12.6 二次曲线极赤道
章节大纲
-
Introduction
::导言Janet is working on a physics problem that involves planets in orbit around a star. She tried to set up the problem in rectangular form , but the resulting equations were very messy. Janet needs a way to simplify her problem so she can manipulate the equations more easily. Can you help using polar form ?
::珍妮特正在研究一个物理学问题,它涉及行星环绕恒星的轨道。她试图用长方形设置问题,但由此产生的方程式非常混乱。珍妮特需要一种简化问题的方法,这样她就可以更容易地操作方程式。你能帮助使用极方形吗?
Janet is trying to model the paths of two planets and a comet around a star. By putting the equations of her orbiting objects into polar form, she can easily create a graph to model her problem and work with the equations in a simpler format. For instance, suppose she's tracking the paths of two planets and a comet around a star. All these objects will have the sun as one of the focal points of their orbits, so it's easy to represent their paths using polar equations.
::珍妮特试图模拟两个行星和一颗彗星围绕一颗恒星的路径。 通过将轨道物体的方程式设置为极形, 她可以很容易地创建一个图形来模拟她的问题, 并以更简单的格式与方程式一起工作。 比如, 假设她正在跟踪两个行星和一颗彗星围绕一颗恒星的路径。 所有这些天体都将太阳作为它们轨道的焦点之一, 因此使用极方程式来代表它们的路径很容易。Polar Equations of Conics
::二次曲线的极平方Recall that the eccentricity e is the measure of how much the conic section deviates from being circular. T he eccentricity is equal to the ratio of the focal radius to the semi-major axis (half the length of the longer axis). e = c a
The value of the eccentricity defines the conic section.
::回顾偏心率e是测量二次曲线部分偏离圆形的程度的尺度。偏心率等于焦半径与半主轴(半长轴长度的一半)之比。e=偏心值是二次曲线部分的定义。-
If
e
=
0
,
then the conic is a circle.
::如果 e=0,则二次曲线为圆。 -
If
0
<
e
<
1
,
then the conic is an ellipse.
::如果 0<e<1, 则二次曲线为椭圆 。 -
If
e
=
1
,
then the conic is a parabola.
::如果e=1,则二次曲线为抛物线。 -
If
e
>
1
,
then the conic is a hyperbola.
::如果 e>1, 则二次曲线为双曲线 。
Ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas have a common general polar equation. Note there are other ways of representing these relations using cofunction and . However, this general form is easiest to use because each parameter can be immediately interpreted in a graph. r = k ⋅ e 1 − e ⋅ cos ( θ − β )
::Ellipses, parabolas, 和 perbolas 具有共同的普通极极方程。 注意有其他方法使用 共函数来表示这些关系 。 但是, 这种一般形式最容易使用, 因为每个参数都可以在图表中立即解释 。 r=ke1- ecos () 。If the conic is an ellipse, the angle β indicates the angle towards the center. If the conic is a parabola, the angle β indicates the opening direction. If the conic is a hyperbola, the angle β indicates the angle away from the center. The constant k is the distance from the focus at the pole to the nearest directrix. This directrix lies in the opposite direction indicated by β .
::如果二次曲线是椭圆形, 角度 β 表示向中点的方向。 如果二次曲线是抛物线, 角度 β 表示开口方向。 如果二次曲线是超博拉, 角度 β 表示离中点的角。 常数 k 是从极点到最近的直线的距离。 此直线位于 β 表示的相反方向 。The distance from the focus at the pole to the nearest directrix, k , can be calculated using these equations :
::从极点到最近的直线阵列的距离 k 可以用下列方程式计算:-
Ellipses:
k
=
a
2
c
−
c
::椭圆: k=a2c-c -
Hyperbolas:
k
=
c
−
a
2
c
::超光谱: k=c-a2c
where the focal radius.
::a 是半主轴, c 是焦半径。The following video demonstrates how to write the polar equation for a parabola given the rectangular form.
