12.5 极赤道系统
章节大纲
-
Introduction
::导言Graphing systems or simultaneous functions in the coordinate plane allows us to find solutions, or points of intersection, that can be helpful in determining important calculations, including the break-even point for a business or product.
::坐标平面上的绘图系统或同步功能使我们能够找到解决办法或交叉点,有助于确定重要的计算方法,包括企业或产品的平衡点。The same is true when graphing equations in polar form and/or on a polar graph. When you graph the intersection of multiple polar equations, you treat them just as you would rectangular equations: Graph both and find the points that are true for both equations.
::当用极形和/或极图绘制方程式时,情况也是如此。当用极形和/或极图绘制方程式的交叉点时,当用图形绘制多个极方程式的交叉点时,对待这些方程式的方式与矩形方程式一样:用图形绘制两个方程式,并找到两个方程式都符合的点。Systems of Polar Equations
::极赤道系统Polar equations can be graphed using . Graphing two polar equations on the same axis may result in finding the point(s) of intersection.
::极方程式可使用 . 绘制同一轴上的两极方程式图,可能会找到交叉点。One method of finding the point(s) of intersection for two polar graphs is by setting the equations equal to each other. Thus, the p oints of intersection are when . Then solve the resulting trigonometric equation.
::找到两个极地图的交叉点的方法之一是将方程设置为对等。因此,交叉点是当 r1=r2 时,然后解决由此产生的三角方程。All points on a polar graph are coordinates that make the equation valid. The coordinates of the point(s) of intersection when substituted into each equation will make both equations valid.
::极图上的所有点都是使方程式有效的坐标。将交叉点的坐标替换为每个方程式时,使两个方程式都有效。The following video explains how to find points of intersection on a polar graph:
::以下影片解释如何在极地图上找到交叉点:
Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Determine the point(s) of intersection for and .
::确定 r1 = 3sin 和 r2 = 3cos 的交叉点。Solution:
::解答:3sin_3cos_3sin_3cos_3cos_3cos_3cos_3cos_1}33_00_1}33_6或76Substitute into either one of the two polar equations to obtain .
::以 r=1.5 的 r = 6 替代 = 6 的两种极方程之一。Substitute into either one of the two polar equations to obtain .
::在两个极方程中的任何一个方程中,代之以76,以获得r1.5。Note : The coordinates and represent the same polar point, so there is only one solution to this equation.
::注:坐标(1.5, 6)和(-5.7, 6)代表同一极点,因此这一方程只有一个解决办法。If we look at the graphs of and , we can see there is another point of intersection:
::如果我们看看r1和r2的图表,我们可以看到还有另一个交叉点:When goes through the point (0, 0).
::=0, r1=3sin=0=0, 所以 r1 进入点( 0, 0) 。When so goes through the point .
::2, r2=3cos=2=0, 所以 r2 穿过点 (0, 2)。Therefore, both graphs also go through the pole .
::因此,两个图表也通过极 r=0。The pole was NOT revealed as a point of intersection using the first step! (Why? Hint: How many ways are there to represent the pole in polar coordinates?) This shows that after you use algebraic methods to find intersections at points other than the pole, you should also check for intersections at the pole.
::该极不是使用第一步作为十字路口的一个点被暴露的! (为什么? 提示: 在极坐标中代表极线的路径是多少? ) 这表明在使用代数法在极以外点找到交叉点之后, 您也应该检查在极线上的交叉点 。Example 2
::例2Determine the point(s) of intersection for and .
::确定 r1 =1 和 r2 = 2sin @%2 的交叉点。Solution:
::解决方案 :
::1=2sin212=sin22Substitute to solve.
::要解决的替代22。
::12=sin 6,56Since , solve for by dividing each answer by 2 .
::自2222,通过将每个回答除以2来解 22 。Recall that usually has the range However, since we solved for we actually need to consider values of with the range Why? Recall that has two cycles between 0 and , add two more solutions:
::回想一下 通常有 02。 但是,既然我们解决了 02, 我们实际上需要考虑 04的值。 为什么? 回想一下 sin2有两个周期在 0 和 2之间, 增加两个额外的解决方案 :so
::so so, so, so, so, so, so, so, so, so,Finally, we need to consider solutions when because and yield the same polar graph .
::最后,我们需要考虑当 r1, 因为 r=1 和 r1 产生相同的极点图时的解决方案。 - 12 = sin 76, 116 。Then
::然后是7 -12,11 -12,19 -12,21 -12In total, there are eight solutions to this set of equations.
