14.11 线性关系
章节大纲
-
Introduction
::导言Statistics is largely concerned with the relationship between the values of one variable and the values of an associated variable. Bivariate data are data that have two variables that are often paired up like coordinate points. Is there any relationship between the following data? If there is, does it mean that doctors cause cancer?
::统计主要涉及一个变量的值与一个相关变量的值之间的关系。 双变量数据是有两个变量的数据,通常与坐标点相配。 以下数据之间是否有任何关系? 如果有,这是否意味着医生致癌?Number of Doctors 27 30 36 60 81 90 156 221 347 Cancer Rate 0.02 0.07 0.16 0.20 0.43 0.87 1.21 2.80 3.91 
Linear Correlation
::线条关联A scatterplot creates an point from each data pair. When making a scatterplot, you can try to assign the independent variable to and the dependent variable to ; however, it often will not be obvious which variable is the dependent variable, so you will just have to pick one.
::撒布点从每个数据配对中创建一个点( x,y) 。 当绘制撒布点时, 您可以尝试将独立变量指定为 x, 并将依附变量指定为 y; 但是, 通常并不明显哪个变量是依附变量, 所以您只需要选择一个变量 。Once you plot the data and zoom appropriately, you will see the points scattered about. Sometimes there will be a clear linear relationship , and sometimes it will appear random . The correlation coefficient , , is a number that quantifies two aspects of the relationship between the data:
::一旦您适当绘制了数据并缩放, 您就会看到数据分布的点。 有时会有一个清晰的线性关系, 有时它会随机出现。 相关系数 r 是一个数, 它量化了数据之间关系的两个方面 :-
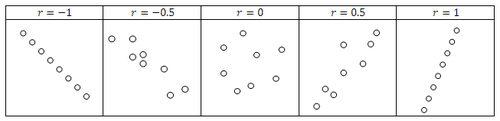
The correlation coefficient is either negative, zero, or positive.
-
If the correlation coefficient is negative, then the data are negatively correlated. This means that as one variable tends to increase, the other variable tends to decrease.
::如果相关系数为负值,则数据为负相关,这意味着随着一个变数增加,另一个变数减少。 -
If the correlation coefficient is zero, then the data
have no linear
correlation
. This means that the two variables tend to not be related in a linear pattern.
::如果相关系数为零,则数据没有线性关联。这意味着这两个变量在线性模式中往往没有关联。 -
If the correlation coefficient is
positive
, then the data are
positively
correlated. This means that the two variables tend to increase together.
::如果相关系数是正数,则数据是正对数,这意味着这两个变数往往同时增加。
::相关系数是负的、 零的或正的。 如果相关系数是负的, 那么数据是负的。 这意味着当一个变量倾向于增加时, 另一个变量倾向于减少。 如果相关系数是零, 那么数据就没有线性相关关系。 这意味着这两个变量在线性模式中往往没有关联。 如果相关系数是正的, 那么数据是正的。 这意味着这两个变量往往一起增加。 -
If the correlation coefficient is negative, then the data are negatively correlated. This means that as one variable tends to increase, the other variable tends to decrease.
-
The correlation coefficient is a number between
indicating the strength of correlation. If
or
, then the data are perfectly linear. Note that a perfectly linear relationship includes lines with slopes other than 1.
::相关系数是- 1 和 1 之间的数, 表示关联的强度。 如果 r= 1 或 r 1, 则数据是完全线性的。 请注意, 完全线性关系包括与 1 以外斜坡的线条。
Consider the examples below to see what different correlation coefficients will look like in data:
::考虑以下实例,看数据中不同相关系数的外观:Once the data are determined to be sufficiently linear, the regression line or line of best fit can be used to approximate data within the set of beyond the set. In other words, this line represents the linear relationship of the data, and is the line closest to all the data points. Your calculator can perform a regression to produce the equation of a line that attempts to model the trend of the data. The regression line may actually pass through all, some, or none of the data points. This regression line is represented in statistics by
::一旦确定数据足够线性,可将回归线或最适合的线用于在数据集之外一组内比较数据。换句话说,这条线代表数据的线性关系,是最接近所有数据点的线性关系。您的计算器可以进行回归,得出试图模拟数据趋势的线的方程。回归线实际上可能通过所有、部分或任何数据点。该回归线在统计中代表的是该数据线。
::ya+bx。The symbol is pronounced “ -hat” and is the predicted -value based on a given -value. Occasionally, you may also calculate the predicted -value given a -value, however, this is less mathematically sound. Also notice that the linear regression model is simply a rearrangement of the standard equation of a line, .