::以下视频展示了如何根据矩形形式写出抛物线的极方程。The general polar equation used with ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas does not apply to circles. Since e = 0 for circles, the equation would simplify to r = 0 , which does not tell us much about the circle. Instead, the polar equation of a circle with radius r = a 2 , or a equal to the diameter of the circle, passing through the origin, and having a center located at an angle β counterclockwise from the positive x -axis, is r = a ⋅ cos ( θ − β ) .
::用于椭圆、 parabolas 和 超双球体的普通极方程式不适用于圆圈。 由于 e= 0 圆圈, 此方程式会简化为 r=0 , 这不会告诉我们圆圈的情况。 相反, 圆圆的极方方程式, 半径为 r=a2 , 或与圆的直径相等, 穿过圆的源头, 并在正轴为x轴的 β 反时针角上设置一个中心, 是 ir=açcos () 。
Just as with the other conic sections, t here are other ways of representing a circle like this using and coterminal angles.
::与其他二次曲线部分一样,还有其他方法可以代表像这样的圆形使用和共同终点角度。The following video demonstrates how to determine the equation of a circle in rectangular form and polar form from the graph of a circle:
::以下视频展示如何从圆形图中以矩形形式和极形确定圆形的方程:Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Identify the following conic sections:
::确定下列二次曲线部分:1) r = 10 5 + 5 cos θ
::1) r=105+5cos___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________Solution:
::解决方案 :r = 10 5 − 5 cos θ ⋅ 1 5 1 5 = 2 1 − cos θ
::r=105-5cos1515=21-cose = 1 , so this conic is a parabola.
::e=1,所以这个二次曲线是抛物线。2) r = 5 10 − 3 cos θ
::2) r=510-3cos___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________Solution:
::解决方案 :r = 5 10 − 3 cos θ ⋅ 1 10 1 10 = 1 2 1 − 3 10 cos θ
::r=510-3cos=110110=121-310cose = 3 10 , so this conic is an ellipse.
::e=310,所以这个二次曲线是一个椭圆。3) r = 4 1 − 2 cos θ
::3) r=41-2cos______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________Solution:
::解决方案 :e = 2 , so this conic is a hyperbola.
::e=2,所以这个二次曲线是一个双曲线。Example 2
::例2A great way to discover new types of graphs in is to experiment with graphing software such as Desmos or GeoGebra. Can you determine the two equations that would create the following graphs?
::发现新类型的图表的好方法就是实验像 Desmos 或 GeoGebra 这样的图形化软件。 您能够确定创建下图的两种方程式吗 ?
Solution:
::解决方案 :The circle in blue has a center at 90 ∘ and a diameter of 2. Its equation is r = 2 cos ( θ − 90 ∘ ) .
::蓝色圆的中枢为90°C,直径为2°C,方程式为 r=2cos(90°C)。The red ellipse appears to have its center at (2, 0), with a = 4 and c = 2 . This means the eccentricity is e = c a = 2 4 = 1 2 .
::红色椭圆的中心似乎在2,0,A=4和C=2,这意味着偏心度为e=ca=24=12。To write the equation in polar form, you still need to find k .
::要以极形写出方程式, 您还需要找到 k 。k = a 2 c − c = 4 2 2 − 2 = 8 − 2 = 6
::k=a2c-c=422-2=8-2=6Thus, the equation for the ellipse is r = 6 ⋅ 1 2 1 − 1 2 ⋅ cos ( θ ) = 3 1 − 1 2 ⋅ cos ( θ ) .
::因此,椭圆的方程为r=6121-12cos()=31-12cos()。Example 3
::例3Convert the following conic from polar form to rectangular form: r = 3 2 − cos θ .