::总共有八种办法可以解决这组方程式的问题。Note: Recall that where the angle is requires looking at all potential values between 0 and When the angle is as it is in this case, be sure to look for all potential values between 0 and
::注:当角度为 ° 时,需要查看 0 和 2 ° 之间的所有潜在值。当角度为 2 ° 时,请确定查找 0 和 4 ° 之间的所有潜在值 。The graph reveals eight points of intersection.
::图表显示了八个交叉点。
Example 3
::例3Determine the point(s) of intersection for and
::确定r1=2和r2=sec的交叉点。Solution:
::解决方案 :Here we will use a table of values based on the unit circle for each function. Compare the values in the tables below to determine the intersection points for each quadrant. Recall that the period of is
::在此, 我们将使用基于每个函数单位圆的数值表。 比较下表中的数值, 以确定每个象限的交叉点 。 回顾 秒的周期为 2 。For the 1st quadrant
::用于第 1 象限θ (angle) 0 r 1 (distance) 2 2 2 2 2 r 2 1 1.15 1.4 2 undefined For the 2nd quadrant
::第二象限θ (angle)
r 1 (distance) 2 2 2 2 r 2 -2 -1.4 -1.15 -1 For the 3rd quadrant:
::对于第3象限:θ (angle) r 1 (distance) 2 2 2 2 r 2 -1.15 -1.4 -2 undefined For the 4th quadrant
::用于第4象限θ (angle) r 1 (distance) 2 2 2 2 r 2 2 1.4 1.15 1 Note that the 3rd and 4th quadrant repeat 1st and 2nd quadrant values.
::请注意,第三和第四象限重复第一和第二象限值。Observe in the table of values that and are the two points of intersection. When looking at the graph, you can see that the curves have only two intersecting points.
::在数值表中观察两个交叉点是两个交叉点(2,3,3,3,3,5,3)。在查看图表时,可以看到曲线只有两个交叉点。Example 4
::例4Determine the point(s) of intersection for and
::确定 r= 2+4sin 和 60 的交叉点。Solution:
::解决方案 :The equation is a line making a 60° angle with the -axis.
::方程式 60 是一个线条 以 r- 轴为角, 以 r- 轴为角, 以 60 度为角 。Make a table of values for
::绘制 r= 2+4sin 的数值表。For the 1st quadrant:
::对于第一个象限 :θ (angle) 0° 30° 45° 60° 90° R (distance) 2 4 4.83 5.46 6 For the 2nd quadrant:
::对于第二个象限 :θ (angle) 120 135° 150° 180° R (distance) 5.46 4.83 4 2 For the 3rd quadrant:
::对于第3象限:θ (angle) 210° 225° 240° 270° R (distance) 0 -.83 -1.46 -2 For the 4th quadrant
::用于第4象限θ (angle) 300° 315° 330° 360° R (distance) -1.46 -.83 0 2 Notice there are two solutions in the table: (5.46, 60° ) and (-1.46, 240° ) = (1.46, 60°). Recall that when , a point is plotted by rotating 180 o or
::表中有两个解决办法:5.46, 60°)和(1.46, 240°) = (1.46, 60°) = (1.46, 60°).回顾,当 r < 0 时,一个点(r, )是用旋转180o 或 ° 绘制的。Finally, we need to check the pole. is a straight line that passes through the pole. passes through the pole when Thus, a 3rd point of intersection is at the pole,
::最后,我们需要检查杆子。60是一条直线,穿过杆子。 r=2+4sin通过杆子, r=210和330。 因此,在杆子上有一个第三个交叉点, r=0。Example 5
::例5Determine the point(s) of intersection for and .
::确定 r1 = 2cos 和 r2 = 1 的交叉点。Solution:
::解决方案 :
::2 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =3 =4 =3 =3 =3 =3 =2 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =3 =3 =3 =4 =3 =3 =3 =3 =1 =2 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =3 =3 =3 =3 =3 =3 =3 =3 =3 =3 =3 =3 =2 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =1 =3 =3 =3 =3 =3 =3 =3 =3 =3Thus, there are two unique solutions, . There are also two repeated solutions in this set. (Can you find them?)
::因此,有两种独特的解决办法,即“3,4,4,3”3。 这套办法中还有两种重复的解决办法。 (你能找到它们吗? )Here is a graph showing the two solutions:
::以下是一个图表,显示两种解决办法:Summary
::摘要-
Graphing simultaneous polar equations can yield solutions where the graphs meet.
::绘制同步极方程式可产生图形相交的解决方案。 -
Setting two polar equations equal to each other and solving will determine the coordinate of a solution of the system.
::确定两个对等极方程和解决将决定系统解决方案的协调。 -
Solutions at the pole or repeat solutions can be found manually.