::y 的符号是“ y-hat ” , 是基于给定的 x 值的预测 y 值。 有时, 您也可以计算给给定的 y 值的预测 x 值, 但是, 这在数学上不那么合理 。 另外请注意, 线性回归模型只是线性线性回归模型对 y=mx+b 线的标准方程的重新排列 。The following video explains how to create a scatterplot using Desmos, a free online calculator:
::以下影片解释如何使用免费在线计算器Desmos创建散射图:The following video explains how to find the equation for the line of best fit , using Desmos:
::以下影片解释如何使用 Desmos 找到最合适线的方程式:Play, Learn, and Explore with Regression and Linear Correlation : .
::以回归和线性关联来玩、学习和探索: .Examples
::实例Example 1
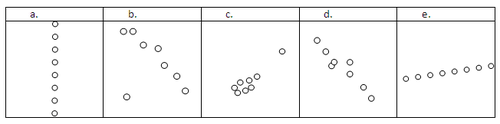
::例1Estimate a correlation coefficient for the following scatterplots.
::估计下列散点的相关系数。Solution:
::解决方案 :-
. Because the height
">
does not seem to be dependent on the
, the data are uncorrelated. Another way to see this is that the slope appears to be undefined.
::r0. 由于高度似乎并不取决于 x, 数据是不相干的。 另一种看到这一点的方法是, 斜坡似乎没有定义 。
-
. If the solo point in the bottom left is an
outlier
, you could choose to not include it in the data. Then the
value would be closer to -1.
::r\\\ 0.7. 如果左下角的单点是一个外端, 您可以选择不将其包含在数据中 。 那么 r 值将更接近 - 1 。 -
. The clump of data seems to be slightly positive correlated, and the single point in the upper left has a strong effect indicating positive slope.
::r0.8. 数据组合似乎略为正相关,左上角的单点具有强烈效果,表明正斜坡。 -
. The data seem to be fairly strongly negatively correlated.
::r0.8. 数据似乎具有相当强烈的负相关关系。 -
. The data seem to be perfectly linearly correlated.
::r1. 数据似乎完全线性相关。
Example 2
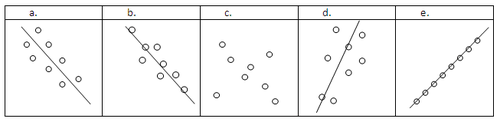
::例2Draw a regression line through the following scatterplots.
::通过下列散点绘制回归线。Solution:
::解决方案 :Visualize and sketch the "line of best fit" for each set of points.
::为每组点绘制“最合适线”的可视化图和草图。Note that in part a, the regression line does not touch any point. Instead, it captures the general trend of the data. In part c, the correlation is not high enough in any direction to produce a regression line. The calculator may give a regression line for scatterplots that look like part c, but you need to be very skeptical that there is actually a relationship between the two variables.
::请注意, 在 a 部分, 回归线不触动任何点。 相反, 它会捕捉数据的一般趋势。 在 c 部分, 相关关系在任何方向上都不足以产生回归线。 计算器可能会给看起来像 c 部分的撒布点提供一个回归线, 但您需要非常怀疑这两个变量之间实际上存在某种关系 。Example 3
::例3Use your calculator to perform a linear regression on the data below. Then, predict the height of someone who has shoe size 9.
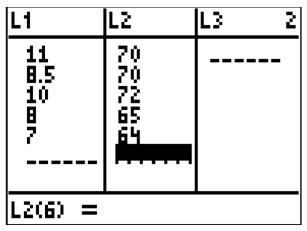
::使用您的计算器对下面的数据进行线性回归。 然后预测鞋尺寸为9的人的高度。Shoe Size Height (in) 11 70 8.5 70 10 72 8 65 7 64 Solution:
::解决方案 :First, enter the data.