::将以下二次曲线从极形转换为矩形:r=32-cos。Solution:
::解决方案 :r = 3 2 − cos θ r ( 2 − cos θ ) = 3 2 r − r ⋅ cos θ = 3 2 r = 3 + r ⋅ cos θ = 3 + y 4 r 2 = 9 + 6 y + y 2 4 ( x 2 + y 2 ) = 9 + 6 y + y 2 4 x 2 + 4 y 2 = 9 + 6 y + y 2 4 x 2 + 3 y 3 + 6 y = 9 4 x 2 + 3 ( y 2 + 2 y + 1 ) = 9 + 3 4 x 2 + 3 ( y + 1 ) 2 = 12 x 2 3 + ( y + 1 ) 2 4 = 1
::r=32-cosr(2-cos)=32r-rcos=32r=3+rcos}3+y4r2=9+6y+y+y24(x2+y2)=9+6y+y24x2+4y2=9+6y+6y+y242+y242+3y3+6y=94x2+3(y2+2y+1)=9+342+3(y+1)2=12x23+(y+1)24=1Example 4
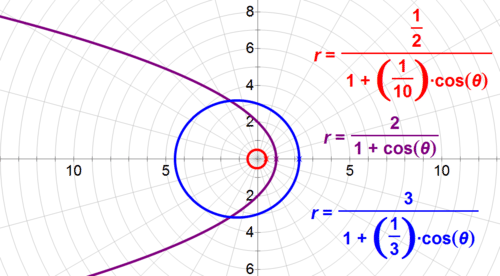
::例4Recall the problem from the Introduction: How would you help Janet model the paths of two planets and a comet around a star using polar equations?
::回顾引言中的问题:你如何帮助珍妮特用极方程式模拟两个行星和一颗彗星围绕恒星的路径?Solution:
::解决方案 :Assume that one planet has an orbit described by the equation r = 1 2 1 + 1 10 cos θ ,
and the other planet has an orbit described by the equation r = 3 1 + 1 3 cos θ .Let the comet's orbit be described by the equation r = 2 1 + cos θ .By graphing the equations on her calculator or w ith graphing software such as Desmos or GeoGebra , Janet can quickly see that the comet will pass between the orbits of the inner planet and the outer planet on its journey past the star, and she can determine where the comet intersects the orbit of the 2nd planet.
::假设一个行星的轨道为 r=121+110cos,另一个行星的轨道为 r=31+13cos。让彗星的轨道用 r=21+cos来描述。 用计算器上的方程图或Desmos或GeoGebra等图形软件来绘制。 珍妮特可以很快看到,彗星在其穿越恒星的旅程中,将在内行星的轨道和外行星的轨道之间传递,她可以确定彗星的轨道与第二行星的轨道交错之处。To see exactly where the orbits will intersect, Janet can set the equation for the planet's orbit equal to the equation for the comet's path, and then solve for θ . So:
::珍妮特可以设定地球轨道的方程 等同于彗星路径的方程 然后解决 。所以:3 1 + 1 3 cos θ = 2 1 + cos θ 3 ( 1 + cos θ ) = 2 ( 1 + 1 3 cos θ ) 3 + 3 cos θ = 2 + 2 3 cos θ 7 3 cos θ = − 1 cos θ = − 3 7 θ = 2.014 , 2 π − 2.014.
::31+13cos @21+cos%3(1+cos%1)=2(1+13cos%3+3cos%2+23cos73cos%1cos @37 @2.014,22.014。Substitute back into one of the original equations to find r .
::换回原来的方程式 找到rr = 2 1 + cos θ = 2 1 + − 3 7 = 2 4 7 = 7 2
::r=21+cos2137=247=72So, the comet will intersect the outer planet's orbit at ( 7 2 , 2.014 ) and ( 7 2 , 4.269 ) .
::因此,彗星将在(72,2.014)和(72,4.269)的外行星轨道上相互交叉。Example 5
::例5Identify the center, foci, vertices, and equations of the directrix lines for the following conic:
::确定以下二次曲线的直线的中心、角、顶点和方程式:r = 20 4 − 5 ⋅ cos ( θ − 3 π 4 ) .
::r=204-5cos(34)。Solution:
::解决方案 :First, rewrite the denominator so that it matches the general form 1 − e ⋅ cos ( θ − β ) .
