?
::13. y=x2和y=x3之间有什么区别?14. What symmetry can be seen with and ?
::14. Y=bx和y=logbx的对称性如何?15. Explain why is not defined for all values of .
::15. 解释为什么y=x没有为 x 的所有值定义。Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。 -
The basic families of functions are used as a starting point to study techniques used to analyze functions.