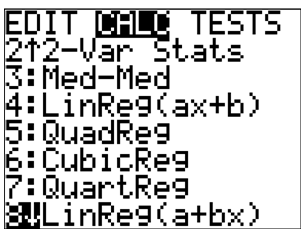
::首先,输入数据。Next, perform the regression. Notice that the calculator can perform linear regression in two ways that are essentially the same. To keep consistent with , use linear regression. This is option 8 in the [STATS], [CALC] menu.
::下一步, 执行回归。 注意计算器可以用两种基本相同的方式进行线性回归。 要与 ya+bx 保持一致, 请使用线性回归。 这是 [STATS] 菜单中的选项 8, [CACLC] 菜单中的选项 8 。Now you need to tell the calculator to perform the regression on the two lists you want, and where to copy the equation. The syntax is
::现在您需要告诉计算器在您想要的两个列表上进行回归, 并在哪里复制公式。 语法是
::LinReg(a+bx)L1、L2、Y1。Note: To find Y1, go to [VARS], [Y-VARS], [FUNCTION], [Y1].
::注:要找到Y1,请转到[瓦 、[Y-VARS]、[发 [Y1]、[Y1]。Notice that the value is about 0.8. This indicates that there is a fairly strong positive correlation between shoe size and height. If your calculator does not display the and lines, then you need to go into the catalog and run the program "DiagnosticOn." This will enable the display of the correlation coefficient.
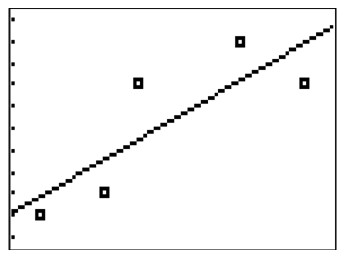
::注意 r 值大约为 0. 8。 这表示鞋大小和高度之间有相当强烈的正相关关系。 如果您的计算器不显示 r 和 r2 线, 那么您需要进入目录并运行“ 诊断 On ” 程序。 这将允许显示相关系数 。You can then graph the scatterplot and the regression line:
::然后您可以绘制散射图和回归线 :The regression equation is
::回归方程是
::y52.4069+1.7745x,where represents shoe size and represents predicted height. The predicted height for someone with size 9 shoe is 68.3774:
::x 代表鞋大小, y 表示预测高度。 9 号鞋的预期高度为 68. 3774 :
::y52.4069+1.77459=68.3774An easy way to use the power of the calculator is to use function notation from the home screen:
::使用计算器功率的一个简单方法是使用主屏幕上的函数符号:Example 4
::例4Recall the problem from the Introduction: Is there any relationship between the data below? If there is, does it mean that doctors cause cancer?
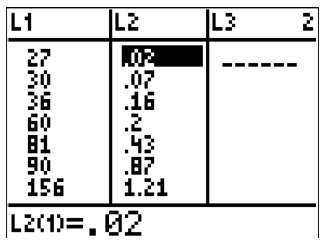
::回顾导言中的问题:以下数据之间是否有任何关系?如果有,这是否意味着医生致癌?Number of Doctors 27 30 36 60 81 90 156 221 347 Cancer Rate 0.02 0.07 0.16 0.20 0.43 0.87 1.21 2.80 3.91 Solution:
::解决方案 :Enter the data onto lists in your calculator:
::在您的计算器中将数据输入到列表中 :Turn on the [STAT PLOT] that compares the two lists of data:
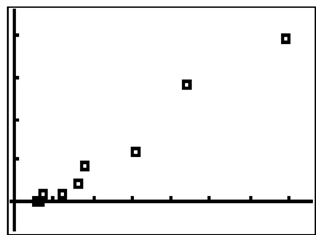
::翻开两个数据清单比较的[STAT PLOT]:Note that the data are extremely linear with a positive correlation coefficient:
::请注意,这些数据极线性,具有正相关系数:One of the most misunderstood concepts in statistics is that correlation does not imply causation. Just because there is a correlation between the number of doctors and the cancer rate doesn't mean that the number of doctors cause cancer. There are dozens of reasons why more doctors might correlate with higher cancer rates. In general, remember that correlation is not the same as causation. Be careful before making any conclusions about change in one variable causing change in another variable.