::首先,重写分母,使其与一般表1-ecos()相匹配。r = 20 4 − 5 ⋅ cos ( θ − 3 π 4 ) ⋅ 1 4 1 4 = 5 1 − 5 4 ⋅ cos ( θ − 3 π 4 ) = 4 ⋅ 5 4 1 − 5 4 ⋅ cos ( θ − 3 π 4 ) e = 5 4 , k = 4 , β = 3 π 4 = 135 ∘
::= r= 204 - 5cos (34) }1414= 51 - 54cos (34) = 4541 - 54cos (34) e= 54,k= 4,34=135Use this information to solve for a and c .
::使用此信息解答 a 和 c 。4 = c − a 2 c 5 4 = c a → 4 5 = a c → 4 c 5 = a 4 = c − ( 4 c 5 ) 2 ⋅ 1 c 4 = c − 16 c 2 25 c 4 = 9 c 25 100 9 = c 80 9 = a
::4=c-a2c54=ca45=ac4c5=a4=c-(4c5)21c4=c-16c225c4=9c251009=c809=aThe center is the point ( 100 9 , 7 π 4 ) , which is much more convenient to write in polar coordinates. The closest directrix is the line r = 4 ⋅ sec ( θ − 7 π 4 ) . The other directrix is the line r = ( 2 ⋅ 100 9 − 4 ) ⋅ sec ( θ − 7 π 4 ) . One focus is at the pole, the other focus is the point ( 200 9 , 7 π 4 ) . The vertices are at the center, plus or minus a in the same angle: ( 100 9 ± 80 9 , 7 π 4 ) .
::中心是点( 109, 74) , 这个点更方便以极地坐标书写。 最近的直线是 r= 4sec( 74)。 最近的直线是 r = 4sec( 74)。 另一个直线是 r = ( 1009 - 4) sec( 74)。 其中一个焦点是 极地线, 另一个焦点是 点(2009, 74)。 顶部位于中心, 加上或减去一个相同角度: (1009+809, 74)。Example 6
::例6Graph the conic from Example 2.
::从例2绘制二次曲线图。Solution:
::解决方案 :Example 7
::例7Graph the following conic: r = 3 2 − cos ( θ − 30 ∘ ) .
::图如下二次曲线:r=32-cos(30)。Solution:
::解决方案 :r = 3 2 − cos ( θ − 30 ∘ ) r = 3 2 − cos ( θ − 30 ∘ ) ⋅ 1 2 1 2 = 3 2 1 − 1 2 ⋅ cos ( θ − 30 ∘ ) = 3 ⋅ 1 2 1 − 1 2 ⋅ cos ( θ − 30 ∘ ) k = 3 , e = 1 2 , β = 30 ∘
::r=32 -cos(30)r=32 -cos(30)r=32 -cos(30)r=121212=321 -12cos(30)=312 -12cos(30)k=3,e=12,30Summary
::摘要-
The eccentricity
e
is the measure of how much the conic section deviates from being circular.
The value of the eccentricity defines the conic section.
-
If
e
=
0
,
then the conic is a circle.
::如果 e=0,则二次曲线为圆。 -
If
0
<
e
<
1
,
then the conic is an ellipse.
::如果 0<e<1, 则二次曲线为椭圆 。 -
If
e
=
1
,
then the conic is a parabola.
::如果e=1,则二次曲线为抛物线。 -
If
e
>
1
,
then the conic is a hyperbola.
::如果 e>1, 则二次曲线为双曲线 。
::偏心度 e 是测量二次曲线部分偏离圆形的程度。 偏心值定义二次曲线部分。 如果 e=0, 则二次曲线为圆形。 如果 0 < e < 1, 则二次曲线为椭圆形。 如果 e=1, 则二次曲线为双曲线。 如果 e=1, 则二次曲线为双曲线。 如果 e>1, 则二次曲线为双曲线 。 -
If
e
=
0
,
then the conic is a circle.
-
Ellipses, parabolas, and hyperbolas have a common general polar equation:
r
=
k
⋅
e
1
−
e
⋅
cos
(
θ
−
β
)
.