::极地或重复解决方案可以人工找到。
Review
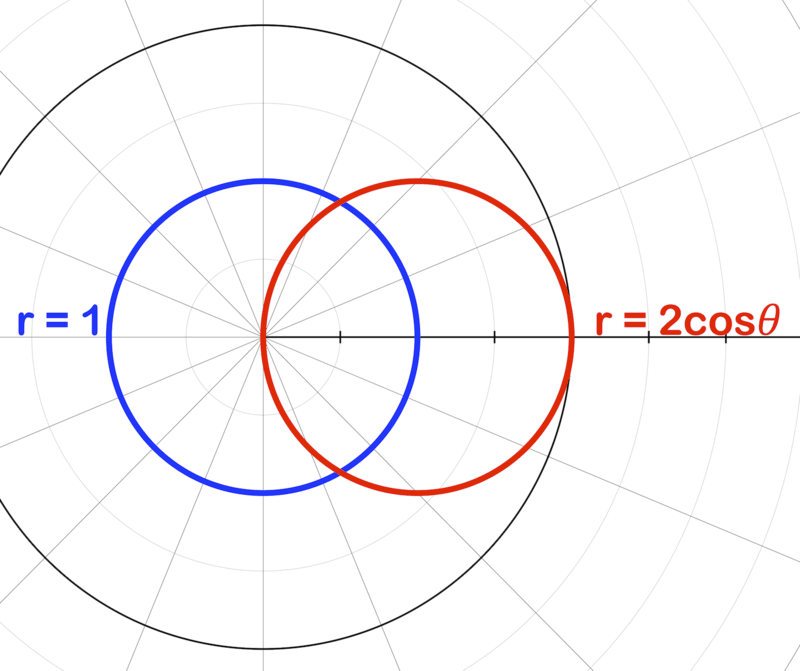
::回顾The graphs of and are shown below.
::r=1和r=2cos的图示如下。-
How many times do they intersect?
::它们交叉了多少次? -
In which quadrants do they intersect?
::在哪些四分法中,它们相互交错? -
At what points do the intersections occur?
::十字路口在哪里发生?
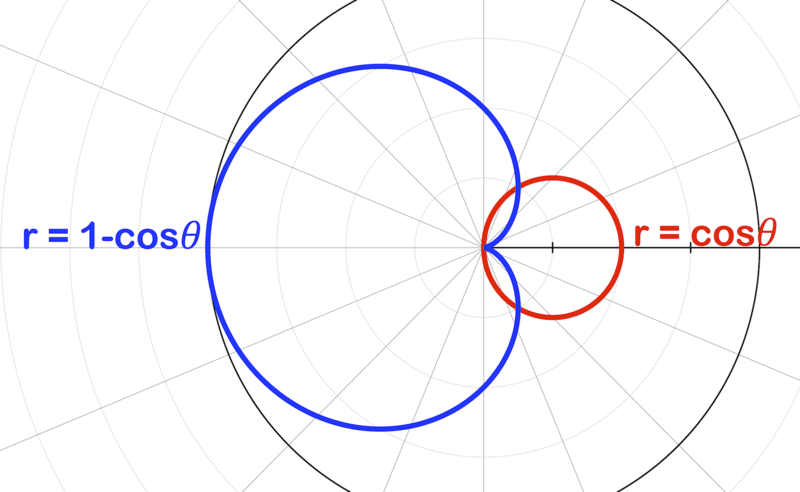
Answer questions 4-5 based on the image below and the following information: the intersection of the graphs of and
::回答问题4-5基于以下图像和以下信息:r=cos和r=1-cos图的交叉点。-
How many times do they intersect?
::它们交叉了多少次? -
At what points do the intersections occur?
::十字路口在哪里发生?
Determine the points of intersection of the following pairs of curves:
::确定以下两组曲线的交叉点:-
,
::r=2,r=2cos -
::r=2sin r=2sin r=2sin r=2} r=2sin r=2sin r=2} r=2sin r=sin r=2} r=2sin r=2} r=2sin r=2sin r=2sin * r=2} r=2sin * r=2sin * r=2sin r=2sin r=2sin * r=2r=2sin * -
::r=2+2sin,r=2-2cos -
,
::r=3cos,r=2_cos
Determine the points of intersection for each system of equations below. Graph to verify your solution.
::确定以下每个方程式系统的交叉点。 用于校验您的解决方案的图表 。-
,
::r=2sin r=2sin r=2sin r= r=csc r=2sin r=2sin r=2sin r=2sin r=2sin r=2sin r=2sin -
::r=1+sin,r=1+sin -
::r=sin,r=sin2 -
:: -
::r=9cos -
::r=4cos=3
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。 -
Graphing simultaneous polar equations can yield solutions where the graphs meet.