16.9新生代板块构造
章节大纲
-
How does the Cenozoic end?
::基因组的结局如何?We don't know how the Cenozoic ends. We're still in it! The Cenozoic has been going on for 65 million years. Toward the very end of this time, humans have evolved. We are now witness to the geology of the Cenozoic. What came earlier in this era looks a lot like what is going on now.
::我们不知道基因组的结局。 我们还在其中! 基因组已经持续了6500万年了。 到这个时候, 人类已经进化了。 我们现在见证了基因组的地质学。 这个时代早期出现的东西看起来和现在的情况非常相似。Cenozoic
::蛋甲醚The Cenozoic began around 65.5 million years ago. We say that it begins after the Cretaceous extinction. We are still in the Cenozoic today. The Cenozoic accounts for only about 1.5% of Earth’s total history. But since it's the the most recent era, it is the one we know the most about. Much of what has been discussed elsewhere in this text describes the geology of the Cenozoic. A few highlights are mentioned here.
::切诺zoic始于大约6,550万年前。我们说,它始于白鲸灭绝之后。我们今天仍在切诺索科中。切诺zoic只占地球历史总数的1.5 % 。 但是,由于它是最近一个时代,我们最了解它。本文本其他部分讨论的许多内容描述了切诺索科的地质学。这里提到了几个亮点。Plate Tectonics
::热点构造构造The plate tectonics of the Cenozoic are still going on today. Early in the Cenozoic, blocks of crust uplifted to form the Rocky Mountains . Subduction off of the Pacific Northwest formed the Cascades volcanic arc. Crust is being pulled apart to form the Basin and Range province that centers on Nevada.
::切诺zoic 的板块构造今天仍在继续。 在早期的Cenozoic, 地壳被提升成落基山脉。 太平洋西北的俯冲形成岩礁火山弧。 Crust正被拆开,形成内华达的盆地和山脉省。Evolution of the San Andreas Fault
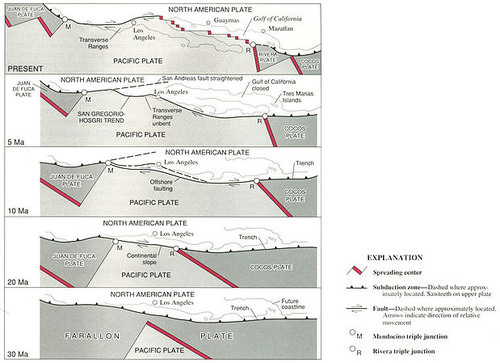
::圣安德烈亚斯断层的演变The San Andreas is where the Pacific and North American plates meet ( Figure ). How did the San Andreas Fault form? The Farallon Plate was subducting beneath the North American Plate. This began about 30 million years ago. By 20 million years ago, the Pacific Plate and East Pacific Rise spreading center had started to subduct. This split the Farallon Plate into two smaller plates. The plates started a transform motion where the Pacific and North American plates meet. This formed the San Andreas Fault. The fault moved inland.
::圣安德烈亚斯是太平洋和北美板块相交的地方(图 ) 。 圣安德烈亚斯板块是如何形成的 ? 法拉隆板块在北美板块下沉。 大约3000万年前就开始了。 在2000万年前, 太平洋板块和东太平洋峰顶扩张中心开始下沉。 这把法拉隆板块分割成两个较小的板块。 牌子开始了太平洋和北美板块相交的变换运动。 这形成了圣安德烈亚斯板块。 断层移到内陆 。This figure shows the evolution of the San Andreas Fault zone from 30 million years ago (bottom) to present (top).
::这一数字显示圣安德烈亚斯断层区从3 000万年前(底部)到现在(顶部)的演变情况。Most Cenozoic plate tectonic activity involves continents moving apart. But smaller regions are coming together. Africa collided with Eurasia to create the Alps. India crashed into Asia to form the Himalayas.
::大部分的蛋白质板块构造活动都涉及各大洲的分化。 但较小的区域正在形成。非洲与欧亚相撞,建立了阿尔卑斯山。印度冲进亚洲形成喜马拉雅山。Ice Ages
::冰河年龄The Pleistocene ice ages began 2.6 million years ago. advanced and retreated four times ( Figure ). During the retreats, the climate was often warmer than it is today.
::Pleistocene冰河时代始于260万年前,四度向后退(图 ) 。 在撤退期间,气候往往比今天暖和。Glacial ice at its maximum during the Pleistocene.
::冰雪在冰原期间的顶峰These continental ice sheets were extremely thick, like the Antarctic ice cap is today. The Pleistocene ice ages guided the evolution of life in the Cenozoic, including the evolution of humans.
::这些大陆冰原非常厚,就像南极冰冠今天一样。 冰原冰河时代指引着基因组生物的进化,包括人类的进化。Summary
::摘要- During the Cenozoic, Pangaea began to split up.
::在Cenozoic期间,Pangalea开始分裂。
- Subduction of the Farallon plate has resulted in the formation of the Rocky Mountains and the San Andreas Fault.
::法拉隆板块的采掘导致了洛基山脉和圣安德烈亚斯断层的形成。
- The Pleistocene was marked by four advances of ice. The remnants of the last advance of glaciers are found today.
::冰原的特征是四个冰层的进化过程,最后的冰川进化过程的残余于今天被发现。
Review
::回顾- Why do we know so much more about the Cenozoic than the other eras of geologic time?
::为什么我们比地质时代的时代 更了解基因组学呢?
- How do plate tectonics processes explain the Rocky Mountains? The San Andreas Fault? The Himalayas?
::板块构造过程如何解释落基山脉?圣安德烈亚斯断层?喜马拉雅山?
- What were the Pleistocene ice ages? What did the ice ages do to the evolution of life?
::冰河时代对生命的进化有何影响?
- During the Cenozoic, Pangaea began to split up.