::椭圆、parabolas和超光子有一个共同的一般极等式:r=ke1-ecos()。 -
A circle has the equation
r
=
a
⋅
cos
(
θ
−
β
)
.
::一个圆的方程式为 r=acos()。
Review
::回顾Convert the conics below from polar form to rectangular form. Then identify the conic section described by the equation.
::将下面的二次曲线从极形转换为矩形形。然后标明方程式描述的二次曲线区域。1. r = 5 3 − cos θ
::1. r=53-cos2. r = 4 2 − cos θ
::2. r=42-cos3. r = 2 2 − cos θ
::3. r=22-cos4. r = 3 2 − 4 cos θ
::4. r=32-4cos__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________5. r = 5 cos ( θ )
::5 r= 5cos( __ )Graph the following conics:
::图形如下二次曲线:6. r = 5 4 − 2 cos ( θ − 90 ∘ )
::6. r=54-2cos(90)7. r = 5 3 − 7 cos ( θ − 60 ∘ )
::7. r=53-7cos(60)8. r = 3 3 − 3 cos ( θ − 30 ∘ )
::8 r= 33-3cos (30)9. r = 1 2 − cos ( θ − 60 ∘ )
::9. r=12-cos(60)10. r = 3 6 − 3 cos ( θ − 45 ∘ )
::10.r=36-33cos(45)Translate the following conics to polar form:
::将下列二次曲线转换为极形:11. ( x − 1 ) 2 4 + y 2 3 = 1
::11. (x-1)24+y23=112. ( x − 5 ) 2 + ( y + 12 ) 2 = 169
::12. (x-5)2+(y+12)2=16913. x 2 + ( y + 1 ) 2 = 1
::13. x2+(y+1)2=114. ( x − 1 ) 2 + y 2 = 1
::14. (x-1)2+y2=115. − 3 x 2 − 4 x + y 2 − 1 = 0
::15.-3x2-4x+y2-1=0Calculate the value of the eccentricity e . Then identify the conic section described by the equation.
::计算偏心值 e。 然后标明方程式描述的二次曲线部分 。16. r = 4 1 − cos θ
::16 r= 41-cos______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________17. r = 2 4 + 2 cos θ
::17 r=24+2cos18. r = 8 6 − 6 cos θ
::18 r=86-6cos19. r = 12 2 + 4 cos θ
::19. r=122+4cos______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________20. What are the differences between creating the graphs of conics on the polar grid as opposed to the rectangular grid?
::20. 在极地网格上创建二次曲线图与矩形网格之间有什么区别?Review (Answers )
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。Resource: A Note When Using TI-Calculators
::资源: 使用 TI-计算器时的说明On the TI-84, the mode can be switched to polar in the mode menu. This changes the graphing features. You can choose to be in radians or degrees, and the graphs will look the same. When you graph a circle of the form r = 8 ⋅ cos θ , you should see the following on your calculator:
::在 TI- 84 上, 模式可以在模式菜单中切换为极。 这可以更改图形特征。 您可以选择以弧度或度表示, 图形将看起来相同。 当您绘制窗体 r= 8cos= 的圆时, 您应该在计算器上看到以下内容 :When you go to the window setting, you should notice that in addition to X m i n , X m a x , there are new settings called θ m i n , θ m a x and θ s t e p .
::当您去窗口设置时, 您应该注意到, 除了 Xmin, Xmax 之外, 还有新的设置, 叫做 min, max 和 step 。If θ m i n and θ m a x do not span an entire period, you may end up missing part of your polar graph.
::如果 min 和 max 不跨越整个周期, 最终可能会丢失极图的一部分 。The θ s t e p controls how accurate the graph should be. If you put θ s t e p at a low number like 0.1, the graph will plot extremely slowly because the calculator is doing 3,600 cosine calculations. On the other hand, if θ s t e p = 30 , then the calculator will do fewer calculations, producing a rough circle, but it will probably not be accurate enough for your purposes.
::\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\"\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\可以\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\ -
If
e
=
0
,
then the conic is a circle.