::统计数据中最误解的概念之一是,相关性并不意味着因果关系。 仅仅因为医生人数和癌症发病率之间存在关联,并不意味着医生人数会引起癌症。 有很多原因说明更多的医生可能与癌症发病率高有关。 总的来说,记住相关性与因果关系不同。 在对导致另一个变量变化的一个变量的变化做出任何结论之前,要小心谨慎。Example 5
::例5The data below represent the average number of working words in an elementary-school student's vocabulary as it relates to shoe size. Perform a linear regression that models the data.
::以下数据代表小学生词汇中与鞋尺寸有关的平均工作字数。进行线性回归,以模拟数据。Shoe Size 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 Vocabulary 1135 1983 2501 4113 5431 7891 9320 11041 Solution:
::解决方案 :Let represent shoe size and represent vocabulary.
::x 表示鞋大小,y 表示词汇表。
::y2, 660.4167+2, 940.9333x
::r=0.9865 r=0.9865The correlation coefficient is very close to positive one. This is a strong indication that the data can be modeled by a linear relationship.
::相关系数非常接近正值系数,这有力地表明数据可以通过线性关系模拟。Example 6
::例6Use the equation from Example 1 to predict the vocabulary for someone who has a 1.0 shoe size (see table in Example 5). Does this prediction seem reasonable given the data? Why or why not?
::使用例1中的方程式来预测鞋尺寸为1.0的某人的词汇(见例5中的表格),考虑到数据,这一预测是否合理?为什么或为什么不?Solution:
::解决方案 :
::y2,660.4167+2,940.93331
::y 280.4167This number seems remarkably low considering the data. This point is very close to the -intercept, which can be found using algebra:
::考虑到数据,这个数字似乎非常低。 这个点非常接近 X 界面, 可以用代数找到 :
::02,660.4167+2,940.9333x
::0.9046=xThe interpretation of the point (0.9046, 0) from the model is that when someone has a shoe size of just under 1.0, then that person's predicted vocabulary is 0. Shoe sizes below 0.9046 will have a negative vocabulary. Is this reasonable? It certainly does not make sense that someone could have a negative number of words in their vocabulary. Newborn babies are born without knowing any words, and this number stays flat at 0 for some length of time. Therefore, this model is not accurate for very low shoe sizes.
::模型对点( 0. 9046, 0) 的解释是, 当某人的鞋尺寸略小于 1. 0 时, 此人的预测词汇为 0 。 低于 0. 9046 的鞋尺寸将有一个负词汇。 这合理吗 ? 肯定不合理, 某人的词汇中可能有负数。 新生儿出生时不知道任何单词, 这个数字会保持在0 位不变, 一段时间内。 因此, 这个模式对于鞋尺寸非常低, 并不准确 。Example 7
::例7Shaquille O'Neal has size 23 shoes. Based on this sentence, and using the data from Example 5, can you make any inferences about his vocabulary? Does a larger shoe size result in a larger vocabulary?
::Shaquille O'Neal 有23码鞋。 根据此句, 并使用例5的数据, 您能否推断出他的词汇? 更大的鞋大小是否会导致更大的词汇?Solution:
::解决方案 :Shaquille's shoe size is significantly beyond the scope of the data that the model is based on. The data relate to elementary-school students, and a size 23 shoe is beyond the relevant domain. This means it wouldn't make sense to use this model to predict the size of Shaquille's vocabulary. Shoe size does not cause vocabulary, but the two variables are strongly correlated because over time both tend to grow.
::Shaquille的鞋尺寸大大超出了模型所基于的数据范围。 数据与小学生有关, 一个23号鞋的尺寸超出了相关领域。 这意味着使用这个模型来预测Shaquille的词汇大小是没有意义的。 鞋尺寸不引起词汇问题, 但这两个变量密切相关, 因为随着时间的流逝, 两者都呈增长趋势 。Summary
::摘要-
A
scatterplot
creates an
point from each data pair.
::散射图为每对数据创建一个(x,y)点。 -
Bivariate data
are data that have two variables that are often paired up like coordinate points.
::双重数据是有两个变量的数据,这些变量往往与坐标点相配。 -
The
correlation coefficient
,
, is a number in the interval [-1, 1]. It indicates the strength of the correlation between two variables.
::相关系数(r)是间隔[-1,1]中的一个数字,表示两个变量之间相互关系的强度。
Review
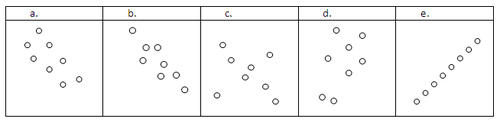
::回顾Determine if the scatterplots below have positive, negative, or no correlation.
::确定下面的散块是否有正、负或无关联关系。For each correlation coefficient, describe what it means for data to have that correlation coefficient, and sketch a scatterplot with that correlation coefficient.
::对于每一相关系数,说明数据具有相关系数意味着什么,并用该相关系数绘制散射图。4.
::4. r=15.
::5 r0.56.
::6 r 17.
::7 r = 08.
::8 r=0.8The data below show the SAT math score and GPA for seven different students.
::以下数据显示7名不同学生的SAT数学分数和GPA。SAT math score 595 520 715 405 680 490 565 GPA 3.4 3.2 3.9 2.3 3.9 2.5 3.5 9. Use your calculator to perform a linear regression that models the data. What is the regression equation? What is the correlation coefficient?
::9. 使用计算器进行线性回归,以模拟数据。回归方程是什么?关联系数是什么?10. Use the equation from the previous problem to predict the GPA for a student with an SAT score of 500. Does this prediction seem reasonable given the data? Why or why not?
::10. 利用前一个问题中的方程式,预测GPA对于成绩达500沙特德士古德的学生来说是GPA,考虑到数据,这一预测是否合理?为什么或为什么不合理?11. Does a high SAT math score cause a high GPA?
::11. 高SAT数学分数是否导致高GPA?The Price of Apple Stock from Oct. 2009 to Sept. 2011 (Source: Yahoo! Finance)
::2009年10月至2011年9月苹果股票价格(资料来源:Yahoo!Finance)10/09 11/09 12/09 1/10 2/10 3/10 4/10 5/10 6/10 7/10 8/10 9/10 $181 $189 $198 $214 $195 $208 $236 $249 $266 $248 $261 $258 10/10 11/10 12/10 1/11 2/11 3/11 4/11 5/11 6/11 7/11 8/11 9/11 $282 $309 $316 $331 $345 $352 $344 $349 $346 $349 $389 $379 12. Use your calculator to perform a linear regression that models the data. What is the regression equation? What is the correlation coefficient?
::12. 使用计算器进行线性回归,以模拟数据。回归方程是什么?关联系数是什么?13. Use the equation from Number 12 to predict: What would be the price of the stock in January 2012?
::13. 使用第12号方程式预测:2012年1月的库存价格是多少?14. What conclusions can you make about these data?
::14. 你能对这些数据得出什么结论?Total Number of Home Runs Hit in Major League Baseball, 2000–2010 (Source: Baseball Almanac)
::2000-2010年主要联盟棒球击打家庭跑总次数(资料来源:棒球月球)2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 5,693 5,458 5,059 5,207 5,451 5,017 5,386 4,957 4,878 4,655 4,613 15. Use your calculator to perform a linear regression that models the data. What is the regression equation? What is the correlation coefficient?
::15. 使用计算器进行线性回归,以模拟数据。回归方程是什么?关联系数是什么?16. Use the equation from Number 15 to predict, how many total home runs should be hit in 2011?
::16. 用第15号方程式预测,2011年应击败多少全垒打总全垒打?17. What conclusions can you make about this data?
::17. 你能对这些数据得出什么结论?18. Explain in your own words what the correlation coefficient measures.
::18. 请用您自己的语言解释相关系数的衡量标准。19. Explain why a larger sample size will cause a more accurate correlation coefficient.
::19. 解释为什么较大的样本规模将产生更准确的关联系数。Review (Answers )
::回顾(答复)Please see the Appendix.
::请参看附录。 -
The correlation coefficient is either negative, zero, or positive.